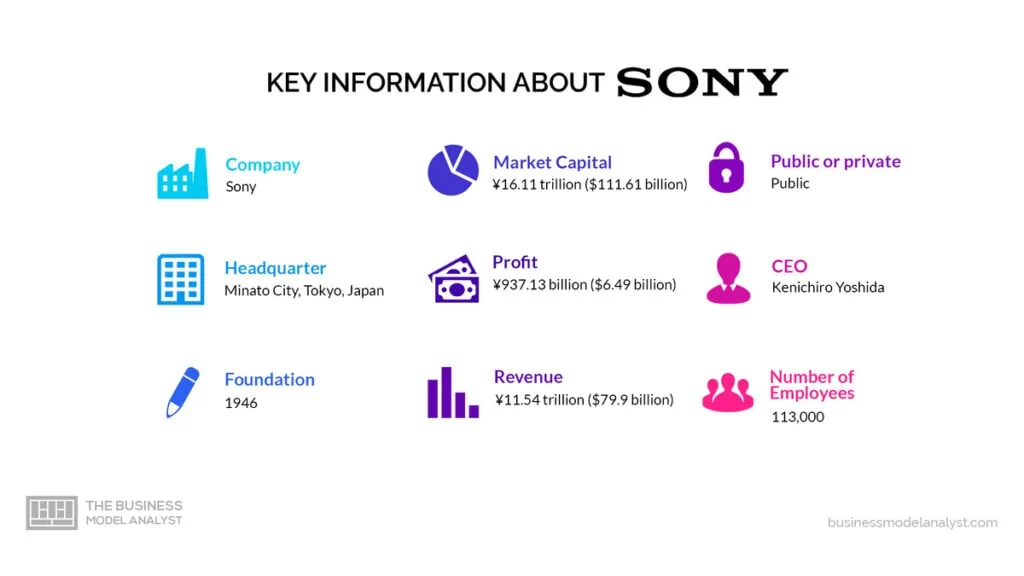
At the core of the Sony business model is its commitment to delivering cutting-edge technology and immersive entertainment experiences to consumers. A global leader in consumer electronics and entertainment, Sony has a business model that spans diverse industries and product categories.
Founded in 1946 in Tokyo, Japan, the company has grown to become one of the most influential companies in the world. With a focus on innovation and quality, Sony offers a wide range of products, including televisions, cameras, gaming consoles, audio equipment, and movies.
By leveraging its expertise in hardware, software, and content creation, Sony has created a seamless ecosystem that captivates and delights customers around the globe. Through strategic partnerships and acquisitions, Sony has expanded its reach in the entertainment industry, establishing itself as a major player in film production and distribution.
With a strong emphasis on research and development, Sony continuously pushes the boundaries of what is possible in areas such as virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and mobile gaming. This commitment to innovation has allowed the company to stay ahead of its competitors and maintain its position as a market leader.
Contents
A brief history of Sony
The history of Sony can be traced back to May 7, 1946, when Masaru Ibuka and Akio Morita in Japan founded Tokyo Tsushin Kogyo K.K. (Tokyo Telecommunication Engineering Corporation). The company started with a capital of 190,000 yen and had a workforce of only eight employees.
Initially, Tokyo Telecommunication Engineering Corporation focused on repairing and modifying electronic equipment. However, in 1950, they made a major shift by developing their own products. This marked the beginning of Sony’s journey as an innovative electronics company.
Sony’s first major success came in 1957 with the introduction of the TR-63, a small portable transistor radio. This breakthrough product revolutionized the industry and made Sony a household name worldwide. It started Sony’s commitment to creating innovative and practical products that enhance people’s lives.
In 1958, the company changed its name to Sony Corporation, derived from the Latin word “sonus,” meaning sound, combined with the popular American slang word “sonny.” This new name reflected the company’s ambition to become a global audio and electronic technology leader.
Throughout the 1960s and 1970s, Sony continued to innovate and expand its product lineup. They introduced the world’s first all-transistor television, the TV8-301, in 1959, which quickly became a global bestseller. Sony also ventured into the consumer market by introducing the first home video cassette recorder, the Betamax, in 1975.
In the 1980s, Sony made significant strides in personal entertainment and technology. They launched the iconic Walkman portable cassette player in 1979, revolutionizing how people listened to music, and became a cultural phenomenon. Sony also developed the Compact Disc (CD) technology in collaboration with Philips, which changed how music was recorded and played.
The 1990s marked another important milestone for Sony as they entered the gaming industry with the launch of the PlayStation in 1994. The PlayStation became one of the best-selling game consoles of all time and solidified Sony’s position as a leader in the entertainment industry.
Sony continued to diversify its product portfolio and expand into new markets in the new millennium. They introduced the PlayStation 2 in 2000, which became the most successful game console in history, selling over 155 million units worldwide. Sony also ventured into the digital camera market, releasing the Cyber-shot series, quickly gaining consumers’ popularity.
However, Sony faced various challenges and internal struggles in the 2000s and early 2010s. The company experienced financial losses, partially due to the failure of Betamax and the Blu-ray format war against HD DVDs. Additionally, they faced competition from other electronics giants, such as Apple and Samsung.
Sony underwent a major restructuring to regain its competitive edge and refocused its efforts on core areas, such as gaming, imaging, and entertainment. They launched the PlayStation 4 in 2013, which became the fastest-selling console in history. Sony also introduced successful products like the PlayStation VR, mirrorless cameras, and high-resolution audio devices.
In recent years, Sony has continued to innovate and adapt to the rapidly changing technology landscape. They have embraced advancements like 4K and HDR (High Dynamic Range) in their televisions and expanded their presence in the streaming and content production industry with platforms like PlayStation Network and Sony Pictures Entertainment.
Today, Sony Corporation is a global conglomerate with diverse products and services. The company has become a leader in consumer electronics, gaming, entertainment, and professional solutions.
Who Owns Sony
According to Sony, as of March 2022, the major shareholders include:
- The Master Trust Bank of Japan, Ltd. (Trust Account)
Stake: 19.0%
Shares Held: 234,657,000
- Citibank as Depositary Bank for Depositary Receipt Holders
Stake: 9.5%
Shares Held: 117,454,000
- Custody Bank of Japan, Ltd. (Trust Account)
Stake: 7.2%
Shares Held: 88,689,000
- State Street Bank West Client – Treaty 505234
Stake: 1.9%
Shares Held: 22,916,000
- JPMorgan Chase Bank 385632
Stake: 1.7%
Shares Held: 20,435,000
- Ssbtc Client Omnibus Account
Stake: 1.5%
Shares Held: 19,055,000
- Government Of Norway
Stake: 1.5%
Shares Held: 19,038,000
- GIC Private Limited – C
Stake: 1.5%
Shares Held: 18,165,000
- JPMorgan Chase Bank 385781
Stake: 1.3%
Shares Held: 16,644,000
- The Bank Of New York Mellon 140042
Stake: 1.2%
Shares Held: 14,600,000
These shareholders represent a diverse group of institutional entities, including trust banks, depositary banks, and financial institutions.
Sony Mission Statement
Sony’s mission statement is “A company that inspires and fulfills your curiosity.”

How Sony works
Sony’s business model centers around developing, producing, and distributing a wide range of consumer electronics, including televisions, smartphones, cameras, audio equipment, and gaming consoles. The company also offers services such as streaming platforms, music publishing, and financial services.
To interact with Sony’s products and services, customers can visit Sony’s physical retail stores or access them through online platforms. Sony’s online presence includes its official website and various e-commerce platforms, providing a convenient and accessible way for customers to explore and purchase their desired products.
Once a customer purchases a Sony product, they benefit from Sony’s commitment to quality and customer support. Sony provides warranties, repair services, and technical support to ensure customer satisfaction and product longevity. These services are available through dedicated customer service centers, authorized service providers, and online resources.
Sony also offers users a variety of features and services, depending on the industry:
- Sony Electronics: This division focuses on creating innovative and high-quality electronic products, including televisions, cameras, audio equipment, and smartphone devices. Sony’s emphasis on cutting-edge technology and design allows customers to enjoy immersive entertainment experiences and stay connected digitally;
- Sony PlayStation: As a leader in the gaming industry, Sony’s PlayStation division offers gaming consoles, accessories, and a vast library of video games. The PlayStation Network provides online multiplayer capabilities, digital game downloads, and exclusive content to enhance the gaming experience;
- Sony Music: With a vast catalog of music artists and labels, Sony Music is one of the world’s largest music publishing companies. It operates as a record label, releasing and distributing albums across various genres. Sony Music also offers music streaming platforms, enabling customers to access and enjoy a vast collection of songs and playlists;
- Sony Pictures Entertainment: This division focuses on producing and distributing movies, television shows, and other forms of entertainment. Sony Pictures Entertainment owns and operates film studios, production companies, and streaming platforms, allowing customers to enjoy a wide range of visual content;
- Sony Financial Services: Sony provides various financial services, including insurance, banking, and credit services. Sony offers customers access to personalized financial solutions through partnerships and subsidiaries, making managing their money and protecting their assets easier.
How Sony makes money
Sony operates a diversified business model with multiple revenue streams. The following are the primary ways through which Sony generates its revenue:
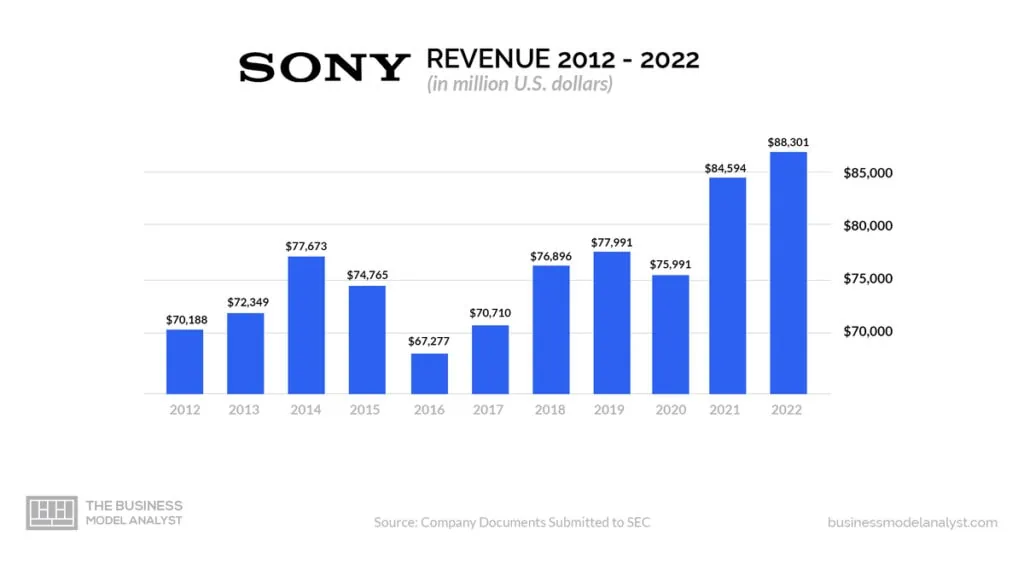
Sale of Consumer Electronics and Devices
Sony is renowned for manufacturing and selling a wide range of consumer electronics and devices. These include televisions, video and digital cameras, audio equipment, gaming consoles, smartphones, and home appliances. Sony’s consumer electronics division contributes a significant portion of the company’s revenue.
Software and Services
In addition to hardware, Sony offers various software and services across its product lines. For instance, the PlayStation Network (PSN) provides online gaming services and access to digital content such as games, movies, and music. Sony also offers subscription-based services such as PlayStation Plus, which provides subscribers with additional features and exclusive game content. These software and services generate recurring revenue for Sony.
Entertainment and Media
Sony operates in the entertainment and media industry through its subsidiary, Sony Pictures Entertainment. This division produces and distributes movies, television shows, and digital content. Sony also owns various music labels and operates streaming platforms such as Spotify. Revenue is generated through ticket sales, licensing deals, advertising, and digital content distribution.
Imaging and Photography
Sony is well-known for its high-quality cameras and imaging devices. The company’s imaging division produces professional and consumer-grade cameras, lenses, and related accessories. Sony also offers various photography services and solutions, such as professional photography equipment rental and image editing software. The sale of cameras and related services contributes to Sony’s revenue.
Financial Services
Sony operates a financial services division, which includes insurance and banking services. Sony Financial Holdings offers life insurance, non-life insurance, and banking services, primarily in Japan. These financial services generate revenue through insurance premiums, banking fees, and investment activities.
Semiconductors and Components:
Sony is a leading manufacturer of semiconductors and electronic components. The company produces image sensors, display panels, and other electronic components used in various industries, including smartphones, automotive, and robotics. Revenue is generated through the sale of these components to other manufacturers.
Sony Business Model Canvas
The Sony Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
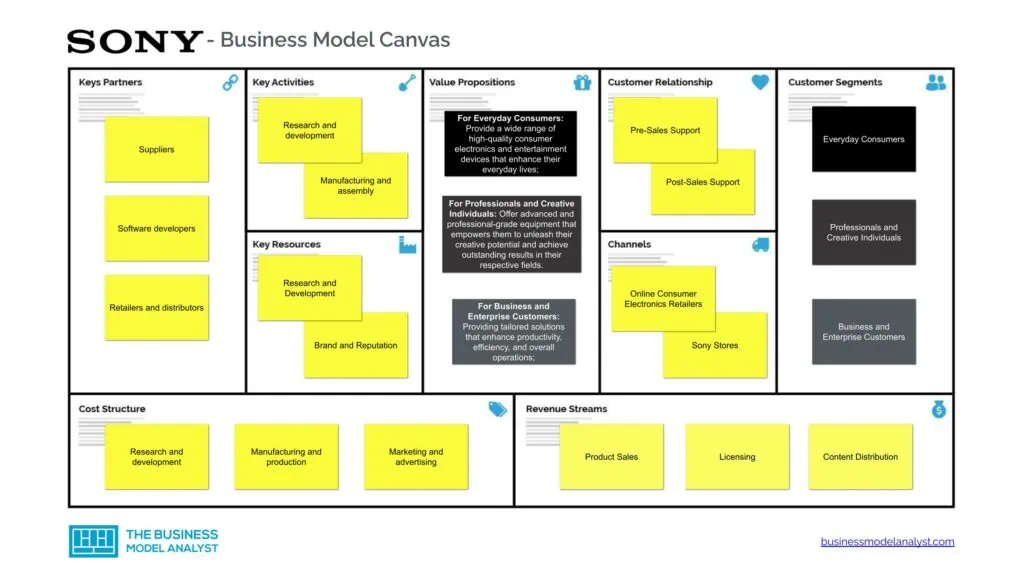
Sony Customer Segments
Sony’s customer segments consist of the following:
- Everyday Consumers: Sony’s products cater to everyday consumers looking for high-quality electronics and entertainment devices. This includes individuals who purchase Sony’s TVs, audio systems, cameras, gaming consoles, smartphones, and other consumer electronics for personal use. Sony targets a wide age range, from young adults to mature individuals, focusing on delivering innovative and user-friendly technology;
- Professionals and Creative Individuals: Sony also caters to professionals and creative individuals who require advanced and professional-grade equipment for their work. This includes photographers, videographers, musicians, producers, and designers who rely on Sony’s cameras, professional audio equipment, professional displays, and software solutions for their creative endeavors. Sony offers a range of high-performance and specialized products to meet the specific needs of professionals in various industries;
- Business and Enterprise Customers: Sony provides solutions for businesses and enterprise customers, offering a range of products and services tailored to meet their requirements. This includes businesses in sectors such as healthcare, education, hospitality, transportation, and more. Sony’s offerings in this segment include professional displays, video conferencing systems, security solutions, data storage, and business projectors. Sony aims to enhance productivity, efficiency, and overall operations for businesses of all sizes;
- Content Creators and Influencers: Sony recognizes the growing importance of content creation and influencer marketing. They target this customer segment by providing tools and devices that enable content creators to produce high-quality videos, photos, and audio content. Sony’s range of cameras, camcorders, audio recorders, and related accessories appeal to this segment, enabling them to create engaging and professional content for online platforms and social media;
- Gaming Enthusiasts: Sony’s PlayStation gaming division targets enthusiasts of all ages seeking immersive gaming experiences. The PlayStation console and related accessories, including controllers and virtual reality (VR) devices, cater to this segment. Sony offers a wide range of exclusive games, online gaming services, and community features that appeal to gamers worldwide;
Sony Value Propositions
Sony’s value propositions consist of:
- For Everyday Consumers: Sony’s value proposition for everyday consumers is to provide a wide range of high-quality consumer electronics and entertainment devices that enhance their everyday lives;
- For Professionals and Creative Individuals: Sony’s value proposition for professionals and creative individuals is to offer advanced and professional-grade equipment that empowers them to unleash their creative potential and achieve outstanding results in their respective fields;
- For Business and Enterprise Customers: Sony’s value proposition for business and enterprise customers centers around providing tailored solutions that enhance productivity, efficiency, and overall operations;
- For Content Creators and Influencers: Sony’s value proposition for content creators and influencers revolves around empowering them to produce captivating and professional-grade content for online platforms and social media;
- For Gaming Enthusiasts: Sony’s value proposition for gaming enthusiasts is to deliver immersive gaming experiences through their PlayStation gaming division. They offer the PlayStation console and a wide range of exclusive games, online gaming services, and community features.
Sony Channels
Sony’s channels consist of:
- Online Consumer Electronics Retailers: Sony sells its products through various online consumer electronics retailers such as Amazon, Best Buy, and Walmart.
- Sony Stores: Sony operates physical stores where customers can experience and purchase its products directly.
- E-commerce Website: Sony has its own e-commerce platform where customers can browse and buy its products online.
- Distributors: Sony partners with distributors who help them sell their products to retailers and resellers.
- Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs): Sony collaborates with OEMs who integrate Sony components and technologies into their own products.
Sony Customer Relationships
Sony’s customer relationships consist of:
- Pre-Sales Support: Sony provides customer support through various channels, including phone, email, and chat, to assist customers before purchasing.
- Post-Sales Support: Sony offers customer support services after purchase, including technical assistance, warranty services, and repair services.
- Loyalty Programs: Sony offers loyalty programs to incentivize customers to stay engaged and loyal to their brand and products.
- Community Engagement: Sony actively engages with customers through social media platforms, forums, and online communities to build relationships and gather feedback.
- Personalization: Sony collects customer data to personalize marketing messages, recommend products, and offer tailored services based on individual preferences.
Sony Revenue Streams
Sony’s revenue streams consist of:
- Product Sales: Sony generates revenue by selling a wide range of consumer electronics and related accessories.
- Licensing: Sony licenses its intellectual property rights and technologies to other companies in exchange for royalties or licensing fees.
- Content Distribution: Sony generates revenue by distributing movies, music, and other entertainment content through its movie and music divisions.
- Subscription Services: Sony offers subscription-based services like PlayStation Plus, which provides access to online gaming and exclusive content, generating recurring revenue.
- Advertising: Sony generates revenue by selling advertising space on its e-commerce platform and entertainment properties.
Sony Key Resources
Sony’s key resources consist of:
- Research and Development: Sony invests in R&D activities to develop new technologies, enhance existing products, and drive innovation.
- Brand and Reputation: Sony’s well-established brand and reputation contribute to customer trust and loyalty.
- Manufacturing Facilities: Sony owns and operates manufacturing facilities worldwide to produce its products.
- Intellectual Property: Sony owns a vast portfolio of intellectual property, including patents, trademarks, and copyrights, which give them a competitive advantage.
- Distribution Network: Sony maintains a global distribution network that enables the efficient delivery of its products to a wide customer base.
Sony Key Activities
Sony’s key activities consist of:
- Research and development
- Manufacturing and assembly
- Content creation and design
- Distribution and marketing
- Customer support
- Intellectual property management
Sony Key Partners
Sony’s key partners consist of:
- Suppliers
- Software developers
- Retailers and distributors
- Advertising agencies
- Collaborative partners
- Sponsors and endorsers
Sony Cost Structure
Sony’s cost structure consists of:
- Research and development
- Manufacturing and production
- Marketing and advertising
- Distribution and logistics
- Licensing and royalties
- Administrative expenses
Sony Competitors
Sony faces intense competition from several major players in the technology and entertainment industries. Here are some of Sony’s key competitors:
- Apple: Apple competes with Sony in various segments, including consumer electronics, smartphones, and digital content distribution. Apple’s strong brand image, innovative products, and ecosystem of services make it a formidable competitor for Sony;
- Samsung: Samsung is a global leader in consumer electronics, including smartphones, televisions, and home appliances. Samsung’s extensive product range and aggressive marketing strategies pose a significant challenge to Sony’s market share;
- Microsoft: While primarily known for software, Microsoft competes with Sony in the gaming industry through its Xbox consoles and gaming services. Microsoft’s robust gaming ecosystem, including Xbox Game Pass, brings fierce competition to Sony’s PlayStation consoles;
- Amazon: Amazon’s diverse business portfolio includes devices like the Kindle e-reader and Fire tablets, as well as streaming services like Prime Video. Amazon competes with Sony in the e-reader market and, to some extent, in the home entertainment sector
- Netflix: As a leading global streaming service, Netflix rivals Sony’s video entertainment offerings, including Sony Pictures Entertainment. Netflix’s vast content library and popular original series pressured Sony to continually produce compelling content;
- Canon and Nikon: In the digital camera market, Sony fiercely competes with Canon and Nikon. These established camera manufacturers have loyal customer bases and continuously strive to innovate regarding image quality, features, and lens ecosystem;
- LG: LG Electronics competes with Sony in various segments, including televisions and home appliances. LG focuses on developing cutting-edge display technologies and consumer-friendly features to stay competitive against Sony;
- Google: Google competes with Sony through its line of Pixel smartphones and various software products. Google’s Android operating system powers many smartphones, including Sony’s, creating competition in the fiercely competitive smartphone market.
Sony SWOT Analysis
To gain a comprehensive understanding of Sony’s business model, it is essential to analyze its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT). This analysis provides insights into the internal and external factors that impact Sony’s performance and future prospects.
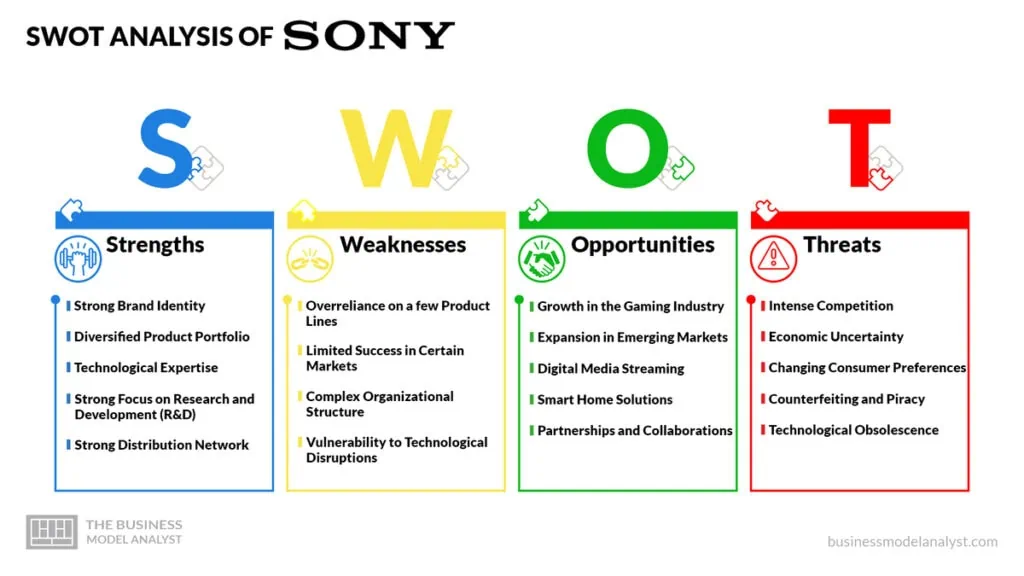
Sony Strengths
- Strong Brand Identity: Sony has established itself as a globally recognized brand known for innovative and high-quality products across various industries;
- Diversified Product Portfolio: Sony operates in multiple sectors, including electronics, gaming, music, and entertainment, which enables it to mitigate risks and benefit from cross-selling opportunities;
- Technological Expertise: Sony has a long history of technological innovation, contributing to its ability to develop cutting-edge products that meet consumer needs;
- Strong Focus on Research and Development (R&D): The company invests heavily in R&D, allowing it to stay at the forefront of emerging technologies and bring forth innovative products;
- Strong Distribution Network: Sony has an extensive global distribution network, enabling it to effectively reach customers across different markets and maximize its sales potential.
Sony Weaknesses
- Overreliance on a few Product Lines: Despite diversifying its product portfolio, Sony is heavily dependent on its gaming division, which accounts for a significant portion of its revenue. This concentration poses a risk if there are disruptions or declining demand in that segment;
- Limited Success in Certain Markets: Sony faces challenges in penetrating and gaining significant market share in some regions, primarily due to intense competition and varying consumer preferences;
- Complex Organizational Structure: Sony’s organizational structure can sometimes be perceived as bureaucratic and slow in decision-making, making it challenging to adapt quickly to market changes;
- Vulnerability to Technological Disruptions: As a technology-driven company, Sony faces the risk of its products becoming obsolete due to rapid technological advancements from competitors;
- Image Perception: Sony’s reputation in terms of customer service and perceived value for money can sometimes be seen as inferior when compared to its competitors, impacting consumer perception.
Sony Opportunities
- Growth in the Gaming Industry: The increasing demand for gaming consoles, virtual reality, and online gaming presents opportunities for Sony to further expand its market share and revenue in the gaming sector;
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: Sony can focus on expanding its presence in emerging markets, such as India and China, to tap into the rising middle-class population and the increasing disposable income;
- Digital Media Streaming: The growth of online entertainment platforms provides opportunities for Sony’s music and entertainment divisions to capitalize on the shift towards digital media consumption;
- Smart Home Solutions: The integration of Sony’s technology and electronics expertise with smart home products offers an opportunity for the company to create innovative solutions in this emerging market;
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Sony can explore strategic partnerships with other companies to leverage complementary strengths and enhance its market position in areas like artificial intelligence, healthcare, and electric vehicles.
Sony Threats
- Intense Competition: Sony faces intense competition from established players and emerging companies across various industries it operates in, including Apple, Samsung, Microsoft, and Amazon;
- Economic Uncertainty: Macroeconomic factors such as recessions, currency fluctuations, and trade disputes can impact consumer spending and adversely affect Sony’s sales and profitability;
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Rapidly evolving consumer preferences and trends pose a threat to Sony’s ability to develop and deliver products that align with customer demands;
- Counterfeiting and Piracy: The prevalence of counterfeit products and piracy can negatively impact Sony’s sales and brand image, especially in markets with weak intellectual property protection;
- Technological Obsolescence: The rapid pace of technological advancements can render Sony’s products outdated, making it critical for the company to keep up with the latest trends and maintain its competitive edge.
Conclusion
Sony’s business model has proven to be a successful strategy for the company. By focusing on innovation, diversification, and a strong brand presence, Sony has adapted to changing market conditions and maintained a competitive edge.
The company’s ability to seamlessly integrate its various businesses, such as electronics, entertainment, and gaming, has allowed it to capture a wide customer base and generate consistent revenue streams.
In addition, Sony’s commitment to research and development, along with strategic partnerships and acquisitions, has enabled it to stay at the forefront of technological advancements. While challenges remain, Sony’s robust business model positions it well for future growth and continued success in the global marketplace.

