The Chipotle business model is centered on providing a fast-casual dining experience that emphasizes quality ingredients, customization, sustainability, and efficiency. A distinguishing feature of Chipotle’s business model is the ability for customers to create their own meals.
The “build-your-own” approach allows patrons to customize their orders with a wide range of proteins, salsas, toppings, and sauces. This level of personalization enhances the dining experience and caters to individual tastes, making each Chipotle visit unique and satisfying. Chipotle’s digital innovation has also been pivotal in its business model.
By investing in technology and creating a user-friendly mobile app, the company offers customers a convenient way to place orders, make payments, and earn rewards through the “Chipotle Rewards” program. This tech-savvy approach has bolstered customer engagement and loyalty, contributing to the company’s continued success.

Contents
A brief history of Chipotle
Chipotle Mexican Grill was founded in 1993 by Steve Ells, a classically trained chef, in Denver, Colorado. The idea for Chipotle was born out of Ells’ desire to create a fast-casual restaurant that served high-quality, flavorful Mexican food using fresh ingredients and classic cooking techniques.
The first Chipotle restaurant opened its doors in a former Dolly Madison ice cream shop in Denver on July 13, 1993. From the outset, the restaurant’s concept differed from the traditional fast-food chains that dominated the market then. Chipotle offered a menu featuring burritos, tacos, bowls, and salads, with a focus on made-to-order meals and a “build-your-own” approach. The restaurant’s name, “Chipotle,” is derived from the Nahuatl word “chilpoctli,” which refers to a smoked and dried jalapeño chili pepper, a key ingredient in many Mexican dishes.
Chipotle faced the challenge of attracting customers early on, but its dedication to using high-quality ingredients and a unique dining experience quickly gained attention. The restaurant’s popularity began to grow through word-of-mouth. By the late 1990s, Chipotle had gained a loyal following, particularly among young adults and college students.
In 1998, Chipotle caught the attention of McDonald’s, the global fast-food giant, which saw potential in the growing fast-casual segment. McDonald’s made an initial investment in Chipotle, allowing for more rapid expansion. However, despite the investment, Chipotle continued to operate independently and maintained its focus on quality and sustainability.
The following years saw steady growth and expansion for Chipotle, both in terms of the number of locations and its reputation for providing a unique dining experience. The company continued to prioritize its “Food With Integrity” philosophy, emphasizing the use of responsibly-sourced ingredients and naturally-raised meats.
In 2006, McDonald divested its stake in Chipotle, allowing the company to operate fully as an independent entity. This move allowed Chipotle to pursue its own growth trajectory and stay true to its core values.
Throughout the 2000s and into the 2010s, Chipotle’s popularity soared. The company embraced digital innovation, launching mobile ordering and a user-friendly mobile app, further enhancing its appeal to tech-savvy consumers.
However, in the mid-2010s, Chipotle faced significant challenges due to several food safety incidents involving E. coli, salmonella, and norovirus outbreaks in some of its locations. These incidents had a negative impact on Chipotle’s reputation and financial performance.
In response, Chipotle implemented comprehensive food safety measures and launched aggressive marketing campaigns to regain the trust of its customers. The company also doubled down on its commitment to sustainability and transparency, renewing its focus on quality ingredients and ethical sourcing.
Despite the setbacks, Chipotle’s brand resilience and dedication to its business model allowed it to recover and regain its momentum. The company continued its expansion into new markets, both in the United States and internationally.
Who Owns Chipotle
Chipotle Mexican Grill is a publicly traded company, meaning its shareholders own it. The largest shareholders of Chipotle are investment companies, including The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and State Street Corporation.
These four shareholders collectively own about 30% of Chipotle’s shares. Various other investors own the remaining shares, including individuals, pension funds, and mutual funds. Steve Ells, the founder and former CEO of Chipotle, owns about 10% of the company’s shares. However, Ells is no longer the majority shareholder of Chipotle, and he does not have control over the company’s operations.
Chipotle Mission Statement
Chipotle’s mission statement is “to cultivate a better world through real food.”

How Chipotle works
Chipotle operates as a fast-casual restaurant chain with a unique operational model focusing on efficiency, customization, and quality. Here’s an overview of how Chipotle operates:
Restaurant Layout
Chipotle’s restaurant layout is designed to be simple and open, creating an inviting and efficient space for customers. Upon entering the restaurant, customers can easily see the menu displayed on boards above the counter. The single service line ensures a streamlined ordering process, minimizing confusion and wait times. This layout allows customers to move seamlessly through the ordering and customization process, enhancing the overall dining experience.
Technology Integration
Chipotle has embraced technology to enhance customer convenience and engagement. The company offers online and mobile app-based ordering, allowing customers to place orders ahead of time for pickup or delivery. This integration of technology reduces wait times and increases efficiency, catering to the growing demand for digital solutions in the restaurant industry.
Ordering Process
Chipotle’s ordering process is straightforward and starts with customers choosing the base of their meal. They have a selection of options, including burrito bowls, salads, tacos, and kids’ meals. Next, customers choose their protein: chicken, steak, barbacoa, carnitas, sofritas (tofu), or vegetarian options. This step allows customers to tailor their meals to their dietary preferences.
Customization
One of Chipotle’s distinctive features is its “build-your-own” approach, enabling customers to customize their meals with a wide range of ingredients. As customers move along the assembly line, they have the freedom to choose from various salsas, toppings, and sauces. This level of personalization empowers customers to create a meal that suits their individual tastes, making each visit to Chipotle a unique and satisfying experience.
Food Preparation
Behind the counter, Chipotle employees, known as “crew members,” prepare the orders in front of the customers. This interactive food preparation process allows customers to see their meals being assembled with fresh ingredients, fostering transparency and confidence in the quality of the food. Crew members grill the proteins, heat the tortillas, and assemble the meals according to each customer’s specifications.
Dine-In, Takeout, and Delivery
Chipotle provides customers with multiple options to enjoy their meals. Customers can choose to dine in the restaurant, enjoying the vibrant atmosphere and social experience. Alternatively, they can opt for takeout, picking up their orders to enjoy elsewhere. Chipotle also offers delivery services in select locations, providing added convenience for those who prefer to have their meals brought to their doorstep.
How Chipotle makes money
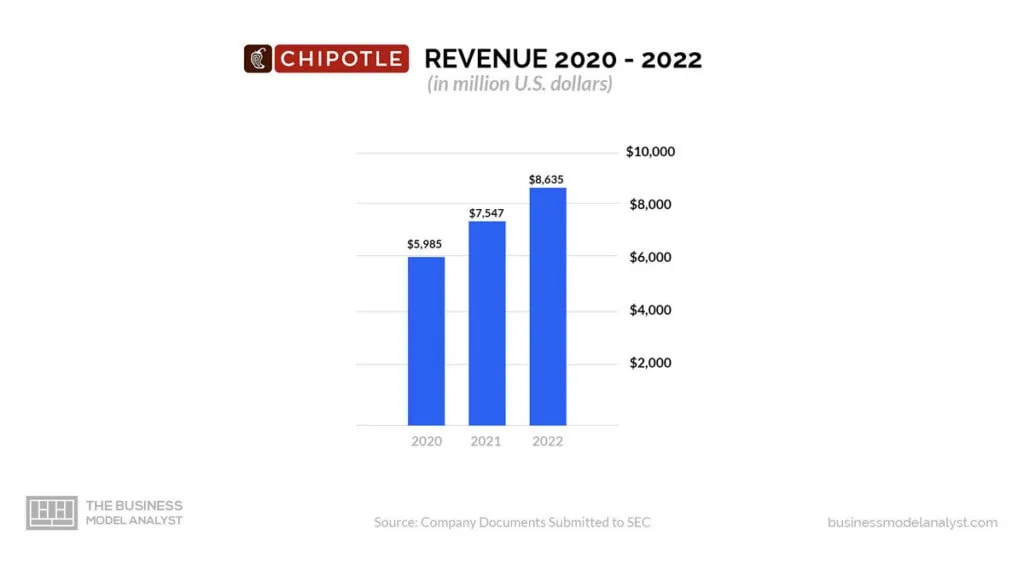
Here are the major ways Chipotle generates revenue:
Food and Beverage Sales
Chipotle’s primary revenue source comes from the sale of its menu items, including burrito bowls, tacos, salads, and more. Customers pay for their orders at the time of purchase, both in-store and through online or mobile app-based ordering.
Delivery Services
Chipotle provides delivery services in select locations, partnering with third-party delivery platforms. Customers can have their meals brought to their doorstep, and the company earns revenue through delivery fees or commissions from these partnerships.
Catering Services
Chipotle offers catering services for large orders, such as for parties, events, or corporate gatherings. This catering option allows the company to tap into the business and event catering market, generating additional revenue.
Limited-Time Promotions and Collaborations
Chipotle occasionally collaborates with other brands or sponsors events to introduce limited-time menu items or promotions. These partnerships can attract new customers and drive sales during specific periods, boosting revenue.
Gift Card Sales
Chipotle sells physical and digital gift cards, which customers can purchase and use for themselves or gift to others. Gift card sales represent a source of immediate revenue, as customers pay for the card upfront.
Chipotle Business Model
Let’s take a look at the Chipotle Business Model Canvas below:
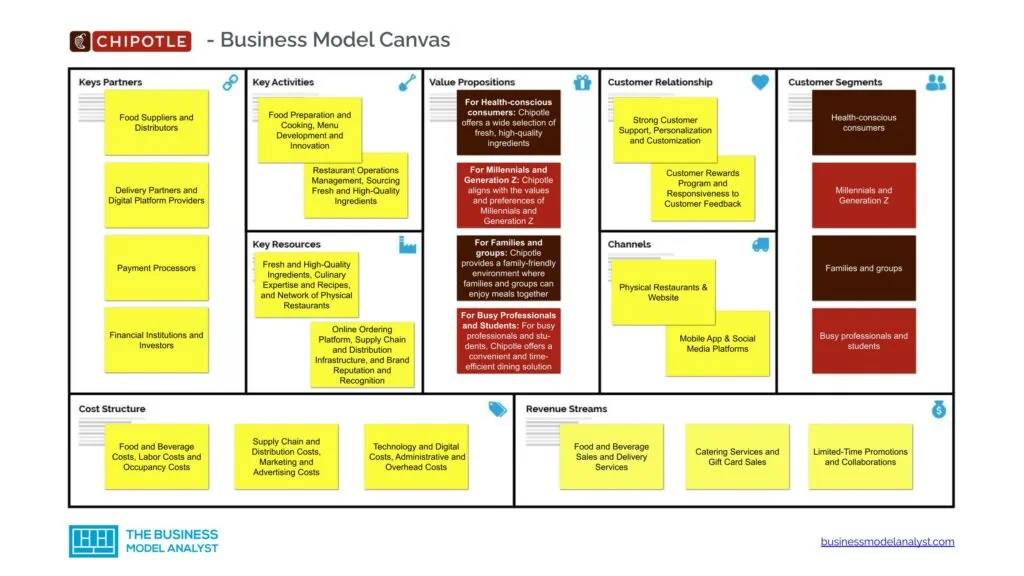
Chipotle Customer Segments
Chipotle’s customer segments consist of:
- Health-conscious consumers: Health-conscious consumers are individuals who prioritize and actively seek out products, services, and lifestyle choices that promote good health and well-being. They are concerned about the nutritional value, ingredients, and overall impact of their choices on their physical and mental health;
- Millennials and Generation Z: Millennials and Generation Z refer to two demographic groups within the population. Millennials typically include individuals born between the early 1980s and mid-1990s to early 2000s, while Generation Z includes those born from the mid-1990s to the mid-2010s. Both groups are characterized by growing up in the digital age and are often associated with specific behavioral traits and preferences. They are tech-savvy, socially conscious, and value experiences over material possessions;
- Families and groups: This category includes households consisting of family members or close-knit groups of individuals who frequently make decisions together. It can include nuclear families (parents and children), extended families, roommates, or close friends living together;
- Busy professionals and students: Busy professionals and students are individuals who have demanding schedules due to work or education commitments. Professionals may have full-time jobs or run businesses, while students are enrolled in schools, colleges, or universities. This group typically values time efficiency and convenience in their choices;
- Vegetarians and vegans: Vegetarians are individuals who avoid eating meat (including poultry and fish) but may still consume animal products like dairy and eggs. Conversely, Vegans avoid all animal-derived products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and even honey. Both vegetarians and vegans choose their dietary lifestyle for various reasons, including ethical, environmental, and health concerns.
Chipotle Value Propositions
Chipotle’s value propositions consist of:
- For Health-conscious consumers: Chipotle offers a wide selection of fresh, high-quality ingredients, including responsibly sourced meats, organic produce, and wholesome options. Health-conscious consumers can customize their meals to meet their specific dietary preferences and nutritional needs. Chipotle promotes transparency in its sourcing and preparation processes, appealing to those who prioritize nutritious and sustainable food choices;
- For Millennials and Generation Z: Chipotle aligns with the values and preferences of Millennials and Generation Z by offering a fast-casual dining experience with an emphasis on customization and individuality. With a focus on fresh, flavorful ingredients and a variety of dietary options, Chipotle caters to the desire for unique and socially responsible dining experiences that resonate with these younger generations;
- For Families and groups: Chipotle provides a family-friendly environment where families and groups can enjoy meals together. The ability to customize each order allows everyone to select dishes that suit their taste preferences, making it easier for groups with diverse dietary needs to dine together. Chipotle’s efficient service also appeals to families and groups looking for quick and hassle-free dining options;
- For Busy Professionals and Students: For busy professionals and students, Chipotle offers a convenient and time-efficient dining solution. The fast-casual setup allows them to get a fresh and customizable meal without the long wait associated with traditional sit-down restaurants. The availability of online ordering and delivery options further enhances the convenience factor, catering to individuals with hectic schedules;
- For Vegetarians and vegans: Chipotle’s menu features a range of plant-based options, making it a go-to destination for vegetarians and vegans. From sofritas (spicy tofu) to a variety of veggie toppings and sides, Chipotle ensures there are plenty of choices to satisfy plant-based dietary preferences. Their commitment to using non-GMO ingredients and sustainable practices may also resonate with environmentally conscious vegetarians and vegans.
Chipotle Channels
Chipotle’s channels consist of:
- Physical Restaurants
- Website
- Mobile App
- Social Media Platforms
Chipotle Customer Relationships
Chipotle’s customer relationships consist of:
- Strong Customer Support
- Personalization and Customization
- Customer Rewards Program
- Responsiveness to Customer Feedback
Chipotle Revenue Streams
Chipotle’s revenue streams consist of:
- Food and Beverage Sales
- Delivery Services
- Catering Services
- Limited-Time Promotions and Collaborations
- Gift Card Sales
Chipotle Key Resources
Chipotle’s key resources consist of:
- Fresh and High-Quality Ingredients
- Culinary Expertise and Recipes
- Network of Physical Restaurants
- Online Ordering Platform
- Supply Chain and Distribution Infrastructure
- Brand Reputation and Recognition
- Skilled Workforce and Employees
- Financial Capital and Funding
Chipotle Key Activities
Chipotle’s key activities consist of:
- Food Preparation and Cooking
- Menu Development and Innovation
- Restaurant Operations Management
- Sourcing Fresh and High-Quality Ingredients
- Customization of Orders for Customers
- Online and Mobile Ordering Management
- Food Delivery Coordination
- Supply Chain and Inventory Management
- Quality Control and Food Safety Practices
- Marketing and Promotions
- Customer Service and Support
- Staff Training and Development
Chipotle Key Partners
Chipotle’s key partners consist of:
- Food Suppliers and Distributors
- Delivery Partners
- Digital Platform Providers
- Payment Processors
- Financial Institutions and Investors
Chipotle Cost Structure
Chipotle’s cost structure consists of:
- Food and Beverage Costs
- Labor Costs
- Occupancy Costs
- Supply Chain and Distribution Costs
- Marketing and Advertising Costs
- Technology and Digital Costs
- Administrative and Overhead Costs
- Training and Development Costs
- Compliance Costs
Chipotle Competitors
- Qdoba Mexican Grill: Qdoba Mexican Grill is a fast-casual restaurant chain that offers a similar concept to Chipotle. Customers can build their own burritos, tacos, bowls, and salads from a variety of fresh ingredients. Qdoba differentiates itself by providing a more comprehensive range of protein options, such as pulled pork and queso burritos, which can appeal to customers seeking more diverse flavor profiles. The restaurant also offers Queso, a popular cheese sauce, which Chipotle doesn’t have. Additionally, Qdoba has experimented with various limited-time menu items to keep its offerings fresh and enticing to customers;
- Moe’s Southwest Grill: Moe’s Southwest Grill, like Chipotle and Qdoba, operates on a build-your-own concept. It distinguishes itself with a vibrant and fun atmosphere, using quirky names for its menu items like “Homewrecker” burritos and “Stacks” (tacos). Moe’s prides itself on its extensive toppings bar, which includes unique salsa options and free chips with every meal. The chain has also collaborated with celebrities and introduced innovative marketing campaigns to attract customers;
- Taco Bell: While not a direct fast-casual competitor, Taco Bell is a significant player in the fast-food industry, offering Mexican-inspired items with a broader appeal. It positions itself as a go-to destination for quick, affordable, and diverse menu options. Taco Bell’s menu features a mix of traditional Mexican fare, like tacos and burritos, along with more Americanized choices like nachos and Doritos Locos Tacos. By targeting a broader demographic, Taco Bell competes with Chipotle on price, convenience, and its unique menu offerings;
- Baja Fresh: Baja Fresh is a fast-casual restaurant that emphasizes its commitment to using fresh, high-quality ingredients in its Mexican cuisine. The chain offers made-to-order burritos, tacos, salads, and other dishes, much like Chipotle. Baja Fresh differentiates itself by incorporating some West Coast influences in its menus, such as grilled mahi-mahi tacos and Baja shrimp burritos. The brand’s focus on freshness and California-inspired flavors attract customers seeking a different take on Mexican fast-casual cuisine;
- Del Taco: Del Taco is a unique competitor as it combines Mexican and American fast-food offerings. The menu includes classic Mexican dishes like tacos and burritos, alongside items like burgers, fries, and milkshakes. By catering to a diverse audience, Del Taco positions itself to capture customers looking for a mix of traditional Mexican flavors and familiar fast-food options. This broader approach allows Del Taco to compete in multiple markets and appeal to different tastes and preferences.
Chipotle SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT analysis of Chipotle:

Chipotle Strengths
- Strong Brand Identity: Chipotle has developed a powerful brand identity centered around its commitment to “Food with Integrity.” This emphasis on sourcing high-quality, fresh ingredients and promoting ethical and sustainable practices has resonated with its customer base;
- Customization and Choice: Chipotle’s menu offers a wide range of options, allowing customers to customize their meals to suit their preferences. The ability to create personalized burritos, bowls, and tacos attracts a diverse customer base;
- Efficient and Fast Service: Chipotle’s fast-casual dining model ensures quick service without compromising on quality. Customers appreciate the speed and convenience of ordering and receiving their meals;
- Transparency: Chipotle has been transparent about its sourcing practices, food preparation methods, and ingredient origins. This transparency fosters trust with customers who value knowing where their food comes from;
- Loyal Customer Base: Chipotle has built a loyal following of customers who appreciate its unique dining experience and the consistency of its offerings across locations;
- Strong Digital Presence: Chipotle has invested in digital technologies, including its mobile app and online ordering platform. These offerings cater to the preferences of younger, tech-savvy customers and enhance convenience.
Chipotle Weaknesses
- Food Safety Concerns: Chipotle has faced some food safety incidents in the past, leading to negative publicity and a decline in customer trust. Ensuring consistent food safety practices is an ongoing challenge for the company;
- Limited Menu Diversity: While Chipotle offers customizable options, its core menu centers around Mexican-inspired cuisine. This limited menu diversity may not appeal to customers seeking a broader range of cuisines or dietary preferences;
- Price Sensitivity: Chipotle’s emphasis on high-quality, fresh ingredients can result in slightly higher prices compared to some fast-food competitors. This pricing may make it less attractive to price-sensitive consumers;
- Dependence on the U.S. Market: Chipotle’s significant revenue reliance on the United States market can pose risks to the company. While the company has successfully expanded its presence across various states and cities within the U.S., it also means that it is more exposed to economic fluctuations, regional challenges, and market-specific factors that could impact its financial performance.
Chipotle Opportunities
- International Expansion: Chipotle has the opportunity to further expand its presence in international markets. Entering new countries or regions with a strong demand for fast-casual dining and a growing appreciation for Mexican-inspired cuisine can drive revenue growth and increase brand recognition globally;
- Menu Innovation and Diversification: Chipotle can continue to innovate its menu by introducing new and exciting offerings that cater to changing consumer preferences. Expanding menu options to include new proteins, plant-based alternatives, and diverse flavors can attract a broader customer base and keep existing customers engaged;
- Loyalty Program Enhancements: Strengthening its customer loyalty program or introducing new features, such as personalized rewards, birthday offers, or exclusive events, can foster stronger relationships with existing customers and encourage repeat visits;
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Collaborating with popular brands, influencers, or local organizations can create exciting marketing opportunities and expand Chipotle’s reach to new audiences.
Chipotle Threats
- Intense Competition: The fast-casual dining industry is highly competitive, with numerous players vying for market share. Chipotle faces competition not only from other fast-casual Mexican food chains like Qdoba and Moe’s Southwest Grill, but also from various other fast-food and fast-casual restaurants offering similar menu customization options;
- Negative Publicity and Social Media: In today’s digital age, negative publicity and social media backlash can spread quickly and significantly impact a company’s reputation. Any harmful incidents, customer complaints, or social media controversies can harm Chipotle’s image and affect customer perceptions;
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Chipotle relies on a complex supply chain to source its fresh ingredients. Disruptions in the supply chain, such as adverse weather conditions, transportation issues, or shortages of specific ingredients, can lead to supply constraints, increased costs, or temporary closures of certain menu items;
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: The restaurant industry is subject to various regulations related to food safety, health standards, labor practices, and advertising. Non-compliance with these regulations can lead to fines, legal disputes, and damage to the company’s reputation;
- Shifts in Consumer Preferences: Changes in consumer preferences, such as a shift away from fast-casual dining or evolving trends in healthy eating, may impact Chipotle’s popularity and demand for its menu offerings.
-> Read More About Chipotle’s SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
Chipotle’s business model is a testament to the power of prioritizing quality, customization, sustainability, and efficiency in the fast-casual dining industry. The “build-your-own” concept has proven to be a key differentiator, providing customers with a sense of ownership over their meals and an enjoyable dining experience tailored to their preferences.
Moreover, Chipotle’s commitment to digital innovation has been pivotal in staying ahead in a competitive market. The investment in technology, mainly through developing a user-friendly mobile app and implementing the “Chipotle Rewards” program, has elevated the level of customer convenience and engagement.
As the fast-casual industry continues to evolve, Chipotle’s business model serves as a shining example of how a customer-centric focus, coupled with innovation, can drive success and set a standard for the restaurant industry.

