As an online American daily fantasy sports company, the DraftKings business model revolves around allowing users to bet daily and weekly on a player’s performance and win money.
The company has five major American sports: Major League Baseball (MLB), the National Football League (NFL), the National Hockey League (NHL), the Professional Golf Association of America (PGA), and the National Basketball Association (NBA).
It also has other sports, such as the Premier League, the UEFA Champions League, tennis, WWE, NASCAR auto racing, the Canadian Football League, the Arena Football League, and mixed martial arts (MMA).
According to reports, DraftKings has over ten million users.
Contents
A brief history of DraftKings
DraftKings was founded in 2012 by Matthew Kalish, Paul Liberman, and Jason Robins, who were Vistaprint employees at the time.
Robins was a fan of fantasy sports and had played in over 200 different fantasy sports leagues, while Mattew Kalish conceived the idea of compressing the traditional setting into a lesser time frame of a week or even just one match day.
They started the game from the Libeermans’ house in Boston, from which they later moved to the main office at 225 Franklin Street in Boston, Massachusetts, USA. DraftKings grew to have other branches in New York and London, with over 350 employees.
At first, it was just a one-on-one baseball game that was launched on the opening day of MLB in 2012 with a prize of just $100.
A few months after the baseball launch, DraftKings got its first-ever outside investment from the head of Cambridge-based Accomplice, known as Ryan Moore, and other investors who empowered the company with about $1.4 million.
In 2013, DraftKings got more investments from other professional leagues, such as BDS Venture Fund, GGV Capital, and Redpoint Ventures, which gave the sum of $24 million, as well as from MLB, which invested an undisclosed amount.
DraftKings got popular with about 1 million registered users, and that same year, they had a competition that included different kinds of sports, like hockey, football, basketball, baseball, and soccer. They paid over $48 million as a reward prize to winners.
Just before December 2014, DraftKings entered into a long-term agreement with the National Hockey League (NHL), which gave them rights to the hockey league’s intellectual property and made them a monopoly in the league.
In the middle of 2015, DraftKings got another major contract from Major League Baseball, and it became the authorized fantasy sport of DraftKings. Around August of that same year, DraftKings got the license to operate in the UK, which they started later in 2016.
DraftKings bought some daily fantasy sites and finally became the leading brand in the daily fantasy sports industry.
Meanwhile, DraftKings got into some legal issues with the FTC and state attorneys general from New York and Massachusetts, which they resolved and got the Supreme Court ruling in their favor in May 2018, which made New Jersey permit legal online sportsbooks and opened the doors of opportunity for DraftKings. They were able to get their first legal sportsbooks known as DraftKings sportsbooks and also DraftKings casino.
They expanded to other states, which included Indiana, New Hampshire, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia, and then, in 2020, they merged with other companies such as SBTech and Diamond Eagle Acquisition Corporation and made more than $6 billion from the reverse merger.
Who Owns DraftKings
DraftKings is owned by DraftKings Inc., and the CEO of DraftKings is Jason Robins, the co-founder of DraftKings. DraftKings has ten other shareholders, which are also known as “owners.”
These include The Vanguard Group, Inc., ARK Investment Management LLC, Nikko Asset Management Americas, Capital Research & Management Co., BlackRock Fund Advisors, Raine Capital LLC, T. Rowe Price Investment Management, Wellington Management Co. LLP, SSgA Funds Management, Inc., and Geode Capital Management LLC. The vanguard group has the highest number of shares at 34,122,539.
DraftKings Mission Statement
DraftKings’ mission statement is “Make life more exciting by responsibly creating the world’s favorite games and betting experiences.”
How DraftKings makes money

To fully understand how DraftKings makes its money, let’s first get into how it works. DraftKings is a daily fantasy sports company, and users are allowed to participate in this sport through the company’s website or mobile app.
The game is in a traditional fantasy setting, where the players will choose their team, which will earn points according to how they played. For example, a football fantasy league would award points for assists, goals, etc. The player with the most points wins that game.
Due to this idea, DraftKings restricts the time frame so that the players can create their teams on one game day, and at the end, a winner is acknowledged. It continues like that, the next game day, they select their teams and strive for prizes.
Also, the players can play in tournaments and engage in what is known as head-to-head contests and gain cash, but it is dependent on the number of players in the team and the amount of the entry fee for the tournament.
Besides the fantasy league, DraftKings has an app called DraftKings Sportsbook, where users from a few selected states can bet on the final results of games, and also another app called iGaming, which gives users access to an online casino where they can play interesting games like blackjack.
Finally, DraftKings operates through the NFT marketplace in partnership with the Autograph platform of Tom Brady, and users can access this platform through the company’s website or mobile app. Now let’s look at the revenue.
Fantasy League
Most of DraftKings’ revenue comes from this sport. The users have to pay the entry fee, which would be divided into two — 10% to the company and 90% to the prize that would be given to the winners.
The Sportsbook app
Users from the selected states are allowed through this app to place bets on games. The concept is that DraftKings would get revenue when the user loses the bet and take the commission for setting the bet. And this is called “vigorish” in the industry.
iGaming
The mode of revenue generation from iGaming is similar to that of DraftKings’ sportsbook. They would provide over 400 casino games and generate money when the player bets on the final result or outcome of a game and lose the game. This model is even more profitable because it is set by the company in such a way that it distorts the game to win rather than lose the bet.
Advertising
After fantasy leagues, advertising is another major source of revenue for DraftKings. Since 2016, DraftKings has partnered with so many companies, including Buffalo Wild Wings, Hooters, Jägermeister, and many more. This partnership brings about the sponsorship of sports tournaments. For instance, if any of the companies partnering with DraftKings is sponsoring a tournament, DraftKings would be paid to advertise the events, and they would be paid even more if the competition happens to have many participants.
B2B
DraftKings merged with SBTech in 2020. And SBTech plays a significant role in the B2B space because it operates as the salesperson for gambling and betting products. So the merger between SBTech and DraftKings gives DraftKings a complete license to the B2B products, which they would sell to other online-based gambling firms and get a managed service fee for. The managed service fee is the share of the profit from the sales, and it’s about 10 to 20%.
DraftKings Business Model Canvas
DraftKings Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
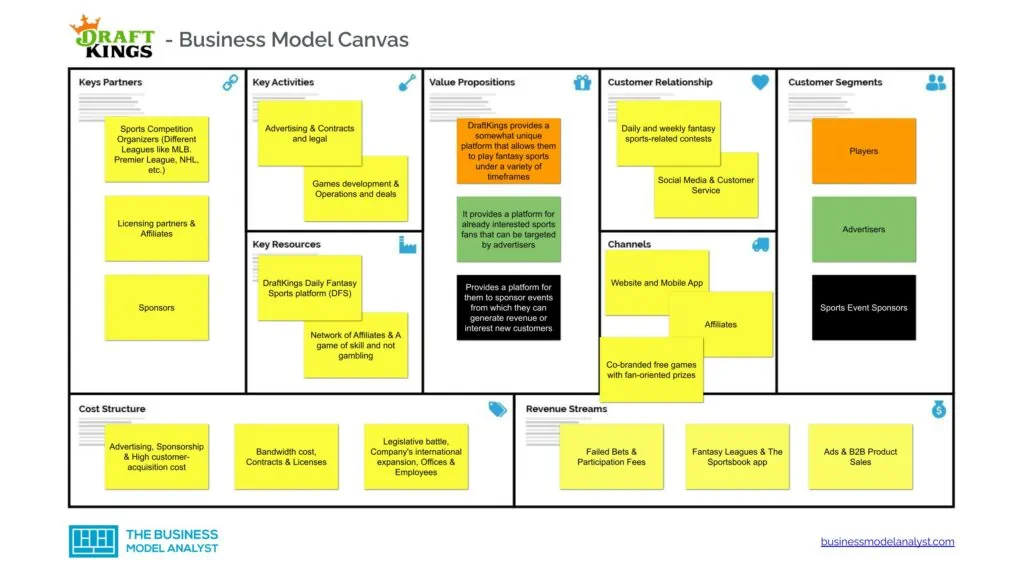
DraftKings Customer Segments
DraftKings’ customer segments consist of:
- Players: People make use of the DraftKings fantasy competitions platform, as well as bettors;
- Advertisers: Advertisers that pay to have their products promoted on the DraftKings platform;
- Sports Event Sponsors: Sports event sponsors that seek the help of DraftKings in organizing fantasy sports events.
DraftKings Value Propositions
DraftKings’ value propositions consist of the following:
- Players: For players, DraftKings provides a somewhat unique platform that allows them to play fantasy sports under a variety of timeframes. It changes the way they interact with sports and seeks to do sports better by making better sports fans. It gives them access to a wide variety of sports contests as well as a variety of professional sports to play. And since it’s a big platform, players can always find someone to play against;
- Advertisers: It provides a platform for already interested sports fans that can be targeted by advertisers;
- Sports Event Sponsors: Since this customer segment sponsors fantasy sporting events hosted by DraftKings, the company provides a platform for them to sponsor events from which they can generate revenue or interest new customers.
DraftKings Channels
DraftKings’ channels include:
- Website
- Mobile apps
- Affiliates
- Social Media
- Newsroom
- Co-branded free games with fan-oriented prizes
- In-venue ad placements during marquee NHL events
- Yahoo! Sports
DraftKings Customer Relationships
DraftKings’ customer relationships include:
- Daily and weekly fantasy sports-related contests
- Social Media
- Customer Service
DraftKings Revenue Streams
DraftKings’ revenue streams include:
- Failed Bets
- Participation Fees
- Fantasy Leagues:
- The Sportsbook app
- Ads
- B2B Product Sales
DraftKings Key Resources
DraftKings’ key resources include:
- DraftKings Daily Fantasy Sports platform (DFS)
- Historical performance data
- Network of Affiliates
- A game of skill and not gambling
- Sponsorship contracts
- Advertising deals
- Smartphone Apps
DraftKings Key Activities
DraftKings’ key activities include:
- Advertising
- Contracts and legal
- Product design
- Games development
- IT Maintenance
- Operations and deals
DraftKings Key Partners
DraftKings’ key partners include:
- Sports Competition Organizers (Different Leagues like MLB. Premier League, NHL, etc.)
- Licensing partners
- Affiliates
- Sponsors
DraftKings Cost Structure
DraftKings’ cost structure includes the following:
- Advertising
- Sponsorship
- High customer-acquisition cost
- Bandwidth cost
- Contracts
- Licenses
- Legislative battle
- Company’s international expansion
- Offices
- Employees
DraftKings Competitors
DraftKings’ top ten competitors include:
- BetMGM: An online-based New Jersey sports betting and gaming entertainment company that was founded in 2018;
- Underdog: A fantasy football app that needs less maintenance and management for players;
- Generation Esports: Founded in 2012, based in Kansas City, Missouri, very competitive gaming sports, serving schools and communities in North America;
- Wagr: A mobile sports betting app, founded in 2020, it has social gaming dimensions to sports betting;
- FanDuel: A fantasy sports game just like DraftKings, but it is designed to last for just one day. It was founded in 2009;
- Caesars Entertainment Corporation: Provides casino entertainment, and it is a combination of three brands Caesars Entertainment Operating Company, Caesars Entertainment Resort Properties, and Caesars Growth Properties. Founded in 2020;
- OwnersBox: A sports tech enterprise. That goes beyond the normal daily sports experience by using social and gamification factors to make users enjoy a new experience. Founded in 2020;
- SportsLock: A simple sports gaming app that has a lot of engaging and fun-filled features;
- Victiv.com: A daily fantasy sports betting company for NFL;
- DraftDay: Offers a chance for players to exercise their fantasy skills for money. It consists of a variety of sports games and has no long-season commitment.
DraftKings SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of DraftKings:
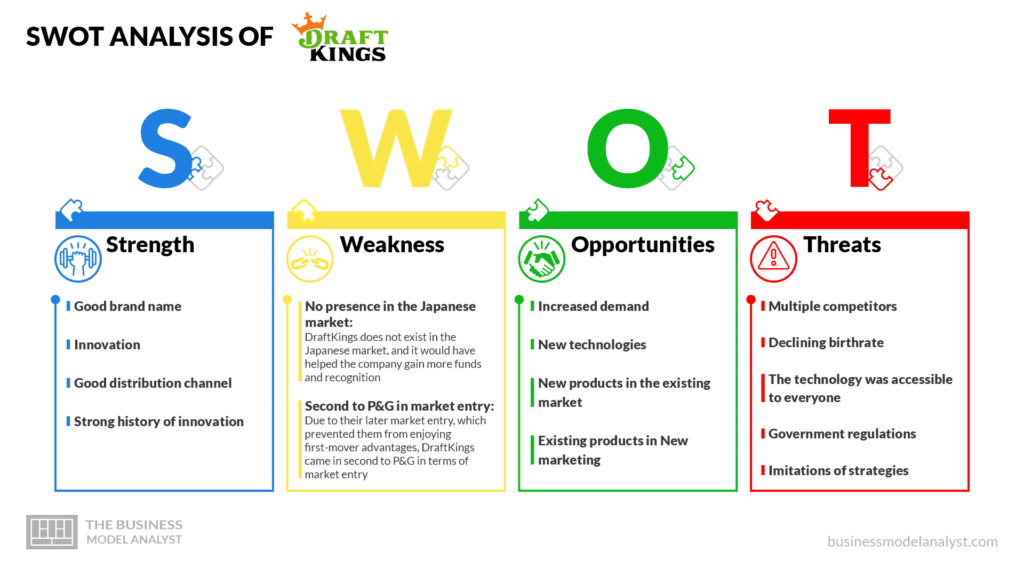
DraftKings Strength
- Good brand name: Being one of the top platforms and dominating fantasy sports games, DraftKings has created a strong and good brand name for itself. It has a good record of advancement and development;
- Innovation: One of their strengths includes the industry innovations that DraftKings pioneers;
- Good distribution channel: DraftKings has a lot of distribution channels such as websites, Social Media, Mobile apps, Affiliates, etc.;
- Strong history of innovation: DraftKings has a long record of innovations.
DraftKings Weaknesses
- No presence in the Japanese market: DraftKings does not exist in the Japanese market, and it would have helped the company gain more funds and recognition;
- Second to P&G in market entry: Due to their later market entry, which prevented them from enjoying first-mover advantages, DraftKings came in second to P&G in terms of market entry.
DraftKings Opportunities
- Increased demand: Through more advertising, many people would get to understand the concept of DraftKings, which could lead to an increase in demand;
- New technologies: The company has the opportunity to make use of the new advanced technologies in production, which would lead to fewer expenses in production and also be able to sell their services at a lower cost;
- New products in the existing market: Through the new technologies, there could also be new products and innovations in the market;
- Existing products in New marketing: The company has the opportunity to improve its existing products by providing more friendly features in the products and also expand the operations and make them accessible in worldwide marketing.
DraftKings Threats
- Multiple competitors: DraftKings has so many competitors in the fantasy Sports industry, which puts the company in a radical competition and may cause huge damage to the company;
- Declining birthrate: No much increase in profitability due to the use of the old method of technology;
- The technology was accessible to everyone: Everyone got access, and it became misused;
- Government regulations: The government regulations regarding DraftKings have proven to be the most crucial threat to the industry;
- Imitations of strategies: Rivals are very fast to imitate any innovative idea the company brings, which is a threat to the brand’s growth.
Conclusion
Allowing consumers to play daily fantasy games and rewarding the winners with prizes is essentially the basic idea behind DraftKings’ business model. Despite having numerous rivals and other difficulties, the company still holds the top spot for fantasy sports brands in the market. With the opportunities available to them, DraftKings is well-positioned to make greater progress within the industry, which would keep them at the top for a long time.

