The hospitality sector is not left out in the recent gravitation towards the use of technological innovations in business operations by small firms and big corporations. The internet and software applications have led to the emergence of a system that allows customers to find and patronize service providers with ease, while it also enables service providers to render services to customers remotely without getting in touch with them directly and at lower costs.
Contents
What is a Ghost Kitchen?
Ghost kitchens are restaurants that use food delivery apps to render services to their customers without the use of dining halls and other features made available by conventional restaurants. It refers to the physical space where fast food service providers make food for off-premises (pick-up or delivery) services. They grant online orders to customers that require food delivery services.

Difference between Ghost Kitchen and Virtual Restaurant
Ghost kitchens are also referred to as cloud or virtual kitchens, though both terms are considered to be similar and even used interchangeably. There exists a slight difference between the two.
Virtual Restaurant
These restaurants which are also called cloud restaurants operate out of existing kitchens or restaurants. They create new diets by slightly altering the ingredients used for making popular foods. ‘Wings’ is a good example of a virtual restaurant, it operates out of existing ‘Chili’s and ‘Maggiano’s Kitchens.
Ghost kitchens
These types of kitchens which are also called cloud kitchens have an online presence and also render dine-in services, albeit in a space rented by or shared with a third party. They do not operate out of existing restaurants nor have counterparts who run conventional kitchen operations.
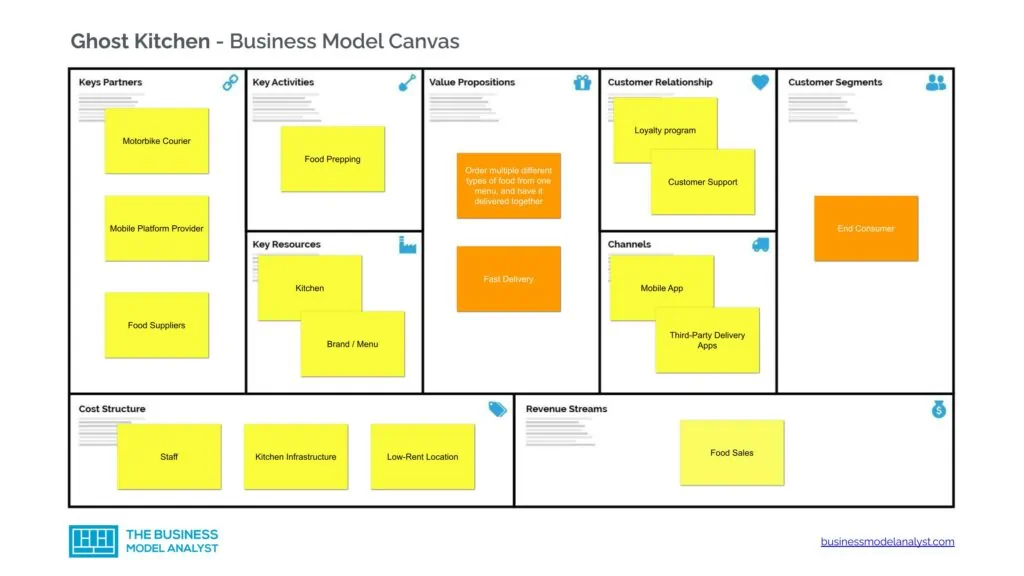
Ghost Kitchen Business Model Canvas
Let’s take a look at the Ghost Kitchen business model canvas below:
Basic Features of Ghost Kitchens
Various ghost kitchens exhibit peculiar characteristics that are not common to other ghost kitchens; however, some features are common to most of them. Some of these characteristics include:
Virtual Presence
Ghost kitchens have more online presence than physical presence. Some of them may have a physical presence through third-party arrangements, but most of them tend to be more active online.
Adjustable Menu
Ghost kitchens have rich and adjustable menus that could be adjusted/manipulated to suit the specifications of customers. This unique feature provides the platform for the kitchens to avail customers with customized recipes.
Lower Cost
With the ghost kitchen business model, entry into the restaurant or fast food industry is made a lot easier and less expensive. The huge capital outlay required to rent and furnish a space is saved, while their online presence is a cheaper means of marketing their products.
Lower Risk
The risk of embarking on a business venture is usually higher when a huge cost is incurred at the onset while the chances of the survival of the business and the tendency to break even are still hanging in the balance. The lower cost of setting up a ghost kitchen implies lesser risk.
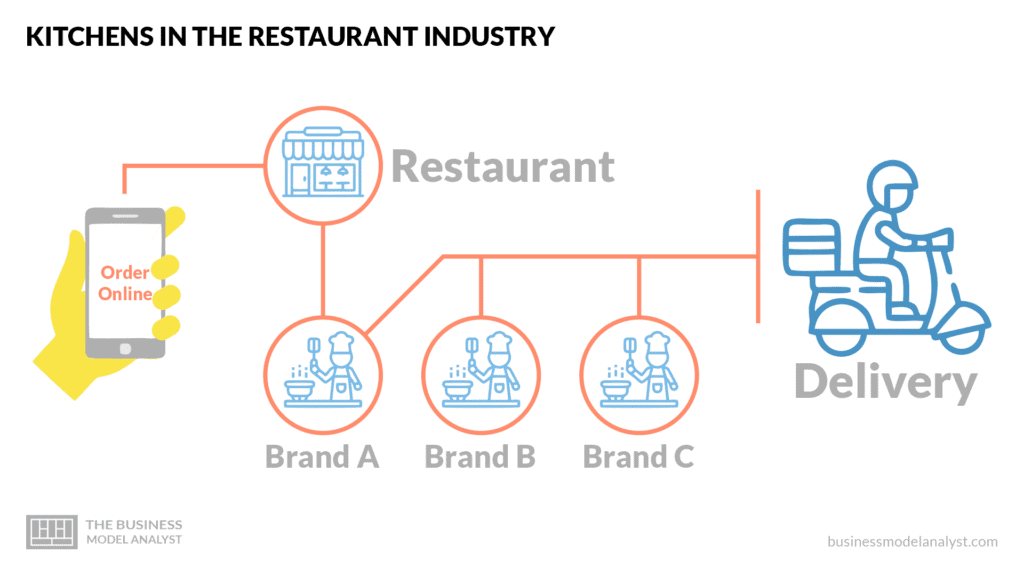
Classifications of Ghost Kitchen Models
Ghost kitchens have several business models that could be classified based on ownership, brand-oriented cooking, third-party food delivery, structure, and origin. We will briefly consider three classifications.
Ownership
It is the most popular classification of ghost kitchen business model. A ghost kitchen could either be owned independently by the operating restaurant or by a third party which is usually a bigger restaurant working in collaboration with smaller kitchen operators. Examples of the most popular Ghost Kitchen models that belong in this category are briefly explained below.
Commissary/ Shared Kitchens
Commissary or shared kitchens are usually owned by large corporations which rent premises in adherence to requisite stipulations for setting up restaurants, setting up the necessary kitchen accessories, and renting out to virtual kitchen operators. The relatively lower rent and lesser startup capital make the model visibly more affordable.
Incubator/ Pop-up Kitchens
Popo-up kitchens which are largely owned by entrepreneurs who own restaurants or chains of restaurants are offshoots of existing kitchens offering eatery services the conventional way. They are strictly online orders and delivery operations incorporated into kitchens that offer dine-in services.
Kitchen Pods
Kitchen pods are mostly owned by newcomers in the industry. It refers to the cozy kitchens with factory-fitted or smartly installed kitchen accessories that render online services to customers. They normally do not have affiliations or work in collaboration with big firms. Other classifications are as stated below.
Structure
This classification emphasizes the operational structure of a ghost kitchen. A ghost kitchen could be operated by an individual operator in collaboration with other independent ghost kitchen operators, or under the umbrella of a bigger restaurant or fast food business. Ownership as stated above appreciably determines the operations.
Origin
Some ghost kitchens are offshoots of chain restaurants trying to get larger shares of the ghost kitchen market or trying to meet up increasing demands of their teeming customers without setting up new dine-in restaurants. Some others are just new operators in the block, either working in collaboration with bigger firms in the industry or independently.
Reasons behind the Increasing Prevalence of Ghost Kitchen Model
The benefits that are associated with ghost kitchens exist in both the demand and supply sides of the business model, though they have attendant drawbacks.
Benefits
- The relatively lower capital outlay required to venture into the ghost kitchen business does not only make entry into the industry easier but also makes the risk lower.
- The absence of a physical space for operations which implies nonpayment of rent, electricity bills, and other bills suggests that the overhead cost of running the business is a lot cheaper than what obtains in conventional restaurants.
- Unlike the traditional restaurant where there is a limited number of customers that could be entertained in the dining hall simultaneously, in the ghost kitchen model an unlimited number of customers could be attended to concurrently in the comfort of their abodes.
- A very little amount of capital investment is needed in the short run after the initial capital outlay is invested in setting up a functional kitchen at the beginning of the ghost kitchen business. In conventional restaurants, the expensive furnishings and decorations are changed from time to time.
Hitches
Making delivery with precision and timeliness is necessary for a successful ghost kitchen business. The difficulty with which apartments are located in cities where properties are developed indiscriminately and the frequency of recorded traffic jams are some of the impediments to meeting these requirements.
The rare physical interaction between ghost kitchen operators and their customers makes it challenging for operators to build a good relationship with their loyal customers.
The absence of other value-added services such as serving alcohol and soft drinks, playing music, and taking special orders as done in traditional restaurants takes away some of the means of making customers more satisfied and loyal.
Even though the internet presents cheaper media for advertising and marketing services, some customers rely on the rankings of ghost kitchen ranking agencies to decide on kitchens to patronize. This puts new and unpopular kitchens at a disadvantage.
The ease with which menus are adjusted in ghost kitchen business models could create scenarios where replicating prepared recipes tend to be difficult.
Steps on how to Start a Ghost Kitchen
Ghost kitchen allows the operators to provide customized or tailor-made services to their various customers through third-party delivery apps. They are somewhat easy to set up and hold huge profit potential. The following are some of the simple steps required to set up a ghost kitchen.
- Estimate the total cost of all the necessary smart kitchen accessories that would ensure smooth and effective culinary undertakings. Juxtaposing the estimate with an entrepreneur’s startup capital reveals the possibility and feasibility of venturing into the business.
- Identify a specific market. Indicating a market of choice will help an entrepreneur to analyze extensively the present situation of the market, reach out to the target population with ease, identify an existing gap and inform them on how to convert the inherent opportunities to wealth.
- Create a basic but tightly flexible menu. This stresses the need to have a menu that is comprised of the popular cuisines among the target population, with a few other food recipes that are specially requested alone or together with the more popular ones.
- Set up a smart and effective service delivery process. This highlights the entire procedure that culminates in the customer deriving maximum satisfaction. It entails the preparation of rich and delicious cuisines which are prepared and delivered in time.
Conclusion
Large corporations are increasingly toeing the path of using apps to facilitate their business operations. This initiative which has been in existence for a while enjoyed accelerated and more ubiquitous acceptance in the height of the COVID-19 pandemic. Providing services to customers remotely makes entry into an industry relatively easier due to the lesser capital required to set up a shop and lower cost of business operations.

