The HP business model harmoniously combines sales, services, and subscription offerings to drive its success. By blending these elements seamlessly, HP cultivates a multi-faceted approach that maximizes revenue generation and customer satisfaction. At the core of HP’s business model lies its hardware sales strategy.
The company thrives by offering an extensive range of hardware products, including personal computers, laptops, tablets, printers, and imaging devices. This allows HP to cater to the diverse needs of both individual consumers and businesses, establishing a solid foundation for revenue generation. In addition to its core hardware sales, HP has strategically integrated services and subscription models to deliver comprehensive solutions to its customers.

Contents
A brief history of HP
HP (Hewlett-Packard) has a rich and transformative history that spans over eight decades, marked by innovative breakthroughs, strategic acquisitions, and successful transitions. The company’s journey began in 1939 when Bill Hewlett and Dave Packard founded HP in a one-car garage in Palo Alto, California.
Initially, the company focused on producing precision audio oscillators. Their commitment to engineering excellence and entrepreneurial spirit laid the foundation for HP’s future growth and success.
In the 1940s, HP expanded its product line to include electronic testing equipment, and by the 1950s, the company had established itself as a leading provider of electronic measurement instruments. HP’s instruments were known for their reliability, accuracy, and ease of use, making them popular among engineers and scientists.
The 1950s marked a significant milestone in HP’s history with its initial public offering (IPO) in 1957. This provided the necessary capital for the company’s expansion and diversification. HP continued to innovate and introduced several groundbreaking products, including its first desktop computer, the HP-85, in 1980.
The HP-85 was a self-contained personal computer that featured a built-in screen, keyboard, tape drive, and printer. It was primarily used for data processing and scientific applications. The introduction of the HP-85 marked HP’s entry into the desktop computer market and was an important milestone in the company’s history. Prior to the launch of the HP-85, HP entered the computer market with the launch of the HP 3000 minicomputer in 1972 to cater to business customers.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, HP experienced significant growth and underwent various strategic transitions. A Notable acquisition during this period included Apollo Computer in 1989, strengthening HP’s workstation capabilities.
In May 2002, HP made history with its merger with Compaq Computer Corporation, creating one of the world’s largest technology companies at the time. This transformative move allowed HP to expand its product portfolio and global reach, positioning itself as a comprehensive technology solutions provider.
HP adapted to the changing market dynamics as the technology landscape evolved in the 2000s. The company emphasized services, solutions, and software offerings to complement its hardware business. This strategic shift aimed to provide end-to-end solutions, encompassing consulting, IT infrastructure services, software applications, and managed services.
In 2015, HP split into two separate entities — HP Inc. and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE). HP Inc. retained the personal systems and printing businesses, while HPE focused on enterprise technology solutions and services.
Who Owns HP
As a publicly owned company, HP Inc. is owned by a diverse group of individual and institutional shareholders who hold its common stock. These shareholders include individuals, mutual funds, pension funds, hedge funds, and other investment entities.
HP Mission Statement

The HP’s mission statement is “to engineer experiences that amaze each and every one of our customers.”
How HP works
HP works through a combination of research and development, manufacturing, marketing, and sales to deliver its products and services. Here is a general overview of how HP operates:
Research and Development
HP invests in research and development (R&D) to drive innovation and create new technologies and solutions. This involves conducting in-depth research, exploring emerging trends in the industry, and analyzing customer needs. The company’s research and development teams work on developing new products, improving existing ones, and exploring cutting-edge technologies that can enhance user experiences and address market demands.
Product Design and Manufacturing
Once new products are conceptualized, HP’s teams focus on product design, engineering, and manufacturing. This involves designing the hardware components, developing the software solutions that power the devices, and ensuring quality control throughout manufacturing. HP’s manufacturing facilities are responsible for producing and assembling the hardware, ensuring high standards of quality and reliability.
Marketing and Sales
HP employs marketing strategies to promote its products and reach its target customers. This includes creating advertising campaigns, engaging in digital marketing efforts, establishing partnerships with other companies, and participating in industry events and trade shows.
HP’s sales teams, both online and through physical stores, interact with customers directly to understand their needs, provide product information, and facilitate purchasing. Additionally, HP collaborates with channel partners, such as retailers and resellers, to expand its market reach.
Services and Support
HP provides a range of services to support its customers. The services include consulting services, IT infrastructure services to assist with system setup and management, technical assistance for troubleshooting and problem resolution, and managed services to handle specific IT functions on behalf of the customer. These services ensure that customers can maximize the value of their technology investments and overcome any challenges they may encounter.
Subscription and Managed Print Services
HP offers subscription-based services and managed print services as an alternative to traditional product purchases. With subscription services, customers pay a recurring fee to gain ongoing access to hardware, software, supplies, and support, allowing for more predictable budgeting and upgrades.
Managed print services provide comprehensive print management solutions, including hardware, supplies, maintenance, and support, with costs typically based on a monthly or per-page pricing model. These services enable customers to streamline their printing operations, reduce costs, and increase efficiency.
How HP makes money
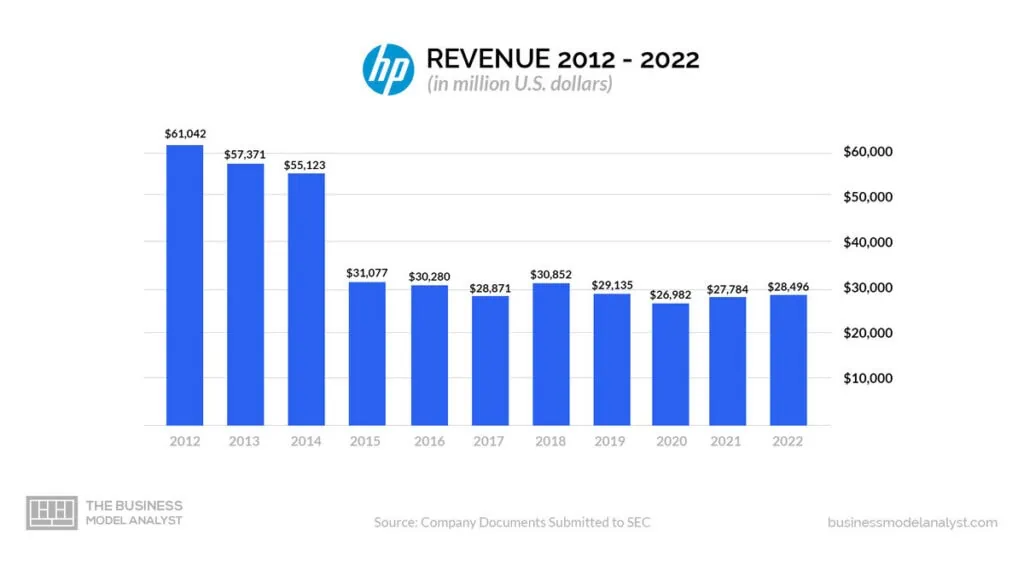
HP generates revenue from the following:
Sales of Hardware and Accessories
HP manufactures and sells a wide range of hardware products, including personal computers, laptops, printers, scanners, tablets, workstations, servers, storage devices, and networking equipment. In addition to hardware sales, HP also produces and sells supplies and accessories that complement its products.
These include ink cartridges, toners, paper, 3D printing materials, batteries, cables, and other peripherals. Revenue is generated when customers purchase these devices and associated supplies and accessories directly from HP or through authorized retailers. The price of each product is determined based on factors such as manufacturing costs, competition, and market demand.
Services
HP offers a range of services that generate revenue for the company. These services include consulting, IT infrastructure, technical, managed, and software support. Revenue is generated through fees charged for these services, which can vary based on the scope and complexity of the service provided.
Consulting services involve expert advice and guidance to help customers optimize their technology infrastructure and strategies. IT infrastructure services assist customers with setting up, managing, and optimizing their IT systems. Technical support services provide assistance and troubleshooting for hardware and software issues.
Managed services involve HP taking responsibility for specific IT functions on behalf of the customer. Software support services offer ongoing assistance, updates, and upgrades for HP’s software solutions. These service offerings contribute to HP’s revenue by providing value-added services to customers and establishing long-term relationships.
Subscription and Managed Print Services
HP generates revenue through subscription-based services and managed print services. Subscription services involve customers paying recurring fees to access hardware, software, supplies, and support on an ongoing basis.
Revenue is generated through these recurring fees, which provide customers with continuous access to the latest technology updates and upgrades. Managed print services encompass comprehensive print management solutions, including hardware, supplies, maintenance, and support. HP charges fees for these services based on a monthly or per-page pricing model.
These services enable businesses to streamline their printing operations, reduce costs, and receive regular supplies and maintenance without the need for in-house management. The subscription and managed print services revenue provide HP with a predictable and recurring revenue stream.
Licensing and Intellectual Property
HP generates revenue by licensing its intellectual property to other companies, including patents, trademarks, and copyrights. Other companies can use HP’s technology and innovations in their products or services through licensing agreements.
In exchange for using HP’s intellectual property, licensing fees or royalties are paid to HP. This revenue stream allows HP to monetize its intellectual property assets and leverage its technological advancements in various industries.
Financing and Leasing Services
HP offers financing and leasing options to customers, allowing them to acquire HP products and solutions through flexible payment plans. Revenue is generated through the interest charges and fees associated with these financing arrangements.
HP enables customers to acquire its products without needing upfront capital investment by providing financing and leasing services. This revenue stream benefits both HP and its customers by facilitating the purchase of HP products while spreading the cost over time.
HP Business Model Canvas
Let’s take a look at the HP Business Model Canvas below:
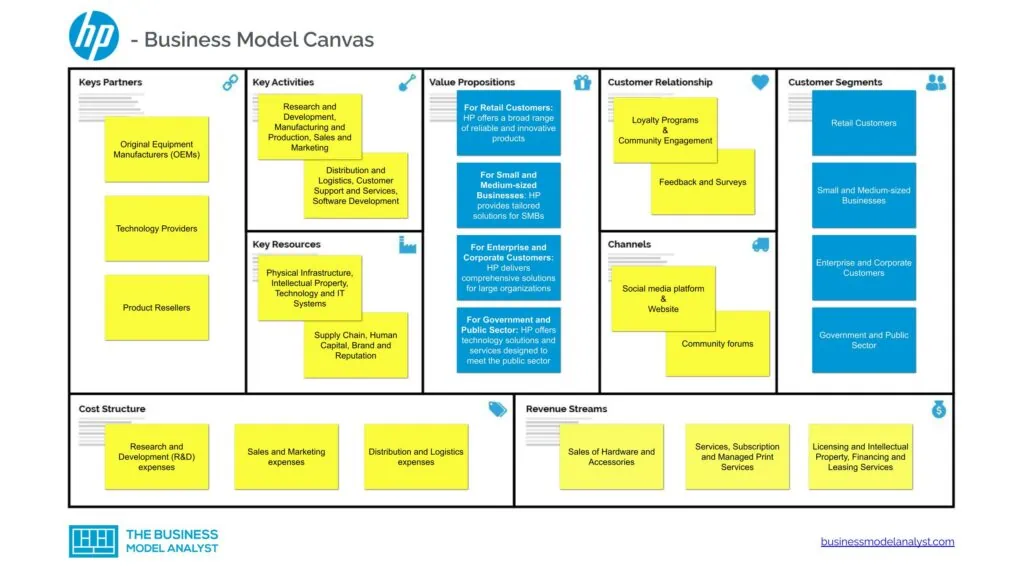
HP Customer Segments
HP’s customer segments consist of:
- Retail Customers: These are individual consumers who purchase HP products for personal use. They can include students who need laptops for studying, professionals who require desktop computers for work, home users who want printers for personal use, and technology enthusiasts who enjoy the latest gadgets and devices;
- Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs): SMBs are businesses with a moderate scale of operations. They can include startups, local businesses, and companies that employ a few workers. HP provides solutions tailored to the needs of SMBs, offering hardware such as desktops, laptops, printers, and servers, as well as software solutions, managed services, and support to enhance productivity and support their business growth;
- Enterprise and Corporate Customers: Enterprise and corporate customers are large organizations and corporations with complex IT infrastructure needs. They often require high-performance computing solutions, advanced servers, storage systems, and networking equipment to support business processes and operations. HP offers a comprehensive range of products and services designed to meet the unique requirements of these customers, including enterprise-level software solutions and IT infrastructure management services;
- Government and Public Sector: The government and public sector customer segment includes government agencies at various levels, such as federal, state, and local governments, as well as public sector organizations. HP provides technology solutions tailored to the public sector’s specific requirements and compliance standards, including hardware, software, and services that enable efficient and secure operations;
- Education Sector: The education sector comprises K-12 schools, colleges, and universities. HP offers various products and solutions for educational institutions, including laptops, desktops, printers, interactive displays, educational software, and management systems. These solutions aim to enhance learning experiences, facilitate administrative tasks, and support the digital transformation efforts of educational institutions;
- Financial Services Industry: The financial services industry encompasses banks, insurance companies, and other entities involved in financial transactions and services. HP offers technology infrastructure solutions, data storage systems, security solutions, and secure printing solutions to meet the specific requirements of the financial services sector. These solutions help ensure data security, streamline operations, and meet regulatory compliance standards;
- Creative Professionals: Creative professionals include individuals working in fields such as graphic design, photography, video editing, animation, and other creative disciplines. HP provides high-performance workstations, displays, and software solutions that are optimized for creative workflows. These solutions help creative professionals achieve high-quality results, improve productivity, and bring their creative visions to life;
- Healthcare and Medical Industry: This segment encompasses healthcare providers, medical facilities, hospitals, clinics, research institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and other organizations involved in the delivery of healthcare services and products.
HP Value Propositions
HP’s value propositions consist of:
- For Retail Customers: HP offers a broad range of reliable and innovative products, including laptops, desktops, tablets, and printers, designed to deliver high performance and versatility for personal use. With cutting-edge technology and user-friendly interfaces, HP provides retail customers with devices that enhance their digital experience and cater to their individual needs;
- For Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs): HP provides tailored solutions for SMBs, offering hardware, software, and services that boost productivity, efficiency, and business growth. From cost-effective desktops, laptops, printers, and servers to software solutions and managed services, HP supports SMBs in streamlining operations and maximizing resources;
- For Enterprise and Corporate Customers: HP delivers comprehensive solutions for large organizations, including high-performance servers, storage systems, networking equipment, and software solutions. These offerings support complex IT infrastructure requirements and digital transformation initiatives, ensuring seamless operations, improved productivity, and reliable technical support;
- For Government and Public Sector: HP offers technology solutions and services designed to meet the public sector’s specific needs and compliance standards. By providing secure and efficient hardware, software, and services, HP helps government agencies and public sector organizations carry out their operations effectively while ensuring data security and supporting the delivery of public services;
- For Education Sector: HP provides products and solutions that enhance learning experiences and streamline administrative tasks within educational institutions. The products and solutions include durable laptops, desktops, printers, and interactive displays, as well as educational software solutions and management systems that foster creativity, support digital learning, and simplify administrative processes;
- For Financial Services Industry: HP provides technology infrastructure, data storage solutions, security solutions, and secure printing solutions that meet the stringent requirements of the financial services sector. These offerings help financial institutions safeguard customer data, optimize data management processes, enhance operational efficiency, and comply with industry regulations;
- For Creative Professionals: HP offers high-performance workstations, displays, and software solutions optimized for creative workflows. These solutions provide the processing power, color accuracy, and performance needed for graphic design, photography, video editing, and other creative disciplines. These solutions enable professionals to unleash their creativity and achieve exceptional results;
- For Healthcare and Medical Industry: HP serves the healthcare and medical industry with specialized technology solutions, including hardware and software for healthcare information systems, medical imaging devices, and secure printing solutions. These offerings streamline workflows, improve patient care, and ensure the security and privacy of sensitive medical information.
HP Channels
HP’s channels consist of:
- Social media platform
- Website
- Community forums
HP Customer Relationships
HP’s customer relationships consist of:
- Loyalty Programs
- Community Engagement
- Feedback and Surveys
HP Revenue Streams
HP’s revenue streams consist of:
- Sales of Hardware and Accessories
- Services
- Subscription and Managed Print Services
- Licensing and Intellectual Property
- Financing and Leasing Services
HP Key Resources
HP’s key resources consist of:
- Physical Infrastructure
- Intellectual Property
- Technology and IT Systems
- Supply Chain
- Human Capital
- Brand and Reputation
HP Key Activities
HP’s key activities consist of:
- Research and Development
- Manufacturing and Production
- Sales and Marketing
- Distribution and Logistics
- Customer Support and Services
- Software Development
HP Key Partners
HP’s key partners consist of:
- Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs)
- Technology Providers
- Product Resellers
HP Cost Structure
HP’s cost structure consists of:
- Research and Development (R&D) expenses
- Sales and Marketing expenses
- Distribution and Logistics expenses
- Support and Services expenses
- Administrative and Overhead expenses
- IT Infrastructure expenses
- Intellectual Property expenses
- Acquisitions and Integration expenses
HP Competitors
- Dell Technologies: Dell Technologies is a global technology company that offers a wide range of hardware, software, and IT services. The company is known for its expertise in personal computers, servers, storage devices, networking equipment, and solutions for digital transformation. Dell was founded in 1984 by Michael Dell and has grown to become one of the world’s leading technology providers. With its direct-to-customer sales model, customization options, and a strong focus on enterprise solutions, Dell competes with HP in the PC market and offers comprehensive IT solutions for businesses;
- Lenovo: Lenovo is a multinational technology company headquartered in China that specializes in the design, development, and manufacturing of personal computers, tablets, smartphones, servers, and other related products. The company was founded in 1984 as Legend and later acquired IBM’s PC division, which helped Lenovo gain a global presence. Lenovo is recognized as one of the largest PC vendors worldwide and competes directly with HP in the PC and enterprise hardware markets. Lenovo’s competitive advantages lie in its strong presence in the Chinese market, innovative designs, and focus on emerging technologies;
- Apple Inc.: Apple Inc. is a multinational technology company that has revolutionized the consumer electronics industry. Founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, Apple is known for its iconic products like Mac computers, iPhones, iPads, Apple Watches, and various software and services. While Apple primarily focuses on consumer markets, its high-end MacBooks and iMac computers compete indirectly with HP’s premium laptops and workstations. Apple’s competitive strengths lie in its strong brand loyalty, integration between hardware and software, and emphasis on design and user experience;
- Microsoft Corporation: Microsoft Corporation is a global technology company that develops, licenses, and supports a wide range of software, hardware, and cloud services. The company was founded in 1975 and is known for its flagship products like the Windows operating system, Office productivity suite, Azure cloud platform, and Surface devices. While Microsoft primarily operates in the software industry, it competes with HP in areas such as PCs, laptops, and enterprise solutions. Microsoft’s Surface line of devices competes directly with HP’s laptops and hybrid devices. Additionally, Microsoft offers cloud-based services that compete with HP’s offerings in the enterprise software and cloud computing space.
HP SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT analysis of HP:
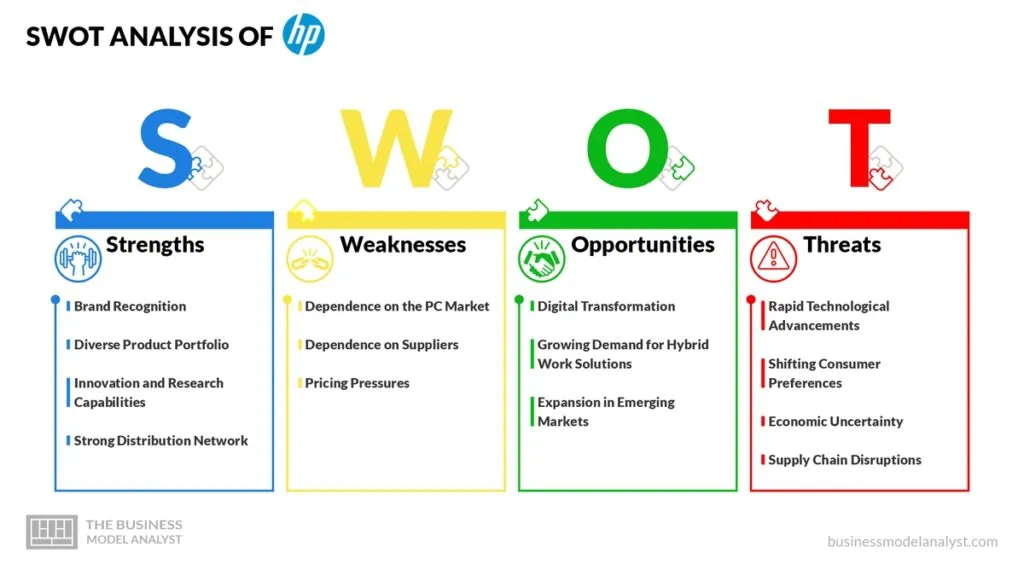
HP Strengths
- Brand Recognition: HP is a globally recognized brand with a long-standing history in the technology sector. The company has established a strong reputation for delivering high-quality products and services, which helps build trust and loyalty among its customers;
- Diverse Product Portfolio: HP offers a wide range of products, including personal computers, laptops, printers, scanners, servers, storage solutions, and software. This diverse portfolio allows HP to cater to different market segments and meet the varied needs of consumers, businesses, and enterprises;
- Innovation and Research Capabilities: HP has a strong focus on innovation and invests significantly in research and development. The company constantly strives to develop cutting-edge technologies, enhance product performance, and introduce new features that differentiate its offerings in the market;
- Strong Distribution Network: HP has a robust distribution network that spans the globe. The company has established partnerships with channel partners, resellers, and retailers, enabling it to reach a wide customer base effectively. This extensive distribution network helps HP expand its market reach and enhance customer accessibility.
HP Weaknesses
- Dependence on the PC Market: HP has a significant dependence on the PC market, which can be a vulnerability. Fluctuations in demand for PCs, changes in consumer preferences towards other devices (such as tablets or smartphones), or disruptions in the supply chain can impact HP’s business and financial performance;
- Dependence on Suppliers: HP relies on a network of suppliers for components and materials used in its products. Any disruptions in the supply chain, such as shortages, price fluctuations, or quality issues, can impact HP’s manufacturing capabilities and product availability;
- Pricing Pressures: The technology industry is characterized by rapid price erosion, and HP faces pricing pressures in various product categories. This can impact the company’s profitability, particularly in highly competitive segments where price becomes a major consideration for customers.
HP Opportunities
- Digital Transformation: The ongoing digital transformation presents significant opportunities for HP. As organizations across industries embrace digital technologies, there is a growing demand for IT infrastructure, cloud computing, cybersecurity solutions, and managed services. HP can capitalize on this trend by offering comprehensive digital transformation solutions to businesses, helping them optimize their operations and stay competitive;
- Growing Demand for Hybrid Work Solutions: The shift towards hybrid work models, combining remote and in-office work, has recently accelerated. This accelerating demand presents an opportunity for HP to provide solutions tailored for hybrid work environments, such as laptops, collaboration tools, and secure connectivity options. HP can leverage its expertise in personal computing and workplace solutions to meet the evolving needs of organizations and individuals;
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: Emerging markets, such as India, China, and other developing countries, offer significant growth potential for HP. These markets are witnessing increased technology adoption and rising disposable incomes, driving demand for PCs, printers, and other technology solutions. By expanding its presence and tailoring its products and services to the unique needs of these markets, HP can tap into new customer segments and drive revenue growth.
HP Threats
- Rapid Technological Advancements: Technology evolves at a rapid pace, and HP faces the threat of disruptive technologies that could render its existing products or business models obsolete. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and quantum computing have the potential to reshape the industry landscape and create new competitors and market dynamics;
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Consumer preferences and trends can pose a threat to HP’s business. For example, the rising popularity of smartphones and tablets has impacted the demand for traditional PCs. HP needs to continually adapt its product portfolio to meet changing consumer needs and preferences, such as the shift towards mobility, touch-enabled devices, and cloud-based solutions;
- Economic Uncertainty: Economic fluctuations and uncertainties can impact HP’s business. During periods of economic downturn, organizations and individuals may reduce their IT spending, affecting demand for HP’s products and services. Additionally, currency exchange rate fluctuations and trade disputes can impact HP’s international operations and profitability;
- Supply Chain Disruptions: HP relies on a global supply chain to source components and materials for its products. Disruptions in the supply chain, such as natural disasters, geopolitical issues, trade restrictions, or manufacturing challenges, can impact product availability, increase costs, and affect HP’s ability to meet customer demand.
Conclusion
HP’s business model exemplifies a well-rounded approach that leverages hardware sales, services, and subscription offerings to drive its success. The business model showcases the power of synergy between sales, services, and subscriptions.
This holistic approach enables the company to maximize revenue generation, cultivate strong customer relationships, and remain at the forefront of the technology industry. As technology continues to shape our world, HP’s ability to adapt and innovate will continue to drive its growth and influence in the industry.

