Apple Business Model focuses primarily on selling its products and offering services through subscriptions. Sales of Apple products like the iPhone, iPad, Apple Watch, and MacBook make up a large percentage of Apple’s revenue, while its services include Apple TV+, Apple Fitness+, Apple Music, iCloud+, and Apple Arcade, although a small percentage of its revenue, net them a whopping average of $13 billion per quarter.
Apple has surpassed the trillion-dollar market cap mark through its business model, making it the first company to ever manage such a feat.
Contents
A brief history of Apple:
Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, two college dropouts, founded Apple on April 1, 1976, using Jobs’ garage as their main office. They aimed to revolutionize the way people saw computers. They wanted to make computers small enough to fit in people’s homes and offices. In effect, their first product, the Apple 1 — a hand-built computer —, included only functional hardware modules like CPU, RAM, and basic textual-video chips, and excluded features like monitors, keyboards, and other Human Interface Devices.
On their second product, the Apple II, expansion slots were included for attaching floppy disk drives and other components and Human Interface Devices. This second product increased their sales from $7.8 million in 1978 to $118 million in 1980 (when they went public).
A few years later, in 1983, Wozniak left the company, and Jobs followed suit in 1985, after hiring PepsiCo’s John Sculley as president. He was ousted after the growing friction between him and Sculley resulted in him organizing a ‘coup’ to remove Sculley. This coup backfired, however.
Steve Jobs founded his NeXT software company soon afterward, after buying Pixar from George Lucas. However, his departure was short-lived, and in 1997 Apple bought his company. This was done to bring him back to the company in order to save their declining market shares. The changes he implemented after coming back saved the company from impending doom, and in 2007, they launched one of their most successful product, the iPhone.
They have launched other successful products and services since then, which helped them become the first company ever to cross the trillion-dollar mark, this was in 2018. In 2020, they doubled their market cap by doubling down on their highly successful business model.
Who Owns Apple:
According to 2021 shareholder data, Apple’s major shareholders included corporations like The Vanguard Group (7.68%), BlackRock, Inc. (6.47%), Berkshire Hathaway Inc. (5.56%), and private investors like Tim Cook, Apple’s CEO, Artur Levinson, Jeff Williams, Al Gore, Dave Adams, and Andrea Jung.
Apple’s mission statement:
Apple’s Mission Statement is: “To bring the best user experience to customers through innovative hardware, software, and services.” – Bstrategyhub
How Apple makes money
Apple leverages its unique ability to design and develop its own operating systems, hardware, application software, and services to provide its customers with products and solutions with innovative design, superior ease of use, and seamless integration — 10-K 2017.
Apple makes money by designing, manufacturing, and selling smartphones, tablets, personal computers, wearables, and accessories. Their main products include iPhones, MacBooks, iPads, Apple Watch, AirPods, and the Apple TV. They also generate revenue by offering subscription services like their iCloud cloud services, Apple TV+ subscriptions, Apple Arcade, and iTunes. The company recently announced its plans to start hardware subscription services for its products.
Furthermore, Apple makes money when the users of its products pay fees for the extension of their warranties. In addition to their products, they also sell compatible third-party accessories and apps.
As a passive revenue source, Apple also makes money through in-app purchases on iPhones, and app sales on their App Store — they take a 30% cut from every transaction.
Their largest and most profitable revenue source is the sales of their products, however, their subscription services generate the highest gross margins in comparison to product sales.
Apple’s Business Model Canvas
Let’s take a look at the Apple Business Model Canvas below:
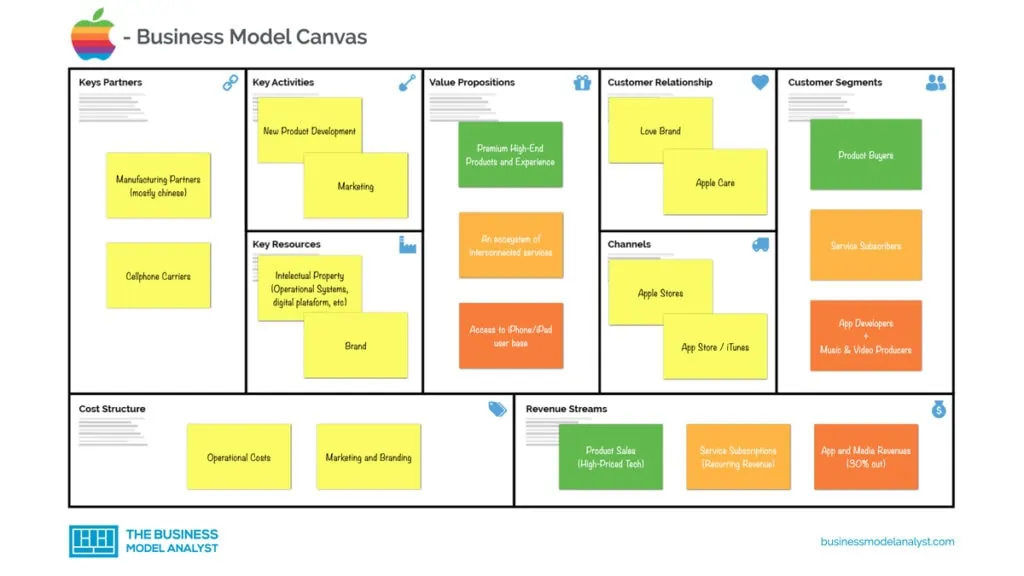
Apple’s Customer Segments
Apple’s customer segments consist of:
- Product Buyers: These include people that buy their products for their high-end performances and people who use them as their primary devices regardless of performance. A section of their customers also buys their products because of the brand name;
- Service Subscribers (most service subscribers overlap as product buyers): These include subscribers of Apple Arcade — their games’ subscription service —, Apple TV+, iCloud+, and their warranty extension services.
- App Developers (and music producers): Anyone that would like to sell their apps and music to the Apple user base and monetize through app store or iTunes.
Apple’s Value Propositions
Apple’s value propositions consist of:
- Premium High-end Products (with a focus on privacy): Apple offers its customers carefully crafted products with a focus on performance, stability, and privacy, a number of its customers have stayed around because of this.
- An ecosystem of interconnected services: Apple’s line-up of services (and products) are well integrated with each other, offering users hassle-free inter-use of their products and services.
- Access to iPhone/iPad user base: one of the richest user bases in the world that are willing to spend much more than Google Android user base.
Apple’s Channels
Apple’s channels consist of:
- Website
- Apple Stores
- Third-party Stores
- Telecom Companies (Apple’s iPhones are typically bundled with a mobile plan to reduce costs by offering monthly repayment packages)
- Resellers
Apple’s Customer Relationships
Apple’s customer relationships consist of:
- Social Media
- Customer Service
- Apple Stores
- Website
- Operating Systems
- Loyal Community
Apple’s Revenue Streams
Apple’s revenue streams consist of:
- Sale of Products
- Subscription Services
- App Store and in-app purchase percentage cuts
- Licensing Fees
- Cloud Services
Apple’s Key Resources
Apple’s key resources consist of:
- Brand Name and Recognition
- Patents
- Employees
- Management Team
Apple’s Key Activities
Apple’s key activities consist of:
- Innovation
- Design & Manufacturing
- Marketing & Sales
- Customer Service
- Branding
Apple’s Key Partners
Apple’s key partners consist of:
- Hardware Suppliers, such as Qualcomm, Samsung, Cisco, etc.;
- Software Providers: cloud service providers, such as Google and Amazon;
- Investors/Shareholders
- Telecom Companies
Apple’s Cost Structure
Apple’s cost structure consists of:
- Manufacturing & Distribution
- Salaries
- Marketing
- Platforms Maintenance Fees
- Payment Processing Fees
- Management & Administration
Apple’s Competitors
- Samsung: One of Apple’s main competitors in the smartphone space, Samsung holds a whopping 20% share of the global smartphone market. Samsung’s entrance into the market with its Samsung Galaxy and Note series has negatively influenced the sales of iPhones globally, however, they are not the only company that has contributed to this, others include Xiaomi, Vivo, and Oppo.
- Dell: Dell Technologies (DVMT) is a company that makes desktop and mobile computing devices, including laptops, tablets, and mobile phones. Dell’s biggest competitor is Apple; the two companies have a long history of competing against one another. In fact, in 2004 Dell released a product to compete with Apple’s iPod music player: Dell DJ.
- HP: Hewlett-Packard Co. (HPQ), established in 1939, is known as the founding company of Silicon Valley as well as for making affordable consumer computers. HP has expanded its presence in recent years to include computers for a broader range of consumers around the globe. Apple Inc. is a leading competitor for HP outside the United States.
Apple’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT Analysis of Apple:

Apple’s Strengths
- Pricing Strategy: Apple’s high prices makes it possible for the company to sell a small number of products and still rake in a large amount of revenue;
- Subscription Services: The company’s subscription services and the principles of the subscription business model enables Apple to have a predictable chunk of revenue;
- Performance: Apple’s insistence on rolling out its products with high-performance processors has cemented its name as a go-to company for high-quality products;
- Brand Recognition: Their popularity and fame as a goto company for quality products and services has helped them increase and maintain their market cap;
- Loyal Community: Apple’s community of loyal customers allows them to have customer feedback aimed at improving the quality of their products and services. This community also enables Apple to have a somewhat stable revenue proposition.
Apple’s Weaknesses
- Pricing Strategy: Apple’s prices make it a luxury company in developing countries, thus driving away most middle-class and lower-class potential customers;
Apple’s Opportunities
- Products and Pricing Strategy: Although being partially implemented, the design and manufacturing of products aimed at middle-class and lower-class consumers will enable Apple to increase its already high revenue and market cap.
Apple’s Threats
- Market Trends: As a result of Apple’s yearly release of products, the market trend is a big factor that determines the revenue yield of its new line-up of devices. Because most customers already have recent versions of their products or do not have plans of purchasing new ones, Apple’s yearly revenue yield at new product launches seems to be reducing year by year, and will most likely continue;
- Competition: Competitors like Samsung are already affecting Apple’s customer base via their offering of flexible and customizable OS in their products. The arrival of better competitors aimed at the high and middle classes of developed countries will most likely affect Apple’s user base.
-> Read More About Apple’s SWOT Analysis.
Conclusion
Through the success of its application, Apple’s business model is worth considering for new entrants into the tech space. However, do not expect overnight success since Apple experienced its fair share of challenges even with its implementation of its business model. Apple’s combination of the subscription business model and their product sales was a major factor that determined their huge revenue growth and as such, if you are to adopt the Apple business model, do not overlook the subscription business model.

