The Dunkin’ Donuts business model is a franchise-based business model, meaning that most Dunkin’ Donuts locations are owned and operated by independent franchisees rather than company-owned. The franchise model enables Dunkin’ Donuts to tap into the skills and resources of motivated individuals who are passionate about the brand, while sharing in the risks and rewards of business ownership.
Franchisees are responsible for day-to-day operations, including staffing, inventory management, customer service, and financial management. They benefit from the established Dunkin’ Donuts brand, proven systems, and ongoing support provided by the company.
Franchisees enter into a contractual agreement with Dunkin’ Donuts, which outlines the terms and conditions of the franchise relationship. As part of this agreement, franchisees typically pay an initial franchise fee to gain access to the Dunkin’ Donuts brand, trademarks, and operating systems. They also agree to pay ongoing royalty fees, usually calculated as a percentage of sales, as well as contribute to national and regional advertising funds.
Contents
A brief history of Dunkin’ Donuts
Dunkin’ Donuts was founded in 1950 by William Rosenberg in Quincy, Massachusetts. Originally called “Open Kettle,” the shop served donuts and coffee. In 1955, the name was changed to Dunkin’ Donuts to reflect the popular practice of Dunkin’ Donuts in coffee.
The brand quickly gained popularity, and in the 1950s, Dunkin’ Donuts began offering franchise opportunities, allowing entrepreneurs to open their own Dunkin’ Donuts locations. This led to rapid expansion, and by the end of the 1960s, there were over 100 Dunkin’ Donuts stores across the United States.
During the 1970s and 1980s, Dunkin’ Donuts continued to grow and diversify its menu. They introduced new items such as bagels, breakfast sandwiches, and other bakery products, expanding their offerings beyond donuts.
In the 1990s, Allied Domecq, a multinational food and beverage company, acquired Dunkin’ Donuts. This acquisition provided the resources and expertise to accelerate international expansion. Dunkin’ Donuts opened stores in various countries, including Canada, Japan, South Korea, and the United Kingdom.
In 2004, a significant event took place in the food service industry, as Dunkin’ Donuts and Baskin-Robbins merged to form Dunkin’ Brands. This merger was facilitated by a consortium of private equity firms, including Bain Capital Partners, the Carlyle Group, and Thomas H. Lee Partners.
Prior to the merger, Dunkin’ Donuts and Baskin-Robbins operated as separate entities, each renowned for their strong brand recognition and franchise operations. However, the decision to combine their strengths and resources led to the creation of Dunkin’ Brands.
Under the merger agreement, the private equity firms successfully acquired Dunkin’ Donuts and Baskin-Robbins, establishing Dunkin’ Brands as the parent company. This strategic consolidation allowed for the sharing of resources, operational efficiencies, and the exploitation of synergies between the two renowned brands.
In 2018, Dunkin’ Donuts underwent a rebranding effort and became known as Dunkin’, reflecting its focus on beverages beyond donuts. The company strongly emphasized technology, launching a mobile app for convenient ordering and introducing digital kiosks and drive-thru technology to enhance the customer experience.
In 2020, Dunkin Brands was acquired by Inspire Brands, a restaurant company that owns several other well-known brands. This acquisition positioned Dunkin’ within a larger organization and provided opportunities for further growth and expansion.
Who Owns Dunkin’ Donuts
Inspire Brands owns Dunkin’ Donuts through its acquisition of Dunkin’ Brands, which is the parent company of Dunkin’ Donuts. In December 2020, Inspire Brands completed the acquisition of Dunkin’ Brands, making it the new owner of Dunkin’ Donuts.
Dunkin’ Donuts Mission Statement

Dunkin’ Donuts’ mission statement is “to be the world’s leading baked goods and coffee chain, serving delicious, high-quality products that bring joy and fuel our customers’ day.”
How Dunkin’ Donuts works
Dunkin’ Donuts operates through a franchising system that allows qualified individuals or groups to own and operate Dunkin’ Donuts stores. Each franchise of Dunkin’ Donuts engages in various operations to run their individual stores effectively:
Store Management
Franchisees are responsible for managing the day-to-day operations of their Dunkin’ Donuts store. They oversee staffing, including hiring, training, and scheduling employees. Franchisees also manage inventory levels, ensuring they have an adequate supply of ingredients, packaging, and other necessary items.
Product Preparation
Franchisees are responsible for adhering to Dunkin’ Donuts’ standardized recipes and preparation methods to maintain consistency across the brand. They oversee the production of donuts, coffee, beverages, and other menu items, ensuring they meet Dunkin’ Donuts’ quality standards.
Financial Management
Franchisees handle financial aspects such as sales reporting, cash management, and financial record-keeping. They monitor costs, control expenses, and work towards achieving profitability while complying with Dunkin’ Donuts’ financial policies and reporting requirements.
Marketing and Promotions
Dunkin’ Donuts franchisees actively participate in local marketing efforts. While the company conducts national marketing campaigns, franchisees engage in localized advertising, community outreach, and promotions to drive customer traffic and awareness in their specific market.
Catering
Dunkin’ Donuts also offers catering services for larger orders or events. Customers can place catering orders in advance, selecting from a range of menu options suitable for gatherings or meetings. The catering order can be picked up at the store or, in some cases, delivered to the specified location.
How Dunkin’ Donuts makes money
Here are the primary ways Dunkin’ Donuts generates its revenue:
Franchise Fees
Dunkin’ Donuts operates on a franchise business model, where individuals or groups (franchisees) pay an initial franchise fee to obtain the rights to own and operate a Dunkin’ Donuts store. This fee provides franchisees access to the Dunkin’ Donuts brand, trademarks, operating systems, and ongoing support.
Royalty Fees
Dunkin’ Donuts collects ongoing royalty fees from its franchisees as part of the franchise agreement. These fees are typically based on a percentage of the franchisees’ gross sales and are paid regularly, often weekly or monthly. The royalty fees allow franchisees to continue using the Dunkin’ Donuts brand and receive ongoing support and resources.
Advertising Fees
Dunkin’ Donuts requires its franchisees to contribute to a national advertising fund. The advertising fees are used for regional and national marketing campaigns, promotional activities, and brand-building efforts. This collective advertising fund helps promote the Dunkin’ Donuts brand and benefits all franchisees by driving customer traffic to their stores.
Product Sales
The primary source of revenue for Dunkin’ Donuts stores is the sale of its menu items, including donuts, breakfast sandwiches, coffee, beverages, and other baked goods. The company earns money from the sale of these products, and the revenue is shared between Dunkin’ Donuts corporate and the individual franchisees.
Licensing and Merchandising
In addition to its traditional store-based operations, Dunkin’ Donuts may generate revenue through licensing agreements and merchandising. This can include selling Dunkin’ Donuts-branded merchandise, such as mugs, apparel, and accessories, in stores or online.
Dunkin’ Donuts Business Model
Let’s take a look at the Dunkin’ Donuts Business Model Canvas below:
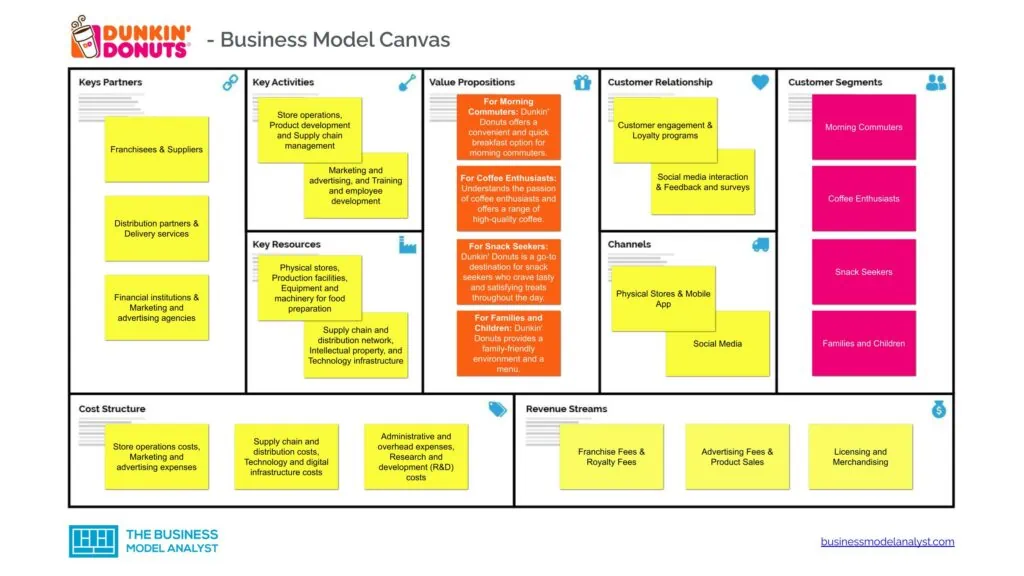
Dunkin’ Donuts Customer Segments
Dunkin’ Donuts’s customer segments consist of:
- Morning Commuters: Morning commuters refer to individuals who travel to work or other destinations during the morning hours, typically on weekdays. They are usually on their way to their workplace or educational institution and use various modes of transportation, such as cars, buses, trains, or bicycles;
- Coffee Enthusiasts: Coffee enthusiasts are people who have a deep appreciation and love for coffee. They often seek out high-quality coffee and may be knowledgeable about different brewing methods, origins, and flavors. Coffee enthusiasts enjoy exploring the world of coffee;
- Snack Seekers: Snack seekers are individuals who actively search for and enjoy snacks. They may have a particular fondness for a wide range of snacks, including donuts, cookies, candies, and other portable food items. Snack seekers often look for quick and convenient options to satisfy their cravings, and may be inclined to try new and interesting flavors;
- Families and Children: Families and children refer to groups of parents or guardians with their young ones. They typically engage in activities together and often prioritize spending quality time as a family unit. They see Dunkin’ Donuts as a family-friendly destination where they can indulge in delicious treats, enjoy a relaxed atmosphere, and spend quality time together;
- Students and Study Groups: Students and study groups include individuals enrolled in educational institutions, such as schools, colleges, or universities. They may come together in groups to collaborate, share knowledge, and support each other in their learning endeavors. Students and study groups often engage in studying, conducting research, working on assignments, and preparing for exams.
Dunkin’ Donuts Value Propositions
Dunkin’ Donuts’s value propositions consist of:
- For Morning Commuters: Dunkin’ Donuts offers a convenient and quick breakfast option for morning commuters. With a wide selection of freshly brewed coffee, breakfast sandwiches, and grab-and-go snacks, Dunkin’ Donuts provides a hassle-free solution for commuters looking for a delicious and energizing start to their day. The fast service, easy accessibility of locations, and the availability of breakfast items make Dunkin’ Donuts a preferred choice for time-conscious morning commuters;
- For Coffee Enthusiasts: Dunkin’ Donuts understands the passion of coffee enthusiasts and offers a range of high-quality coffee options to satisfy their discerning tastes. From classic blends to specialty coffee drinks, Dunkin’ Donuts focuses on delivering a consistently delicious and customizable coffee experience. With a commitment to freshness and the ability to personalize the strength, sweetness, and flavors of their coffee, Dunkin’ Donuts caters to the preferences of coffee enthusiasts who value the art and science of brewing;
- For Snack Seekers: Dunkin’ Donuts is a go-to destination for snack seekers who crave tasty and satisfying treats throughout the day. From a wide assortment of donuts and pastries to savory snacks like bagels and muffins, Dunkin’ Donuts offers a variety of options to fulfill snack cravings. The convenience of quick service, the availability of both sweet and savory choices, and the occasional limited-time offerings make Dunkin’ Donuts an appealing choice for those seeking a quick and indulgent snack;
- For Families and Children: Dunkin’ Donuts provides a family-friendly environment and a menu that caters to the tastes and preferences of both parents and children. With a range of donut flavors, breakfast sandwiches, and kid-friendly options like munchkins and milkshakes, Dunkin’ Donuts offers something for everyone in the family. The welcoming atmosphere, availability of seating, and the ability to accommodate different dietary preferences make Dunkin’ Donuts an attractive choice for families looking to enjoy a treat together;
- Students and Study Groups: Dunkin’ Donuts provides a comfortable and relaxed setting for students and study groups to meet, work, and recharge. With free Wi-Fi, ample seating, and a variety of caffeinated and non-caffeinated beverage options, Dunkin’ Donuts offers an inviting space for studying, collaborating, or taking a break. The availability of snacks and the flexible menu choices make it convenient for students and study groups to fuel their productivity and enjoy a refreshing break during their study sessions.
Dunkin’ Donuts Channels
Dunkin’ Donuts’s channels consist of:
- Physical Stores
- Mobile App
- Social Media
Dunkin’ Donuts Customer Relationships
Dunkin’ Donuts’s customer relationships consist of:
- Customer engagement
- Loyalty programs
- Social media interaction
- Feedback and surveys
Dunkin’ Donuts Revenue Streams
Dunkin’ Donuts’s revenue streams consist of:
- Franchise Fees
- Royalty Fees
- Advertising Fees
- Product Sales
- Licensing and Merchandising
Dunkin’ Donuts Key Resources
Dunkin’ Donuts’s key resources consist of:
- Physical stores
- Production facilities
- Equipment and machinery for food preparation
- Supply chain and distribution network
- Intellectual property
- Technology infrastructure
- Workforce
- Suppliers and vendor relationships
- Financial resources and capital
Dunkin’ Donuts Key Activities
Dunkin’ Donuts’s key activities consist of:
- Store operations
- Product development
- Supply chain management
- Marketing and advertising
- Training and employee development
- Customer relationship management
- Franchise management
Dunkin’ Donuts Key Partners
Dunkin’ Donuts’s key partners consist of:
- Franchisees
- Suppliers
- Distribution partners
- Delivery services
- Financial institutions
- Marketing and advertising agencies
- Technology providers
Dunkin’ Donuts Cost Structure
Dunkin’ Donuts’s cost structure consists of:
- Store operations costs
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Supply chain and distribution costs
- Technology and digital infrastructure costs
- Administrative and overhead expenses
- Research and development (R&D) costs
- Cost of Goods Sold
Dunkin’ Donuts Competitors
- Starbucks: Starbucks was founded in 1971 in Seattle, Washington, by three partners – Jerry Baldwin, Zev Siegl, and Gordon Bowker. Initially, Starbucks focused on selling high-quality whole coffee beans and coffee-making equipment. However, in the 1980s, the company shifted its focus to the coffeehouse concept, offering a cozy and inviting space for customers to enjoy freshly brewed coffee. Starbucks competes with Dunkin’ Donuts by focusing on its premium coffee offerings and creating a unique coffeehouse experience. Starbucks is known for its high-quality Arabica coffee beans and a wide range of specialty beverages, including espresso-based drinks and seasonal favorites. The company emphasizes a cozy and inviting atmosphere in its stores, providing comfortable seating and creating a “third place” for customers to relax and socialize. Starbucks invests heavily in its brand image, promoting sustainability and ethical sourcing practices, which resonates with socially conscious consumers. The company also leads in digital innovation, offering a highly successful mobile app and rewards program to enhance customer engagement and convenience;
- McDonald’s: McDonald’s, founded in 1940 by Richard and Maurice McDonald, initially operated as a hamburger stand in San Bernardino, California. However, it was in the 1950s that McDonald’s transformed into a fast-food restaurant chain, emphasizing speed, affordability, and consistency. McDonald’s competes with Dunkin’ Donuts by leveraging its extensive global presence and drive-thru convenience. McDonald’s is renowned for its fast and efficient service, offering a wide range of breakfast options, including breakfast sandwiches, muffins, and coffee. The company emphasizes affordability and convenience, attracting customers looking for a quick and accessible breakfast on the go. McDonald’s also invests in menu innovations, introducing limited-time offerings and expanding its McCafé line of coffee beverages to compete in the coffee segment. The company’s vast network of locations and strong brand recognition give it a competitive edge in the QSR industry;
- Tim Hortons: Tim Hortons was founded in 1964 in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, by Tim Horton, a professional ice hockey player, and Ron Joyce. The company started as a small donut and coffee shop and quickly gained popularity. Tim Hortons’ focus on quality coffee and baked goods resonated with Canadians, and the brand grew rapidly across the country. Tim Hortons competes with Dunkin’ Donuts, especially in the Northeastern United States, by offering a variety of coffee, baked goods, and breakfast options. It emphasizes affordability and convenience, catering to customers looking for a quick and satisfying meal or snack. Tim Hortons highlights its Canadian heritage, using it as a point of differentiation and appealing to customers who appreciate the brand’s origins. The company continually introduces new menu items and promotions to engage customers and compete in the highly competitive QSR market.
Dunkin’ Donuts SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT analysis of Dunkin’ Donuts:
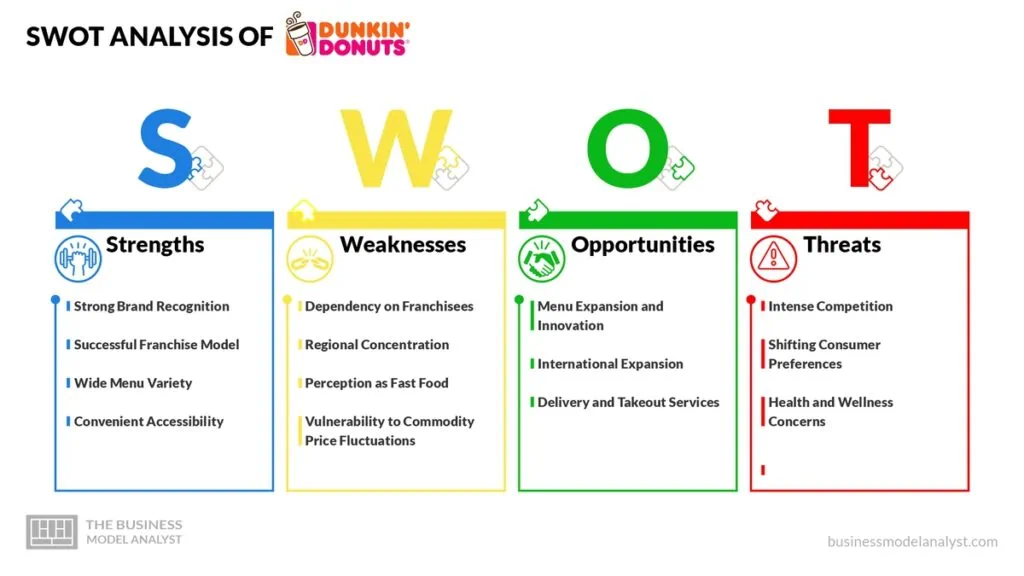
Dunkin’ Donuts Strengths
- Strong Brand Recognition: Dunkin’ Donuts is a well-known and respected brand with a long history in the industry. The company has established a strong presence and brand awareness, making it instantly recognizable to consumers. This recognition helps drive customer loyalty and attracts new customers who trust the brand for its quality products and services;
- Successful Franchise Model: Dunkin’ Donuts operates primarily through a franchise model, which has contributed to its rapid expansion and widespread presence. The franchise model allows local entrepreneurs to invest in the brand, ensuring consistency in product quality and customer experience across various locations. This scalability has fueled the company’s growth and market reach;
- Wide Menu Variety: Dunkin’ Donuts offers a diverse menu that appeals to a broad range of customer preferences. In addition to their famous donuts, they provide an extensive selection of breakfast items such as sandwiches, bagels, muffins, and croissants. They also offer a variety of beverages, including coffee, espresso drinks, iced coffee, teas, and frozen beverages. This wide menu variety allows customers to find something they enjoy and increases the likelihood of repeat visits;
- Convenient Accessibility: Dunkin’ Donuts has a widespread presence, with thousands of stores located in various regions globally. This accessibility makes it convenient for customers to find a Dunkin’ Donuts location nearby. Additionally, many stores have drive-thru service, allowing customers to quickly grab their favorite items on the go. The combination of accessible locations and drive-thru service enhances convenience for busy customers and contributes to the brand’s popularity.
Dunkin’ Donuts Weaknesses
- Dependency on Franchisees: Dunkin’ Donuts operates primarily through a franchise model, with franchisees responsible for individual store operations. While this model enables rapid expansion, it also poses challenges in terms of maintaining consistent brand standards and customer experiences across all locations. Variations in service quality or store management among different franchisees can impact the overall brand perception;
- Regional Concentration: Dunkin’ Donuts’ presence is heavily concentrated in specific regions, particularly the Northeastern United States. This regional concentration leaves the company more vulnerable to economic downturns or shifts in consumer preferences within those areas. Expanding and establishing a stronger presence in other regions or internationally may be crucial for long-term growth and diversification;
- Perception as Fast Food: Despite efforts to position itself as a quick-service restaurant focusing on beverages and breakfast, Dunkin’ Donuts is still often perceived as a fast-food chain. This perception may deter health-conscious customers or those seeking healthier food options, as fast-food chains are often associated with less healthy menu choices;
- Vulnerability to Commodity Price Fluctuations: As a coffee-focused brand, Dunkin’ Donuts is exposed to fluctuations in the price of coffee beans and other commodities used in its products. Changes in commodity prices, such as increases in coffee bean costs, can impact the company’s profitability and pricing strategies.
Dunkin’ Donuts Opportunities
- Menu Expansion and Innovation: Dunkin’ Donuts can explore opportunities to expand and diversify its menu further. By introducing new food items, snacks, and beverages, the company can attract new customers and cater to evolving consumer preferences. Innovations such as plant-based options, healthier menu choices, and trendy flavors can help differentiate Dunkin’ Donuts and stay relevant in a competitive market;
- International Expansion: While Dunkin’ Donuts has a global presence, there are still opportunities for further international expansion. The company can enter new markets and leverage its brand recognition to gain market share. Expanding into emerging markets with growing coffee consumption and demand for quick-service dining options can contribute to long-term growth;
- Delivery and Takeout Services: The growing demand for food delivery and takeout presents an opportunity for Dunkin’ Donuts to expand its services. By partnering with third-party delivery platforms or developing its own delivery infrastructure, the company can reach customers who prefer the convenience of having their favorite Dunkin’ Donuts products delivered to their doorstep or picked up on the go.
Dunkin’ Donuts Threats
- Intense Competition: The quick-service restaurant and coffee industry is highly competitive, with numerous established players and new entrants vying for market share. Competitors such as Starbucks, McDonald’s, Tim Hortons, and local/regional coffee shops pose a threat to Dunkin’ Donuts’ customer base, brand loyalty, and market positioning;
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Consumer preferences and trends can change over time, posing a threat to Dunkin’ Donuts if the company fails to adapt. For example, the increased demand for healthier food options, organic ingredients, and sustainable practices may lead some customers to choose alternatives that better align with their preferences. Failure to meet changing consumer expectations can result in a loss of market share;
- Health and Wellness Concerns: Rising awareness of health and wellness issues can impact Dunkin’ Donuts’ sales, particularly with regard to sugary and high-calorie products. Consumers are increasingly mindful of their dietary choices and may opt for healthier alternatives or reduce their consumption of indulgent treats like donuts. Dunkin’ Donuts must address these concerns by offering healthier menu options and transparent nutritional information to retain health-conscious customers.
Conclusion
Dunkin’ Donuts’ franchise-based business model has been a crucial driver of its success and growth. Dunkin’ Donuts has created a mutually beneficial relationship through the contractual agreements with franchisees. Franchisees gain access to the Dunkin’ Donuts brand, trademarks, and operating systems, enabling them to leverage a recognized and trusted name in the industry.
However, like any business model, there are challenges that Dunkin’ Donuts must navigate. Maintaining consistent brand standards across a vast network of franchisees, addressing changing consumer preferences, and managing the complexities of franchisee relationships require ongoing efforts and strategic decision-making.

