The Oracle business model is focused on selling its software, cloud services, and hardware products to businesses and organizations. The company operates under a mixed business model, combining elements of subscription-based and traditional sales-based business models. At the core of Oracle’s business model is its customer segmentation strategy. Oracle has identified and targeted specific market segments with unique needs and requirements. By segmenting the market, Oracle can tailor its products and services to meet the particular needs of each customer segment, providing them with personalized solutions.
In addition to customer segmentation, Oracle has a clear value proposition. The company offers a wide range of products and services designed to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes. Oracle’s value proposition centers on providing its customers with high-quality and secure technology solutions to help them achieve their business objectives.
Contents
A brief history of Oracle
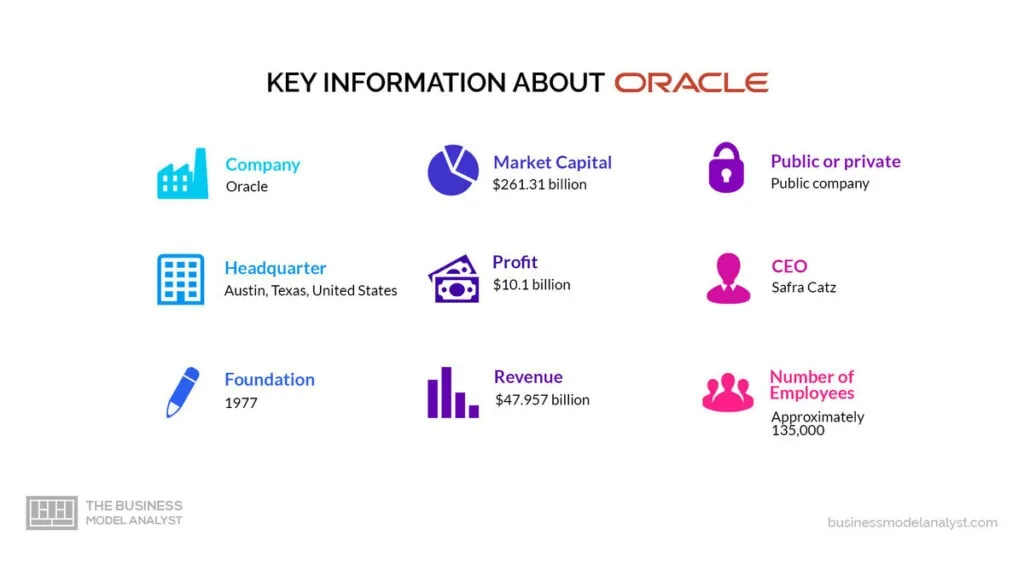
Oracle was founded in 1977 by Larry Ellison, Bob Miner, and Ed Oates. Ellison. In the company’s early days, Oracle focused on developing and selling relational database management systems (RDBMS) for midrange computers. The company’s first product, Oracle Version 2, was released in 1979. Oracle Version 3, released in 1983, was the first commercially available RDBMS to support SQL, the standard language for accessing and manipulating data in a relational database.
Throughout the 1980s, Oracle continued to grow and expand its product offerings. The company introduced new database products, such as Oracle Rdb for Digital Equipment Corporation’s VMS operating system and Oracle SQL/DS for IBM mainframe computers. Oracle also began to develop application software, such as Oracle Financials and Oracle Manufacturing.
In the 1990s, Oracle continued expanding its product offerings and global reach. The company introduced Oracle7, the first database to support distributed computing, in 1992. Oracle also launched Oracle Applications, a suite of business software products, in 1990. The company expanded its international presence, opening offices in Europe, Asia, and Latin America. In recent years, Oracle has shifted its focus to cloud computing. The company offers a range of cloud services, including software-as-a-service (SaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) offerings.
Who Owns Oracle
According to the company’s recent proxy statement, Larry Ellison, one of the co-founders of Oracle, owns approximately 1.1 billion Oracle shares, representing about 27% of the company’s outstanding shares. This makes him the largest individual shareholder of Oracle. However, institutional investors like The Vanguard Group, BlackRock, and State Street still own a significant portion of the company’s shares, so they also have a say in the company’s decisions and direction.
Oracle Mission Statement

Oracle’s mission statement is “to help people see data in new ways, discover insights, and unlock endless possibilities.”
How Oracle works
Oracle works by providing its customers with customized technology solutions that help them address their unique challenges and improve their business performance. Oracle does the following to offer solutions to its customers:
Collaborates with Customers
Oracle collaborates with its customers to understand their unique business needs and challenges. By doing this, Oracle can develop tailored technology solutions that address these challenges and help its customers improve their business performance. This collaboration may involve consultations, data analysis, and testing.
Delivers customized Technology solutions
Oracle provides customized technology solutions to its customers based on their specific business requirements. These solutions can be either software, hardware, or a combination. For instance, Oracle’s flagship database software is a powerful tool that helps businesses store and manage their data.
Offers a Variety of Products
Oracle offers a variety of products that cater to different business needs. These products are designed to help businesses improve their productivity, efficiency, and overall performance. Some of Oracle’s products include its database software, ERP software, CRM software, cloud-based services, and more.
How Oracle makes money
Oracle generates revenue from the following:
Software licenses
Oracle sells software licenses for its various products, such as its database, enterprise resource planning (ERP), and customer relationship management (CRM) software. Customers can purchase perpetual licenses, which allow them to use the software indefinitely, or term licenses, which provide access to the software for a specific period.
Cloud services Fees
Oracle offers a range of cloud-based services, including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). These services provide customers with access to computing resources, software applications, and other tools which they can use to run their businesses more efficiently. Customers pay for these services on a subscription basis, which provides recurring revenue for Oracle.
Maintenance and support services fees
Oracle provides maintenance and support services to its customers, including software updates, technical support, and training. Customers typically pay an annual fee for these services, which can be a significant source of recurring revenue for Oracle.
Hardware sales
In addition to its software offerings, Oracle also sells hardware products, such as servers, storage systems, and networking equipment. These products support the company’s software offerings, and customers can purchase them either as standalone products or as part of a larger solution.
Consulting services fees
Oracle offers consulting services to help customers implement its software and hardware products effectively. These services can include everything from design and planning to implementation and training. Customers pay for these services on a project basis, which can be a lucrative source of revenue for Oracle.
Oracle Business Model Canvas
Let’s take a look at the Oracle Business Model Canvas below:
Oracle Customer Segments
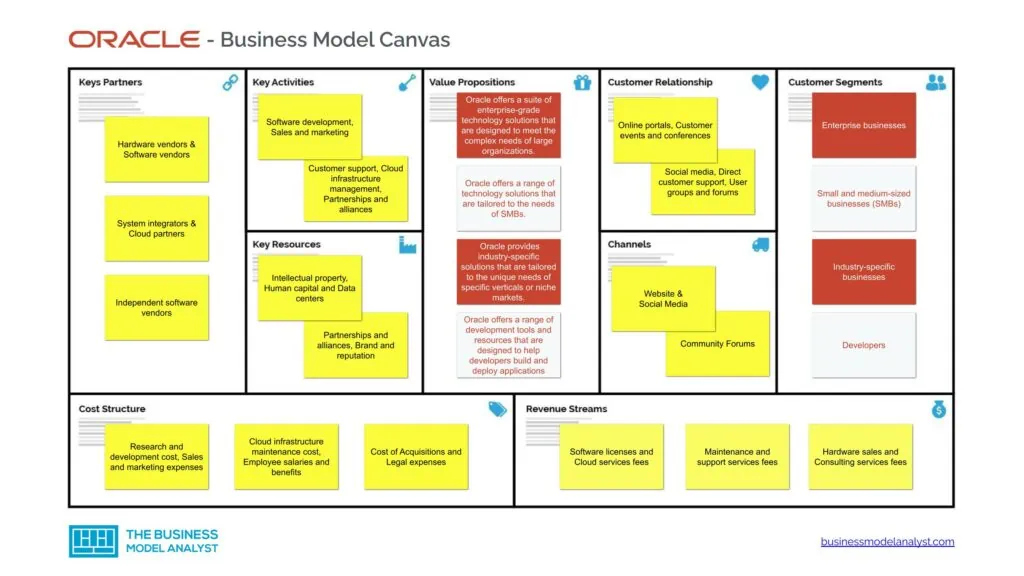
Oracle’s customer segments consist of:
- Enterprise businesses: Enterprise businesses are large organizations with complex IT needs. These businesses typically require robust technology solutions to manage their operations, and often have multiple locations and business units. Examples of enterprise businesses include multinational corporations, financial institutions, and government agencies;
- Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs): Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are companies with fewer than 500 employees. These businesses typically have more limited IT resources and require more streamlined technology solutions to manage their operations. Examples of SMBs include local retailers, healthcare providers, and professional services firms;
- Industry-specific businesses: Industry-specific businesses are companies that operate within a particular vertical or niche market. These businesses have unique technology needs that are tailored to their specific industry, such as healthcare, retail, or hospitality;
- Developers: Developers are individuals or teams responsible for building software applications or customizing existing software to meet specific business needs. Oracle provides a range of development tools and resources to help developers build and deploy applications on its platforms, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and Oracle Database.
Oracle Value Propositions
Oracle’s value propositions consist of:
- For enterprise businesses: Oracle offers a suite of enterprise-grade technology solutions that are designed to meet the complex needs of large organizations. These solutions include enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and supply chain management software. Oracle’s value proposition to enterprise businesses provides scalability, reliability, security, and performance, as well as a deep understanding of the needs of large organizations;
- For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs): Oracle offers a range of technology solutions that are tailored to the needs of SMBs, including cloud-based software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications, hardware, and infrastructure solutions. Oracle’s value proposition to SMBs includes affordability, ease of use, and scalability, as well as the ability to integrate with existing IT infrastructure;
- For industry-specific businesses: Oracle provides industry-specific solutions that are tailored to the unique needs of specific verticals or niche markets. For example, Oracle offers healthcare-specific solutions, such as electronic medical records (EMR) software, that are designed to meet the needs of healthcare providers. Oracle’s value proposition to industry-specific businesses includes deep domain expertise, a tailored approach, and the ability to address unique business challenges;
- For Developers: Oracle offers a range of development tools and resources that are designed to help developers build and deploy applications on its platforms, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and Oracle Database. Oracle’s value proposition to developers includes easy-to-use development tools, extensive documentation and resources, and a broad ecosystem of partners and developers who can provide support and guidance.
Oracle Channels
Oracle’s channels consist of:
- Website
- Social Media
- Community Forums
Oracle Customer Relationships
Oracle’s customer relationships consist of:
- Online portals
- Customer events and conferences
- Social media
- Direct customer support
- User groups and forums
Oracle Revenue Streams
Oracle’s revenue streams consist of:
- Software licenses
- Cloud services fees
- Maintenance and support services fees
- Hardware sales
- Consulting services fees
Oracle Key Resources
Oracle’s key resources consist of:
- Intellectual property
- Human capital
- Data centers
- Partnerships and alliances
- Brand and reputation
Oracle Key Activities
Oracle’s key activities consist of:
- Software development
- Sales and marketing
- Customer support
- Cloud infrastructure management
- Partnerships and alliances
Oracle Key Partners
Oracle’s key partners consist of:
- Hardware vendors
- Software vendors
- System integrators
- Cloud partners
- Independent software vendors
Oracle Cost Structure
Oracle’s cost structure consists of:
- Research and development cost
- Sales and marketing expenses
- Cloud infrastructure maintenance cost
- Employee salaries and benefits
- Cost of Acquisitions
- Legal expenses
Oracle Competitors
- Microsoft: Microsoft is a multinational technology company that develops and licenses a wide range of software products, including operating systems, productivity applications, and cloud services. The company was founded in 1975 and is headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Microsoft competes with Oracle in several areas, including database management systems, cloud computing, and enterprise software;
- IBM: IBM is a global technology company that provides hardware, software, and consulting services to businesses and governments. The company was founded in 1911 and is headquartered in Armonk, New York. IBM competes with Oracle in several areas, including database management systems, cloud computing, and enterprise software;
- SAP: SAP is a multinational software company that develops enterprise software applications for managing business operations and customer relations. The company was founded in 1972 and is headquartered in Walldorf, Germany. SAP competes with Oracle in several areas, including enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and supply chain management;
- Salesforce: Salesforce is a cloud-based software company that provides customer relationship management (CRM) and other enterprise software solutions. The company was founded in 1999 and is headquartered in San Francisco, California. Salesforce competes with Oracle in the CRM market;
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is a subsidiary of Amazon that provides cloud computing services to businesses and individuals. The company was founded in 2006 and is headquartered in Seattle, Washington. AWS competes with Oracle in the cloud computing market.
Oracle SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT analysis of Oracle:
Oracle Strengths
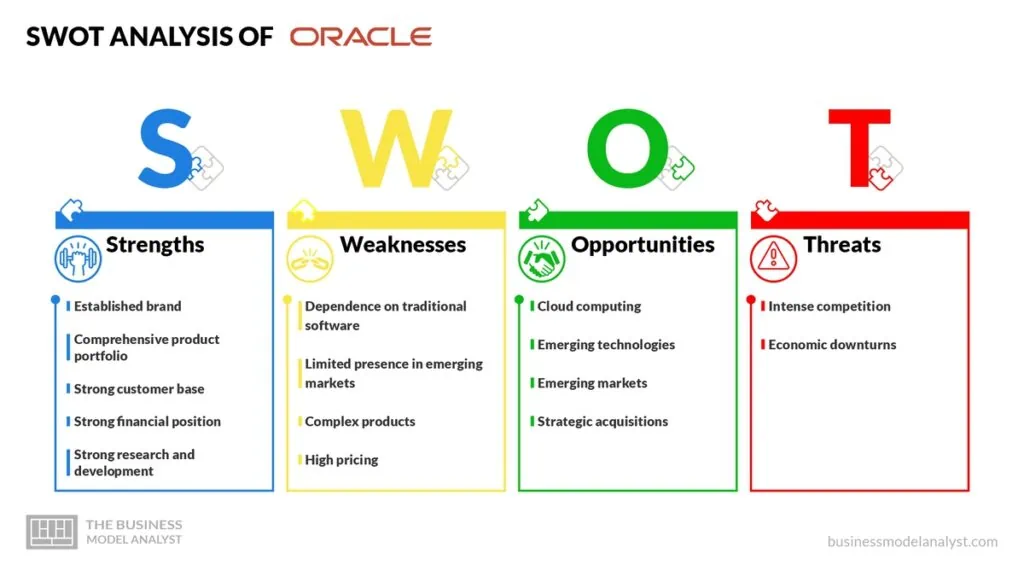
- Established brand: Oracle is a well-known and established brand in the technology industry, with a strong reputation for quality and reliability. Its reputation is an important strength for Oracle, as it helps to establish trust with customers and creates a positive image for the company. A strong brand can also help to attract new customers and retain existing ones;
- Comprehensive product portfolio: Oracle offers a wide range of products and services, including enterprise software, cloud computing, and hardware. The comprehensive portfolio helps the company meet the diverse needs of customers and creates cross-selling opportunities. Additionally, an extensive product portfolio can help to reduce the risk of revenue loss due to changes in market demand for specific products;
- Strong customer base: Oracle has a large and diverse customer base, including large enterprises and government organizations. A solid customer base is a necessary strength, as it helps the company generate significant revenue and reduces its dependence on any one industry or customer group;
- Strong financial position: Oracle has a robust financial situation, with a high level of cash reserves and strong revenue growth in recent years. Its strong financial position provides the company with the resources needed to invest in research and development, expand its product portfolio, and pursue strategic acquisitions;
- Strong research and development: Oracle invests heavily in research and development, which helps it develop new products and stay ahead of competitors. This is an important strength, as it allows the company to innovate and create products that meet evolving customer needs.
Oracle Weaknesses
- Dependence on traditional software: Oracle’s traditional software products, such as its database software, continue to generate the majority of its revenue. Such dependence leaves the company vulnerable to market shifts and disruptive technologies that may reduce demand for these products;
- Limited presence in emerging markets: Oracle has a limited presence in emerging markets, which limits its growth opportunities in these regions. This is a weakness, as emerging markets represent significant growth opportunities for technology companies;
- Complex products: Some of Oracle’s products require significant expertise to implement and use. This complexity may make them less attractive to some customers, who may prefer more straightforward and user-friendly products;
- High pricing: Oracle’s products and services are often priced at a premium compared to competitors. High pricing may make them less attractive to price-sensitive customers, who may opt for cheaper alternatives.
Oracle Opportunities
- Cloud computing: Oracle has the opportunity to expand its cloud computing offerings and capture a larger share of the growing cloud market. This is a significant opportunity as the demand for cloud services continues to grow;
- Emerging technologies: Oracle has the opportunity to invest in and develop emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things. This opportunity could help the company stay ahead of competitors and meet evolving customer needs;
- Emerging markets: Oracle has the opportunity to expand its presence in emerging markets, which represent significant growth opportunities. Leveraging this opportunity could help the company reduce its dependence on mature markets and create new revenue streams;
- Strategic acquisitions: Oracle has the opportunity to acquire strategic companies and technologies that could complement its existing product portfolio and expand its capabilities. Strategic acquisitions could help the company enter new markets, create new products, and increase its revenue.
Oracle Threats
- Intense competition: Oracle faces intense competition from other technology companies, including Amazon, Microsoft, and Google. Such competition could limit its market share and revenue growth, as customers have more options;
- Economic downturns: Economic downturns could reduce demand for Oracle’s products and services, particularly in industries such as finance and government, which are major customers.
Conclusion
Oracle’s business model is a dynamic and effective approach to selling software, cloud services, and hardware products to businesses and organizations. By combining elements of both subscription-based and traditional sales-based business models, Oracle has created a unique approach to delivering value to its customers.
Through customer segmentation and a clear value proposition, Oracle has maintained its position as a major player in the technology industry. Its diversified channels, revenue streams, key resources, and strategic partnerships have also contributed to its success.
Despite the intense competition in the industry, Oracle’s business model is well-equipped to continue providing innovative solutions to its customers and maintain its leadership in the industry for years to come.

