With close to 40,000 restaurants in more than 100 countries, the McDonald’s business model depends mainly on the sale of McDonald’s products by their franchisees, which usually lease properties owned by McDonald’s. The business model was first adopted by the brothers Richard James and Maurice James McDonald, who sold their business to Ray Kroc, their first franchise agent, at the then heavy sum of US$ 2.7 million, back in 1961.

Contents
A brief history of McDonald’s:
Launched in 1948, Speedee Service System was the forerunner of McDonald’s. It was launched by the two McDonald’s brothers, who adopted the drive-in and franchising concept for fast-food delivery. Their first franchise agent was Ray Kroc, who opened the first McDonald’s franchise back in 1955. He bought the rights to their business for US$ 2.7 million in 1961, after seeing what their business and its business model could become.
Through its business model and insistence on offering quick service and delivery of products of a consistent quality, in 2021 McDonald’s became the most valuable QSR brand with a brand value of US$ 154.9 billion and worldwide revenue of US$ 19.21 billion.
McDonald’s mission statement:
McDonald’s mission statement is “to be our customers’ favorite place and way to eat and drink.”
How McDonald’s makes money
While McDonald’s business model focuses mainly on franchising, they also generate income in other ways. However, under franchising, they operate three different types of it. They are:
Developmental License
Under this type of franchising, the franchisee invests their own capital in setting up their restaurant, which includes operational and real estate costs.
McDonald’s supplies the products and receives a percentage as royalty from the sale. The company also charges a predetermined amount for every franchise that wants its license.
This type is the exact opposite of conventional franchising and is in use in more than 6.950 restaurants in over 80 countries.
Conventional Franchising
This structure is the most effective in the McDonald’s business model. The company either obtains a long-term lease or owns the land where the restaurant is built, while the franchisee pays a minimum rent for a 20-year period and ongoing royalty to the company.
The franchisee also pays for the signs and interior decor of the restaurant, while getting innovative and operational help from their parent company. This structure ensures that McDonald’s revenue stream is stable and predictable, while maintaining profitability amidst low operational costs.
Affiliates
This structure receives the lowest investment from the company and accounts for equity investments.
It’s mostly in use in China and Japan, where companies pay a percentage of sales as royalty for McDonald’s products. These products include hamburgers, french fries, milkshakes, soft drinks, salads, coffee, and desserts.
Company-Operated Restaurants
While few, McDonald’s has a number of restaurants that they own and operate, hiring employees and ordering supplies by themselves. However, the company’s goal is to have 5% percent of its restaurants company-owned, while 95% will be owned and operated by franchisees.
McDonald’s most profitable business model structure, the conventional franchising, allows them to keep up to 82% of revenue generated by their franchises, unlike the company-operated restaurants that only keep about 16% of their revenue. The success of their strategies in the international market has resulted in the term ‘McDonaldization’.
Over the years, McDonald’s has developed and improved upon its marketing strategies with the intent of increasing profits for its franchisees and the parent company. Such strategies include the enhancement of customer experience, by focusing on people, products, price, place, and promotion, which works together with its mission statement.
They have also worked on their growth strategies by working on strategies for retaining existing customers, regaining lost clients, and converting non-customers. This was their 2017 continuous growth plan and was listed as:
- Retain
- Regain
- Convert
In their efforts to carry this out, they made improvements on their digital platform, such as delivery services, while adding an experience of the future (EOTF) by the introduction of new technologies in their restaurants.
To further boost growth, they have also worked on diversity with the proposition of “Diversity IS Inclusion” and the acquisition of other companies, such as Donatos Pizza in 1968, and Boston Market in 2000.
McDonald’s Business Model Canvas
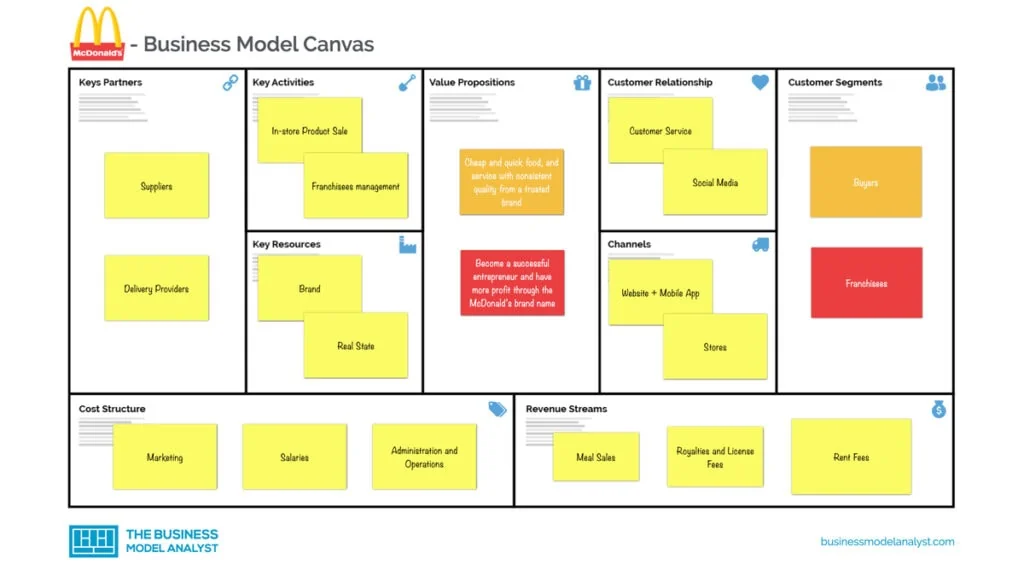
McDonald’s customer segments
- Buyers: People who want to buy McDonald’s products like hamburgers, french fries, desserts, etc.;
- Franchisees: Restaurants that want to increase their profit, by using the McDonald’s brand name.
McDonald’s value proposition
- Buyers: Cheap and quick food, and service with consistent quality from a trusted brand;
- Franchisees: Become a successful entrepreneur and have more profit through the McDonald’s brand name.
McDonald’s channels
- Website
- App for iOS and Android
- Franchisees/Restaurants
Mcdonald’s customer relationships
- Social Media
- Customer Service
- Community Service
McDonald’s revenue streams
- Royalties
- Rent Fees
- License Fees
McDonald’s key resources
- Brand
- Supplier Network
- Real State
- Platform
McDonald’s key activities
- In-store Product Sale
- Delivery
- Payment Processing
- Innovation Testing and Implementation
McDonald’s key partners
- Suppliers
- Delivery Providers: Uber Eats & Door Dash
McDonald’s cost structure
- Salaries
- Marketing
- Payment Processing
- Administration and Operations
McDonald’s competitors
- Burger King: Available in more than 90 countries and at over 18,000 locations, Burger King is the most direct competitor of McDonald’s and has approximately 90% of its restaurants as franchisees;
- Subway: In terms of size, the privately-owned Subway has one of the largest QSR chains, and they have a presence in more than 80 countries at over 37,000 restaurants;
- Chipotle: With its slogan as “Food with Integrity”, Chipotle operates more than 2,800 restaurants with none of them franchised. Their fast-foods have higher prices than their competitors, and they also serve fast-foods that are a bit different, like tacos, salads, and burritos;
- Yum brands (KFC, Taco Bell, Pizza Hut): Yum brands operate top fast-food restaurants, such as Taco Bell, Pizza Hut, and KFC. Altogether they make up a worldwide chain of more than 50,000 restaurants, with about 98% of them franchised;
- Wendy’s: With a market cap of US$ 5.1 billion and stock trading at US$ 23 per share in 2021, Wendy’s operates its fast-food restaurant chain in more than 6,800 locations worldwide. Just like McDonald’s and Burger King, they serve burgers, fries, and a few other American foods;
- Starbucks: Operates the largest coffeehouse chain in nearly 90 countries, and at over 32,000 locations. They serve coffee, pastries, espresso, tea, sandwich, cappuccino, etc. And just like Chipotle, their products have higher prices than their competitors.
McDonald’s swot analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of McDonalds:
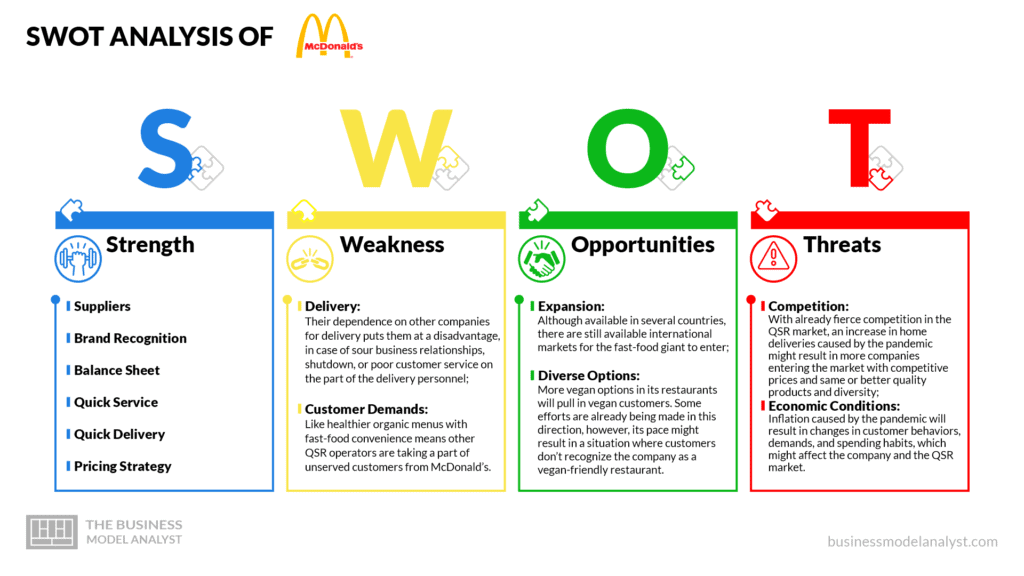
McDonald’s Strengths
- Suppliers: McDonald’s choice of suppliers have ensured that they and their franchisees always have enough items in stock to satisfy their 25 million daily customers;
- Brand Recognition: McDonald’s brand name has enabled it to gain and keep its customers and franchisees. Franchisees purchase the company’s license and become affiliated with it to increase their profits through its brand reputation and recognition. On the other hand, customers visit McDonald’s restaurants because of their brand name and their insistence on consistent quality on cheap fast-foods;
- Balance Sheet: The company’s high revenue generation allows it to test out innovations on some restaurants and implement them efficiently in its other franchisees;
- Quick Service: Their consistent quality and fast service have gained them the trust of customers;
- Quick Delivery: McDonald’s use of popular delivery services with a strong presence in several countries helps them to ensure a quick delivery;
- Pricing Strategy: McDonald’s pricing strategy of offering cheap meals allows them to maintain a huge chunk of the QSR market.
McDonald’s Weaknesses
- Delivery: Their dependence on other companies for delivery puts them at a disadvantage, in case of sour business relationships, shutdown, or poor customer service on the part of the delivery personnel;
- Customer Demands: Like healthier organic menus with fast-food convenience means other QSR operators are taking a part of unserved customers from McDonald’s.
McDonald’s has tried to offer healthier options, like the removal of all preservatives, fake colors, and other artificial ingredients from seven of its burger products, adding a Southern Grilled Chicken Salad to its menu, the option to add apple slices to kid’s apple meal, and recently, the introduction of McPlant. However, they are still yet to meet up with other restaurants that offer several fast-casual options.
McDonald’s Opportunities
- Expansion: Although available in several countries, there are still available international markets for the fast-food giant to enter;
- Diverse Options: More vegan options in its restaurants will pull in vegan customers. Some efforts are already being made in this direction, however, its pace might result in a situation where customers don’t recognize the company as a vegan-friendly restaurant.
McDonald’s Threats
- Competition: With already fierce competition in the QSR market, an increase in home deliveries caused by the pandemic might result in more companies entering the market with competitive prices and same or better quality products and diversity;
- Economic Conditions: inflation caused by the pandemic will result in changes in customer behaviors, demands, and spending habits, which might affect the company and the QSR market.
-> Read more about Mcdonalds’ SWOT Analysis.
Conclusion
As stable as it may seem, McDonald’s grasp in the QSR industry might — because of changing demands and economic conditions — see a few shoves and push, in the coming years. However, its revenue won’t be impacted as much, because people still need to eat. Also, because of their innovative nature and strategies, they will eventually bounce back in the long run. Their franchising business model will be of help in their recovery and/or growth.

