The Yelp business model revolves around offering users reviews of local businesses from real people, as well as offering businesses a way to reach local customers looking for where to make a purchase. Yelp is a community review site where users can rate and evaluate their experiences at local establishments, including restaurants, spas, etc.
Yelp generates revenue through the sale of tailored advertisements to local businesses, partnership commissions, and service tool subscription fees. The business model used by the firm is that of an “aggregator.”
Contents
A brief history of Yelp
Yelp, co-founded in 2004 by two ex-PayPal employees (Jeremy Stoppelman and Russel Simmons), is today the most widely used platform for consumer reviews of local businesses in the United States. Before it became what it is now, Yelp was supposed to be an email-based recommendation network, but the idea never caught on with anybody outside the founders’ and consumers’ inner circles. Users were not only replying to emails, but also leaving reviews independently using the “Real Reviews” feature.
When Yelp updated its user interface in 2005, it set the stage for the company’s meteoric rise in popularity among users and investors. By 2010, Yelp had earned $30 million in revenue, 5 million reviews, and $125 million in funding over many rounds.
Yelp began expanding internationally in 2009. By 2012, Yelp had spread to more than 20 countries. At that time, Google and Yahoo also tried to purchase Yelp; however, negotiations fell through. Since 2012, Yelp has been a publicly traded company. Since then, however, Yelp’s stock has yet to do much for its owners.
As part of its commitment to long-term, profitable development, Yelp revealed an extensive, multi-year strategy to change the company’s business operations in 2019. The plan’s goals were to grow the company by developing cutting-edge products, expanding its marketing reach, and opening new locations.
Recently, Yelp has been experiencing a mass exodus of staff due to the detrimental impacts of the ongoing coronavirus pandemic. In April 2020, Yelp announced that it would fire 17% (1,000) of its employees.
Yelp currently has over 220 million reviews from consumers all across the globe. It is utilized in over half a million communities throughout the globe, making it one of the largest review sites in existence.
Who Owns Yelp
While the company was founded by Russel Simmons and Jeremy Stoppelman, who remain the company’s CEO, it has become a publicly traded company, with its top 5 stockholders including BlackRock Fund Advisors, The Vanguard Group, Inc., Prescott Investors, Inc., Fisher Asset Management LLC, and SSgA Funds Management, Inc.
Yelp’s Mission Statement
The Yelp mission statement is “To connect people with great local businesses.”
What is Yelp and How Does it Work?
Yelp is a website that lists and shows reviews of various local businesses, such as restaurants, salons, and other similar establishments. Yelp users get access to a plethora of information on local businesses, including where they are, when they are open, what they sell, and how highly rated they are by other users.
Yelp’s ratings, reviews, and images of businesses are all contributed by users. Consumers are more likely to buy from a business they learn to trust through the reviews of other consumers. Users may further refine their results by choosing factors like the kind of business, their price range, and any other features they might be interested in (such as outdoor seating, etc.).
Yelp’s revenue strategy is based on the robust user communities that generate the site’s content. These users offer their own experiences using local businesses using a variety of mediums, including reviews, ratings, photos, and videos.
How Yelp makes money
Yelp generates revenue through the sale of advertising space, the facilitation of transactions, and the provision of ancillary services. Yelp’s current role is that of an aggregator. As a result, the company collects data on millions of places and presents it to clients in an insightful format.
The high number of monthly users makes Yelp’s platform enticing to advertisers. Consequently, local businesses are Yelp’s customers.
Below, we’ll take a closer look at how Yelp makes money.
Advertising
More than 90% of Yelp’s income comes from its advertising services. Cost-per-click (CPC) pricing is how Yelp makes money from businesses. This implies that whenever a user clicks on an advertisement, the advertising business’ spending budget is deducted.
There is a large disparity in CPCs across industries and between geographic regions. Restaurants, for instance, pay a far lower fee than more costly enterprises like those in the financial sector. Ads may be shown in a variety of places across the system. These may show up on the Yelp pages of competing businesses or in the results of relevant searches.
Yelp’s premium profiles are the company’s second advertising option. Two Yelp premium packages are available; these include:
- Branded Profiles: included in this plan are the integration of slideshows, better CTA buttons, an “About” section, and the option to upload videos;
- Enhanced Profiles: offering branded profile functionality and the ability to hide the adverts of rivals.
In addition, businesses may establish their legitimacy by having their licenses verified. Verified content is denoted by a blue shield with a white check in the center. Yelp requires a paid subscription for access to these premium profiles. A company’s monthly subscription fee is dependent on its entire advertising budget. The higher their advertising budget, the lower their fee.
Last but not least, Yelp offers a program for advertisers to promote their own partners. These third-party advertisers may then promote the businesses they work with on Yelp’s website. According to the revenue-sharing arrangement, Yelp will get a percentage of the advertising budget.
Transactions
Commissions on the transactions that Yelp helps facilitate for its partners are how the company makes money. Yelp Deals, gift certificates, Eat24’s partnership with Grubhub, and the company’s own platform are the primary ways in which the firm makes money through transactions.
Yelp Deals are discounted, pre-paid vouchers that consumers may use at local businesses. Yelp gets a cut of the action whenever a voucher is used. The same may be said with gift certificates. Rather than being purchased for one’s own use, they are more frequently used in the context of a gift.
In 2015, Yelp acquired Eat24; then, in 2017, it sold the company to Grubhub. Despite this, there is still a strong integration between the two parties. Customers can still place orders on Grubhub and Eat24 without ever leaving the Yelp site. A commission is paid to Yelp for each successful order made via the site.
Last but not least, Yelp generates revenue from its role as an intermediary in transactions that take place inside the Yelp Platform. Customers may make purchases without leaving the Yelp app or website because of the company’s many partnerships. Purchasing and making payments inside their ecosystem fall under this category.
Other Services
Business partners may make use of Yelp’s many offerings, which can include software solutions. Other services include subscriptions, payment for API access to Yelp’s data, and making money from partnerships with other companies.
The two most profitable services for Yelp are Yelp Reservations and Yelp Reservations. With the aid of these tools, restaurant owners may enable services like online reservations, text message reminders, waitlists, and more. With Yelp Knowledge, companies may get location-specific, review-specific, and category-specific data-driven insights.
Yelp’s Business Model Canvas
The Yelp Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
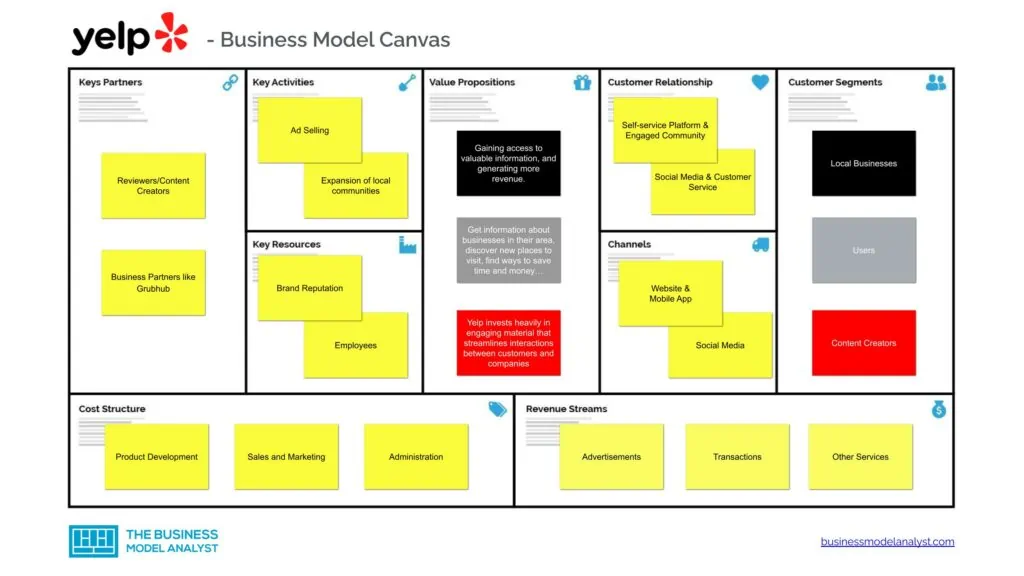
Yelp’s Customer Segments
Yelp has three customer segments, namely local businesses, users, and content creators.
- Local Businesses: These include businesses grouped into several categories like the type of service, price points, location, hours of operation, takeout and delivery services, etc.;
- Users: These include users that visit the website to check out reviews of local businesses;
- Content Creators: These are users who actively review businesses on the website.
Yelp’s Value Propositions
The Yelp value propositions consist of:
- Local businesses: Because it allows local businesses to connect with and get exposure from a sizable audience, while simultaneously providing a valuable audience-finding resource, Yelp has earned a solid reputation as a reliable platform for local businesses. It takes care of things like taking bookings and filling up waiting lists, helping businesses increase profitability, gaining access to valuable information, and generating more revenue;
- Users: Users may get information about businesses in their area, discover new places to visit, find ways to save time and money, browse photos and videos, compare prices and quality ratings, and learn from the experiences of other customers;
- Content creators: Yelp invests heavily in engaging material that streamlines interactions between customers and companies, and in exchange, it offers elite status in the platform and other benefits to those that contribute to the platform.
Yelp’s Channels
The Yelp channels consist of the following:
- Website
- Smartphone Apps
- Social Media
- Webpages targeted towards developers that make use of Yelp API and business owners
- Blog
Yelp’s Customer Relationships
The Yelp customer relationships consist of the following:
- Self-service Platform
- Engaged Community
- Social Media
- Customer Service
Yelp’s Revenue Streams
The Yelp revenue streams consist of the following:
- Advertisements
- Transactions
- Other Services
Yelp’s Key Resources
The Yelp key resources consist of the following:
- Brand Reputation
- Employees
- Partnerships
- Community
- High-Quality Content/Reviews
Yelp’s Key Activities
The Yelp key activities consist of the following:
- Ad Selling
- Expansion of local communities
- Improving and maintaining customer experience
- Website and App management and maintenance
- Day-to-day Administration
- Platform Growth
- Network Effects
Yelp’s Key Partners
The Yelp key partners consist of:
- Reviewers/Content Creators
- Business Partners like Grubhub
Yelp’s Cost Structure
The Yelp cost structure consists of the following:
- Product Development
- Sales and Marketing
- Administration
- Cost of Revenue
Yelp’s Competitors
- TripAdvisor: With more than 859 million reviews covering 8.6 million unique destinations, TripAdvisor is by far the most comprehensive travel site in the world. An estimated 463 million individuals use this website each month to reserve transportation from one place to another, hotels, and share their opinions.
Yelp and TripAdvisor, both popular review websites, provide reviews and ratings from diners about local restaurants. TripAdvisor, on the other hand, is comprehensive, offering not just hotel and restaurant reviews but also reviews on airlines, attractions, tours, and cruises.
- Angi: Angie’s List, currently known as Angi, is a website for locating and reviewing service providers in one’s locality that specialize in home-related services. A large portion of the site’s material is contributions from users. Much like Yelp, Angi users may provide reviews of local establishments and services.
- Zagat: Zagat is an online resource that compiles customer reviews and ratings of restaurants in a certain area in order to provide its users with personalized suggestions. Google acquired Zagat for more than $150 million in 2011 and absorbed it into its Geo and Commerce team. Zagat’s user interface, dining guide, and geotargeted search functions were all improved by Google. In 2018, The Infatuation acquired Zagat from Google for an unknown sum.
- Facebook Recommendations: Facebook is the most popular social media site in the world, with over 2.9 billion active monthly users. Facebook Recommendations replaces Yelp’s “Rate this business out of 5” format with a simpler “Do you recommend this company?” question. Users are prompted to provide a binary yes/no response.
- Nextdoor: Nextdoor, a social networking app, offers a recommendation feature much like Facebook. This site focuses on supporting local businesses and acts as a central location for community members to organize and share information about events and activities.
- Yellow Pages: The Yellow Pages not only lists businesses, but also includes reviews from previous customers. Before the rise of the Internet, the yellow pages were the first place people turned to get contact information for nearby companies. A transition from paper to an electronic database took place over time. Worldwide, users of yellow pages can rate and review businesses. Yelp, in contrast to Yellow Pages, offers ratings and reviews on more local businesses.
Yelp’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Yelp:
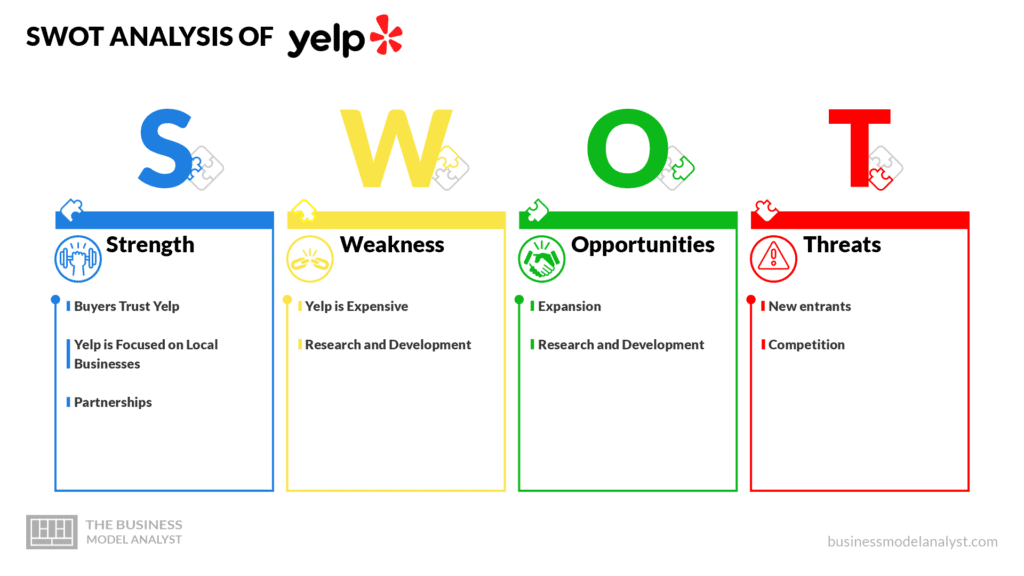
Yelp’s Strengths
- Buyers Trust Yelp: In 2019, the site averaged over 150 million monthly visitors who saw four pages throughout their visit. Search engines like Google and Bing account for the vast majority of Yelp’s traffic sources. Since it is organic, this is the most desired kind of site visitor and indicates the trust in Yelp that users have;
- Yelp is Focused on Local Businesses: While Yelp has impressive metrics, what really sets it apart is its focus on the local community. This is intrinsic to their business model. Yelp is all about local information and local search, from the reviews to the profiles of the businesses that utilize the site;
- Partnerships: Yelp forms strategic alliances with its providers, dealers, merchants, and other relevant parties. In the future, this can come in handy.
Yelp’s Weaknesses
- Yelp is Expensive: If you wish to advertise on Yelp, you will pay a per-click price, just as you would with Google Ads. CPCs in both situations range from $0.30 to $40, with the former corresponding to low-interest themes like sushi in Texas and the latter to high-priced legal services in certain locations;
- Research and Development: Yelp spends more than the industry average on R&D, but far less than a small number of competitors whose unique products have given them a substantial competitive edge.
Yelp’s Opportunities
- Expansion: Yelp has expanded internationally; however, there are still certain regions where the service could be better established. These regions present exploration opportunities;
- Research and Development: By exploring new ways of generating revenue as well as experimenting with new or better features and products, Yelp can significantly improve its bottom line.
Yelp’s Threats
- New entrants: Since so many new companies have entered the market, the revenues of the more established ones have been steadily dwindling. Yelp might lose customers to its rivals as a result of this;
- Competition: Yelp faces fierce competition among its current competitors like Facebook and Google Maps since they have a higher user reach and user base who naturally have a tendency to prefer familiar platforms to others.
Conclusion
Yelp understands the value of the different sorts of user-generated content on its platform. Yelp is more of a data platform than a genuine review site. An abundance of consumer data means it might become the go-to place for businesses of all kinds to get insights into their target demographic.
Yelp has come a long way in establishing and maintaining business ties and partnerships. The appropriate financial investment might help it become a truly global brand, expanding into new markets in Asia and Africa.
There have been scandals in the past, such as review manipulation and intricate relationships with small businesses, but the company has been able to recover because of its strong PR efforts and is only going to get better from here.

