The Citigroup Business Model, rooted in a venerable institution with a history spanning more than a century, is a shining example of its enduring significance in the world of banking and financial services. Nestled in the bustling heart of New York City, Citigroup’s influence stretches far and wide, operating on a scale that few can rival.
Citigroup’s journey has been characterized by resilience and ingenuity, showcasing its ability to remain adaptable in the face of economic fluctuations and technological progress. Throughout its history, it has weathered economic challenges, embraced technological revolutions, and extended its global footprint. Presently, Citigroup stands as a multifaceted institution, providing a wide array of financial services, including retail and commercial banking, wealth management, investment banking, and more.
The Citigroup Business Model is a complex ecosystem constructed upon the pillars of trust, financial expertise, and an unwavering commitment to its diverse clientele. Leveraging an extensive network of branches, digital platforms, and strategic partnerships, it efficiently delivers its services to millions of customers worldwide. With a presence in over 150 countries, Citigroup’s global reach underscores its dedication to facilitating international trade and finance.

Contents
A brief history of Citigroup
The roots of Citigroup can be traced back to the early 19th century, when it was a humble banking institution known as the City Bank of New York. Founded in 1812, the bank was established as a response to the need for a stable financial institution in the rapidly growing and ever-changing landscape of New York City.
During its early years, the City Bank of New York weathered various financial crises and economic challenges. It managed to survive and even thrive, gradually building a reputation for financial stability and reliability
In 1865, the bank underwent a significant transformation when it became the National City Bank of New York. This change was prompted by the passage of the National Banking Act, which aimed to create a more uniform and regulated banking system across the United States.
Over the ensuing decades, National City Bank continued to expand its operations and influence. It played a vital role in financing the growth of American industries, particularly during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, when the country experienced unprecedented industrialization.
In 1933, in response to the economic challenges posed by the Great Depression, the United States government introduced the Glass-Steagall Act. This landmark legislation sought to separate commercial banking activities from investment banking, aiming to prevent financial instability. As a result of this regulatory change, National City Bank underwent yet another transformation, becoming the First National City Bank of New York.
The mid-20th century brought further changes and expansions for the bank. It extended its reach internationally, establishing branches and operations in various countries around the world. By the 1960s, First National City Bank had become one of the largest banks in the United States.
In 1976, the bank underwent another significant rebranding effort, adopting the name Citibank, N.A. This change marked the beginning of a new era for the institution, as it signaled its intention to become a global financial powerhouse.
The late 20th century saw Citibank engage in a series of mergers and acquisitions, aiming to diversify its financial services and expand its global reach. One of the most notable mergers occurred in 1998 when Citibank alternatively known as Citicorp merged with Travelers Group, a financial services conglomerate. This merger created Citigroup Inc., a financial behemoth that combined banking, insurance, and investment services under one roof.
Throughout its history, Citigroup has faced its fair share of challenges, including economic downturns and financial crises. It weathered the storm of the 2008 global financial crisis, which had far-reaching implications for the entire financial industry. The bank underwent significant restructuring and government assistance during this period.
In recent years, Citigroup has continued to adapt to the changing landscape of finance, focusing on streamlining its operations, improving its risk management practices, and strengthening its presence in key markets around the world.
Today, Citigroup stands as one of the world’s largest and most diversified financial institutions, offering a wide range of financial products and services to individuals, businesses, and governments across the globe. Its history is a testament to its resilience, adaptability, and enduring commitment to the principles of banking and finance.
Who Owns Citigroup
Citigroup is a publicly traded company with a diverse ownership structure. The ownership of Citigroup is distributed among a wide range of institutional investors, individual shareholders, and company executives.
Note that Citigroup is subject to fluctuations in ownership due to its status as a publicly traded company. Shareholders can buy and sell Citigroup’s stock on various stock exchanges.
As of 10 October 2023, Citigroup’s ownership structure is as follows:
- Institutional Investors: A significant portion of Citigroup’s shares is held by institutional investors, including investment management firms, mutual funds, and pension funds. These institutions invest in Citigroup as part of their diversified portfolios. The Vanguard Group, Inc. is one of the largest institutional shareholders of Citigroup, with a substantial ownership stake of 8.40%;
- Individual Shareholders: Many individual investors own shares of Citigroup. These shareholders can include retail investors who buy and hold Citigroup stock as part of their personal investment strategies. According to CNN Money, individual stakeholders currently hold a 0.62% stake in the company;
- Company Executives: Historically, key executives within Citigroup, such as the CEO and top management, have held shares in the company as part of their compensation packages. These shares serve as incentives to align their interests with those of shareholders;
- Employee Stock Ownership: Some employees of Citigroup may own shares of the company through employee stock ownership plans (ESOPs) or stock options provided by the company as part of their compensation;
- Public Market: Citigroup’s shares are traded on major stock exchanges, including the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), under the ticker symbol NYSE: C. This means that members of the public can buy and sell Citigroup stock on these exchanges.
Citigroup Mission Statement
Citigroup’s mission statement is “to serve as a trusted partner to our clients by responsibly providing financial services that enable growth and economic progress.”

How Citigroup works
Citigroup offers a wide range of financial products and services to individuals, businesses, and institutions.
Citigroup Diverse Financial Services
At the heart of Citigroup’s business model lies a commitment to providing a comprehensive suite of financial services to meet the diverse needs of its clients. This includes offerings such as personal banking, commercial banking, investment banking, wealth management, and global markets services.
Accessibility through Technology
Citigroup leverages cutting-edge technology and data analytics to ensure its financial services are accessible and tailored to each customer’s unique requirements. The company’s online platform, available through its website and mobile app, serves as the gateway for customers to access and manage their accounts, execute transactions, and explore various financial products.
Getting Started with Citigroup
To begin their journey with Citigroup, customers are required to create an account either through the website or the mobile app. This serves as the foundation for exploring the extensive range of financial products and services offered by Citigroup.
Tailored Recommendations and Efficient Application Process
Citigroup’s technology-driven platform employs advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms to provide personalized recommendations to customers. Whether it’s applying for a credit card, a mortgage, or investment advice, the platform streamlines the application process, making it quick and hassle-free.
Ongoing Support and Financial Guidance
Once a customer becomes part of the Citigroup ecosystem, they benefit from continuous support to manage their finances effectively. This support extends to educational resources, financial planning tools, and access to a team of expert financial advisors, empowering customers to make informed decisions and work toward their financial goals.
Key Features and Services
Citigroup offers an array of features and services, including:
- Banking: A comprehensive suite of personal and commercial banking services, including checking and savings accounts, loans, and credit cards;
- Investments: Access to a wide range of investment options, from stocks and bonds to mutual funds and alternative investments, supported by personalized recommendations and portfolio management tools;
- Insights: A robust repository of educational resources and financial planning tools, complemented by expert guidance from Citigroup’s financial advisors;
- Insurance: Tailored insurance solutions, covering life, health, property, and more, with personalized recommendations to meet individual insurance needs.
How Citigroup makes money
Citigroup employs a multifaceted business model to generate revenue. This model encompasses a range of financial services, each contributing to the company’s overall profitability. Below, we delve into the diverse ways in which Citigroup makes money:
Traditional Banking Services
Citigroup operates as a traditional bank, offering a wide array of banking services to individuals and businesses. These services include savings accounts, checking accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and loans, such as mortgages and personal loans. Citigroup earns revenue by charging interest on loans it extends to customers. Additionally, fees for various banking services, such as overdraft fees and wire transfer charges, contribute to the bank’s income.
Investment Banking
Citigroup has a prominent presence in the investment banking sector. The company provides advisory services for mergers and acquisitions (M&A), helps companies raise capital through initial public offerings (IPOs), and offers trading services in various financial markets. Citigroup earns fees for facilitating these transactions and providing financial advice to its corporate clients.
Wealth Management and Asset Management
Citigroup offers wealth management services to high-net-worth individuals and institutions. The company manages investment portfolios through its asset management division, including mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Citigroup charges management fees based on the assets under management (AUM) and may also earn performance fees for achieving specific investment goals.
Consumer Banking and Credit Cards
Citigroup issues credit cards to consumers and partners with various retail brands to offer co-branded credit cards. These credit cards generate revenue through annual fees, interest charges on outstanding balances, and transaction interchange fees. Additionally, Citigroup earns fees from merchants each time a customer uses a Citigroup credit card for payment.
Global Markets and Trading
Citigroup participates in global financial markets, trading a wide range of financial instruments, including stocks, bonds, currencies, and commodities. Revenue is generated through trading spreads, brokerage fees, and commissions from clients and counterparties.
Treasury and Transaction Services
Citigroup offers treasury and transaction services to corporate clients, assisting them in managing their cash flow, payments, and treasury operations. Fees are collected for these essential financial services, which help businesses optimize their financial processes.
Asset-backed Securities and Securitization
Citigroup engages in securitization activities, bundling assets such as mortgages, auto loans, and credit card receivables into securities, which are then sold to investors. The bank earns fees for structuring and distributing these securities.
Global Private Banking
Citigroup’s global private banking division serves high-net-worth clients worldwide, providing tailored financial solutions. Fees for investment advisory services, estate planning, and wealth management contribute to revenue in this segment.
Insurance Products
Citigroup offers various insurance products, including life insurance, home insurance, and credit protection insurance. Revenue is generated through commissions and fees paid by insurance providers.
Digital Banking Services
In the digital era, Citigroup provides online and mobile banking services, allowing customers to manage their accounts, pay bills, and conduct transactions electronically. The bank may earn fees for certain digital banking services and may also benefit from cost savings associated with reduced branch operations.
Asset Custody and Fund Services
Citigroup offers custody and fund services to institutional investors, including asset managers and pension funds. Fees are collected for safeguarding and administering clients’ assets.
International Operations
Citigroup operates globally, and its international branches and subsidiaries contribute significantly to its revenue. The bank earns income from international banking services, foreign exchange transactions, and cross-border trade finance.
Citigroup Business Model Canvas
The Citigroup Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
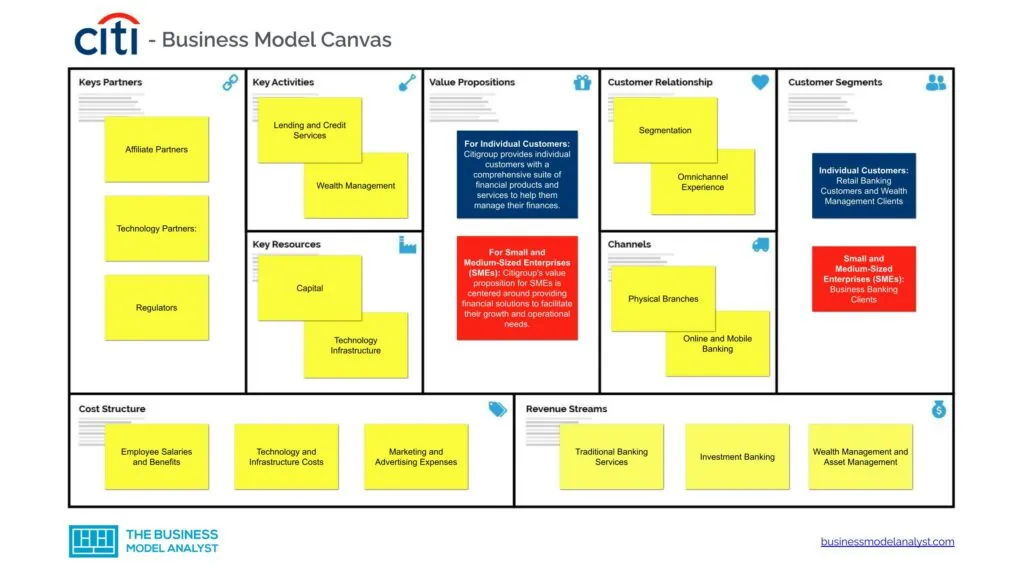
Citigroup Customer Segments
Citigroup caters to a diverse customer base with unique segments, each playing a crucial role in its business model. These customer segments include:
- Individual Customers:
- Retail Banking Customers: Citigroup serves individual consumers across the globe, offering a wide range of retail banking services, including savings and checking accounts, mortgages, personal loans, and credit cards. These customers comprise a significant portion of Citigroup’s customer base and contribute to the bank’s deposit and lending businesses;
- Wealth Management Clients: Citigroup provides wealth management services to high-net-worth individuals and families. These clients benefit from personalized investment and financial planning, trust and estate services, and access to exclusive investment opportunities.
- Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs):
- Business Banking Clients: Citigroup supports SMEs by offering a suite of banking solutions, including business accounts, lines of credit, and merchant services. These services are designed to facilitate their day-to-day operations and growth.
- Corporations and Multinational Companies:
- Corporate Banking Clients: Citigroup has a significant presence in serving large corporations and multinational companies. It provides a range of financial services, such as treasury management, trade finance, and access to global capital markets. These clients rely on Citigroup for efficient financial solutions to facilitate their international operations;
- Investment Banking and Advisory: Citigroup is a prominent player in the investment banking arena, offering strategic advisory services, underwriting, and mergers and acquisitions expertise. Corporations and institutions turn to Citigroup for assistance with capital raising and complex financial transactions.
- Institutional Investors:
- Asset Management Clients: Citigroup operates an asset management business that serves institutional investors, such as pension funds, insurance companies, and sovereign wealth funds. These clients entrust Citigroup with managing their investments in a diverse array of asset classes;
- Trading and Capital Markets Participants: Citigroup plays a vital role in global capital markets, serving as a counterparty for trading in various financial instruments, including equities, fixed income, and foreign exchange. Institutional investors and traders engage with Citigroup to execute transactions and manage their risk.
- Government and Public Sector Entities:
- Public Sector Clients: Citigroup provides specialized financial services to government entities, municipalities, and public organizations. These clients rely on Citigroup for funding, cash management, and financial solutions tailored to the public sector’s unique needs.
Each of these customer segments contributes to Citigroup’s multifaceted business model.
Citigroup Value Propositions
Citigroup value propositions consist of:
- For Individual Customers: Citigroup provides individual customers with a comprehensive suite of financial products and services to help them manage their finances. They can rely on Citigroup for:
- Convenient and accessible retail banking services, including savings and checking accounts, credit cards, and personal loans;
- Wealth management expertise that offers tailored investment solutions, financial planning, and estate services;
- Access to a global network of ATMs, branches, and digital banking platforms, ensuring ease of banking wherever they are.
- For Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs): Citigroup’s value proposition for SMEs is centered around providing financial solutions to facilitate their growth and operational needs. They benefit from:
- Tailored business banking services, including accounts, credit lines, and merchant services;
- Expert advice and insights to navigate financial challenges and seize opportunities;
- Access to international markets and trade finance services for global expansion.
- For Corporations and Multinational Companies: Citigroup’s value proposition for corporations and multinational companies is built on their specific financial requirements. They receive:
- Comprehensive corporate banking solutions, including treasury management, trade finance, and access to global capital markets;
- Expertise in strategic advisory services and capital raising for mergers, acquisitions, and financing;
- A global network that enables them to operate efficiently across international markets.
- For Institutional Investors: Institutional investors turn to Citigroup for professional asset management and capital market services. Citigroup’s value proposition to them includes:
- Diverse asset management options and strategies designed to meet their investment objectives;
- Efficient trading and risk management solutions, spanning equities, fixed income, and foreign exchange;
- A wealth of research, analytics, and market insights to make informed investment decisions.
- For Government and Public Sector Entities: Citigroup’s value proposition for government and public sector entities focuses on their unique financial needs. They benefit from:
- Specialized financial services tailored to the public sector, including funding and cash management solutions;
- Advisory services to manage public funds, debt issuance, and infrastructure financing;
- Access to Citigroup’s global network and expertise in navigating complex financial environments.
Citigroup Channels
These channels refer to the bank’s various distribution and communication methods to reach its customers and deliver its financial products and services. They play a critical role in Citigroup’s business model, allowing the bank to interact with clients, facilitate transactions, and provide access to its suite of banking and financial services. Here are some of the key channels employed by Citigroup:
- Physical Branches: Citigroup operates a network of physical bank branches in various locations globally. These branches serve as a traditional channel for customers to conduct banking transactions, seek financial advice, and access banking professionals for personalized services;
- Online and Mobile Banking: Citigroup offers online and mobile banking platforms, enabling customers to access their accounts, check balances, transfer funds, pay bills, and perform various banking activities via web and mobile applications. These digital channels enhance convenience and accessibility for tech-savvy customers;
- ATMs: Citigroup has a widespread network of automated teller machines (ATMs) that allow customers to withdraw cash, deposit funds, and perform other basic transactions 24/7;
- Call Centers: The bank operates call centers where customers can get assistance, inquire about products and services, and resolve issues through telephone communication with customer service representatives;
- Corporate and Institutional Banking: Citigroup has a dedicated channel for corporate and institutional clients, offering customized solutions, advisory services, and access to global financial markets;
- Digital Banking Apps: The bank provides digital applications that are compatible with various devices, including smartphones and tablets. These apps offer a range of features and services, from mobile deposits to investment management;
- Wealth Management Services: Citigroup’s wealth management services include private banking, investment advisory, and trust services, which are delivered through specialized channels to cater to high-net-worth individuals and families;
- Online Trading Platforms: Citigroup provides online trading platforms for clients interested in buying and selling stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. These platforms offer real-time market data and research tools;
- Global Network: Citigroup leverages its extensive global network to provide international services to clients engaged in cross-border business, trade, and finance. This network allows for seamless cross-border transactions and trade financing;
- Affiliate Partnerships: Citigroup often partners with affiliates, including retail and e-commerce platforms, to offer co-branded credit cards and financial products. These partnerships expand the bank’s reach and customer base.
Citigroup Customer Relationships
This refers to the bank’s strategies and approaches to build and maintain relationships with its diverse customer base. Establishing strong customer relationships is essential for Citigroup to foster trust, loyalty, and customer satisfaction. Here are the key aspects of Citigroup’s customer relationships:
- Segmentation: Citigroup segments its customers into various categories, such as retail banking, corporate clients, high-net-worth individuals, and institutional investors. This segmentation helps the bank tailor its services and communication to meet the distinct needs of different customer groups;
- Omnichannel Experience: Citigroup aims to create a seamless and consistent customer experience across all channels, whether customers engage through physical branches, online and mobile banking, call centers, or other touchpoints. This ensures that customers can access their accounts and receive assistance in a way that suits their preferences;
- Customer Service: Citigroup places a strong emphasis on customer service. The bank provides responsive and accessible customer support through various channels, including call centers, chat services, and in-branch interactions. This helps resolve issues and answer inquiries promptly;
- Financial Advisory: For wealth management and investment banking clients, Citigroup offers financial advisory services to help them make informed decisions, manage their portfolios, and achieve their financial goals. These relationships often involve ongoing consultations and advice;
- Long-Term Partnerships: In the corporate and institutional banking sector, Citigroup builds long-term relationships with clients by providing tailored financial solutions, trade financing, and advisory services. These partnerships are crucial for supporting clients’ business growth and international expansion;
- Compliance and Security: Citigroup places a strong emphasis on maintaining a secure and compliant environment to protect customer data and assets. This is crucial for building trust with customers, particularly in the digital age.
Citigroup Revenue Streams
Citigroup revenue streams consist of:
- Traditional Banking Services
- Investment Banking
- Wealth Management and Asset Management
- Consumer Banking and Credit Cards
- Global Markets and Trading
- Treasury and Transaction Services
- Asset-backed Securities and Securitization
- Global Private Banking
- Insurance Products
- Digital Banking Services
- Asset Custody and Fund Services
- International Operations
Citigroup Key Resources
Citigroup key resources consist of:
- Capital: Citigroup relies on significant financial capital to fund its operations, lending activities, and investments;
- Technology Infrastructure: The bank heavily invests in technology and data infrastructure to support its digital banking, trading, and transaction processing capabilities;
- Human Capital: A skilled workforce, including banking professionals, financial analysts, and customer service representatives, is a critical resource for providing banking and financial services;
- Branch Network: Citigroup’s physical branch network serves as a key resource for retail banking and customer engagement;
- Global Network: The bank’s extensive international presence and relationships are valuable resources for serving global clients and facilitating cross-border transactions.
Citigroup Key Activities
Citigroup key activities consist of:
- Lending and Credit Services: Citigroup’s core activity involves providing loans and credit to individuals, businesses, and governments;
- Wealth Management: The bank engages in wealth management and investment services, offering financial advisory and portfolio management to high-net-worth clients;
- Trading and Investment Banking: Citigroup actively participates in financial markets through trading activities and investment banking services, including underwriting, M&A advisory, and securities trading;
- Consumer Banking: This activity includes offering deposit accounts, credit cards, personal loans, and related consumer financial services;
- Corporate and Institutional Banking: Citigroup caters to corporate and institutional clients by providing a wide range of financial solutions, including treasury management, trade finance, and foreign exchange services;
- Digital Banking: Developing and maintaining digital banking platforms and applications is a critical activity to provide online and mobile banking services.
Citigroup Key Partners
Citigroup key partners consist of:
- Affiliate Partners: Collaborations with retail and e-commerce partners to offer co-branded credit cards and financial products;
- Technology Partners: Partnerships with technology providers and fintech companies to enhance digital banking capabilities and customer experience;
- Regulators: Engagement with regulatory authorities and compliance partners to ensure adherence to financial regulations and standards;
- International Correspondent Banks: Relationships with other financial institutions globally, facilitating international transactions and trade;
- Investment Banking Clients: Partnerships with corporations and institutions seeking advisory and financial services in mergers and acquisitions, capital raising, and other financial transactions.
Citigroup Cost Structure
Citigroup cost structure consists of:
- Employee Salaries and Benefits: Employee compensation and benefits are a significant portion of Citigroup’s expenses, given the need for a skilled workforce;
- Technology and Infrastructure Costs: Maintaining and upgrading technology systems, as well as data security measures, is a substantial cost component;
- Marketing and Advertising Expenses: Costs associated with marketing campaigns, advertising, and customer acquisition;
- Compliance and Regulatory Costs: Expenses related to compliance and regulatory requirements to ensure adherence to financial regulations;
- Interest Expenses: The interest paid on deposits and other sources of funding represents a cost for the bank;
- Loan Loss Provisions: Citigroup sets aside funds to cover potential loan losses, which can vary with economic conditions and credit risk;
- Operational and Administrative Costs: General operational and administrative expenses, including rent, utilities, and office maintenance;
- Capital Expenditures: Investments in physical branch networks, ATMs, and digital banking infrastructure.
Citigroup Competitors
Citigroup faces competition from various financial institutions and firms across different segments of the banking and financial services industry. Its competitors include:
- JPMorgan Chase & Co.: As one of the largest banks in the United States, JPMorgan Chase competes with Citigroup in areas like retail banking, investment banking, asset management, and credit card services;
- Bank of America: Bank of America is another major U.S. bank that competes with Citigroup, offering similar retail and commercial banking services, credit cards, and investment banking solutions;
- Wells Fargo: Wells Fargo is a key competitor in retail and commercial banking, mortgage lending, and wealth management services;
- Goldman Sachs: In the investment banking and securities trading space, Goldman Sachs competes with Citigroup by offering advisory services, underwriting, and trading services;
- Morgan Stanley: Morgan Stanley is a strong competitor in investment banking, wealth management, and asset management, with a focus on high-net-worth and institutional clients;
- HSBC: As a global bank, HSBC competes with Citigroup in international banking, trade finance, and cross-border financial services;
- Barclays: Barclays competes with Citigroup in various areas, including investment banking, credit card services, and retail banking in the United Kingdom and other markets;
- Fintech Companies: Emerging fintech firms, such as Square, PayPal, and Robinhood, compete with Citigroup in digital payment solutions, consumer banking, and brokerage services;
- Regional and Community Banks: Local and regional banks often compete with Citigroup in specific geographic markets, offering similar retail and commercial banking services to local communities.
Citigroup SWOT Analysis
This SWOT analysis provides an overview of Citigroup’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats, which the bank must consider when making strategic decisions and managing risks in its dynamic business environment.
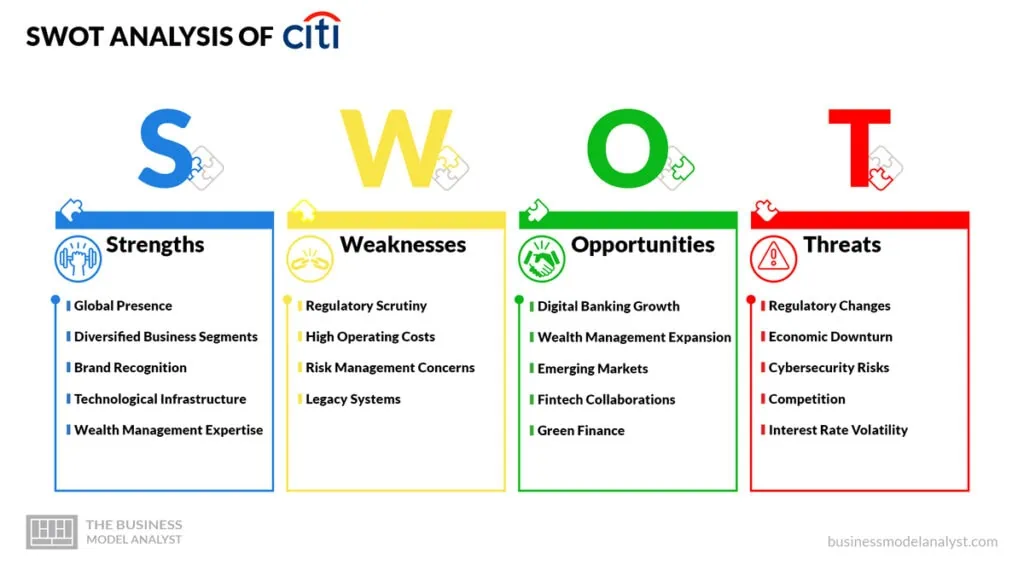
Citigroup Strengths
- Global Presence: Citigroup has a vast international network, allowing it to serve customers in numerous countries and access diverse markets;
- Diversified Business Segments: The bank operates in various financial segments, including retail banking, investment banking, and wealth management, providing multiple sources of revenue;
- Brand Recognition: Citigroup is a well-known global brand with a long history, which can help in attracting customers and investors;
- Technological Infrastructure: The bank has invested in robust digital banking platforms, enhancing customer engagement and operational efficiency;
- Wealth Management Expertise: Citigroup’s strength in wealth management caters to high-net-worth individuals and generates substantial fees and income.
Citigroup Weaknesses
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Citigroup has faced regulatory challenges and legal issues in the past, which can lead to fines and damage to its reputation;
- High Operating Costs: Maintaining a global presence and technological infrastructure results in significant operating expenses;
- Risk Management Concerns: The bank’s exposure to risk, especially in trading and investment activities, can lead to potential losses and volatility;
- Legacy Systems: The integration of legacy systems with new technology can be challenging and may hinder agility and innovation.
Citigroup Opportunities
- Digital Banking Growth: The increasing adoption of digital banking provides opportunities to expand the bank’s customer base and reduce costs;
- Wealth Management Expansion: The growing number of high-net-worth individuals worldwide presents opportunities for Citigroup to expand its wealth management services;
- Emerging Markets: Expansion into emerging markets can tap into new sources of revenue as these markets continue to develop;
- Fintech Collaborations: Partnering with fintech companies can enhance Citigroup’s digital offerings and customer experience;
- Green Finance: The trend toward sustainable and green finance presents opportunities for Citigroup to invest in environmentally responsible projects and services.
Citigroup Threats
- Regulatory Changes: Evolving financial regulations and compliance requirements can impact the bank’s operations and increase costs;
- Economic Downturn: Economic downturns can lead to increased loan defaults and reduced demand for financial services;
- Cybersecurity Risks: The bank is vulnerable to cybersecurity threats, which can result in data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage;
- Competition: Intense competition from other financial institutions and emerging fintech companies can erode market share and pricing power;
- Interest Rate Volatility: Changes in interest rates can affect Citigroup’s net interest margin and profitability.
Conclusion
Citigroup’s business model has evolved over the years to become a globally diversified financial services conglomerate. With a strong presence in consumer banking, investment banking, and wealth management, Citigroup has demonstrated resilience and adaptability in a dynamic financial landscape.
While its size and complexity have posed challenges, the company’s commitment to risk management and regulatory compliance has been central to its survival and success. As Citigroup continues to navigate the ever-changing financial industry, its ability to innovate, expand its digital offerings, and effectively manage risk will remain key factors in its ongoing growth and sustainability.

