Twitter is an American communications company that operates worldwide as a microblogging and social networking service. Based in San Francisco, California, Twitter is one of the most widely-used social media platforms around the world. With the Twitter Business Model, users can post text with limited characters, images, and videos, known as tweets, on their timelines. These tweets can be liked, retweeted, and quoted by other people, depending on the user’s privacy settings.
With over 200 million users, Twitter is the 15th most-used social media platform in 2022. It is popularly used by businesses, media influencers, journalists, politicians, brands, entertainers, celebrities, and private users. Users can access the social media platform through the Android and iOS mobile apps or web browsers on their mobile or desktop devices. Twitter users can also send private messages (DMs) to their followers and other users, depending on their privacy settings.
Since its creation, Twitter has experienced tremendous growth that can be attributed to its modes of operation. Therefore, in this article, we will be analyzing Twitter’s processes, business model, history, strengths, weaknesses, and every factor that has contributed to its growth so far.
Contents
A brief history of Twitter
The origin of Twitter can be traced back to a podcasting company named Odeo, in South Park, San Francisco. Odeo was a website and directory used for the publishing and aggregation of podcasts. The company made a considerable amount of progress, however, it faced stiff competition from other tech giants, such as Apple, who provided the same services. Therefore, the founders and board at Odeo decided to pursue a different path.
To decide the best direction for the company to head, board members at Odeo had to break up into small teams to hold a daylong brainstorming session that later produced the idea of Twitter. During the brainstorming session, Jack Dorsey, an undergraduate at the New York University, at the time, pitched the idea of Twitter to his fellow team members. Jack described his idea as “a service that uses SMS to tell small groups what you are doing”.
Jack further described his idea as a dispatch service that connects everybody on their phones through texts. Everyone in Jack’s brainstorming team loved and bought the idea. Later on, every brainstorming group presented their ideas and Jack’s idea was among the few that were selected for prototyping. Demos of the selected ideas were made, and Jack and two other people were assigned to build version 0.1. The remaining members of the company went back to maintaining Odeo.com, in case Jack’s new idea failed.
Twitter was founded on 21st March 2006 by Jack Dorsey and cofounders Evan Williams, and Biz Stone, when the first version of Jack’s idea was created. At 12:50 pm PST UTC-08:00 of the same day, Jack made the first ever tweet, “just setting up my twttr”. This version of Twitter was entirely web-based. The original project name for Jack’s idea was “twttr“, coined by Noah Glass, an American technology entrepreneur who is a part of Twitter’s success story.
The project codename, “twttr“, was inspired by the fact that the American SMS short codes are five characters in length and Flickr, the popular American image and video hosting service. Another reason for the use of the codename twttr was that someone else had registered the twitter.com domain. However, about 6 months after the launch of Jack’s project idea, they were finally able to purchase the twitter.com domain and the service was rebranded and renamed Twitter.
Initially, Twitter had only about 50 users because its user base was limited to members of Odeo and their immediate families. This was to prevent the idea from leaking to competitors while development was ongoing. A while later, Twttr Beta was launched and the user base was slightly expanded. On July 15, 2006, the full version of Twitter was publicly released.
In October, Jack Dorsey, Evan Williams, Biz Stone, and some other members of Odeo formed a new company named Obvious Corporation. The new company later acquired Odeo and its assets (odeo.com and twitter.com). Twitter was later spun off into its own entity in April 2007.
After spinning off into its own company, Twitter experienced rapid growth as its user base expanded, and it recorded more tweets. Popular celebrities and politicians like Britney Spears, Oprah Winfrey, and Barack Obama started joining the social media platform. Amidst all of these, Jack Dorsey became the CEO of Twitter. By January 2009, Twitter had grown so much that it became the second-highest social networking site from being the twenty-second. In the same year, the company also won the “Breakout of the year” Webby Award.
In 2010, Twitter began to roll out new features and revamp the existing version of the service. Users could see images and watch videos from supported sites, such as Flickr and YouTube, without having to leave Twitter. By Twitter’s sixth birthday on 21st March 2012, it had already registered 140 million users and was recording 340 million tweets per day. In 2013, Twitter went public and started trading on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol $TWTR. In the same year, Twitter acquired some services such as Crashlytics, Trendrr, and MoPub to help it improve the services it renders.
In the following years, Twitter kept redesigning its software, and by 2019, it was said to be the 10th most downloaded mobile app of the decade (2010-2019). Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Twitter experienced more growth in 2020. However, the platform was sometimes used to spread misinformation, and this led to Twitter marking tweets that are perceived to have misleading information. Also, tweets and accounts of prominent persons have been brought down occasionally.
On April 14, 2022, Elon Musk, a renowned business magnate and investor, made a bid of $43 billion to acquire Twitter. However, this was short-lived as Elon Musk withdrew his proposal on July 8 of the same year, citing Twitter’s breach of some parts of the agreement as the reason for the withdrawal. On October 27, 2022, Elon Musk completed the acquisition process of Twitter and became CEO following the dissolution of the company’s board.
Who Owns Twitter
Twitter is now owned by Elon Musk after he completed a $44 billion purchase on 27th October 2022. Before Elon Musk acquired Twitter, the social media service was a publicly traded company on the New York Stock Exchange as $TWTR. The company’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) before Elon Musk’s takeover was Parag Agrawal. The former CEO of Twitter and other key executives owned shares in the company before its acquisition by Elon Musk.
Parag Agrawal, Twitter’s former CEO owned 128,000 shares valued at $7 million, Ned Segal, the former finance chief owned 394,000 shares valued at $21 million, while Vijaya Gadde, Twitter’s former head of legal policy, trust, and safety owned 600,000 shares valued at $32 million. However, these three executives were fired shortly after Elon Musk became CEO.
Before Elon Musk took over Twitter completely, he bought shares worth a 9.1% stake in the company. At the time, about 80% of Twitter’s stock was owned by institutions, private firms, and investment funds, while private individuals owned the rest. The Vanguard Group, an American investment management company, was the largest Twitter shareholder with 82.4 million shares or a 10.3% stake. Other shareholders include Morgan Stanley Investment Management with an 8.4% stake, BlackRock Fund Advisor with a 6.5% stake, and State Street Corporation with a 4.5% stake. With about 18 million shares and a 2.4% stake, Jack Dorsey, the founder and former CEO of Twitter, held the most individual shares.
However, after acquiring Twitter for $54.20 per share, Elon Musk became the owner and CEO of Twitter. Elon Musk plans to take the company private, therefore, the following day after the acquisition, Twitter shares stop trading on the NYSE. On the 8th of November 2022, Twitter’s ticker symbol, $TWTR, will be delisted from the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
Twitter’s Mission Statement
Twitter’s mission statement is “To give everyone the power to create and share ideas and information instantly without barriers.”
How Twitter makes money
Currently, Twitter operates an advertising-based business model. Companies that run this type of business model rely on advertisers who are willing to market their goods and services on the company’s platform for revenue. Twitter is free to use for individuals and businesses, therefore, how does it make money? Twitter has two major sources of revenue, however, the bulk of its revenue comes from its advertisers. The following are ways through which Twitter makes money:
Sale of Advertising Services
Twitter has over 200 million active monthly users around the world. This large user base attracts brands and businesses who want to showcase their goods and services to people around the world. Therefore, these brands pay Twitter to advertise their products and services on its platform. Twitter’s algorithm ensures that these ads make it to the timelines of its users who make up the target audience of the advertisers, thereby giving the brands and businesses value for their money. There are different types of ads that can be run on Twitter. These include:
- Promoted Ads: Promoted ads are ads that appear like normal tweets on a user’s timeline, however, they are labeled as “promoted”. Promoted ads appear on a Twitter user’s timeline depending on the user’s likes, dislikes, and preferences. This ensures that the ads are shown to people who might have a genuine interest in the products or services advertised. For this type of ad, advertisers can choose the pay-for-performance or pay-for-impression option;
- Promoted Accounts: This type of ad can be used by brands or entities to build a community of Twitter users who might show interest in their products or services. This ad works by suggesting the advertisers to suitable Twitter users as “Who to follow”. With this type of ad, users are targeted by demographics, preferences, location, etc. If the user likes the product or service being advertised, they might follow the business or brand’s page on Twitter, thereby increasing the advertiser’s follower base;
- Promoted Trend Takeovers: On Twitter, trends are a list of the most prevalent topic happening at the moment in a particular location. This list is determined by words and phrases that are mentioned by people in a particular demographic, at a higher rate than others. Some trends have hashtags (#) and this helps people recognize them as relating to the prevalent topic. Twitter trends can be seen in the home timelines, notifications, search results, and profile pages of users in the location where the trend is going on. Therefore, it is an effective way for advertisers to market their goods and services to millions of people at the same time.
The revenue generated from the sale of advertising services is the major way through which Twitter makes money. In 2020, Twitter’s advertising services accounted for 86% of the total revenue generated by the company. By 2021, revenue generated by advertising services rose to 89%. Although Twitter’s advertising services are often carried out on its platform, some of it might also be done on third-party publisher websites.
Data Licensing Services
Data licensing involves a legal agreement between the creator/owner of the data and the end-user or a third party to gain access to or use some kind of data. More than 400 million tweets are made on the Twitter platform daily. This provides a large pool of raw public data, which Twitter refers to as Firehose, that can be used by brands and businesses to improve their services.
Twitter sells data licenses that allow its partners to access, search, and analyze real-time and historical data on its platform. With sophisticated data analysis tools, Twitter’s data partners can use the data gotten from Twitter to generate insights about consumer trends and learn how to meet the needs of their customers. Sometimes, Twitter might share the personal data of its users with advertisers, however, users have to provide consent.
Data licensing is the second major way through which Twitter makes its money. Twitter’s data licensing services accounted for about 14% of Twitter’s revenue model in 2020.
Subscription Service
Also known as Twitter Blue, this is a monthly subscription service that offers exclusive access to premium features. This service was launched in June 2021, and it is Twitter’s first subscription-based service. Twitter Blue is still a pretty new feature, therefore, it is only available in four countries — the U.S., Canada, Australia, and New Zealand. Features of the Twitter Blue subscription include custom app icons, themes, custom navigation, thread reader, top articles, and the ability to undo tweets and bookmark folders. Twitter Blue subscribers also gain early access to all of Twitter’s new features, and they have to pay $4.99 per month.
Twitter’s Business Model Canvas
The Twitter Business Model can be explained with the business model canvas below:
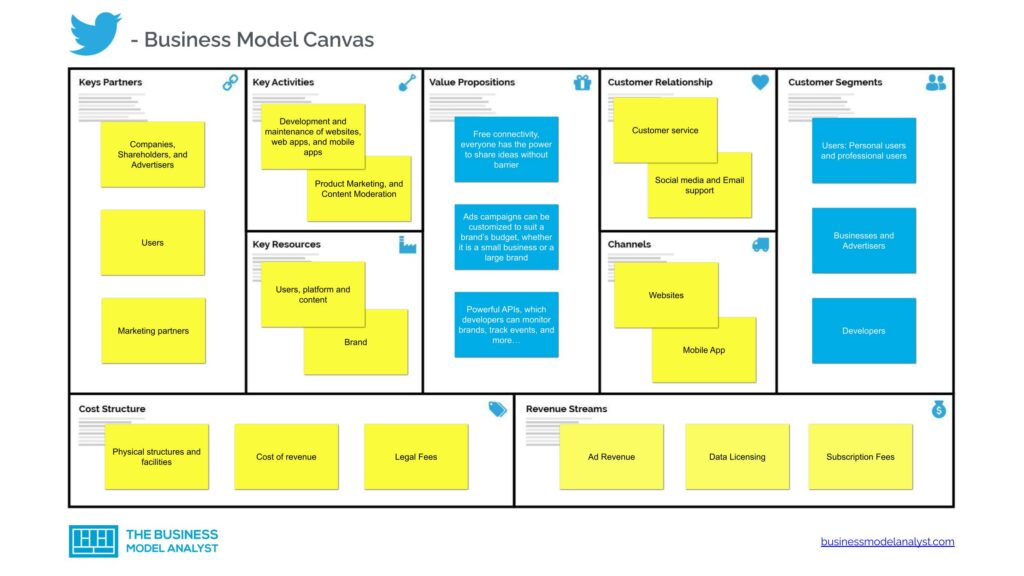
Twitter’s Customer Segments
Twitter’s services are available worldwide, therefore, its customer segment is made up of people all over the world. Twitter’s customer segment consists of the following:
- Users: Twitter users make up a major part of its customer segment. As of Q4 2021, Twitter had 217 million monetizable daily active users (38 million users in the U.S. and 179 million international users). Twitter users are the people who sign up on the Twitter website to use its services for different purposes. About 70.40% of the total number of Twitter users are male and the remaining 29.6% are female. Also, the larger part of Twitter users is between the ages of 25-48 (38.5%). While users do not pay to use Twitter’s services, Twitter cannot generate any revenue without their existence on its platform. There are two major categories of Twitter users. These include:
- Personal Users: Personal users on Twitter are private individuals who use Twitter to connect with other people around the world and for entertainment purposes. These users do not have affiliations with any brands or businesses. They are regular people whose accounts reflect their views, likes, and personality. This category of users makes up the largest part of the total number of users on the Twitter platform.
- Professional Users: Professional users on Twitter are people or entities that use Twitter for commercial purposes. Such users are expected to use professional accounts on Twitter. Professional accounts allow professionals to access tools like Professional profiles, Twitter shopping, quick promote, and other features that make their jobs easier. Until 2022, Twitter users had to apply directly to Twitter before they could convert their accounts to professional accounts. However, on 29th March 2022, Twitter announced that any Twitter user can switch to a professional account through their profile settings.
There are two types of professional accounts – business and creator. The professional business account is best suited for brands, businesses, retail stores, and organizations that are trying to build an online presence or market their goods and services. The professional creator account on the other hand is meant for public figures (politicians, athletes, movie stars, etc.), artists, content creators, social media influencers, etc. While converting to a professional account on Twitter is completely free, some criteria must be met. Users who wish to convert to a professional account must have a complete profile with a display name, a profile picture, and a bio (These details must be authentic and clearly stated). Also, users must not have a history of repeated violations of Twitter’s user agreement. Only existing Twitter accounts can be converted to professional accounts.
- Businesses and Advertisers: This part of Twitter’s customer segment account for Twitter’s source of revenue. Twitter has a large user base, which is a goldmine for brands and businesses that want to market their goods and services to millions of people around the world. To showcase their products and services to users on the Twitter platform, advertisers pay Twitter. Twitter has several types of ads that it uses to target its users and satisfy its advertisers. Twitter helps its advertisers to build brand awareness, nurture customer consideration, and drive sales and conversion. To place ads, advertisers have to go to Twitter Ads, add a payment method, create an ad, then launch and optimize the ads created. Some businesses also subscribe to buy data licensing services. While this category of Twitter’s customer segment is responsible for Twitter’s major source of revenue, it would not exist without the users.
- Developers: This refers to the people that use Twitter’s API to build, integrate, and improve apps through Twitter’s platform. Although this is Twitter’s smallest customer segment, it is very important.
Twitter’s Value Propositions
Twitter has some unique selling propositions (USPs) in place to provide value to every member of its customer segment, generate revenue, and retain its users, advertisers, and developers. Twitter’s value propositions to the members of its customer segment include:
Value Propositions to Users
Twitter has millions of users that depend on the platform for news, entertainment, and business purposes. They make up a huge part of Twitter’s customer segment and are the basis for Twitter’s revenue model. Twitter’s value propositions for its users include:
- Free connectivity: Twitter offers its users a platform on which they can connect with family, friends, and strangers around the world for free. Twitter users can sign up and create an account on its website without paying a dime. This allows them to connect with millions of other users of all backgrounds and nationalities. Twitter users can also share news, opinions, and views with millions of people on their timelines. People who use Twitter for business are also connected to customers and clients from different parts of the world. Twitter also breaks class barriers as regular people can interact with politicians, celebrities, and public figures directly and even send them direct messages on the platform.
- Customization: Twitter gives its users to customize their accounts as they like. Twitter users can personalize their profiles, declare their interests, and decide the kind of tweets they want to see on their timelines. They can also follow accounts they are interested in and mute or block accounts whose tweets they do not want to see. Twitter also has features that let its users choose who they want to see or comment on their tweets. For business owners, Twitter helps to complement their marketing efforts by identifying their target audience.
- Convenience: Twitter is very easy to use, and it is a convenient source of many things for its users. The platform provides its users with real-time information faster than other channels. News organizations and journalists use the platform to share breaking news and disseminate information very quickly. Also, Twitter makes it easy for its creators and business owners to manage their content and access their analytical data.
- Privacy: Twitter has privacy and safety measures put in place to help its users manage what information they can see and share on Twitter. While tweets are public, Twitter offers an option of direct messaging for its users. Users can send private messages to people as they like without other Twitter users seeing the message sent. Also, users can decide who can message them directly and if the people messaging should know when their texts have been seen. Twitter users can protect their tweets in such a way that only their current followers and people they approve of in the future can see and like their tweets.
- Authenticity: Twitter helps to protect its users from impersonation and scams by issuing blue verification badges, also known as a blue tick, to notable users who request it. For users that receive the blue badge, it means that they have been verified by Twitter to be authentic and that ensures that they cannot be impersonated by other users. Other users are also protected from scams carried out by impersonators. While the blue verification badge is currently free, Twitter users must meet some requirements before they can receive the blue tick. Only authentic, notable, and active Twitters are eligible for the blue badge verification. Before becoming verified on Twitter, a user must have a complete profile (including profile picture and profile name), a confirmed e-mail address or phone number, and must have been active in the last six months. Twitter users that wish to be verified must provide a link to an official website, a valid official government-issued identification document, and an official e-mail address.
- Twitter Spaces: A Twitter space is a live audio conversation feature on the Twitter platform that allows users to create audio chat rooms as hosts, speakers, or listeners. On Twitter Spaces, users can share their opinions on different issues of interest verbally. Twitter spaces are free to open and join, therefore, any Twitter user can do this with ease.
Value Propositions to Businesses and Advertisers
Twitter’s advertisers’ share is its major source of revenue, therefore, it must continue to provide value to retain them. The following are the value propositions of Twitter for its advertisers and their businesses:
- Publicity: There are millions of users from different countries of the world on Twitter. Twitter helps to amplify its advertisers’ tweets and market its goods and services to millions of people around the globe. Twitter bridges the gap between advertisers and their potential customers/clients.
- Pricing: Twitter has a flexible pricing model for its advertising services. Twitter campaigns can be customized to suit a brand’s budget, whether it is a small business or a large brand. Twitter ads do not have a minimum required amount and the cost of advertising varies, depending on the type of ads placed. However, advertisers have complete control over the total amount they want their ad campaigns to spend. Also, advertisers are only billed for using Twitter’s ad services when Twitter users like, retweet, reply to their tweets, follow their accounts, or expand/engage any of their promoted tweets.
- Targeting: On Twitter, advertisers can target a particular audience with their ads. Advertisers can decide to show ads to a particular set of people based on their demographics, location, preferences, interests, etc. This ensures that only potential customers see these ads, therefore, giving the advertisers value for their money.
- Ease and Convenience: Twitter ads are easy to set up and can be done by almost anybody. Unlike some other social media networks, businesses and brands on Twitter do not need to hire someone else to run their ads for them.
- Analytics: Twitter provides its advertisers with tools through which they can check the performance of their ads. Through Twitter Pixel, Twitter offers conversion tracking for performance advertising. This helps advertisers to measure the value they get after spending on ads. This can be done by tracking the actions that Twitter users take after viewing, clicking, or engaging ads on Twitter.
- Access to data: Twitter provides businesses that pay for it with its public data. Businesses and brands pay to access Twitter’s public data because they know how beneficial it is to the smooth running of their business on the Twitter platform. Businesses can search and analyze data consisting of public tweets and their content on the Twitter platform. This can help these businesses understand where and how to improve the goods and services that they provide.
Value Propositions to Developers
Developers are the people who build with any service of Twitter. Twitter’s value proposition to its developers includes:
- Powerful APIs: Twitter provides powerful APIs with which developers can monitor brands, track events, manage social media, and uncover consumer insights;
- Awareness: Twitter helps developers to be aware of the latest trends and technologies to update their craft;
- Knowledge: Twitter gives developers an avenue to learn tools and practices that help to build their skills and portfolio;
- Connection: Twitter provides a platform through which developers can connect with their peers.
Twitter’s Channels
Twitter’s channels consist of:
- Websites: Twitter’s websites are its primary channel of distribution through which its users access its services. Advertisers can place their ads through Twitter’s website, developers can get APIs directly from Twitter’s website, and people can sign up and create an account through Twitter’s website. Twitter also has a web app through which its users can access their accounts.
- Mobile Applications: Twitter has mobile applications designed to work on different kinds of operating systems, including Android and iOS. These apps can be downloaded from the Google Play Store or the Apple App Store, as the case may be. Features of the Twitter app include home, search, notifications, messages, etc. Users can access their Twitter account through its mobile application. They can also tweet, retweet, reply to tweets, and like tweets on the mobile application. Tweets from iOS devices are marked “Twitter for iPhone” while tweets from Android devices are labeled “Twitter for Android”.
Twitter’s Customer Relationships
Twitter has measures in place through which it acquires and retains users. Twitter’s customer relationships include:
- Customer service: Twitter provides an automated self-service for its users;
- Website: Twitter has an insights section on its website that caters to all frequently asked questions that a user might have. It also includes articles and a research report;
- Social media support: Twitter provides personal support on social media to some of its users who might be experiencing some difficulties with some of its services;
- E-mail support: Twitter also provides e-mail support to its users. If a user signs up to Twitter’s platform with their e-mail, they are eligible to receive e-mails from Twitter.
Twitter’s Revenue Streams
Twitter’s revenue streams consist of:
- Ad Revenue: This is Twitter’s major revenue stream. Twitter has a large user base, which brands and businesses can take advantage of to market their goods and services to millions of people all over the world. To place different types of ads on Twitter’s platform, these brands and businesses have to pay Twitter. Twitter allows advertisers to target users based on several factors to ensure the effectiveness of the ads;
- Data Licensing: This is the second most important revenue stream for Twitter. Twitter’s large user base provides it with a lot of public data, which Twitter refers to as Firehose. This data of millions of people is beneficial to brands and businesses as they can analyze them to know more about Twitter users (their potential customers) and develop methods to meet their needs. To generate more revenue, Twitter shares this data with businesses and brands who request access. Twitter’s data licensing is legal, and it does not share its users’ personal data without their consent;
- Subscription Fees: While this feature of Twitter is still under development and limited to particular geographical locations, it is still considered a stream of revenue. Twitter has a service called Twitter Blue, which requires a subscription fee of $4.99 to be accessed. Twitter Blue offers Twitter users some premium features for a monthly subscription. This service is only available in the U.S., Canada, Australia, and New Zealand.
Twitter’s Key Resources
Twitter’s key resources include:
- Users: Twitter has millions of active users who use its services as they deem fit. They are a major human key resource for Twitter and the services it provides. Without its users, Twitter’s revenue model would fail, and the platform would cease to exist;
- Platform: Twitter’s platform consists of its websites, web apps, and mobile apps through which its users access its services;
- Content: There are different types of Twitter users and each of them uses the platform for different purposes. While business owners use the Twitter platform to build an online presence and amplify their goods and services, private users use Twitter to read engaging content tweeted by other users. Engaging content is an intellectual key resource for Twitter;
- Advertisers: Twitter can run its platform through the revenue it generates. Advertisers represent the major source of revenue for Twitter, therefore, they can be considered a financial key resource of the social networking service;
- Human Resources: This refers to the people working at Twitter to ensure that the platform is up and running every time. Twitter employees are responsible for the update and maintenance of the platform. There are about 3,700 employees at Twitter after a 50% slash of the workforce following the Elon Musk takeover.
Twitter’s Key Activities
Twitter’s key activities consist of:
- Development and maintenance of websites, web apps, and mobile apps
- Product Marketing
- Maintenance of user data
- Content Moderation
- User base expansion
- Update of existing products
- Customer service
Twitter’s Key Partners
Twitter’s key partners include:
- Companies (including Bloomberg, Hootsuite, Sprinklr, BlackSwan technology, Brandwatch, etc.)
- Shareholders
- Advertisers
- Users
- Marketing partners
Twitter’s Cost Structure
The cost incurred by the development and maintenance of Twitter’s platform, among other things, makes up Twitter’s cost structure. Twitter’s cost structure consists of:
- Physical structures and facilities (offices around the world)
- Cost of revenue
- Sales/ Marketing
- Research and development
- Platform maintenance (website, web app, and mobile app)
- Traffic acquisition
- Employee salaries
- General and Administrative costs
- Legal fees
- Customer service
Twitter’s competitors
There are several social media services available, therefore, Twitter has a lot of competition. While some of these competitors do not offer the same service, they are social media services that offer similar services. Twitter is the 15th biggest social media service in 2022 according to the number of monthly active users (MAUs). Twitter’s competitors include
- Parler: Parler is an American social networking service that is commonly associated with conservatives. The social media app has been described as an alternative platform to Twitter. Some of Parler’s users are people who have been previously blocked on mainstream social networks such as Twitter. Although created in 2018, Parler has witnessed rapid growth and currently has about 20 million followers. Parler is said to be a free speech-focused app and is headquartered in Nashville, Tennessee. Parler poses a threat to Twitter’s domination because of its free speech policy. Twitter has stringent rules that have led to the permanent banning of public figures, such as Donald Trump, the former President of the United States of America. However, Parler claims to support free speech, and it accommodates people who have kicked off Twitter.
- Gab: Gab is an American microblogging and social networking service that is considered a far-right app. Gab was founded in 2016, but was not launched until 2018. The app is said to be a free speech social network and its mission statement is to “defend, protect, and preserve free speech online for all people. Gab is very similar to Twitter, and it works like a mixture of Facebook and Twitter. Its users can publish posts (also known as “gabs” with a 300-character limit), join groups, send private messages, buy products, and Livestream. Gab is a haven for people who have been permanently banned on Twitter. It also reported a surge in the number of its user base when Parler, a competitor, was taken off the internet, a short while after the January 6 Capitol siege in the U.S. Unlike Twitter, Gab does not moderate the content posted by its users. However, it claims to block posts that contain illegal activity, pornography, threats of violence, child exploitation, doxxing, and spam. Gab is a very controversial app because it has been accused of being used to spread antisemitic comments, Neo-Nazism, racism, white supremacy, conspiracy theories, etc under the guise of free speech. While there have been several attempts from big tech companies to bring down the social networking service, the company remains afloat.
- GETTR: Gettr is a social media platform and microblogging site that has its headquarters in New York, U.S. Gettr was founded by Jason Miller, a former aide to former President, Donald Trump, and was officially launched on the 4th of July 2021. The social media platform has been said to be a site for American conservatives. Shortly after its launch, Gettr experienced several issues such as hacking of the platform and some high-profile accounts, uploading of content that violated the terms of service, and a flood of pornography. However, it has since been able to resolve these issues since then. Gettr is a lot like Twitter, however, it claims it is committed to defending free speech, fighting cancel culture, promoting common sense, challenging social media monopolies, and creating a true marketplace of ideas.
- Truth Social: Truth Social is an American social media platform founded by former U.S. President, Donald Trump. The social media platform was created by Trump Media & Technology Group, an American media, and technology company owned by Donald Trump. Like Parler and Gab, Truth Social was created to serve as a competitor to Twitter and Facebook while providing an uncensored alternative. Truth Social was founded on the 20th of October 2021, however, the service was not launched until the 21st of February 2022. Currently, the Truth Social media platform is only accessible to users in Canada and the United States of America. Truth Social is a simulation of Twitter as users can post truths (tweets), re-truth (retweet), like content, and comment. The social media platform, like Twitter, has features like a home tab, search, notifications, and direct messages. The app is available on both the android and iOS operating systems.
- MeWe: MeWe is a social media network and service available globally with its headquarters in Culvert City, California, U.S. Owned by Sgrouples Inc., a company that provides social networking applications, MeWe was founded on 16th May 2022. Although the MeWe platform’s interface is similar to that of Facebook, the company claims it is “anti-Facebook” because it focuses on data privacy. MeWe delivers its services through its platforms (website and mobile apps). These platforms possess the common features seen in most social media and social networking platforms. On MeWe, users can post text and images to their feed, react to other users’ posts with emojis, create groups, post animated GIFs, and chat with other users using private messages. As a competitor to Twitter, MeWe has also seen a large influx of users from other social media networks, cracking down on misinformation, incitement, and threats of violence.
Twitter’s SWOT Analysis
To understand the reason why the Twitter Business Model is a success, we have to examine the analysis of its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The following is a comprehensive SWOT analysis of the Twitter Business Model:
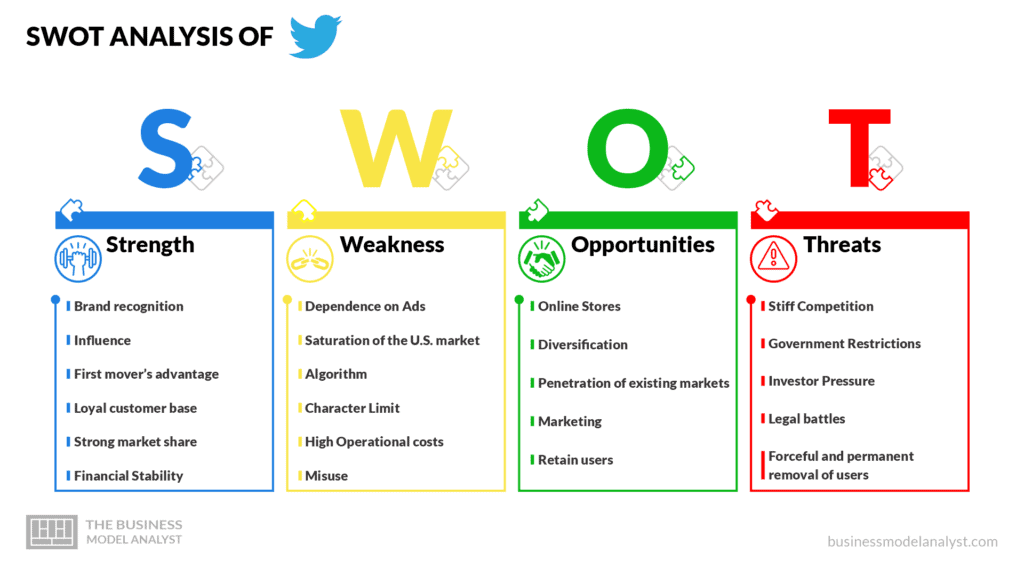
Twitter’s Strengths
- Brand recognition: Twitter has strengthened its brand over the years, therefore, it is easily recognized. Twitter’s logo (bird) and the color blue are easily associated with the brand. Therefore, the Twitter brand being imprinted in the minds of people is one of Twitter’s biggest strengths.
- Influence: Twitter is one of the most influential social media networks in the world. It is a source of authentic news to many as it is home to several journalists and media houses. Unlike some other social media apps, Twitter users are made up of people of different generations (Millennials and Gen-Z). This is uncommon among social media services, and it shows the amount of influence Twitter has. Twitter is also used to amplify social issues and get people involved in a cause. Hashtags on Twitter are so powerful that they can be used to mobilize communities, expose the evils of government, and address injustice.
- First mover’s advantage: Created in 2006, Twitter is one of the first microblogging platforms in the world. It is older than most of its competitors, hence its influence in the market.
- Loyal customer base: As of the second quarter of 2022, Twitter had 237.8 million daily users. Despite the series of controversies that Twitter has been involved in the past, it is still highly preferred by celebrities, government officials, organizations, and several private individuals for business, publicity, and entertainment purposes.
- Strong market share: A market share is the percentage of an industry that is earned by a particular company over a specific period. As one of the biggest microblogging and social media platforms, Twitter has a 25.45% market share. This puts the social media platform in a significant position in the tech industry.
- Financial Stability: Twitter has attained stability, in terms of its financial position. Twitter’s annual revenue has been steadily growing, and this signifies financial maturity for Twitter.
Twitter’s Weaknesses
- Dependence on Ads: Twitter’s major source of revenue is the money gotten from its advertisers in exchange for its marketing services. Over 80% of Twitter’s revenue comes from its advertisers. This means that if advertisers decide to leave Twitter, for any reason, Twitter’s business model might fail and be forced to fold up.
- Saturation of the U.S. market: Although Twitter’s services can be accessed around the globe, the company is still heavily reliant on its U.S. market. In 2019, Twitter generated $3.45 Billion, however, 56% ($1.9 billion) of Twitter’s revenue for 2019 was from the U.S. If Twitter loses the majority of its users from the U.S., this might result in its revenue model crashing.
- Algorithm: Twitter users have complained severely about its faulty algorithm. Sometimes, users might encounter irrelevant/fake tweets and problems with the search functionality. Twitter has been struggling to fix this problem and this is one of its major weaknesses.
- Character Limit: Twitter has a character limit of 280 words, and this can be frustrating for its users when they need to put out a tweet without making it a thread. Twitter users are also limited to a maximum of 2,400 tweets per day.
- High Operational costs: Twitter spends a lot of money to ensure that its products are satisfactory for every member of its customer segment. This is to make sure that the microblogging giant is always a step ahead of its competitors. However, this might decrease productivity, increase operational costs, and threaten profitability.
- Misuse: Twitter can be used negatively by some users to troll other users, spread misinformation, and carry out other illegal activities. If this happens consistently, it might cause a lot of users to leave the platform.
Twitter’s Opportunities
- Online Stores: Twitter already provides a platform through which business owners can market their goods and services to millions of people around the world. Creating an online store would ensure that potential customers can complete the process of purchasing a product or service that was advertised to them on Twitter.
- Diversification: Twitter needs to look into the creation of other products or the provision of other services that can serve as another revenue stream. For example, Twitter can enter the music or video streaming service market. This will offer Twitter more opportunities and provide an avenue to make more money.
- Penetration of existing markets: Although Twitter is a worldwide service, it is more dominant in some locations compared to others. For example, the U.S. alone contributes more than 50% of the total annual revenue generated by Twitter. If Twitter focuses on trying to penetrate more international markets, it can double its revenue.
- Marketing: While Twitter can be considered successful with over 400 million users, it can still do better by doubling the number of users it has. This is made possible through intensive marketing and value proposition.
- Retain users: With the emergence of competitors on the rise, Twitter should ensure that it retains its customers by consistently providing value, improving user experience, and increasing user satisfaction.
Twitter’s Threats
- Stiff Competition: Although Twitter is one of the first microblogging platforms to exist, it now has fast-growing competitors. Since other platforms are offering the same services Twitter does, it is easy for users to quit Twitter and join a competitor to register their displeasure.
- Government Restrictions: Twitter is so influential that autocratic governments sometimes might ban their citizens from accessing Twitter’s services in a bid to curb freedom of speech or prevent their citizens from organizing a revolt against them.
- Investor Pressure: Shareholders in a company can mount undue pressure on its management, which prevents them from functioning as an independent entity. For example, Elliott Management Corp, once Twitter’s biggest investor, pushed for the removal of Founder/CEO Jack Dorsey.
- Legal battles: Twitter has been accused severally of selling user data. On the 25th of May 2022, Twitter was fined $150 million by the Federal Trade Commission and the United States Department of Justice for using its users’ phone numbers and email addresses for targeted advertising contrary to the security reason they gave earlier.
- Forceful and permanent removal of users: Twitter sometimes suspends its members permanently for going against their terms of service. When this is done to a public figure, it can be disastrous. This is a result of the fans and devotees of the public figure who might decide to leave the platform in solidarity.
-> Read More About Twitter’s SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
Twitter is one of the largest social media networks in the world today. It is trusted by government officials, celebrities, public figures, journalists, media houses, and private individuals. Twitter operates an advertisement-based business that registers revenue from people who come to market their goods and services on the platform.
Although Twitter is one of the first market movers, it is experiencing stiff competition from other companies that provide the same services. Lately, Twitter has come under fire for some actions it takes. For example, the permanent ban of notable figures on the platform. This has also enabled the rise of more competitors. In addition, Twitter must also find another source of revenue to complement the existing ones.
Elon Musk, a famous businessman, has purchased Twitter, and he intends to make it private. Elon Musk has introduced new sources of revenue, and he says he is committed to ensuring free speech on the platform.

