The Lego Business Model revolves around creating a platform for limitless construction possibilities, allowing users to build and design their own creations. Lego, a Danish toy company founded in 1932, has become a household name worldwide. Known for its iconic interlocking plastic bricks, Lego has built a successful business model that taps into the creativity and imagination of children and adults alike.
The Lego brick sets are carefully crafted to provide a satisfying building experience, encouraging problem-solving skills, and promoting hands-on play. The company’s dedication to quality and innovation has led to a loyal customer base and a global brand synonymous with creativity and fun.
Through strategic licensing and partnerships, Lego has expanded its product offerings beyond just bricks. Lego has diversified its business model from movies and video games to theme parks and educational programs to cater to different customer segments and expand its reach.
Contents
A brief history of Lego
The foundation of Lego can be traced back to the early 20th century in Billund, Denmark. The company was founded by Ole Kirk Christiansen, a carpenter who started his business by producing wooden toys. Christiansen’s dedication to craftsmanship and quality quickly gained recognition, and his products became popular.
In 1932, Christiansen decided to change the name of his company to “Lego,” derived from the Danish words “leg godt,” which means “play well.” This new name reflected the company’s commitment to providing toys that encouraged creativity and imagination in children.
In the following years, Lego continued to innovate and expand its product offerings. In 1949, the company introduced the “Automatic Binding Bricks,” which marked the introduction of the iconic interlocking brick system that Lego is known for today. This breakthrough design allowed children to easily assemble and disassemble their creations, sparking a new level of play and endless possibilities.
Throughout the 1950s and 1960s, Lego experienced steady growth, introducing new sets and themes to cater to different interests and age groups. The Lego System of Play, which allowed for the interchangeability and combination of various Lego sets, further enhanced the versatility and appeal of Lego toys.
However, Lego faced significant challenges in the 1990s with the rise of digital entertainment and changing consumer preferences. To adapt to these shifting dynamics, Lego underwent a period of restructuring and refocusing. The company recognized the importance of innovation and investing in technology to complement its physical toys. This led to the launch of Lego Mindstorms in 1998, a robotics platform that merged the digital and physical worlds, allowing children to build and program their own robots. Mindstorms was discontinued at the end of 2022.
In the early 2000s, Lego faced financial struggles and embarked on a dramatic turnaround. The company refocused on its core values of creativity, quality, and play, streamlining its product range and strengthening its brand. This strategic shift, combined with successful partnerships with popular franchises like Star Wars and Harry Potter, revitalized Lego’s business and led to significant growth.
Today, Lego continues to thrive and expand its reach globally. The company’s commitment to fostering creativity and imagination remains at the core of its business model. Lego sets encompass a wide range of themes and interests, appealing to children and adult enthusiasts alike. Additionally, Lego has extended its presence beyond physical toys, leveraging digital technologies to enhance the play experience and further engage with its customers.
Who Owns Lego
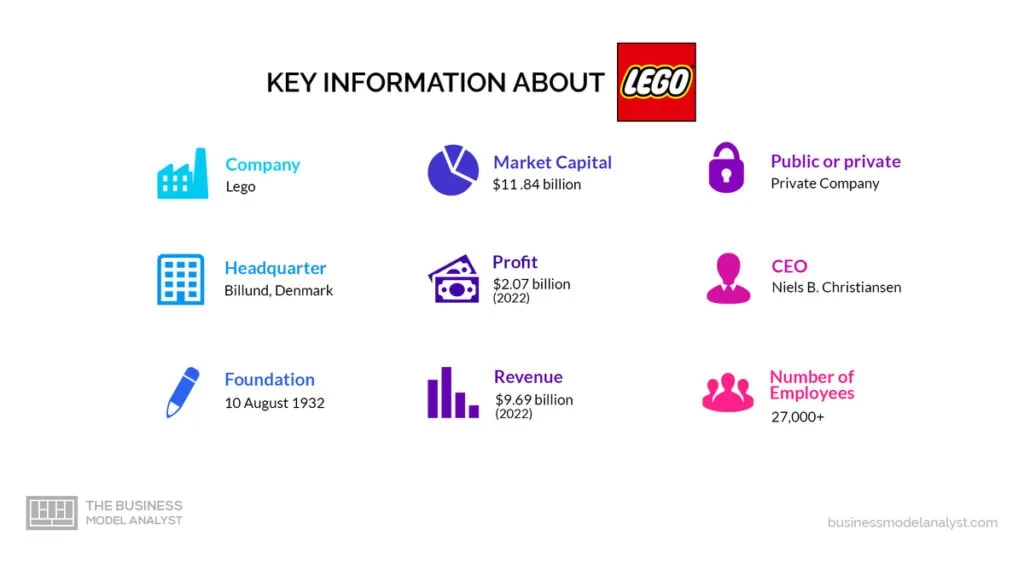
Lego is a privately held company, meaning it is not publicly traded on any stock exchange. As such, the ownership of Lego is not readily available to the public. However, it is known that the Kirk Kristiansen family, descendants of Lego’s founder Ole Kirk Kristiansen, have maintained control and ownership of the company for generations.
The company’s current CEO, Niels B. Christiansen, is also a member of the Kirk Kristiansen family. While specific details about the family’s ownership percentage or distribution of shares are not publicly disclosed, it is widely acknowledged that they retain majority ownership and control over Lego.
Being a private company, Lego is not subject to the same reporting and disclosure requirements as publicly traded companies. Therefore, information about other potential shareholders or stakeholder groups is not readily available.
Lego’s commitment to remaining privately owned allows the company to focus on its long-term vision and values, without the short-term pressures often associated with public ownership. This has enabled it to maintain its status as a global leader in the toy industry while staying true to its core principles of creativity, quality, and learning through play.
Lego Mission Statement
Lego’s mission statement is “to Inspire and Develop the Builders of Tomorrow.”

How Lego works
Lego, a renowned Danish toy company, operates through a unique business model that provides children and adults with imaginative and creative play experiences. With a rich history from 1932, Lego has evolved into a global brand that delivers high-quality building toys and experiences that inspire creativity and learning.
At the core of Lego’s business model is its commitment to product innovation and quality. Lego sets are carefully designed and manufactured to meet the highest safety, durability, and playability standards. The company invests extensively in research and development to create new building elements, themes, and play experiences that captivate its target audience.
Lego’s business model is built on a “system of play” approach, where all Lego elements are designed to be compatible and can be interchanged and combined to create limitless possibilities. This versatility allows customers to imagine and build their own unique creations, fostering creativity, problem-solving skills, and self-expression. Lego sets often include instructions to guide users in building specific models, but the possibilities for creation extend far beyond those instructions.
To make its products accessible, Lego adopts a multichannel distribution strategy. Lego sets are sold through various channels, including company-owned stores, e-commerce platforms, and retail partners worldwide. This broad reach ensures that customers can easily find and purchase Lego products, regardless of location.
Lego also places significant emphasis on customer engagement and community building. Through initiatives like Lego Ideas, a platform that allows fans to submit and vote for new Lego sets, the company actively involves its customers in the development process and embraces co-creation. Lego also organizes events, competitions, and social media campaigns to engage with its passionate fan community and encourage enthusiasts to share their creations and experiences.
In recent years, Lego has extended its business model beyond physical products to incorporate digital experiences. Through partnerships with popular franchises and the development of video games and mobile apps, Lego has expanded its reach into the digital realm while maintaining the essence of creative play. These digital offerings provide additional avenues for customers to engage with the Lego brand, stimulating their imagination and bringing together the physical and virtual worlds.
Lego’s business model thrives on its ability to continuously adapt and innovate. By staying true to its core values of quality and creativity, Lego has become a beloved brand worldwide. The company’s commitment to fostering imagination and learning through play has allowed it to build a loyal customer base that spans generations.
How Lego makes money
Lego operates a business model that primarily relies on revenue from selling its toys and related products. The company’s revenue sources can be summarized as follows:
Sale of Lego Sets and Products
Lego offers a wide range of building block sets, playsets, minifigures, and accessories. These products cater to different age groups and interests, including Star Wars, Marvel, Harry Potter, and City themes. Lego sets are sold through various channels, including Lego brand stores, online platforms, and retail partners. The revenue generated from the sale of Lego sets and products is the company’s main income source.
Licensing Partnerships
Lego has established partnerships with a variety of popular brands, franchises, and entertainment properties. These collaborations allow Lego to create specialized sets based on movies, TV shows, video games, and other intellectual properties. Lego pays licensing fees to these partners, gaining access to their fan base and branding, which helps drive sales and attract new customers.
Theme Parks and Experiences
Lego operates a chain of theme parks known as Legoland, as well as Legoland Discovery Centers, in various locations worldwide. These amusement parks and attractions offer visitors immersive Lego experiences, including rides, shows, and interactive exhibits. The revenue from ticket sales, merchandise, and food and beverage sales at these attractions contributes to Lego’s overall revenue.
Digital Games and Media
Lego has also ventured into the digital space by developing video games and digital entertainment experiences. The company licenses its brand and characters to game developers to create Lego-themed video games. Additionally, Lego produces animated movies, TV shows, and web series featuring its characters and stories. Revenue is generated through the sale of these digital products, as well as licensing fees and partnerships with media platforms.
Education and Learning Solutions
Lego offers educational products and programs that promote learning through play. These include Lego Education sets and curriculum materials used in schools and educational institutions to enhance STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math) education. Lego also conducts workshops and events to support educators in integrating Lego into their teaching practices. Revenue is generated through the sale of educational products and services.
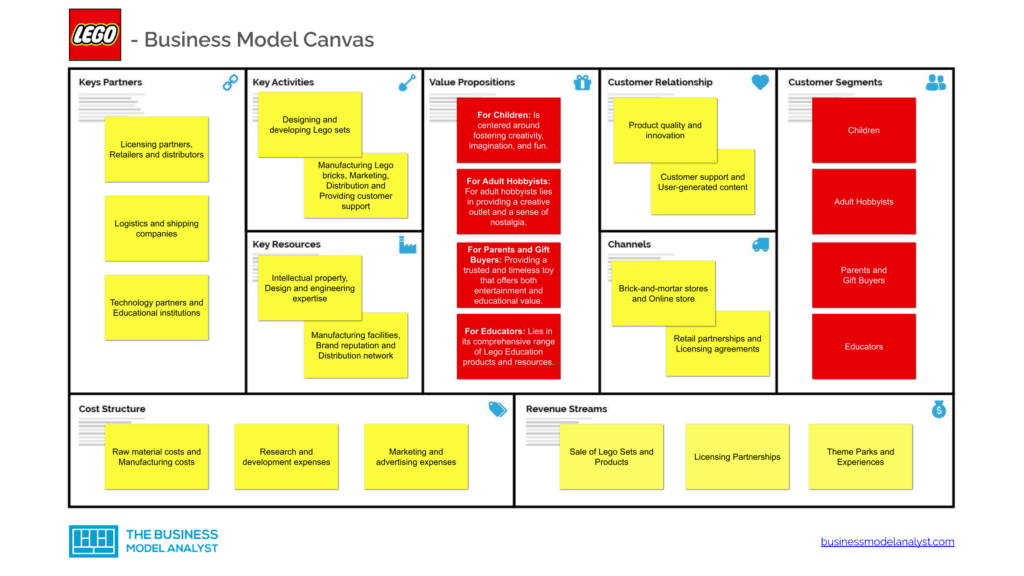
Lego Business Model Canvas
The Lego Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
Lego Customer Segments
Lego’s customer segments are diverse and cater to both individuals and businesses. The following are the key customer segments for Lego:
- Children: A significant portion of Lego’s customer segment consists of children. Lego’s colorful building blocks and various themed sets appeal to children of all ages. Lego’s products encourage creativity, imagination, and problem-solving skills, making them popular among parents and educational institutions;
- Adult Hobbyists: Lego has also captured the attention of adult hobbyists known as AFOLs (Adult Fans of Lego). These individuals collect and build intricate Lego sets, often focusing on specific themes or expert-level creations. Lego offers sets targeted at this customer segment, which includes large-scale models, architectural sets, and collector’s editions;
- Parents and Gift Buyers: Parents and other gift buyers comprise a significant portion of Lego’s customer segment. They purchase Lego sets as gifts for birthdays, holidays, and other special occasions. Lego’s wide range of sets, from small and affordable options to large and intricate ones, provides plenty of choices for parents and gift buyers;
- Educators: Lego also caters to the education sector by offering specialized educational resources, such as Lego Education sets and curriculum materials. These products are designed to enhance learning experiences, promote critical thinking, and develop STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) skills in students of all ages;
- Retailers and Distributors: Lego’s customer segment includes retailers and distributors that sell Lego products. These partners are crucial in reaching the end consumers and ensuring the wide availability of Lego sets in stores and online platforms.
Lego Value Propositions
- For Children: Lego’s value proposition for children is centered around fostering creativity, imagination, and fun. Their colorful building blocks and themed sets provide endless opportunities for children to build, explore, and engage in imaginative play. Lego’s products entertain and promote children’s cognitive and motor skill development. They offer a wide range of age-appropriate sets, from simple starter sets for young children to more complex ones for older kids, ensuring every child can find a Lego set that suits their interests and abilities;
- For Adult Hobbyists: For adult hobbyists, Lego’s value proposition lies in providing a creative outlet and a sense of nostalgia. Their intricate and detailed sets challenge and delight AFOLs, allowing them to indulge in their passion for building and collecting. With expert-level sets and collaborations with popular franchises, Lego offers adult hobbyists the opportunity to showcase their craftsmanship and create impressive displays. The sense of satisfaction and accomplishment that comes with completing a complex Lego model is a unique value proposition for this customer segment;
- For Parents and Gift Buyers: Lego’s value proposition for parents and gift buyers revolves around providing a trusted and timeless toy that offers both entertainment and educational value. Their high-quality building blocks and diverse range of sets make Lego a go-to choice for parents who prioritize the development of their children’s creativity and problem-solving abilities. Lego sets also offer long-term play value and the opportunity for family bonding as parents and children can build and play together. The wide variety of options allows gift buyers to find the perfect Lego set for any occasion, making it a reliable and well-received gift choice;
- For Educators: Lego’s value proposition for educators lies in its comprehensive range of Lego Education products and resources. These offerings are designed to support STEM education and provide hands-on learning experiences. Lego Education sets and curriculum materials enable educators to incorporate play and creativity into their teaching methods, promoting critical thinking and collaboration among students. Through their educational products, Lego helps educators create engaging and impactful learning environments that inspire students to explore and experiment with concepts in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics;
- For Retailers and Distributors: Lego’s value proposition for retailers and distributors is based on its strong brand reputation, product quality, and global demand. By partnering with Lego, retailers gain access to a highly recognized and trusted brand that attracts a loyal customer base.
Through these different value propositions, Lego effectively caters to the needs and desires of each customer segment, making its business model strong and adaptable in a competitive toy market.
Lego Channels
Lego’s channels consist of:
- Brick-and-mortar stores: Lego operates a network of physical stores in various locations worldwide, allowing customers to browse and purchase products directly;
- Online store: Lego has an official e-commerce platform where customers can buy products online and deliver them to their doorstep;
- Retail partnerships: Lego collaborates with third-party retailers and department stores to distribute their products, expanding their reach and availability;
- Licensing agreements: Lego has established partnerships with various entertainment franchises, allowing them to create Lego sets based on popular movies, TV shows, and video games.
Lego Customer Relationships
Lego’s customer relationships consist of:
- Product quality and innovation: Lego focuses on maintaining high-quality products with innovative designs to establish long-term relationships with customers who appreciate the brand’s commitment to creativity and play;
- Customer support: Lego offers customer support through various channels, including phone, email, and social media, to address inquiries and complaints, as well as provide assistance with product-related issues;
- User-generated content: Lego encourages customers to share their creations on social media platforms, fostering community and valuable interactions between Lego enthusiasts.
Lego Revenue Streams
Lego’s revenue streams consist of:
- Sale of Lego Sets and Products
- Licensing Partnerships
- Theme Parks and Experiences
- Digital Games and Media
- Education and Learning Solutions
Lego Key Resources
Lego’s key resources consist of:
- Intellectual property: Lego’s key resource lies in its iconic interlocking brick design and associated patents, protecting its products’ uniqueness and building capabilities;
- Design and engineering expertise: Lego maintains a team of designers and engineers who continuously innovate and develop new products, ensuring that the brand stays relevant and appealing to customers;
- Manufacturing facilities: Lego’s ability to manufacture its products efficiently and at scale is a critical resource for meeting customer demand and maintaining profitability;
- Brand reputation: Lego’s strong brand reputation, built on decades of quality and creativity, is a valuable resource that helps attract loyal customers and generate repeat business;
- Distribution network: Lego’s extensive distribution network, including its own stores, partner retailers, and e-commerce platform, is a key resource for ensuring the widespread availability of its products globally.
Lego Key Activities
Lego’s key activities consist of:
- Designing and developing Lego sets
- Manufacturing Lego bricks
- Marketing
- Distribution
- Providing customer support
Lego Key Partners
Lego’s key partners consist of:
- Licensing partners
- Retailers and distributors
- Logistics and shipping companies
- Technology partners
- Educational institutions
Lego Cost Structure
Lego’s cost structure consists of:
- Raw material costs
- Manufacturing costs
- Research and development expenses
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Distribution and logistics costs
- Licensing fees
- Administrative and operational expenses
- Customer support costs
Lego Competitors
Lego faces competition from several major players in the toy industry. Here are some of its main competitors:
- Mattel: Mattel is a leading toy company known for brands such as Barbie, Hot Wheels, and Fisher-Price. Although primarily focuses on dolls and action figures, it also offers building sets competing with Lego;
- Hasbro: Hasbro is another major toy manufacturer with a wide range of products, including popular franchises like Transformers, My Little Pony, and Nerf. Hasbro’s building sets, such as KRE-O, directly compete against Lego in the construction toy market;
- Mega Bloks: Mega Bloks is a brand owned by Mattel and a direct competitor to Lego. It offers construction sets similar to Lego, targeting a similar demographic;
- K’NEX: K’NEX is a building toy company known for its unique rod-and-connector system. While not as widely recognized as Lego, K’NEX competes in the construction toy segment, offering diverse building experiences;
- Meccano: Meccano is a historic construction toy brand that has existed since the early 20th century. It offers metal-based construction sets that allow kids to build elaborate structures, vehicles, and robots;
- Tinkertoy: Tinkertoy is another construction toy brand that emphasizes creativity and building with rods and connectors. It provides an alternative play experience to Lego and targets younger children. Hasbro and K’NEX currently own the Tinkertoy brand, and they produce a range of sets and parts using both plastic and wood materials. K’NEX operates under license from Hasbro and is responsible for developing and distributing Tinkertoy sets. Hasbro acquired the Tinkertoy brand in 1986, following multiple changes in ownership;
- Playmobil: Playmobil is a German toy company known for its detailed, themed playsets. While not directly competing with Lego’s building sets, Playmobil competes for children’s attention in the toy market and offers a different play experience.
Lego SWOT Analysis
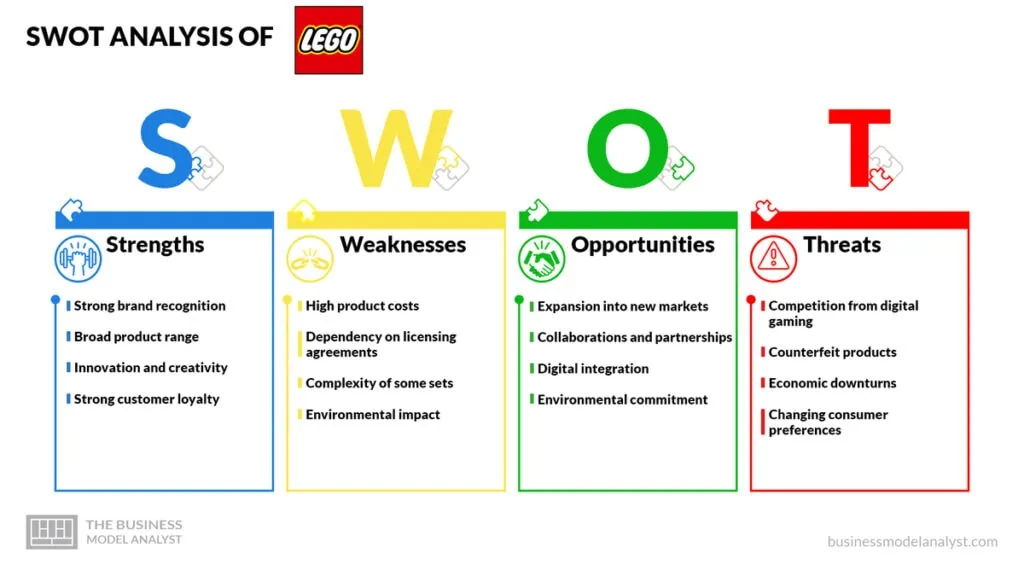
With its iconic building blocks and commitment to fostering creativity and innovation, Lego has become synonymous with quality and timeless play. To gain a deeper understanding of Lego’s strategic position in the market, it is essential to analyze its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats through a SWOT analysis.
Lego Strengths
- Strong brand recognition: Lego is a globally recognized brand known for its high-quality and timeless products;
- Broad product range: Lego offers a diverse range of products, including sets based on movies, TV shows, and popular franchises, appealing to a wide customer base;
- Innovation and creativity: Lego continually releases new sets, incorporating technological advancements and encouraging imaginative play;
- Strong customer loyalty: Lego has a dedicated customer base that appreciates the company’s commitment to quality, reliability, and creativity.
Lego Weaknesses
- High product costs: Lego sets can be relatively expensive, limiting their accessibility for some customers;
- Dependency on licensing agreements: Lego depends heavily on licensing agreements with popular brands and franchises, which can result in increased costs and limited control over product development;
- Complexity of some sets: Advanced Lego sets can be complex and time-consuming to build, potentially reducing their appeal to younger children or casual consumers;
- Environmental impact: Continued plastic use in Lego products raises concerns regarding sustainability and the company’s commitment to addressing environmental issues.
Lego Opportunities
- Expansion into new markets: Lego can expand its reach by targeting emerging markets or diversifying into new product categories;
- Collaborations and partnerships: Lego can continue to form partnerships with popular brands, movies, and celebrities to create exclusive sets and enhance brand exposure;
- Digital integration: There is an opportunity for Lego to leverage technology and expand its presence in the digital space, such as developing interactive mobile apps or online gaming experiences;
- Environmental commitment: By investing in sustainable materials and adopting eco-friendly manufacturing practices, Lego can appeal to environmentally-conscious consumers and meet evolving regulations.
Lego Threats
- Competition from digital gaming: Video games and virtual experiences may threaten traditional physical toys like Lego, as children increasingly engage with digital entertainment;
- Counterfeit products: The prevalence of counterfeit Lego products in the market can undermine the brand’s reputation and impact sales;
- Economic downturns: In times of economic uncertainty or recession, consumer spending on discretionary items like Lego sets may decrease;
- Changing consumer preferences: Evolving consumer preferences and shifting demographics can impact the demand for Lego products, requiring continuous adaptation and innovation.
Conclusion
Lego’s business model is a remarkable example of strategic innovation and adaptability. By focusing on its core product, the iconic Lego brick, and continuously developing new sets and themes, Lego has been able to maintain strong brand equity and foster a loyal customer base.
Their commitment to quality, creativity, and playability has led to a strong competitive advantage in the toy industry. In addition, Lego’s strategic partnerships, licensing agreements, and expansion into digital platforms have allowed them to reach new markets and stay relevant in the ever-evolving world of play.
Lego’s business model demonstrates the importance of staying true to your core product while staying open to embracing new opportunities and technologies to drive sustainable growth and success.

