Opendoor is a user-friendly digital real estate marketplace that buys, sells, and exchanges houses. The Opendoor business model is focused on profitably selling the residences it acquires.
The firm earns money through a sales commission — paid by the home seller — and interest on mortgage loans.
With the support of substantial sums of startup funding, Opendoor combines a proprietary algorithm and public information to assess properties and make swift cash offers. To speed up and enhance its operations, the firm employs artificial intelligence and other technology aids, such as an app.
This way, clients who are looking to sell their homes don’t need to undergo the traditional stress and anxiety that come with it.
Contents
A brief history of Opendoor
In March 2014, Opendoor was launched by entrepreneur Keith Rabois; Eric Wu, the previous founder of Movity; and JD Ross, a general partner at Atomic. The idea for this company came about in 2004 when Keith Rabios sorted out a solution to make real estate less complicated and less time-consuming in converting the investment to cash. Then, 10 years later, he partnered with Eric Wu and began to actualize his vision.
Their aim was to improve the buying and selling experiences of customers to reduce the stress that comes with such ventures. With this motive, they launched a trade-in service in March 2016 that allowed customers to sell their homes and buy a new one in just one transaction.
In 2018, they started partnering with home builders to make buying a new home easier. This way, homeowners avoid a second mortgage and a second move, whether they purchase a ready-to-move-in spec house or one that has yet to be completed. This partnership garnered over $1.5 billion in annualized revenue. By this point, they had received $400 million in funding from the SoftBank Group Vision Fund and had expanded to 12 new markets in the U.S.
2019 came around, and they launched “Buy with Opendoor,” a feature that allows customers to buy their dream house on their own terms, all through their app.
They also launched “Opendoor home loans”, which was designed to enable buyers to secure a mortgage. This way, financing becomes as easy and stress-free as purchasing a home.
They acquired a longtime partnership with OS National (OSN), incorporating title, escrow, and closing services into its business offerings.
In 2020, they were forced to lay off 600 employees because of the pandemic. They also announced that they would pause home buying during the lockdown for the safety of their customers. But they were able to bounce back quickly in May 2020, when they introduced a contact-free feature to allow buying and selling to be done digitally.
It was also in 2020 that Social Capital Hedosophia Holdings Corp II, integrated with Opendoor, and began trading on the NASDAQ under its new name, Opendoor. This valued Opendoor at $4.8 billion in total and sparked a boom in their industry.
Who Owns Opendoor
Eric Wu is the co-founder and CEO of Opendoor. The company has about 577 institutional owners and shareholders, which hold a total of 443,106,427 shares.
Their biggest shareholders include Vanguard Group Inc., TRBCX – T. Rowe Price Blue Chip Growth Fund, Inc., D1 Capital Partners L.P., Sb Investment Advisers (UK) Ltd, Altimeter Capital Management, Price T. Rowe Associates Inc./md/, LP, GGV Capital LLC, Ieq Capital, Llc. BlackRock Inc., and Sylebra Capital Ltd.
Opendoor’s Mission Statement
“To empower everyone with the freedom to move”.
How Opendoor makes money
Opendoor is a good example of the term “spending money to make money”. Opendoor buys and sells properties for a profit, charges a seller fee, and offers related services to make home selling and purchasing easier — home loan program, title, insurance, and escrow. All of these generate revenue sources for Opendoor.
Although they bring in some profit from the resale of properties, their main source of revenue comes from their additional services, such as interest from home loans and title insurance. Their goal has been to modify and reinvent the traditional real estate model with the aid of their tech features and a large reserve of investor funds.
Service fees
Opendoor charges a 5% commission fee for every home they buy. This service fee is based on expenses, risks, and carrying costs, with a little bit of profit. This service charge is low compared to other companies, and clearly draws in a lot of customers.
Add-on services (mortgage, title, etc.)
Opendoor’s most recent revenue plan is to bring the title, mortgage, and escrow services in-house. Their title services have produced excellent outcomes. Title insurance is simple to incorporate into a transaction because it is simply brought in by the seller — Opendoor. They also generate money by charging interest on the loans. Through its “Opendoor Home Loans” business segment, home buyers can borrow money from Opendoor. This new strategy has caused steady growth for them and has significantly increased their bottom line.
Home sales
As an iBuyer, this is their most traditional source of income. The company makes money from reselling bought houses for a profit. And with the assistance of their algorithm, they are able to make accurate deductions for sales and purchase prices.
Opendoor does not lurch any house; each house must meet its criteria before being considered for evaluation. To qualify, single-family homes must be built after 1960 with an average value of $125,000 – $500,000. Once a property meets this standard, Opendoor takes up the responsibility of making it fit for sale.
Opendoor’s Business Model Canvas
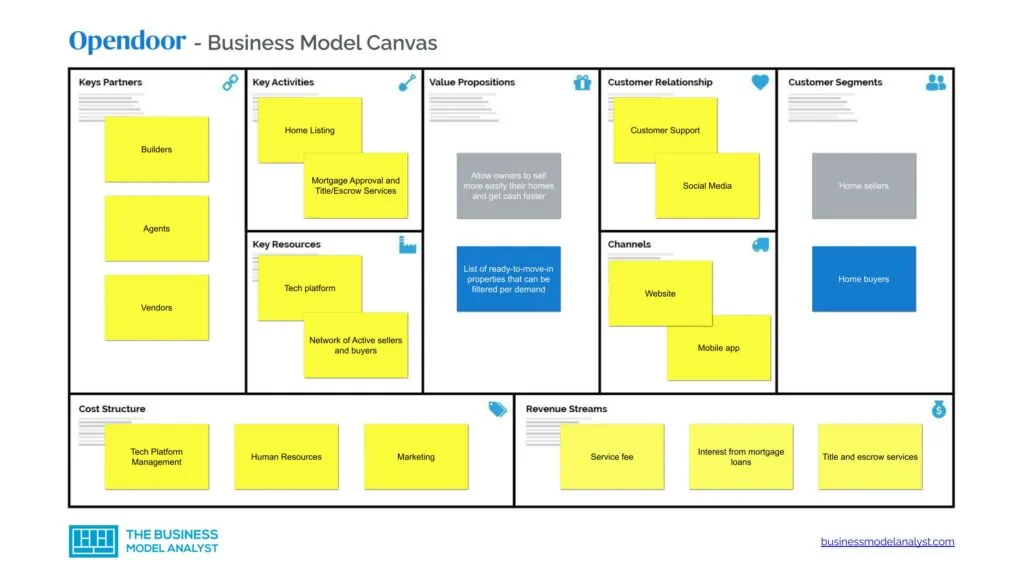
The Opendoor Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
Opendoor’s Customer Segments
Opendoor’s customer segments consist of:
- Home sellers: This category of customers looks to Opendoor to take off the burden of selling their homes;
- Home buyers: These customers aim to purchase new homes from Opendoor, which makes the process easier.
Opendoor’s Value Propositions
Opendoor’s value propositions consist of:
Sellers: The company makes the whole process of selling homes easier with an advantage of getting cash fast. With their valuation process, customers get good prices for property. It creates competitive offers for homes on sale. And receiving a payment quote takes only a few hours.
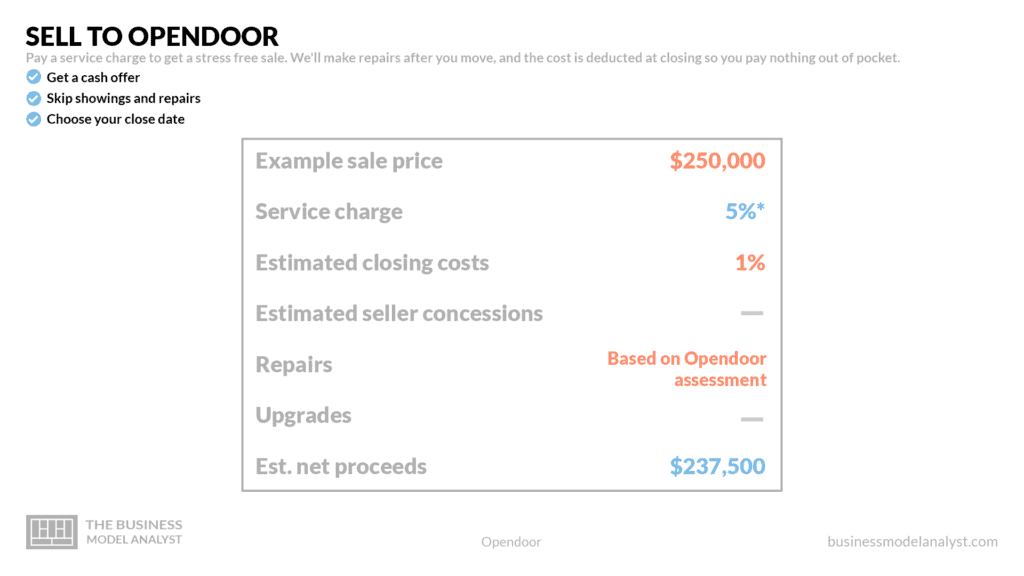
- Buyers: For buyers, they provide listings of ready-to-move-in properties that can be filtered per demand. They also reduce risk by keeping high safety and quality standards. Opendoor offers a guarantee of 30 days, which provides them with the option to sell the house back to the company at its original price.

Opendoor’s Channels
Opendoor’s channels consist of:
- Website
- Mobile app
- Blog
Opendoor’s Customer Relationships
Opendoor’s customer relationships consist of:
- Customer support
- Social media
- Website
- Blog
Opendoor’s Revenue Streams
Opendoor’s revenue streams consist of:
- Service fee
- Interest from mortgage loans
- Title and escrow services
Opendoor’s Key Resources
Opendoor’s key resources consist of:
- Tech platform (Website and apps)
- Network of Active sellers and buyers
Opendoor’s Key Activities
Opendoor’s key activities consist of:
- Home Listing
- Mortgage Approval
- Title and escrow
Opendoor’s Key Partners
Opendoor’s key partners consist of:
- Builders
- Agents
- Vendors
- Investors
Opendoor’s Cost Structure
Opendoor’s cost structure consists of:
- Tech Platform Management
- Marketing
- Human resources
Opendoor’s Competitors
- Offerpad: When it comes to a quick and easy sale, Offerpad is considered. They have a 1% cancellation fee and lower offers. They also pay for free local moves of up to 50 miles;
- RedfinNow: They are also an iBuyer. They have fewer houses than Opendoor and buy more expensive properties;
- Orchard: Orchard is considered to have the best buyer and trade-in services. They are very different from Opendoor, as they’re not an iBuyer, nor does it guarantee home sales. However, their aim is to help you purchase a new home before the old one sells;
- Knock: Just like Orchard, their goal is to assist customers in buying a new property before they sell the old one. Their Home Swap program helps secure a home loan with a down payment addition. Their fee structure is entirely different from that of Opendoor, with their 1.25% service fee.
Opendoor’s SWOT Analysis
Here’s a breakdown of Opendoor’s SWOT analysis:
Opendoor’s Strengths
- Convenience: The main aim of Opendoor is to make real estate quick and easy;
- Real estate services: They provide their customers with three distinct real estate services;
- Customer Base: They have sold over 100,000 homes and have markets in up to 50+ states;
- Low service fee: Compared to their competitors, they have a low service fee of 5%, which attracts customers;
- Tech integration: Unlike traditional real estate firms, they have integrated into their service tech advancements, which improves the quality of service;
- Opendoor Guarantee: They have a 30-day refund guarantee, which allows customers to sell back the house at the price they bought it;
- User-friendly platform: Customers can easily carry out their business with their user-friendly mobile app.
Opendoor’s Weaknesses
- Selective: They have certain criteria to be met before investing in a property. So they’re not very inclusive;
- Limited to a few states: Although they have expanded quite a bit over the years, their market is still limited. And they are known for purchasing houses only in popular places;
- Repairs: After the evaluation of a property, repairs are taken into account. Sellers spend noticeably more on repairs than they normally would;
- Sellers might end up with a loss: During negotiations, sellers may be forced to sell at a lower price, which incurs a loss for them.
Opendoor’s Opportunities
- Business Strategy: Although their current business strategy is risky, it still has promise for greater things. In recent times, they’ve begun to break even, and soon they’ll surpass their expected profit margin;
- Additional services: Their home loans, title insurance, and escrow features have proven to be a mainstream revenue stream and will only increase from there;
Tech advancements: As the first iBuyer in real estate, they have an advantage over competitors. And their algorithm makes their strategy more successful.
Opendoor’s Threats
- Competitors: Although competition can be a motivation to grow, it also has the flip side of being counterproductive. And even if they face some sort of competition from fellow iBuyers, their biggest competitors are actually real estate incumbents. The more success they gain, the more the incumbents will try to take back the market, which poses a threat.
Conclusion
Opendoor was the first iBuyer — a company that buys and sells homes on a large scale using large amounts of venture capital.
Their vision is to empower people with the freedom to move by making the process feel less like work and more like fun.

