The Goldman Sachs business model is centered around providing four primary financial services — Investment Banking, Global Markets, Asset Management, and Consumer & Wealth Management — to individuals, corporations, governments, and institutional clients across the globe. Goldman Sachs is not your ordinary investment bank. It’s a powerhouse of strategic thinking, financial expertise, and unwavering commitment to excellence.
Goldman Sachs has built an empire on its ability to identify and capitalize on market trends. It uses innovative financial instruments and unparalleled industry knowledge to generate profits for itself and its clients. At the heart of Goldman Sachs’ business model lies a relentless pursuit of success. Whether navigating global finance’s complexities, pioneering new investment strategies, or leveraging cutting-edge technology, the firm is always at the forefront of change.
But what truly sets Goldman Sachs apart is its people. With a talent pool that’s second to none, the firm attracts the brightest and most driven minds from around the world. A common goal unites these individuals: to push the boundaries of what’s possible and deliver superior results for their clients. In short, Goldman Sachs is a company that’s constantly pushing forward, innovating, and looking for ways to create value for its stakeholders. It’s a model of success that’s been honed over decades and will continue to shape the future of finance for years to come.

Contents
A brief history of Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs is one of the world’s leading investment banks, providing a wide range of financial services to clients around the globe. Founded in 1869 by Marcus Goldman, a German-born immigrant who established the firm as a small commercial paper trading business in New York City, Goldman Sachs has since evolved into a global financial powerhouse with a reputation for innovation, risk management, and client service. Headquartered in New York City, Goldman Sachs has a global presence with offices in major financial centers worldwide, including London, Tokyo, Hong Kong, and Singapore. The firm operates in more than 40 countries and has over 30,000 employees.
Goldman Sachs’ business model is based on four primary pillars: Investment Banking, Global Markets, Asset Management, and Consumer & Wealth Management. In Investment Banking, Goldman Sachs provides advisory services for mergers and acquisitions, underwriting services for equity and debt securities, and structured finance solutions for clients in various industries. The firm offers trading and market-making services across various asset classes, including equities, fixed income, currencies, and commodities in Global Markets.
In Asset Management, Goldman Sachs manages and invests assets for institutional and individual clients, offering solutions such as mutual funds, private equity, hedge funds, and other alternative investments. Lastly, in Consumer & Wealth Management, the firm provides banking and investment services to high-net-worth individuals and institutional clients, focusing on personalized advice and tailored solutions.
One of the hallmarks of Goldman Sachs is its ability to adapt to changing market conditions and rapidly evolve its business strategies to stay ahead of the curve. This agility is reflected in the firm’s diverse revenue streams, which range from investment banking and trading to asset management and consumer banking. This diversity has helped Goldman Sachs weather the storms of economic uncertainty and remains a top player in the finance industry for over 150 years.
However, Goldman Sachs has faced its fair share of successes and failures. In the early years, the firm played a significant role in helping finance the US economy’s growth, including providing capital for the expansion of the railroad industry. The firm also participated in some of the most significant financial events of the 20th century, including the founding of the World Bank and the initial public offering (IPO) of Ford Motor Company. The company has continued to innovate and expand its business, but it has also faced criticism for contributing to the financial crisis of 2008. The firm has been accused of contributing to the crisis by involving complex and risky financial instruments like mortgage-backed securities.
Despite these challenges, Goldman Sachs has maintained its reputation as one of the world’s most prestigious financial institutions. Goldman Sachs’ strong emphasis on innovation and its ability to adapt to changing market conditions sets it apart from other investment banks. The firm has pioneered technology and digital finance and is willing to experiment with new business models and strategies.
Additionally, Goldman Sachs greatly values building deep and lasting relationships with its clients. This focus on client service has helped the firm to establish a loyal client base and maintain its position as a top player in the finance industry. By taking the time to truly understand the unique needs and objectives of each individual or institution it serves, Goldman Sachs can provide bespoke solutions that deliver real value and drive long-term success.
In conclusion, the Goldman Sachs business model is a testament to the power of innovation, adaptability, and client-centricity. The firm’s ability to navigate changing market conditions and provide customized solutions has allowed it to remain a top player in the finance industry for over a century and a half. Despite facing significant challenges, Goldman Sachs has continued to evolve and grow, cementing its place in the banking industry.
Who Owns Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs is a publicly-traded company, which means it is owned by shareholders who buy and sell its stock on various stock exchanges worldwide. As of May 2023, the largest shareholders of Goldman Sachs are institutional investors, such as mutual funds, pension funds, and hedge funds. The current CEO of Goldman Sachs is David Solomon, who took over the role in October 2018, succeeding Lloyd Blankfein.
Goldman Sachs Mission Statement

Goldman Sachs’ mission statement is “to advance sustainable economic growth and financial opportunity globally.”
How Goldman Sachs works
Goldman Sachs is a multinational investment bank providing financial services to corporations, governments, and individuals. It is widely recognized as a leader in the financial services industry and has built a reputation for delivering innovative and effective solutions to its clients. Here’s how Goldman Sachs works and what differentiates it from other financial institutions.
The first key area of focus for Goldman Sachs is investment banking. The company offers its clients a wide range of investment banking services, including underwriting and distributing securities, advising on mergers and acquisitions, and helping companies raise capital. It is also involved in various trading activities, including buying and selling stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. Additionally, Goldman Sachs manages assets for various clients, including individuals, institutions, and governments. The company’s asset management division includes mutual funds, hedge funds, and private equity.
Asides from asset management, Goldman Sachs, provides insights and recommendations to clients about various financial markets and securities. The company’s research team comprises highly experienced analysts who combine data and analysis to provide clients, traders, and portfolio managers with valuable insights about potential investment opportunities. Furthermore, the company also manages various types of risk, including market, credit, and operational risks.
How Goldman Sachs makes money
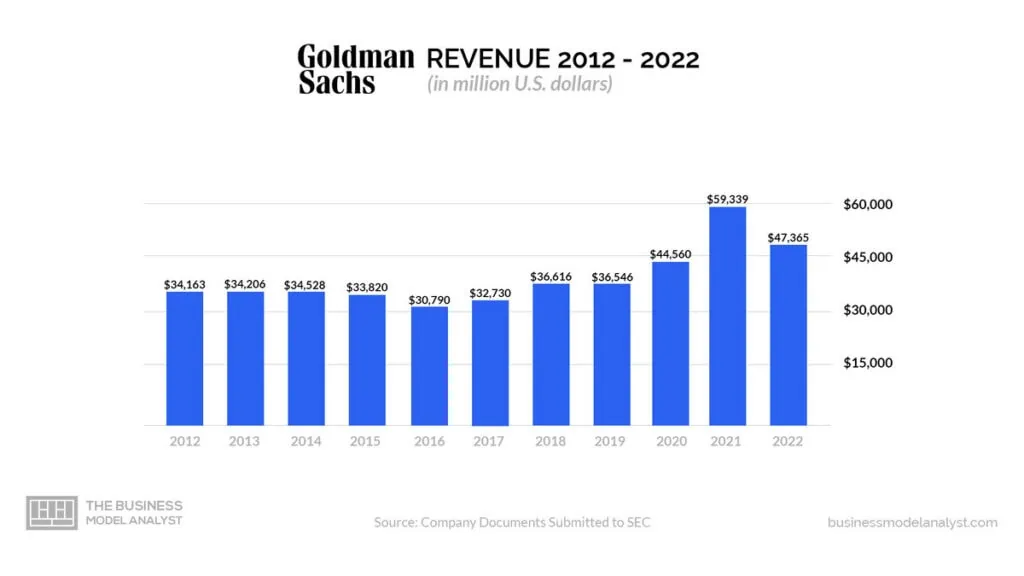
As a financial institution, Goldman Sachs makes money through investment banking, trading, asset management, securities service, and consumer banking. Below are more details on each income stream;
Investment banking
Goldman Sachs works with clients to help them raise capital through various financial products such as initial public offerings (IPOs), bonds, and other types of securities. The bank also advises clients on risk management, strategic planning, and mergers and acquisitions.
Trading
Goldman Sachs is one of the largest trading firms in the world, with a strong presence in equities and fixed-income markets. The company uses sophisticated algorithms and trading strategies to profit from market fluctuations. Additionally, Goldman Sachs engages in market-making activities, acting as a middleman between buyers and sellers of securities.
Asset management
Goldman Sachs manages assets for many clients, including pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, and high-net-worth individuals. The company offers a variety of investment strategies, including passive index-tracking funds, active equity funds, and alternative investments such as hedge funds and private equity.
Securities services
In addition to providing clearing, settlement, and custody services, Goldman Sachs offers financing and securities lending to other financial institutions. These services help clients manage their positions and provide liquidity to the markets.
Consumer banking
In recent years, Goldman Sachs’ consumer banking arm, Marcus, has rapidly grown. In addition to personal loans and savings accounts, Marcus offers credit cards and other financial products. The bank uses sophisticated underwriting models and digital platforms to offer competitive rates and a seamless customer experience. Additionally, Marcus partners with other fintech companies to offer their products through its platform.
Goldman Sachs Business Model Canvas
The Goldman Sachs Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
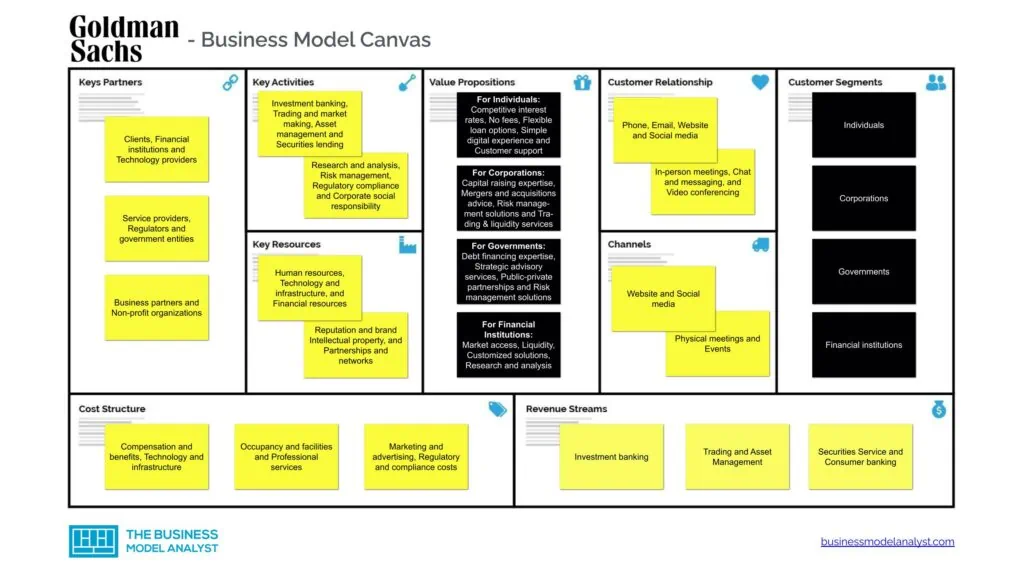
Goldman Sachs Customer Segments
Goldman Sachs’ customer segments are:
- Individuals
- Corporations
- Governments
- Financial institutions
Goldman Sachs Value Propositions
Goldman Sachs’ value propositions are:
Value Propositions for Individuals:
- Competitive interest rates: Marcus, Goldman Sachs’ consumer banking arm, offers competitive interest rates on its personal loans and savings accounts. This allows individuals to earn higher returns on their savings and pay lower interest rates on their loans;
- No fees: Marcus does not charge any fees for personal loans, savings accounts, or other products. This can be a valuable benefit for individuals looking to avoid unnecessary fees;
- Flexible loan options: Additionally, Marcus offers personal loans with flexible repayment terms and no prepayment fees. This allows individuals to customize their loan to their specific needs and pay it off early without penalty;
- Simple digital experience: Marcus provides an easy-to-use digital platform for individuals to manage their accounts and access their funds. This can be especially valuable for individuals who prefer a digital-first banking experience;
- Customer support: Marcus offers dedicated customer support for individuals who need assistance with their accounts or have questions about the products. This support is available through various phone, email, and online chat channels.
Value Propositions for Corporations:
- Capital raising expertise: Goldman Sachs deeply understands capital markets and helps corporations raise capital through various financial products such as IPOs, bonds, and other securities. This expertise allows corporations to access the capital they need to grow and expand their businesses;
- Mergers and acquisitions advice: The company provides strategic advice to corporations on mergers and acquisitions. This includes everything from valuation analysis to negotiation strategies, helping corporations make informed decisions about potential transactions;
- Risk management solutions: Goldman Sachs offers risk management solutions to corporations, including hedging strategies to protect against market volatility and other risks. This helps corporations manage their financial risks and protect their bottom line;
- Trading and liquidity services: Goldman Sachs is one of the largest trading firms in the world, with a strong presence in equities and fixed-income markets. It provides trading and liquidity services to corporations, helping them manage their positions and access the capital markets;
- Industry expertise: Goldman Sachs has deep expertise across various sectors, including healthcare, technology, and energy. This expertise allows the company to provide tailored advice and solutions to corporations in these industries.
Value Propositions for Governments:
- Debt financing expertise: Goldman Sachs has a long history of working with governments on debt financing activities, including bond offerings and other debt securities. The company’s deep expertise in debt financing allows governments to access the capital they need to fund important projects and initiatives;
- Strategic advisory services: The company provides strategic advisory services to governments, including advice on fiscal policy, budget planning, and economic development. This advice can help governments make informed decisions about their financial priorities and long-term goals;
- Public-private partnerships: Goldman Sachs has experience working with governments to develop public-private partnerships (PPPs) that can help fund infrastructure and other projects. These partnerships can provide governments access to private capital and expertise while ensuring that projects are developed and managed financially sustainably;
- Risk management solutions: Governments must manage their financial risks and protect their budgets from unforeseen events. As such, Goldman Sachs offers risk management solutions to governments, including hedging strategies to protect against market volatility and other risks;
- Capital markets expertise: The company also has deep expertise in capital markets, including both equity and debt markets. This expertise allows the company to help governments structure and execute complex financial transactions that can help fund important initiatives.
Value Propositions for Financial Institutions:
- Market access: Goldman Sachs provides financial institutions access to various financial markets, including equities, fixed income, currencies, and commodities. This allows financial institutions to execute trades and manage their positions more effectively;
- Liquidity: The company is one of the largest liquidity providers in the world, offering financial institutions access to deep pools of liquidity in both electronic and voice markets. This can help financial institutions manage their risk and execute trades more efficiently;
- Customized solutions: Also, it offers customized solutions to financial institutions, including risk management products and financing solutions. These solutions can be tailored to the specific needs of each institution, helping them manage their balance sheets and generate additional revenue;
- Research and analysis: Financial institutions need in-depth research and analysis on various markets and sectors. As such, Goldman Sachs provides financial institutions with insightful research to make more informed investment decisions and stay up-to-date on market trends;
- Technology and innovation: Goldman Sachs has invested heavily in technology and innovation, developing cutting-edge trading and risk management platforms. This technology helps financial institutions manage their positions more effectively and make more informed trading decisions.
Goldman Sachs Channels
Goldman Sachs’ channels are:
- Website
- Social media
- Physical meetings
- Events
Goldman Sachs Customer Relationships
Goldman Sachs’ customer relationships comprise:
- Phone
- Website
- Social media
- In-person meetings
- Chat and messaging
- Video conferencing
Goldman Sachs Revenue Streams
Goldman Sachs’ revenue streams are:
- Investment banking
- Trading
- Asset Management
- Securities Service
- Consumer banking
Goldman Sachs Key Resources
Goldman Sachs’ key resources include:
- Human resources
- Technology and infrastructure
- Financial resources
- Reputation and brand
- Intellectual property
- Partnerships and networks
- Regulatory compliance and legal expertise
Goldman Sachs Key Activities
Goldman Sachs’ key activities include:
- Investment banking
- Trading and market making
- Asset management
- Securities lending
- Research and analysis
- Risk management
- Regulatory compliance
- Corporate social responsibility
Goldman Sachs Key Partners
Goldman Sachs’ key partners include:
- Clients
- Financial institutions
- Technology providers
- Service providers
- Regulators and government entities
- Business partners
- Non-profit organizations
Goldman Cost Structure
Goldman Sachs’ cost structure includes:
- Compensation and benefits
- Technology and infrastructure
- Occupancy and facilities
- Professional services
- Marketing and advertising
- Regulatory and compliance costs
Goldman Sachs Competitors
Below are some of Goldman Sachs’ competitors:
- JPMorgan Chase: Founded in 1799 by Aaron Burr, JPMorgan Chase is one of the oldest and largest financial institutions in the United States. Unlike Goldman Sachs, it is large in size and scale, with diverse business segments, including investment banking, commercial banking, asset management, and consumer banking. JPMorgan Chase serves over 60 million customers through its network of over 5,000 branches. Besides its diverse business segments, the bank is known for its technological innovation, which focuses on improving customer experience and efficiency. The bank has also faced regulatory scrutiny following the 2008 financial crisis. JPMorgan Chase has over 250,000 employees worldwide and reported $129.8 billion in revenue in 2020;
- Morgan Stanley: Founded in 1935 by Henry S. Morgan and Harold Stanley, Morgan Stanley is a leading investment bank with a global presence. Its key differentiator from Goldman Sachs is its focus on wealth management. A significant portion of its revenue comes from managing the assets of high-net-worth individuals and institutions. Morgan Stanley serves over 4 million clients through its network of over 1,200 offices in 43 countries. Along with its wealth management focus, Morgan Stanley has a strong reputation for its advisory and underwriting services, particularly in the technology sector. The bank has tried diversifying its revenue streams, including a recent acquisition of Eaton Vance, a leading investment management firm. Morgan Stanley reported $48.2 billion in revenue in 2020 and has over 80,000 employees worldwide;
- Citigroup: Founded in 1812 as the City Bank of New York, Citigroup is a global financial services company with a diverse set of business segments, including investment banking, consumer banking, and credit card services. It focuses on retail banking, serving over 200 million customer accounts across 160 countries. Citigroup has over 2,600 branches worldwide. It has faced challenges recently, including significant regulatory fines and a history of high-risk lending practices. The bank has undergone a restructuring process to simplify its business model and improve efficiency, including a focus on digital banking. Citigroup reported $74.3 billion in revenue in 2020 and has over 200,000 employees worldwide;
- Bank of America: Founded in 1904 as Bank of Italy, Bank of America is a global financial services company that operates in all 50 US states and over 35 countries. It focuses on consumer banking, with a significant portion of its revenue coming from deposits, credit cards, and mortgages. Bank of America serves over 66 million customers through its network of over 4,000 branches. Also, it is known for its strong corporate and investment banking capabilities, particularly in mergers and acquisitions and debt underwriting. The bank has also made a significant commitment to sustainability, including a goal of achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. The bank reported $85.6 billion in revenue in 2020 and has over 200,000 employees worldwide;
- Barclays: Founded in 1690 as a goldsmith banking business, Barclays is a global financial services company with a strong presence in Europe and the United Kingdom. It focuses on retail banking and credit card services and its significant presence in investment banking and wealth management. Barclays serves over 24 million customers across 4,750 branches in 55 countries. Along with its strong presence in the UK, Barclays has a significant presence in Africa and the Middle East through its Barclays Africa Group subsidiary. The bank has faced criticism over its involvement in controversial industries such as fossil fuels and arms trading but has committed to sustainability and reducing its carbon footprint. Barclays reported £21.8 billion in revenue in 2020 and has over 80,000 employees worldwide.
Goldman Sachs SWOT Analysis
Despite its successes, Goldman Sachs is not without its weaknesses. Also, there are some opportunities the company can leverage to strengthen its position in the market while eliminating the threats that stand in its way. Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Goldman Sachs.
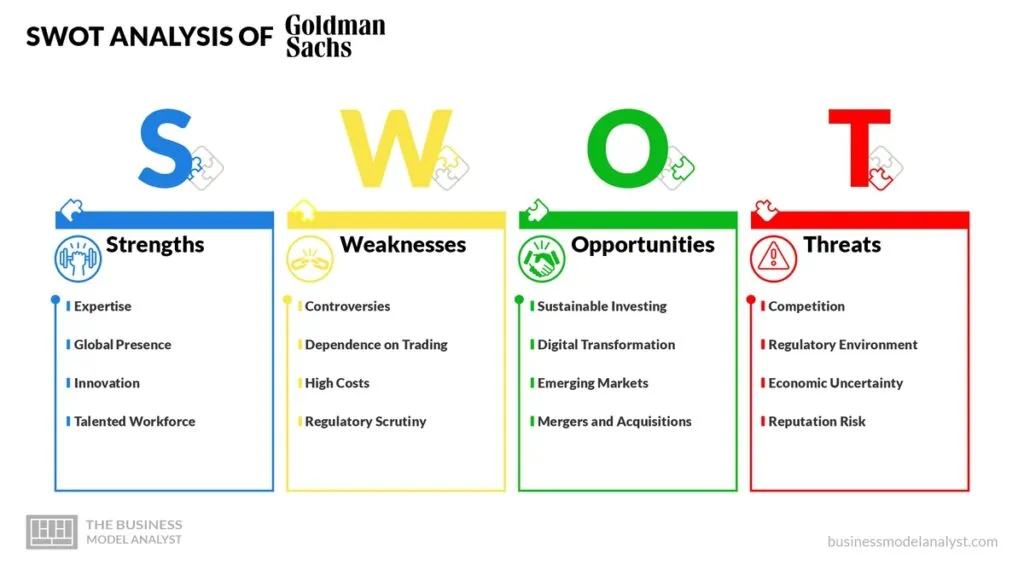
Goldman Sachs Strengths
Below, there are Goldman Sachs’ strengths:
- Expertise: Goldman Sachs has a strong reputation for expertise in investment banking, securities trading, and asset management. This expertise comes from the firm’s history of working with a diverse set of clients and executing complex financial transactions;
- Global Presence: With offices in major financial centers worldwide, Goldman Sachs’s global reach enables it to serve clients in different regions and markets. This presence also gives the firm valuable insights into global economic trends and market conditions;
- Innovation: Often being at the forefront of new financial products and technologies, Goldman Sachs has a track record of innovation. This is evident in the firm’s development of electronic trading platforms, structured products, and other financial innovations;
- Talented Workforce: The company is known for attracting and retaining top talent in the finance industry. The firm’s rigorous hiring process and a strong culture of collaboration and mentorship help to create a talented workforce that can deliver value to clients.
Goldman Sachs Weaknesses
Here are Goldman Sachs’ weaknesses:
- Controversies: Goldman Sachs has faced controversies over the years, including accusations of unethical behavior and conflicts of interest. These controversies have led to legal and regulatory challenges, as well as damage to the firm’s reputation;
- Dependence on Trading: The company generates a significant portion of its revenue from securities trading and market-making activities. This dependence on trading can make the firm vulnerable to market volatility and limit its ability to diversify its revenue streams;
- High Costs: Goldman Sachs has a reputation for being a high-cost firm, with a significant portion of its expenses going toward compensation for employees. This high-cost structure can limit the firm’s ability to compete with lower-cost firms and impact profitability;
- Regulatory Scrutiny: As a large financial institution, Goldman Sachs is subject to significant regulatory scrutiny from various authorities. This scrutiny can lead to increased compliance costs and limit the firm’s ability to pursue certain business opportunities.
Goldman Sachs Opportunities
Below, there are Goldman Sachs’ opportunities:
- Sustainable Investing: With the increasing focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors, Goldman Sachs can capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable investing solutions. It can leverage its expertise and resources to offer ESG-focused products and services to clients;
- Digital Transformation: As the financial industry transforms digitally, Goldman Sachs can seize opportunities to digitize its operations and offer new digital products and services. This includes the development of digital platforms for trading and asset management;
- Emerging Markets: The firm can expand its global presence by targeting emerging markets with high growth potential. This can involve establishing new offices or partnerships in regions such as Asia and Africa, with a growing demand for financial services;
- Mergers and Acquisitions: With its strong expertise in investment banking and M&A, Goldman Sachs can take advantage of opportunities to advise clients on strategic transactions. This can involve helping clients with mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures, as well as providing capital raising and financing solutions.
Goldman Sachs Threats
Lastly, here are Goldman Sachs’ threats;
- Competition: Goldman Sachs faces intense competition from other large financial institutions, as well as new entrants to the market, such as fintech startups. This competition can limit the firm’s ability to win new business and impact pricing and profitability;
- Regulatory Environment: As a large financial institution, Goldman Sachs is subject to significant regulatory oversight and compliance requirements. Changes to the regulatory environment, such as increased scrutiny or new regulations, can impact the firm’s operations and profitability;
- Economic Uncertainty: The firm’s revenue is closely tied to the performance of the global economy and financial markets. Economic uncertainty, such as recession or market volatility, can impact the firm’s revenue and profitability;
- Reputation Risk: Goldman Sachs’ reputation has been damaged by past controversies and negative media coverage. This reputation risk can impact the firm’s ability to attract and retain clients, as well as limit its ability to pursue specific business opportunities.
Conclusion
Goldman Sachs is a leading global financial institution with a reputation for expertise, innovation, and a talented workforce. However, the firm faces challenges such as competition, regulatory oversight, economic uncertainty, and reputation risk. To remain competitive and capitalize on opportunities, Goldman Sachs can focus on sustainable investing, digital transformation, expansion into emerging markets, and providing M&A advisory services. Overall, the firm’s success will depend on its ability to navigate these challenges and adapt to changes in the global financial landscape.

