The IBM business model is based on providing various technological solutions and services to businesses. They make money by charging their clients for several products and services, including cloud storage, computers, upgrades, accessories, systems, and servers.
However, these are not the only services and products offered by this multinational tech corporation. IBM also provides software and consulting, which according to their official website, contributes to over 70% of IBM’s revenue. Other products and services provided by IBM include outsourcing services, data analytics, and artificial intelligence, which play a massive role in the company’s business model.
More recently, IBM has invested in various research and development projects, including big data, quantum computing, and blockchain technology, which may offer new revenue streams in the future.
In this blog post, we’ll go over everything you need to know about IBM’s business model and how the company makes money. We’ll also take a closer look at IBM’s SWOT analysis.
Contents
A brief history of IBM
International Business Machines, simply known as IBM, is one of the oldest multinational tech corporations in the world, as it was founded back in 1911. IBM has its headquarters in Armonk, New York.
In 1911, the Tabulating Machine Company merged with three other firms to form the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR). CTR continued to develop tabulating machines, which were used by businesses and governments to process large amounts of data quickly and accurately.
In 1924, CTR went with a more expansive name, International Business Machines (IBM), and began to expand globally. In the 80s, IBM faced increasing competition from companies such as Microsoft and Apple, which were developing personal computers. IBM responded by introducing its own personal computer, the IBM PC, in 1981, but it wasn’t as successful as it had hoped.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, IBM underwent a major transformation, becoming a services and consulting company that focused on providing business solutions to customers. This shift in focus allowed IBM to become more profitable and adaptable to the rapidly changing technology landscape.
Today, IBM is one of the biggest tech companies in the world, with operations and clients in over 170 countries. According to Fortune, this multinational corp also employs more than 345,000 people worldwide.
According to the official IBM website, this company has $57.4 billion in revenue and $12.8 billion in cash from operations. Yahoo Finance estimates IBM’s market cap is roughly $122.06 billion, with a share traded at $135.02 at the time of writing.
Some of IBM’s recent highlights include teaming up with Microsoft and Google on a special project designed to help solve hacking and other cybersecurity problems. In 2021, this corporation unveiled the world’s smallest and most potent microchip (the size of a fingernail)
Who Owns IBM
Many people and institutions own IBM, as it’s a publicly traded company. According to CNN Business News, institutional investors such as the Vanguard Group, SSgA Funds Management Inc, and BlackRock Fund Advisors make up about 59.73% ownership of IBM. This signifies the highest interest of any other company in the information technology space.
However, the company also has individual shareholders, none more prominent than personnel serving on IBM’s board and management. They include Krishna Arvind, Kavanaugh James, Browdy Michelle, and Rosamilia Thomas. However, individual owners only make up about 0.41% of the total ownership of IBM.
IBM Mission Statement
The IBM mission statement is not officially published on the company’s website. However, this multinational tech company does the following:
“We bring together all the necessary technology and services, regardless of where those solutions come from, to help clients solve the most pressing business problems.”
How IBM works
IBM is one of the leading technology and services companies in the world. They have a large and diverse portfolio of products and services. These services typically fall under cloud computing, AI, data analytics, IT infrastructure, mobile, and cybersecurity. IBM’s core involves developing these products and services for enterprise customers.
IBM designs and manufactures a variety of computer systems on the hardware front. It includes mainframes, servers, and storage devices. Large enterprises use these systems to run critical business functions and applications.
On the software front, IBM develops and sells a range of products, including operating systems, middleware, and enterprise applications. This multinational giant also sells software products designed to help businesses improve productivity, increase efficiency, and reduce costs.
It doesn’t stop there — IBM also offers a variety of consulting and support services to help businesses implement and optimize technology solutions. These services include strategy consulting, digital transformation, technology implementation, and ongoing support and maintenance.
How IBM makes money
To generate revenue, IBM relies on a mix of heavy research and development with a focus on product sales and recurring revenue from services, such as cloud computing and software subscriptions.
Here’s a brief overview of how IBM makes money:
Cloud and Other Software / Cognitive Solutions
IBM offers its premier cloud services under the umbrella term IBM cloud. This service scales the development of small organizations as well as large ones. As you might have learned, cloud-based business models can be classified as IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS, all of which are monetized through subscription models.
IBM cloud services enable customers to access computing resources, software applications, and other services on a pay-as-you-go basis, without having to invest in expensive IT infrastructure. IBM also offers hybrid cloud solutions that combine public and private cloud services, allowing customers to leverage the benefits of both.
IBM generates revenue from the cloud and other software/cognitive solutions through a variety of business models. They include subscription-based pricing, usage-based pricing, and volume-based licensing. The company also generates revenue from professional services, such as consulting and implementation, which help customers integrate and optimize their IBM solutions.
Professional Business Services (Global Business and Global Tech)
IBM is a global brand operating in more than 175 countries. This allows it to access various markets, which are typically diverse, presenting new opportunities to the multinational tech giant. IBM offers professional business services, including outsourcing services.
These services are designed to help clients reduce their costs while optimizing operations and improving efficiency. For instance, IBM’s outsourcing services include business process outsourcing (BPO), information technology outsourcing (ITO), and knowledge process outsourcing (KPO), among others.
IBM also offers various professional business services, including management consulting, digital strategy consulting, and technology consulting. These services are designed to help clients address their most pressing business challenges and opportunities and leverage the latest digital technologies to drive growth and innovation.
Technology Services and IT Consulting
IBM’s consultancy services seek to help businesses transform and implement new technology on a global scale. However, the company’s consultancy services also extend to other areas, including digital transformation, technology strategy, business process improvement, risk management, and supply chain management, among others.
A significant amount of IBM’s revenue comes from consulting services. According to the current CEO at the time of writing, Arvind Krishna, about 70% of all of IBM’s revenue comes from software and consulting.
IBM’s consultancy services also generate revenue through ongoing support and maintenance, such as software upgrades and training. This helps clients maintain and optimize the solutions implemented by IBM’s consultants.
Global Financing (Financing Services)
Although it accounts for about 2% of all IBM’s revenue, financing is still integral to the company’s business model. Through its financing division called IBM Global Financing, the company provides financing and leasing solutions to its customers worldwide.
These financing options include loans, leases, and installment payment plans. Such options allow customers to purchase IBM’s products and services without having to pay the full amount upfront.
IBM Business Model Canvas
The IBM Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
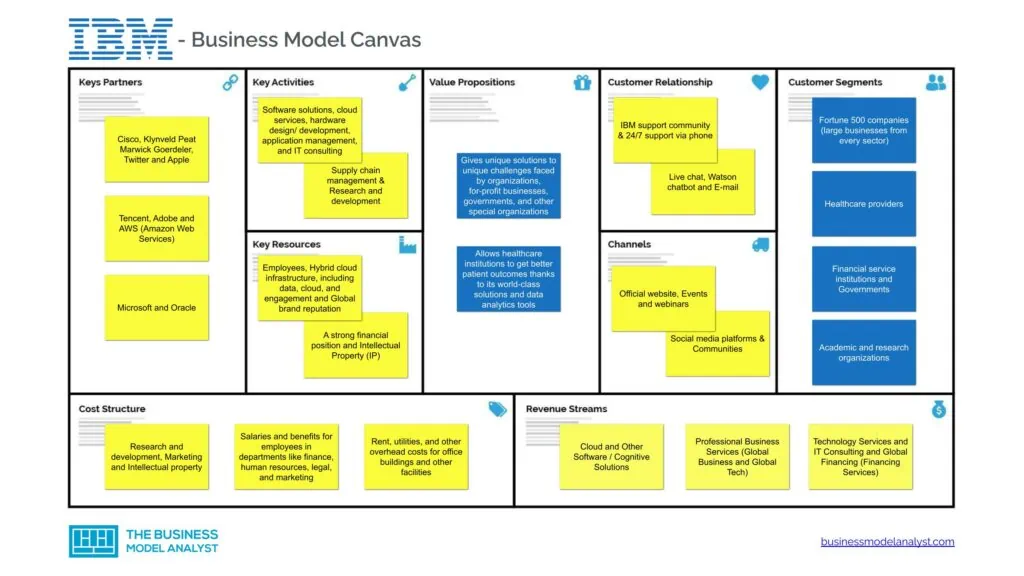
IBM Customer Segments
IBM customer segments consist of:
- Fortune 500 companies (large businesses from every sector): IBM offers its services to some of the largest and most influential companies in the world. This includes large businesses from every sector, including the likes of L’Oréal, Walmart, and Nintendo;
- Healthcare providers: Professionals and institutions in this industry make up one of IBM’s major customer segments. They offer numerous solutions designed specifically for this industry;
- Financial service institutions: IBM offers a suite of solutions that help financial service institutions automate processes, optimize performance, and gain actionable insights from data;
- Governments: Governments around the world rely on IBM’s expertise and innovative solutions to help them tackle complex challenges and deliver better outcomes for their citizens;
- Academic and research organizations: IBM offers a wide range of cutting-edge solutions and services that help academic, and research organizations conduct high-quality research, improve operational efficiency, and advance their understanding of the world.
IBM Value Propositions
IBM value propositions consist of:
- IBM gives unique solutions to unique challenges faced by organizations, for-profit businesses, governments, and other special organizations: Some organizations face unique challenges which require unique solutions. For instance, the government experiences unique challenges in its quest to deliver public services and secure sensitive data. IBM has a ton of experience providing solutions in line with such work;
- IBM allows healthcare institutions to get better patient outcomes thanks to its world-class solutions and data analytics tools: IBM understands that healthcare providers face unique challenges, such as managing and securing sensitive patient data, improving patient outcomes, and reducing costs. To help address these challenges, IBM offers innovative solutions like data analytics, secure data sharing, and clinical decision support.
IBM Channels
IBM channels consist of:
- Official website
- Events and webinars
- Social media platforms (i.e., Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook)
- Communities
IBM Customer Relationships
IBM customer relationships consist of:
- IBM support community
- 24/7 support via phone
- Live chat
- Watson chatbot
IBM Revenue Streams
IBM revenue streams consist of:
- Cloud and Other Software / Cognitive Solutions
- Professional Business Services (Global Business and Global Tech)
- Technology Services and IT Consulting
- Global Financing (Financing Services)
IBM Key Resources
IBM key resources consist of:
- Employees;
- Hybrid cloud infrastructure, including data, cloud, and engagement;
- Global brand reputation;
- A strong financial position — Access to a lot of capital, which increases the company’s spending power;
- Intellectual Property (IP) — IBM has a significant portfolio of patents and trademarks, which it uses to protect its technology and intellectual property rights.
IBM Key Activities
IBM key activities consist of:
- Core business activities include software solutions, cloud services, hardware design/ development, application management, and IT consulting;
- Supply chain management. This includes supply, manufacturing, logistics operations, and outsourcing services;
- Research and development.
IBM Key Partners
IBM key partners consist of:
- Cisco
- Klynveld Peat Marwick Goerdeler (KPMG)
- Apple
- Tencent
- Adobe
- AWS (Amazon Web Services)
- Microsoft
- Oracle
IBM Cost Structure
IBM cost structure consists of:
- Research and development;
- Marketing;
- Intellectual property;
- Salaries and benefits for employees in departments like finance, human resources, legal, and marketing;
- Rent, utilities, and other overhead costs for office buildings and other facilities;
- Travel expenses for sales teams and executives.
IBM Competitors
- Oracle: Oracle is another tech giant, with a history of developing powerful software solutions that help businesses manage their data and applications. Oracle has established itself as a trusted partner for businesses of all sizes and across a range of industries with its top-of-the-line hardware and cloud services;
- SAP: SAP also offers powerful software solutions targeted at helping businesses achieve their goals. Much like IBM, this tech giant also offers a compelling value proposition for businesses looking to improve their operations, gain insights from their data, and stay ahead of the competition;
- Microsoft: Microsoft has grown to become a household name in the tech space. Over the past decades, the company has significantly stepped up its cloud game, making them a formidable competitor in the tech space;
- AWS: AWS, a division of Amazon, has emerged as a major competitor of IBM in the technology space. They offer a huge portfolio of cloud computing solutions and services to businesses worldwide. AWS has earned a reputation as a leader in cloud computing, providing customers with secure, scalable, and flexible cloud solutions that allow them to achieve their business objectives with ease;
- Accenture: Much like IBM, Accenture is a powerhouse in the professional services industry, providing consulting, technology, and outsourcing services to clients around the globe.
IBM SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT Analysis of IBM:
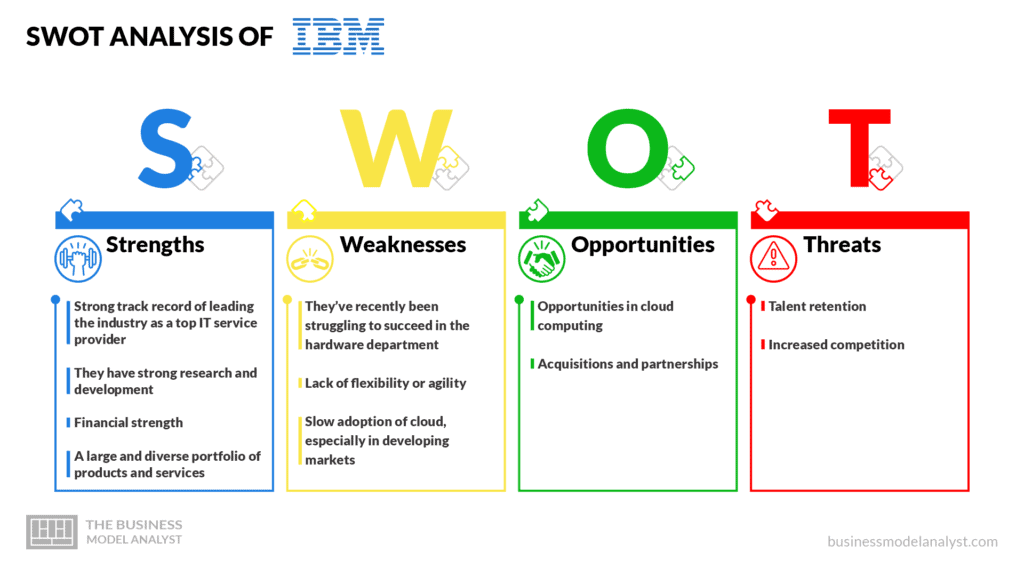
IBM Strengths
- Strong track record of leading the industry as a top IT service provider: IBM is one of the most well-known and respected technology companies in the world. It has been in business for more than a century. Not only that, but IBM has built a reputation for entering into new markets and succeeding while at it;
- They have strong research and development: IBM has a successful track record of innovating and developing new products, including artificial intelligence, blockchain, and quantum computing. This has allowed the company to stay ahead of its competitors and be a leader in innovation;
- Financial strength: IBM has a strong and free cash flow. This allows the company to gain access to resources to expand into new projects;
- A large and diverse portfolio of products and services: IBM has a wide range of products and services, from hardware to software and cloud services. This allows the company to generate revenue from multiple sources, reducing the risk of depending on a single product or market.
IBM Weaknesses
- They’ve recently been struggling to succeed in the hardware department: IBM’s hardware department has been shaky in the past few years, with revenues and margins decreasing and no positive outlook for the future;
- Lack of flexibility or agility: IBM’s large size and bureaucratic structure make it slow to adapt to changes in the market. As a result, the company is losing its market share to more nimble competitors who offer flexible services;
- Slow adoption of cloud, especially in developing markets: IBM’s slow adoption of cloud computing technology has put it behind its competitors, such as Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure.
IBM Opportunities
- Opportunities in cloud computing: Although some markets have been slow to adopt this technology, it’s most certainly inevitable that they will in the future. The cloud computing market is projected to grow significantly over the following decades;
- Acquisitions and partnerships: IBM can strengthen its position through strategic acquisitions and partnerships with other companies. Given its brand reputation and its strong financial position, IBM has the unique opportunity to partner with other companies to strengthen its position. More recently, IBM acquired Red Hat, a move that has been met with a ton of success.
IBM Threats
- Talent retention: IBM has built a reputation for having a world-class workplace with a strong company culture. Its success is mainly dependent on its employees and retaining top talent. However, this has become increasingly difficult as competitors have emerged offering better salaries and perks;
- Increased competition: IBM faces stiff competition from rivals such as Amazon, Microsoft, and Google. However, those are not the only companies, as there are a ton of corporations that are also investing heavily in artificial intelligence and cloud computing.
Conclusion
IBM’s business model primarily involves developing and selling software solutions to client companies in a bid to help them improve their operations and efficiencies while reducing their costs. IBM makes money by offering global financing services, consulting services, and software/cognitive solutions.
This company’s strong financial position, brand reputation, and track record of excellence in diverse markets have helped it reach the very top of the IT industry. However, this position has recently been challenged by many companies that poured billions of money into the research and development of cloud-related services.
Nonetheless, IBM’s profitable business model, fused with emerging opportunities, ensures that IBM will remain one of the best multinational tech companies in the world.

