The Mastercard Business model focuses on partnering with financial institutions to provide network payment cards for consumers. It is headquartered in New York, U.S. Mastercard, through its proprietary global payment network, allows its users, the master account holder, a merchant, or a financial institution, to make payment transactions through their debit, credit, or prepaid cards. These cards, also known as open loop, carry Mastercard’s logo and are issued by member banks. Users can make use of Mastercards anywhere the brand is valid.
As all electronic payment cards perform, Mastercard works with an issuer identification number (IIN), which begins with the cardholder numbers. In cases where the brand logo is not visible, IIN comes to play. Apart from Mastercard, there are other major payment industries such as MasterCard, Visa, Discover, and American Express. MasterCard shapes the digital economy through innovative technology, allowing safer and more direct payment.
Contents
A brief history of Mastercard
The history of Mastercard can be traced to the emergence of BankAmericard, which later became VISA, Mastercard’s strongest competitor. BankAmericard came before Mastercard and had no profit until May 1961. To ward off competition, their profitability wasn’t disclosed until 1966, when their profit became too obvious. In response, the number of newly introduced credit cards jumped from 10 to 440 in the United States. Various banks issued these credit cards. However, they had to join forces because 16 states limited banks having branches, and 15 banned bank branching. Due to the unit banking system, the banks joined a regional bank card association, which will soon become Mastercard. With the association, banks can add credit cards to their financial products and outsource tasking back office functions.
Additionally, credit cards help service both customers and merchants. In 1966, a meeting involving bank representatives was held in Buffalo, New York, resulting in the Interbank Card Association (ICA). ICA changed its brand name and logo in 1969 to compete with BankAmericard, already leading the market. ICA was changed to “Master charge: The interlink bank” and the logo to interlocking orange and yellow circles. Later, Master Charge was refined into Mastercard. Mastercard’s merger with Eurocard allowed it to permeate the European market. Access card also joined the two forces in 1979. In 1983, MasterCard International Inc. pioneered the use of holograms as a means of security. They took over Cirrus’s network of automated tellers in 1985, Access Card in 1997, and merged with Europay International in 1992. The company started selling shares to the public on May 25, 2006.
By August 2010, Mastercard was rebranded as Mastercard worldwide. March 2012 saw the expansion of its mobile contactless payments program. Mastercard acquired many more companies, and by April 2021, they created a calculator that will help customers know how much they contribute to carbon emissions.
Who Owns Mastercard
Institutional shareholders own 75.71 percent of Mastercard. 10.77% Mastercard insiders own 10.77%, while the remaining 13.52% goes to retail investors. The leading shareholder is the Foundation Mastercard, which owns 100.56 million shares, accounting for 10.55% of Mastercard. The value estimate is $36.32 billion. The next largest shareholder after Foundation Mastercard is Vanguard Group, Inc., owning up to 8.21% of company shares.
Additionally, MasterCard is an international membership organization jointly owned by about 25,000 banks which includes financial institutions as well. The setting of annual fees doesn’t fall under the obligation of Mastercard. Member banks are responsible for setting interest rates and yearly expenses and issuing cards under their name.
Before 2006, MasterCard was owned by a bank confirm, a group of banks that came together to ally. In 2006, Robert W. Selander made a public announcement that Mastercard had been listed on the NYSE so that they could build value for both their customers and their stockholders. Ever since then, Mastercard has traded publicly. In January 2021, Michael Miebach took over from Ajay Banga as the CEO of Mastercard.
Mastercard Mission Statement
The Mastercard mission statement is “to connect and power an inclusive digital economy that benefits everyone, everywhere, by making transactions safe, simple, smart, and accessible. Using secure data and networks, partnerships, and passion, our innovations and solutions help individuals, financial institutions, governments, and businesses realize their greatest potential. Our decency quotient, or DQ, drives our culture and everything we do inside and outside our company.”
How Mastercard works
Mastercard is a payment medium that involves various scenes and players. First of all, who are the players? The players are the acquirer, the issuer, and Mastercard. The acquirer is also known as the merchant bank. As a financial institution, Mastercard licenses merchant banks to accept Mastercard. Issuers can be banks, savings and loan associations, credit unions, retailers, or governments giving credit or debit cards to customers or businesses. The role of Mastercard is to provide technology and a network with which the transactions will be made.
The process involves six stages. First, a customer pays a merchant using their Mastercard. The merchant then authenticates the payment by receiving the customer’s account information through a point-of-sale system. This information obtained will be forwarded to the acquirer, who will demand a Mastercard for authorization from the customer’s bank. Mastercard’s role here is to submit the transaction to the issuer, who is expected to authorize the transaction and give feedback to the merchant. Once done, the issuing bank sends money to the merchant’s acquirer, who credits the account. Central to all these activities is the facilitator, which is Mastercard’s network. The network integrates each party and allows them to interact virtually.
How Mastercard makes money
Mastercard had gross revenue of $23.6 in the 2020 fiscal year. In 2021, Mastercard earned $18.9 billion by assessing the number of customers who carry Mastercard brands and aggregating the charges on transaction processing and other products and services involving payments they render. Mastercard’s revenue is classified into five categories, namely:
- Domestic assessment
- Cross-border volume fees
- Transaction processing
- Rebates and incentives (contra revenue)
- Other payments
Domestic assessment
These are charges paid by issuers or acquirers on dollar volume of activities on cards or other devices that carry Mastercard brands. This is applicable where the merchant and issuer country are the same. Domestic assessments account for 45% of Mastercard’s revenue, $6.7 billion of 2020 gross revenue.
Cross-border volume fees
Cross-border volume fees are charges paid by issuers or acquired on dollar volume of activities on cards or other devices that carry the Mastercard logo. However, unlike domestic assessment, this is applicable where the merchant and issuer’s country differ. Cross-border volume fees account for 25% of Mastercard’s revenue.
Transaction processing revenue
This revenue is relevant within and outside country borders. It includes switched transaction revenue, connectivity fees, and other processing fees. Switched transaction revenue is sourced from transaction authorization, clearing, and funds settlement between involved parties. Connectivity fees are charged for network access, settlement messages, equipment, and transmission of authorization of messages. Other processing fees include safety and security, acquirer processing solutions, mobile gateways, and more. This contributes up to 60% to the company’s revenue.
Rebates and incentives (contra-revenue)
Rebates and incentives are variable or fixed payments made to customers upon agreement. When customers pass a threshold, they receive variable incentives and rebates, which are deducted from gross revenue. Fixed incentives are paid to customers upon agreement. With rebates and incentives, revenue is reduced by 60%.
Other payments
These are other products or services rendered by Mastercard in exchange for some fees. These entail costs for consulting and data analytics, loyalty and rewards solution, and cyber and intelligence solution. Plus, they all make up to 15% of Mastercard’s revenue.
Mastercard Business Model Canvas
The Mastercard Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
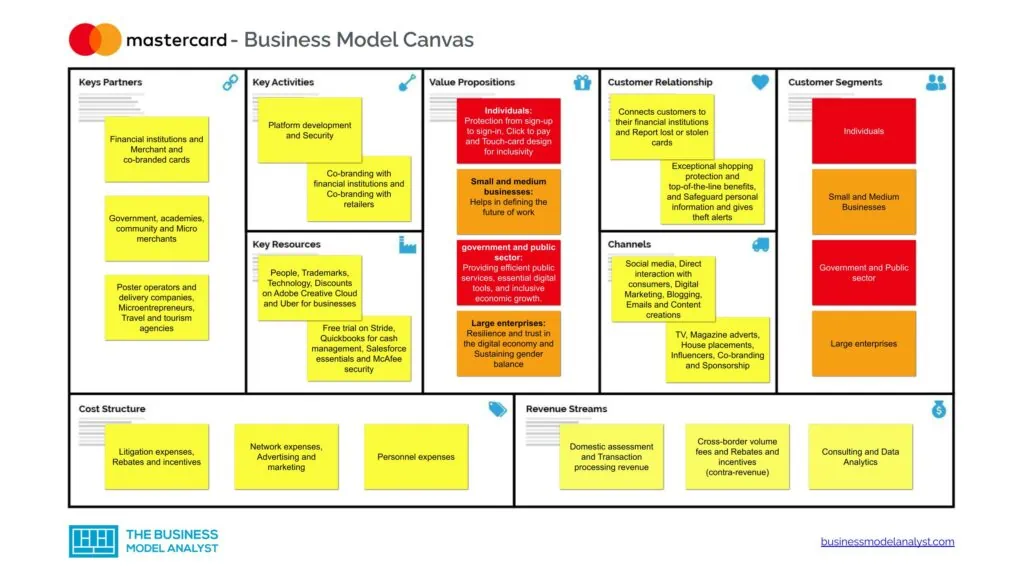
Mastercard Customer Segments
Mastercard’s customer segments consist of:
- Individuals: They enjoy the convenience and financial control of using their credit cards, debit cards, prepaid cards, and gift cards. These cards allow for everyday purchases, flexibility to explore the world, incredible purchasing power, and other benefits of being a Mastercard cardholder;
- Small and Medium Businesses: Mastercard is committed to helping small and medium businesses in creating designs to promote their business, keep their business safe and save through McAfee Total Protection, ship their products through Uber Freight load credit, support customers and employees, enjoy health benefits using Stride, manage social media marketing through Zoho Marketing Plus, build connection, etc.;
- Government and Public sector: Mastercard serves the public by establishing trust and inclusive economic development. It is instrumental in procurement, financial aid and social welfare, collections, digital payments, and tourism innovation hub;
- Large enterprises: Mastercard is an effective partner for large enterprises to send money in a more secure and faster way, prevent fraud, stay afloat with business trends, and also provide cards and ePayables without frustration;
- Banks and Credit Unions: With over 50 years of experience and innovative technology, Mastercard aids issuers in creating sure and safe means of payment. These issuers range from community banks and credit unions to Mid to large financial institutions, independent banks, and processors.
Mastercard Value Propositions
Mastercard’s value propositions consist of:
Value propositions for large enterprises:
- Resilience and trust in the digital economy: In 2021 alone, organizations experienced 83% phishing attacks. Furthermore, there has been a 238% increase in cyberattacks on employees working from home. Therefore, 90% of security leaders feel they have fallen short of expectations. Mastercard reduces risks arising from cyber threats, defends businesses against potential attacks, limits human influence on Al technology breaches, seals third-party risk management, identifies security gaps, conducts onboard risk checks, and prevents data breaches;
- Sustaining gender balance: Mastercard treats its employees equally regardless of gender. Also, Mastercard is involved in programs that help in adding to the number of female founders. They are also committed to driving change in society through partnerships and sensitization.
Value propositions for individuals:
- Protection from sign-up to sign-in. Theft is one of the major concerns of many financial institutions. About 85% experience fraud while opening accounts. It is also important to note that 36M in the USA have at least one digital-only financial account. The importance of a secure and seamless digital account opening process cannot be overestimated. Mastercard solves this problem by creating a digital identity and device insights which protects consumers at every point in their account usage;
- Click to pay: Click to pay allows users to shop without using their card or payment details. This works on a smartphone, tablet, or PC. When checking out online, you can do so with just a click. You no longer need to fear losing your passwords. Click to pay enables peace of mind when checking out. Its benefits include encrypted payment information, sophisticated bot detection, and protection against fraud;
- Touch-card design for inclusivity: The touch card is designed for visually impaired people to access payment cards. They are created with small notches; round-shaped for debit, square-shaped for credit, and triangular for prepaid. These notches allow visually impaired people to recognize their cards by touching them;
- Transforming donations: Mastercard has been able to liberate its cardholder’s power to give on a low and high scale.
Value propositions for banks and credit unions
- Mastercard partners with banks and credit unions to reach customers with the right financial services through the latest innovation and solutions. Banks can also fulfill their promise of security to their customers through Mastercard’s open banking, cyber secure digital payments. This helps give bank and credit union customers convenience and control;
- Modernizing B2B Payments Using Mastercard Track: Often, businesses are concerned about the amount of money (working capital) held up in the value chain, late payments, and invoicing and payment issues. Mastercard track, a Mastercard’s B2B product/service, reduces complexities, costs, and risks while automating the process.
Value propositions for small and medium businesses: Mastercard helps in defining the future of work. Through new technological innovation and exploration of economic models, Mastercard ensures a healthier and happier workforce and a human-centric economy. Mastercard assists small and medium businesses in managing their purchases, allows them to get paid, defends against fraud, and builds customer connection.
Value propositions for government and public sector: Mastercard partners with the government and public sector to enable an inclusive economy by providing efficient public services, essential digital tools, and inclusive economic growth. Through Mastercard, the Government engages in procurement, financial aid and social welfare, collections, digital payments, and tourism building.
Mastercard Channels
Mastercard’s channels consist of:
- Social media
- Direct interaction with consumers
- Digital Marketing
- Blogging
- Emails
- Content creations
- TV
- Magazine adverts
- House placements
- Influencers
- Co-branding
- Sponsorship
Mastercard Customer Relationships
Mastercard’s customer relationships consist of:
- Connects customers to their financial institutions
- Report lost or stolen cards
- Exceptional shopping protection and top-of-the-line benefits.
- Safeguard personal information and gives theft alerts
- Access details and transaction activities on Direct Express App
Mastercard Revenue Streams
Mastercard’s revenue streams consist of:
- Domestic assessment
- Transaction processing revenue
- Cross-border volume fees
- Rebates and incentives (contra-revenue)
- Consulting
- Data Analytics
Mastercard Key Resources
Mastercard’s key resources consist of:
- People
- Trademarks
- Technology
- Discounts on Adobe Creative Cloud
- Uber for businesses
- Free trial on Stride
- Quickbooks for cash management
- Salesforce essentials
- McAfee security
Mastercard Key Activities
Mastercard’s key activities consist of:
- Platform development
- Security
- Co-branding with financial institutions
- Co-branding with retailers
Mastercard Key Partners
Mastercard’s key partners consist of:
- Financial institutions
- Merchant and co-branded cards
- Government, academies, community
- Micro merchants
- Poster operators and delivery companies
- Microentrepreneurs
- Travel and tourism agencies
Mastercard Cost Structure
Mastercard’s cost structure consists of:
- Litigation expenses
- Rebates and incentives
- Network expenses
- Advertising and marketing
- Personnel expenses
Mastercard Competitors
- Visa: Visa Inc. is a digital payment industry that simplifies electronic funds transfer to any part of the world, often through its Visa-branded debit cards, credit cards, and prepaid cards. The company is regarded as one of the most valuable companies in the world;
- Capital One: Capital One is a financial corporation specializing in credit cards, banking, auto loans, and savings accounts. It is headquartered in Virginia;
- American Express: American Express is a versatile, world-class credit card provider. It also provides gift cards, travel, rewards, insurance, personal savings, etc. A characteristic of the American Express credit card is its perk-heaviness;
- PayPal: PayPal is a payment platform that allows users to make payments using either the website or the app. It also enables users to complete purchases, sell, and do more and is faster and safer when compared to other payment methods;
- Discover: Discover is a United States-based credit card brand that offers online banking, reward credit cards, personal loans, home equity loans, and student loans. Discover disrupted the credit card industry with its higher credit limit.
Mastercard SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Mastercard:
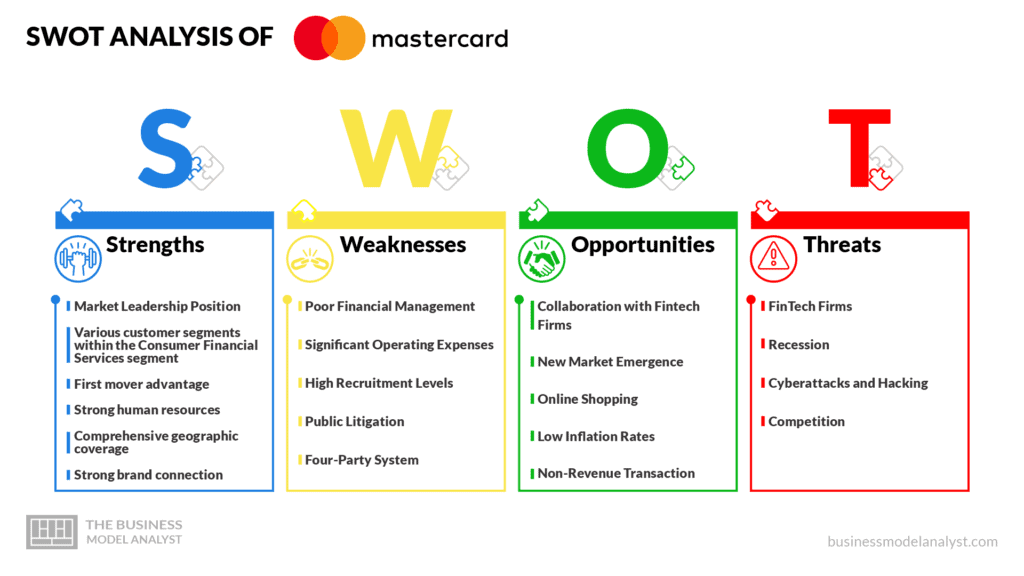
Mastercard Strengths
Below, there are Mastercard’s strengths:
- Market Leadership Position: Due to the market leadership position of Mastercard in the financial services industry, the company’s products and services have the opportunity to scale up the ladder of claiming leadership positions as well;
- Various customer segments within the Consumer Financial Services segment: Matercard’s many offerings allow the company to enter different customer segments in the consumer financial services segment. The organization is also open to a variety of revenue streams;
- First mover advantage: Mastercard enjoys the first mover advantage in saturated markets. They achieve a first-mover advantage due to new products entering the market, hence increasing MasterCard’s market share in the Industry of Consumer Financial Services;
- Strong human resources: Mastercard, through its skill development and talent management, has human resources or employees, which is essential for any Consumer Financial Services industry;
- Comprehensive geographic coverage: Mastercard’s associates and extensive dealer networks help serve consumers well from various locations. With more comprehensive geographic coverage, competitors are kept at bay;
- Strong brand connection: Mastercard’s products and services are reputable for a strong brand connection. With this reputation, it can charge higher than its competitors in the Consumer Financial Services Industry.
Mastercard Weaknesses
Some of Mastercard’s weaknesses include:
- Poor Financial Management: Competing businesses should efficiently manage finances. Despite being a dominant force in the market, poor management would affect the company’s performance;
- Significant Operating Expenses: Businesses enjoy maximum profits if they find ways to lower their operating expenses. Mastercard’s operating expenses are large, as money is spent on innovation to provide the best services to its users;
- High Recruitment Levels: Mastercard’s recruitment level is high, making it spend more on training and employee development to compete with its competitors effectively;
- Public Litigation: The financial industry is regulated worldwide. Therefore, cases of general litigation would affect Mastercard’s smooth operation;
- Four-Party System: Mastercard operates with a Four-company payment network, unlike other companies, such as American Express, which uses an external system that allows direct communication between its users. This allows more control over users than a four-party system.
Mastercard Opportunities
Below, there are Mastercard’s opportunities:
- Collaboration with Fintech Firms: As it is impossible to defeat all company competitors, collaborating with top new Fintech firms would help Mastercard maintain its position;
- New Market Emergence: The request for digital payment systems in developing countries is increasing, which means Mastercard’s potential users are also increasing. Hence, Mastercard would have increased its users and also its revenue;
- Online Shopping: With extensive internet usage, online shopping has become a trend, and the COVID-19 pandemic is also making people shop online; this allows Mastercard to increase its users because payments at online stores are made via credit or debit cards;
- Low Inflation Rates: Low inflation brings about market stability, which decreases the interest rate for users of Mastercard;
- Non-Revenue Transaction: Due to the government’s digital payment system policies and the increased price of non-cash transactions has led to the growth of financial institutions.
Mastercard Threats
Here, there are Mastercard’s threats:
- FinTech Firms: A significant threat to any existing company is competition. The emergence of Fintech firms can reduce the market share of older companies due to its more straightforward payment methods and less expensive services;
- Recession: During the recession, businesses are greatly affected due to the reduction in the living standards of people, thereby creating a reduction in their consumption. In addition, the recession could make people withdraw all their bank funds, endangering companies like Mastercard;
- Cyberattacks and Hacking: Financial institutions like Mastercard are prone to cyber-attacks and hacking. This would make users avoid digital platforms because sensitive user information would be leaked into the wrong hands;
- Competition: The payment industry is very competitive, and the existence of other similar payment networks, like American Express, is a significant competition that causes market share losses.
Conclusion
Mastercard is a popular electronic payment network that has enjoyed positive reception since coming to the limelight. However, the company has experienced tough competition in the financial industry. Therefore, it needs to make good use of its opportunities and reduce its threats to get a competitive advantage. With its innovative ideas and technology, Mastercard has an excellent standing in the digital economy, both presently and in the future, through its straightforward and safe payment methods.

