The Target business model relies on a multilateral sales system, including retail, online, and leasing sales, as well as credit card fees. Regarded as the seventh-largest retailer in the United States of America, Target was established in 1962 with its headquarters in Minneapolis, Minnesota.
The company is a big box department store in America, created as the division of Dayton’s department store in the headquarters, Minneapolis, that year, and it houses over 350,000 employees in the United States of America and abroad. The store’s expansion to other parts of the nation started in 1962, with new store formats introduced under Target in the 1990s. Across all 50 states, there are more than 1,900 store locations.
The corporation developed its stores as the world’s first fully enclosed shopping mall. This was aimed at serving its customers during rainy seasons. In 1956, the corporation started to build an enclosed mall fully. The company decided to expand to Chicago in 1993, but it was met with strong competition in the city. To leave a lifelong impression, it opened 11 stores in one day.
Target provides many products, including beauty, health, clothing, bedding, accessories, food, furniture, electronics, games, pet supplies, shoes, toys, and many more. Aside from its wide range of products which gives customers many options, Target also provides a satisfactory customer experience and convenience. Target’s retail formats are:
- Target, the discount store;
- SuperTarget, the hypermarket;
- Small-format stores previously known as CityTarget and TargetExpress before being consolidated under the Target branding.
In 1969, Dayton Corporation partnered with J.L. Hudson Company, which caused the corporation to be renamed Dayton-Hudson Corporation. The combined corporation established various department stores, such as Hudson’s, Dayton’s, Mervyn’s, and Marshall Field’s. Target now has over 30 subsidiary companies.
Contents
A brief history of Target
Target was founded in 1902 by George Dayton to help his church. George started as a banker. He was born on the 6th of March in 1857 in Clifton Springs. The Clifton Springs-born businessman left the Bank of Worthington. Later, he founded Minnesota Loan and Investment Company, where he got lineated financially. In 1883, George moved to Worthington, Minnesota, with his family.
As early as the 1920s, Target Corporation became a multimillion company. This was possible because George successfully rented out an entire 6-story building in the 1920s. The first expansion was an issue because it was accompanied by acquiring a Minneapolis-based jeweler, J. B. Hudson and Son. It was an issue because the acquisition was poorly timed. It was purchased when the United States faced its worst stock market crash in 1929. The department store made it through, but the freshly acquired jewelry store withstood ghastly net losses.
The corporation now has over 30 subsidiary companies, some larger than others. Target Capital Corporation, Shipt, Dermstore, Target Creative, Target Brands, Inc, Red Tail LLC, TGT Energy LLC, and Westbury Holding Co are the companies that are bigger in comparison to other subsidiaries. The former Target Corporation followed strict Presbyterian guidelines. In the 1920s, when George Dayton established the business, the company had been known for its strict Presbyterian guidelines. Target stores have never sold any alcohol or malicious newspapers, and are closed on Sundays to observe the Sabbath.
However, the company stopped following the Presbyterian guidelines when Donald Dayton took over the business in 1950 so that the company could be more accessible and inclusive. Donald consented that the stores should be opened on Sundays and that alcohol should be sold.
B. Dalton Bookseller was once a chain under Target. It was launched in 1966. It became one of the largest retailers of hardcover books in the country. It had almost 800 stores when it was still functioning. It ceased to be in business in February 2013.
Getting a store name proved to be a grueling task for the corporation’s public relations. There were over 200 potential business names to consider and choose from. The first logo was launched in 1962. It had three red open rings with the word “Target” written in black in the middle.
In 1968, the logo was revamped. Just one ring with a red dot surrounding it was left. Even the brand name, Target, was removed. The corporation celebrated a newly opened outlet in 1968 by showcasing its latest identity. Numerous posters of a woman wearing an earring styled like Target’s logo were released to promote the brand. When it was 1975, the brand name, Target, was added to the logo. But this time, it came in a large black font to the right of the Bull’s Eye icon.
Again in 1989, the company tried to improve its logo by removing the Bull’s Eye icon, and just the brand name was left. “Target” was now written in red italic with a white shadow. However, the company dropped this idea and stuck to its 1975 logo until 2004. But in 2004, a more modern version of Target’s logo was launched, which is still in use today. The new logo came with the brand name “Target” written in red, placed under the Bull’s Eye icon.
In 1995, the company established Archer Farms. At this point, its first grocery stores were already up and running. The company was well-versed in the food industry and launched its groceries for basic foods such as bread, pasta, milk, etc. In 2019, a new grocery brand, Good & Gather, was launched with over 2,000 items, with which the company enlarged its portfolio in the food industry. They vary from organic snacks to fresh salad mixes and frozen food. The company has a food laboratory for its research and overseeing development. Most, if not all, of the company’s latest food products, were studied, developed, and improved on in the laboratory.
Who Owns Target
Target Corporation was established in 1902 by George Dayton. It was initially called Goodfellow Dry Goods in 1902 but later became a partnership company in 1969 when Dayton Corporation and J. L. Hudson Company were merged. It was then renamed to Dayton-Hudson Corporation.
Generally, Target Corporation owns Target, its department stores, and other subsidiaries. The present CEO of The Target Corporation is Brian Cornell. He took over in 2014 and has been leading the company since then.
Target Mission Statement
Target’s mission statement is to present the corporation as the best place to experience the delivery of tremendous value, improving innovation, and the best shopping experience for its customers by fulfilling the brand promise that states: Expect more, pay less.
How Target makes money
It took over two years before Target stores could start making profits because the new business concept did not immediately generate profit. The department stores recorded losses. Later in 1965, when little business changes were made, Target made a profit of $35 million.
On the 18th of October 1967, Target was finally listed in the United States Stock market. After the corporation had recorded many profits between 1965 and 1966, it sought to go nationwide. Hence, it expanded all over. After the company was listed on the United States Stock market, it went public successfully by selling some of its stocks through Initial Public Offering (IPO) on the same day.
Target makes money in three ways:
- Merchandise sales
- Credit card profit sharing
- Other revenue
Merchandise Sales
Target corporation makes the majority of their revenue through retail merchandise sales. 98.7% of Target’s total revenue came from merchandise sales at the end of 2021. Target has over 1,900 stores in the United States of America, which generates revenue from merchandise sales. There are 5 product categories the stores sell – apparel and accessories, food and beverages, décor and home furnishings, hardlines, beauty, and household essentials. Below, there is the breakdown of the percentage that each category generates:
- Apparel and accessories: 17% of store sales;
- Food and beverage: 20% of store sales;
- Decor and home furnishings:19% of store sales;
- Hardlines: 18% of store sales;
- Beauty and household essentials: 26% of store sales.
Only 18.9% of these merchandise sales occurred on the online store, target.com, while 81.1% of the merchandise sales occurred in the stores.
Credit Card Profit Sharing
Credit card profit-sharing accounts for just a tiny bit of Target’s total revenue. However, it is still a means by which Target makes money. Target has a credit card program agreement with a bank, TD Bank, responsible for issuing the RedCard credit cards. The RedCard credit cards are used for credit card profit sharing. With this agreement, Target Corporation has the right to receive a certain percentage of all the profits generated through the RedCard credit cards. There are two types; Target Credit Card and Target Mastercard.
Other revenues
Target Corporation also generates revenues through what they call “other revenues.” Other revenues collectively generated about 1.39 billion dollars as additional revenue for the corporation. According to Target’s Form 10-K page 45, other revenues are from Shipt membership. These commissions were earned during 3rd party sales on target.com; advertising, rental income, service revenues, and miscellaneous revenues.
Target vs. Walmart
Target and Walmart are two of the biggest retail stores in America, but here are some differences between them:
- Target is known to offer higher quality items at the best price, while Walmart aims to be the lowest-priced retailer for its products;
- Although Walmart is a lot larger than Target, Target seems to be more profitable than Walmart;
- Walmart and Target are competitors, but they operate in different markets using different techniques. So, their customer demographic differs;
- Walmart Stores is the world’s largest retail company. It operates in megastores, while Target offers a better in-store experience;
- Target uses a low-price strategy similar to Walmart’s, but it is more focused on the e-commerce platform;
- Walmart has over 10,000 stores in pale comparison to Target, which has a little above 1,900;
- The quality of products from Target is far better than that of Walmart. Target sells quality products at affordable prices;
- There’s a large range of choices at Walmart stores compared to Target.
Target Business Model Canvas
The Target Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
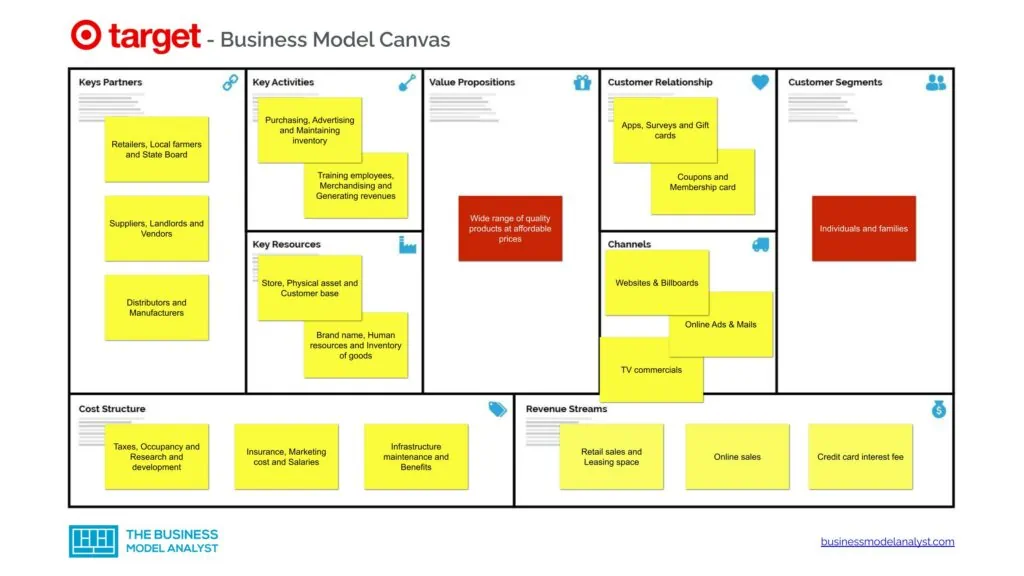
Target Customer Segments
Target customer segments comprise:
- Individuals and families interested in a wide range of products at affordable prices
Target Value Propositions
Target value propositions consist of the following:
- Quality products at affordable prices;
- Competitive and affordable prices;
- All essentials under a roof.
- Convenient locations both in the urban and suburban areas;
- Groceries are made available in stores;
- Clean and large stores to aid great and happy shopping;
- Upscale trending merchandise at reasonable prices;
- Wider aisles, drop ceilings, and more appealing ways of presenting merchandise.
Target Channels
Target channels comprise:
- Websites
- Billboards
- Online Ads
- Mails
- TV commercials
Target Customer Relationships
Target customer relationships consist of:
- Apps
- Surveys
- Gift cards
- Coupons
- Membership card
Target Revenue Streams
Target revenue streams comprise:
- Retail sales
- Leasing space
- Online sales
- Credit card interest fee
Target Key Resources
Target key resources consist of:
- Store
- Physical asset
- Customer base
- Brand name
- Human resources
- Inventory of goods
Target Key Activities
Target key activities comprise:
- Purchasing
- Advertising
- Maintaining inventory
- Training employees
- Merchandising
- Generating revenues
Target Key Partners
Target key partners consist of:
- Retailers
- Local farmers
- State Board
- Suppliers
- Landlords
- Vendors
- Distributors
- Manufacturers
Target Cost Structure
Target cost structure comprises:
- Taxes
- Occupancy
- Research and development
- Insurance
- Marketing cost
- Salaries
- Infrastructure maintenance
- Benefits
Target Competitors
- Walmart: Walmart is a large American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets, discount department stores, and grocery stores in the United States of America. Sam’s Club retail is owned and run by Walmart. It operates not only brick-and-mortar stores, but also an online marketplace. The company has a strong, significant presence in the United States market;
- Amazon: Amazon is an American multinational technology company focusing on e-commerce, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, digital streaming, and online advertising. It offers a wide range of services, such as an online marketplace for buying and selling. It is known for fast delivery and competitive prices, and is referred to as one of the most influential economic and cultural forces in the world;
- Costco: Costco Wholesale Corporation is an American multinational corporation that operates a chain of membership-only big-box retail stores. The company business centers are similar to common Costco warehouses, open to all Costco members. Costco focuses more on enterprises rather than small businesses. Their business centers do not have most customer items like clothing and jewelry. Most of the products found in their business centers are not always found in a common Costco store. Surprisingly, some centers have a food court or a gas station, or both. Most Costco business centers have a print and copy center that provides professional printing services, unlike common Costco stores;
- Best Buy: Best Buy is a multinational American electronics retailer. Originally, it was called Sound of Music. The company operates internationally, but some of its international stores are closed. It sells electronics and other related merchandise and is the 2nd largest musical instrument distributor in the United States;
- The Kroger Company: Also called Kroger, the Kroger Company is an American retail company that operates multi-department and supermarkets throughout the United States of America. Kroger operates grocery stores under its several banners and divisions, including store formats such as marketplace stores, multi-department stores, combo stores, and price-impact warehouse stores. It also has a line of pharmacies, manufacturing plants, supermarket fuel centers, The Little Clinic in-store medical clinics, and jewelry stores. Kroger Company is the United States widest supermarket operator by revenue.
Target SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of the Target Business Model.
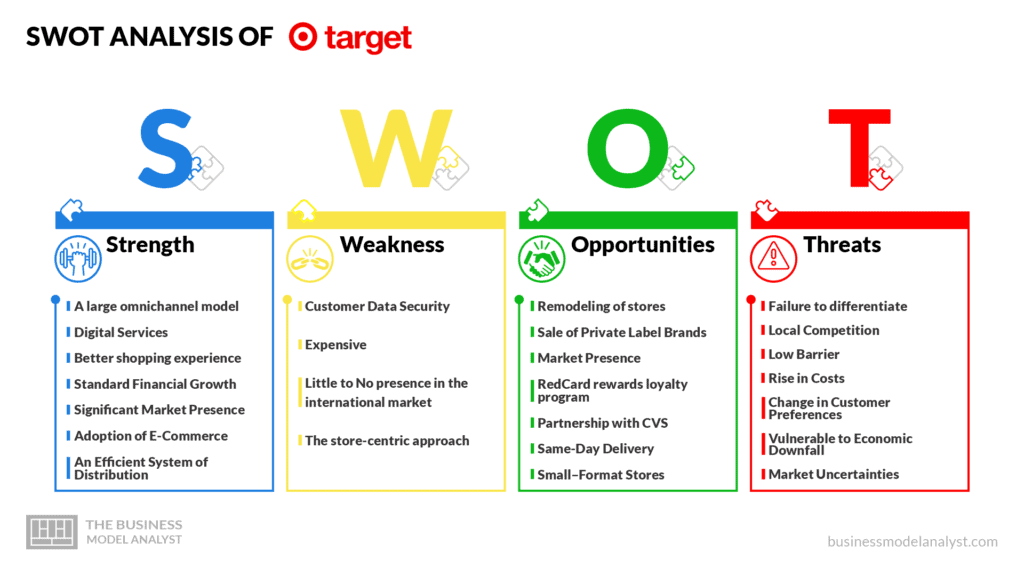
Target Strengths
- A large omnichannel model: Due to Target’s years of investing in its inventory and supply chain visibility in both online and in-store channels, it has delivered one of the best omnichannel models in its sector. The corporation has moved quickly from just in-store models to ship from-store, curbside pickup, and various sales methods;
- Digital Services (delivered as an app): The corporation created a magnificent Cartwheel for its digital customers. With the app’s help, Target online shoppers can check prices and the store inventory, order online, checkout, access offers or coupons, and so on;
- Better shopping experience: Target shoppers enjoy a better shopping experience through better shopping carts, a clean environment, an improved floor plan, and well-lit and marked aisles;
- Standard Financial Growth: The corporation has built a sustainable business model that will continue to catalyze high profit in the long term. The store is currently in its 11th consecutive quarter of positive sales growth. The earnings from online sales have also grown rapidly;
- Significant Market Presence: Target has a very significant and strong presence in the United States market. They have about 1900 stores in the U.S., with the highest number of stores in California, Texas, and Florida;
- Adoption of E-Commerce: Target leveraged e-commerce very effectively in 2020 to fulfill the needs of its customers. The effectiveness of this development resulted in a large increase in digital sales in 2020. Currently, Target is one of the top biggest three e-commerce companies, alongside Amazon and Walmart;
- An Efficient System of Distribution: Target has 40 distribution centers and still partners with other carriers to aid the shipment of general merchandise;
- Designer apparel: To add to the satisfaction of its customers, Target provides designer wears by collaborating with high-standard fashion designers. Almost 20% of their total revenue is from this sector;
- A large range of merchandise: Target is a one-stop shop for all items, from groceries, designer clothes, pharmacies, accessories, home decor, electronics, sporting goods, and so on. The store’s digital channels also offer a large range of merchandise alongside a complementary assortment;
- Position of the brand: Target makes provisions for trendy merchandise of high quality at discounted prices for their customers. Target’s customer base attracts medium to high-income group families.
Target Weaknesses
- Customer Data Security: Target faced a huge data breach in 2014. Close to 70 million customers’ card information was stolen. That incident dented Target’s reputation;
- Expensive: Following a study done by a business insider, it is said that Target charges 15% more on groceries compared to Walmart;
- Little to No presence in the international market: Target tried to expand its stores to Canada in 2011, but failed. 133 stores were opened in Canada, but it was a huge failure, so they had to close all their stores in Canada;
- The store-centric approach: Retailers would adopt e-commerce rather than a store-centric approach. Target has benefited from the rise in online shopping. But still, there’s a decrease in their sales of apparel. Low-margin products have a greater impact on profits.
Target Opportunities
- Remodeling of stores: This is a major growth opportunity for the Target corporation. Although it might look like a big investment, there is a high return on it;
- Sale of Private Label Brands: Label brands, especially private ones, help differentiate between retailers. Also, they have high margins;
- Market Presence: Increasing the number of stores to increase market presence is a good approach to growth;
- RedCard rewards loyalty program: Another great opportunity for Target is expanding its RedCard loyalty program. Provisions should be made on how to gain insights about the change in customers’ preferences;
- Partnership with CVS: CVS Health acquired Target’s pharmacy and clinic in December 2015. This implies that the pharmacy division of Target is now operated by CVS Health. Target customers now have access to better healthcare services in the stores;
- Same-Day Delivery: To make same-day delivery possible, Target acquired a grocery delivery service called Shipt;
- Small–Format Stores: Small-format stores have been opened in dense urban centers, college campuses, and the like. The stores have the potential that can drive Target corporation toward more growth.
Target Threats
- Failure to differentiate: There is a shift of many shoppers towards price-sensitive online shopping. This shift poses a threat to Target. Brand loyalty may be affected due to the failure to differentiate;
- Local Competition: Target corporation is in a low-margin but highly competitive industry. Major competitors like Kroger, Walmart, Costco, Home Depot, and the rest have many stores located close to the local population, thereby affecting their market share. Asides from the onsite competition, there is stiff competition in the e-commerce sector from Amazon. Target has to spend more to keep its customers by using different sales techniques;
- Low Barrier: Since Target is in the retail business, it is easily replicable. Any new corporation may decide to do the same, since there’s a low barrier to entering the business;
- Rise in Costs: The profit of Target in Q1 profit increased by only 64% due to the rising costs of doing business. The corporation has to spend more to ensure safety. The high cost of managing business causes a decline in profit;
- Change in Customer Preferences: Due to the growing trends of online shopping, customers may change their preferences;
- Vulnerable to Economic Downfall: Target’s products rely mainly on macroeconomic factors. Most of their stores are in the United States market. This means that when there is a hiccup in the United States economy, Target corporation will be affected negatively;
- Market Uncertainties: The bottom line of the retail market has been negatively impacted by market uncertainties both in the local and global markets. Fortunately, Target has not had any bad experiences with market uncertainties, but the company has been forced to change some of its plans.
-> Read More About Target’s SWOT Analysis.
Conclusion
The Target Corporation has several stores all over the United States of America, making it easy for people to access their daily needs without much stress. It provides quality products at affordable prices, which makes it different from other department store chains. Besides, the corporation’s commitment to innovation and advanced technology has helped it provide its shoppers with a satisfying shopping experience. However, it can perform better and make more profits if it explores the available opportunities and work to strengthen its brand promise against its threats.

