The Burger King business model focuses on selling its signature fast food products and providing a unique dining experience. Strategically segmenting its market allows Burger King to tailor its menu offerings, marketing strategies, and store designs to meet different customer groups’ distinct preferences and requirements.
Burger King’s value proposition revolves around offering a diverse range of high-quality, quick-service food options. The company aims to provide customers with delicious, convenient meals that satisfy their cravings while maintaining a commitment to quality ingredients and food preparation. This commitment extends to accommodating different dietary preferences, such as introducing vegetarian and plant-based options.
Among other factors, this company’s business model involves technological innovations, strategic partnerships, and a global franchise network.
Contents
A brief history of Burger King
Burger King, one of the world’s largest fast-food chains, has a rich history dating back to its founding in 1954. The company was established by James McLamore and David Edgerton in Miami, Florida, USA. Inspired by the success of the McDonald’s restaurant concept, McLamore, and Edgerton aimed to create a similar fast food experience but with a unique twist.
The first Burger King restaurant opened in Miami in 1954, offering flame-grilled burgers, a signature cooking method that would become synonymous with the brand. This distinctive approach to burger preparation sets Burger King apart from its competitors, giving the company a competitive edge.
In the following years, Burger King grew significantly, expanding its presence through franchising. The company’s success caught the attention of the Pillsbury Company, which acquired Burger King in 1967. Under Pillsbury’s ownership, Burger King experienced a period of rapid expansion, both domestically and internationally, with new restaurants opening across the United States and various countries worldwide.
Historically, Burger King has introduced several iconic menu items, such as the Whopper, a flame-grilled hamburger that quickly became a fan favorite. The company has also been known for its marketing campaigns, including memorable slogans like “Have It Your Way” and the popular “The King” character, which helped build brand recognition and customer loyalty.
Over the years, Burger King went through various ownership changes and corporate restructuring. In 2002, private equity firm 3G Capital acquired the fast food chain for about $11 billion. Under new ownership, the major fast-food restaurant underwent further expansion and strategic initiatives, including menu diversification and international market development.
In 2014, Burger King merged with the Canadian-based Tim Hortons, forming Restaurant Brands International (RBI), which became the parent company of both brands. The merger gave the fast-food giant access to new markets and resources for global growth.
Today, Burger King operates thousands of restaurants worldwide, serving a diverse menu that includes flame-grilled burgers, chicken sandwiches, salads, and breakfast items. The company continues to innovate and adapt to changing consumer preferences while maintaining its commitment to delivering high-quality, customizable, fast food experiences.
Who Owns Burger King
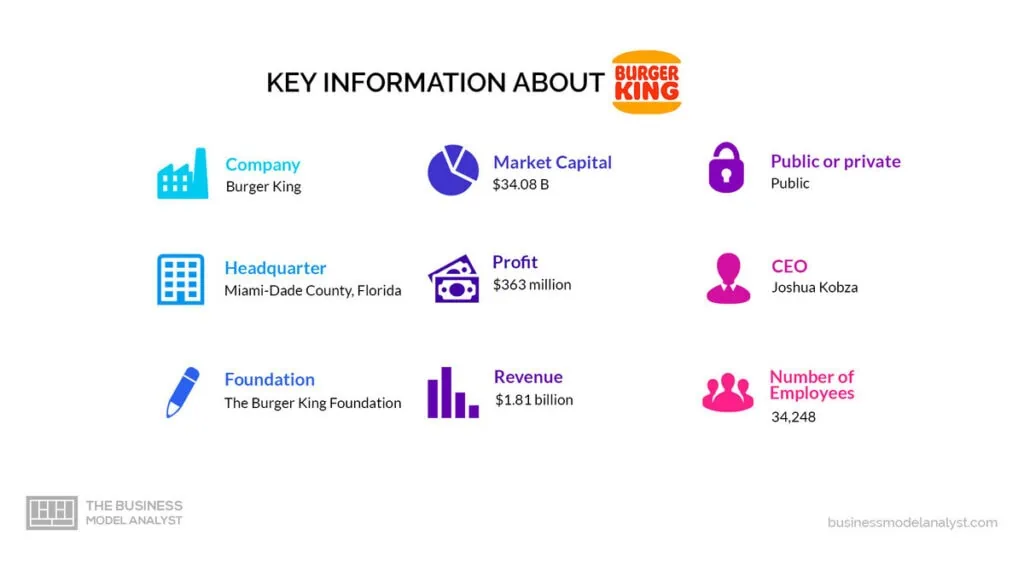
Restaurant Brands International (RBI) owns Burger King. RBI, headquartered in Toronto, Canada, is a publicly-traded company listed on the New York Stock Exchange and the Toronto Stock Exchange. It’s one of the largest fast food companies in the world, with a strong portfolio of brands that includes Burger King, Tim Hortons, and Popeyes Louisiana Kitchen.
Burger King Mission Statement

The Burger King mission statement is “to offer reasonably priced quality food served quickly in attractive, clean surroundings.”
How Burger King works
Burger King works as a globally renowned fast-food chain, serving millions of customers worldwide. Just about all of Burger King’s operations revolve around providing a satisfying dining experience.
Behind the scenes, Burger King operates through a franchise model. Independent franchisees own and operate individual Burger King restaurants, ensuring a widespread presence across the globe.
These franchisees undergo a rigorous selection process, meeting Burger King’s requirements for financial stability and operational competence. Once approved, franchisees receive support from Burger King in various areas, such as restaurant design, marketing campaigns, and ongoing training.
With that said, Burger King operates with a customer-centric approach, offering a diverse menu, convenient ordering options, and a commitment to quality and cleanliness.
How Burger King makes money
Sale of burgers and other fast foods
Perhaps the most significant contributor to Burger King’s revenue comes from the sales generated by its restaurants. Customers who visit Burger King locations and purchase food and beverages earn income from these transactions.
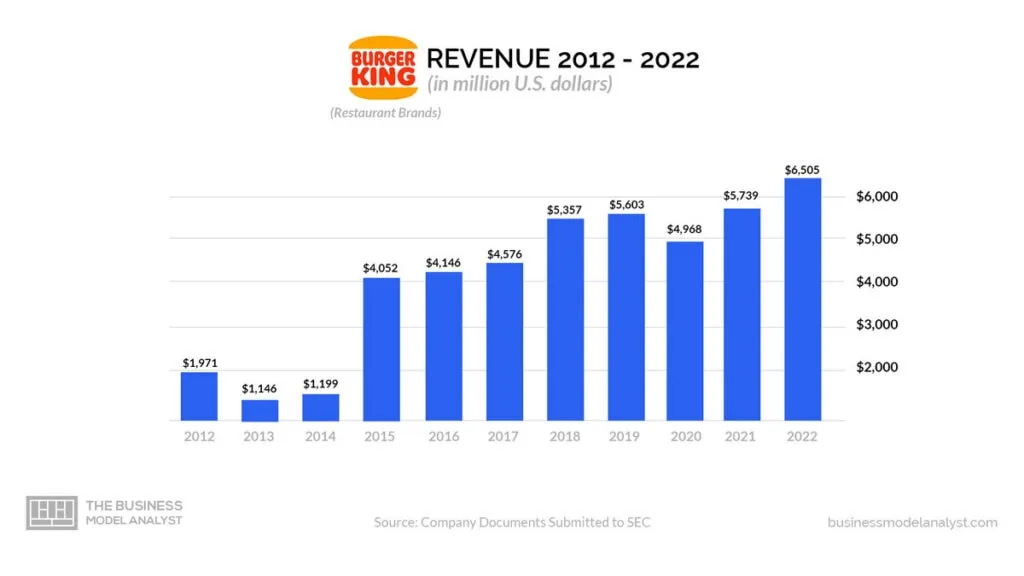
In 2020 alone, Burger King generated about $4.9 billion in revenue, with food sales contributing approximately 50% of the company’s revenue.
Franchise fees, royalties, and property income
Burger King operates primarily under a franchise model, wherein independent franchisees own and operate individual Burger King restaurants. As part of this arrangement, this company collects franchise fees from franchisees when they join the system. These fees cover expenses related to restaurant setup, training, and ongoing support provided by Burger King.
Additionally, Burger King earns ongoing royalties from its franchisees. These royalties are typically a percentage of the franchisee’s sales and serve as a recurring income stream for Burger King, reflecting the brand’s value and ongoing support provided to its franchisees.
Burger King owns about 19,000 restaurants, which are often leased to franchisees. In 2020 alone, Burger King generated about $4.9 billion in revenue, with franchises and property income contributing approximately 50% of the company’s revenue.
Product licensing and merchandising
Burger King has extended its brand beyond the restaurant setting by licensing its name and trademarks for various products and merchandise. This includes partnerships with companies to create and sell Burger King-branded products such as sauces, dressings, snacks, and promotional items.
This revenue is generated through licensing agreements and the sale of these licensed products, expanding the reach of the Burger King brand and providing an additional revenue stream.
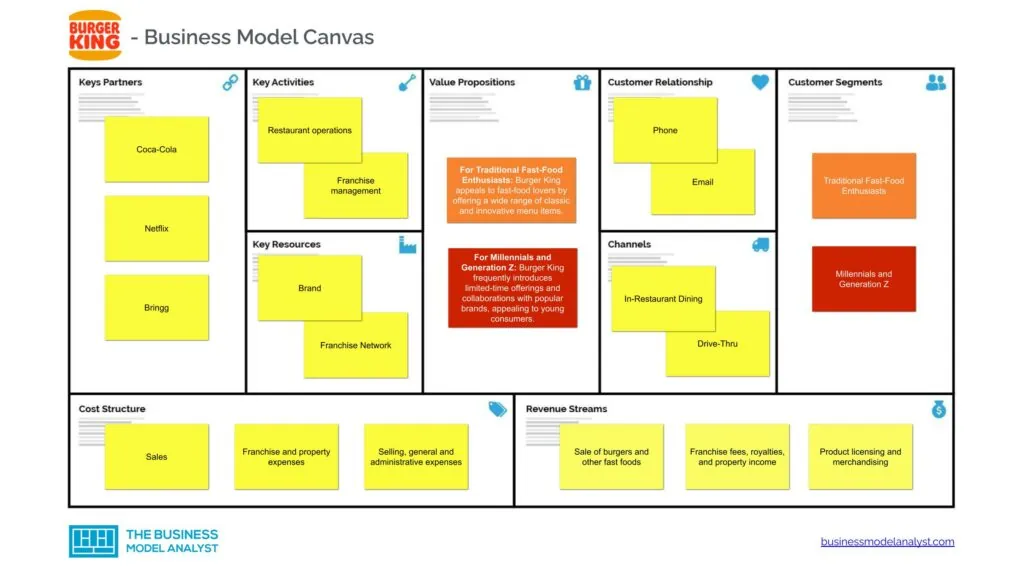
Burger King Business Model Canvas
The Burger King Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
Burger King Customer Segments
Burger King’s customer segments consists of the following:
- Traditional Fast-Food Enthusiasts: This segment comprises customers drawn to Burger King’s classic, no-frills fast-food offerings. These individuals appreciate the brand’s legacy and value affordability, speed, and convenience. Burger King’s wide range of signature flame-grilled burgers, fries, and milkshakes satisfies their cravings for indulgent, familiar comfort food;
- Millennials and Generation Z: These tech-savvy, socially conscious customers are attracted to brands that align with their values and preferences. Burger King has engaged this segment through innovative marketing campaigns and digital initiatives;
- Vegetarians and Vegans: To supply the increasing demand for plant-based options, Burger King introduced the Impossible Whopper and the Rebel Whopper. These offerings appeal to vegetarians and vegans who seek meat-free alternatives without compromising taste;
- Value Seekers: In today’s economic climate, customers seek affordable options without sacrificing quality. Burger King’s value menu, promotional offers, and combo meals supply this segment by providing substantial meals at reasonable prices.
Burger King Value Propositions
Burger King value propositions consist of:
- For Traditional Fast-Food Enthusiasts: Burger King appeals to fast-food lovers by offering a wide range of classic and innovative menu items. From their iconic flame-grilled burgers to their crispy chicken sandwiches and delicious sides, Burger King provides a diverse and indulgent menu for those seeking a satisfying fast-food experience;
- For Millennials and Generation Z: Burger King frequently introduces limited-time offerings and collaborations with popular brands, appealing to young consumers. By constantly innovating its menu, Burger King captures the interest of young customers looking for new and intriguing food choices;
- For Vegetarians and Vegans: Burger King provides a value proposition for those seeking meat-free options without compromising on taste. Burger King recognizes the increasing demand for plant-based options and has made efforts to supply the needs of vegetarian and vegan customers;
- For Value Seekers: Burger King provides customers with busy lifestyles by offering quick service and convenient meal options at affordable prices. With their drive-thru and mobile ordering capabilities, customers can easily enjoy a promotional offer and grab a combo meal on their way to work, during a busy day, or when they’re short on time.
Burger King Channels
Here are the various channels through which you can access Burger King:
- In-Restaurant Dining
- Drive-Thru
- Mobile App
- Website
- Third-party service providers
Burger King Customer Relationships
Here are ways to get in touch with the customer support team at Burger King:
- Phone
- Online Contact Form
- Social Media
- Postal Mail
Burger King Revenue Streams
Here are Burger King’s revenue streams:
- Sale of burgers and other fast foods
- Franchise fees, royalties, and property income
- Product licensing and merchandising
Burger King Key Resources
Here are some of Burger King’s key resources:
- Brand: Burger King’s well-established brand, recognized globally, is a valuable intangible asset. The brand represents quality, convenience, and its signature flame-grilled taste;
- Franchise Network: Burger King’s extensive network of franchisees is a crucial resource. These independent operators invest in and operate Burger King restaurants, expanding the brand’s reach and driving revenue;
- Intellectual Property: Burger King’s intellectual property includes trademarks, logos, and menu items that are protected and recognized by customers worldwide. This intellectual property safeguards the distinctiveness and market positioning of the brand;
- Supply Chain: The efficient supply chain is critical to ensure the availability of fresh ingredients sourced from approved suppliers for Burger King restaurants globally. This resource helps maintain the quality and consistency of the menu offerings;
- Restaurant Infrastructure: Burger King’s physical infrastructure, including its restaurant locations, kitchen equipment, and seating areas, is a vital asset. These facilities provide a platform for the company to serve its customers and generate revenue;
- Technology and Digital Platforms: The adoption of technology and digital platforms has become increasingly important in the fast food industry. Burger King utilizes digital tools, such as mobile apps and online ordering systems, to enhance customer experience and drive sales;
- Marketing and Advertising: Burger King’s marketing and advertising campaigns are essential resources for brand promotion and attracting customers. Strategic marketing initiatives help drive sales and maintain a competitive edge;
- Financial power: The financial resources, including capital investments and financial reserves, play a crucial role in Burger King’s operations. These resources support new restaurant openings, innovation, marketing activities, and overall business growth.
Burger King Key Activities
Here are some of the main activities at Burger King:
- Restaurant operations
- Franchise management
- Menu development
- Supply chain management
- Marketing and advertising
- Quality assurance and food safety
- Employee training and development
- Community engagement and corporate social responsibility
Burger King Key Partners
Here are some of Burger King’s main partners:
- Coca-Cola
- Netflix
- Bringg
- Giants Gaming
- Doritos
- Robinhood
Burger King Cost Structure
According to Burger King’s financial statements, here is a brief overview of Burger King’s cost structure:
- Cost of sales, including the purchase of raw materials, transport, and other direct expenses related to sales;
- Franchise and property expenses;
- Selling, general and administrative expenses such as sales commissions, advertising costs, executive salaries, office rent, legal fees, and employee training expenses.
Burger King Competitors
- McDonald’s: As an industry titan, McDonald’s stands out as Burger King’s primary competitor. Many people believe McDonald’s has the best burger and fries compared to other fast food restaurants. With a vast global presence, McDonald’s has established a strong brand identity and offers a diverse menu that appeals to a broad customer base;
- Wendy’s: Wendy’s, known for its square-shaped burgers, is another major contender. With a focus on fresh ingredients and bold flavors, Wendy’s positions itself as a higher-quality fast food option, competing directly with Burger King’s offerings;
- KFC: Kentucky Fried Chicken (KFC) specializes in fried chicken and competes with Burger King through its expansive menu of chicken-based products. KFC’s strong brand recognition and unique flavor profiles make it a formidable rival in the fast-food landscape;
- Subway: Although primarily known for its submarine sandwiches, Subway has become a notable competitor to Burger King, especially in the quick-service restaurant segment. Subway’s emphasis on healthier choices and customization options sets it apart from traditional burger-focused chains;
- Taco Bell: Taco Bell competes with Burger King through its Mexican-inspired menu offerings, attracting customers seeking a different flavor profile. With a focus on affordability and innovative limited-time offerings, Taco Bell presents a formidable challenge to Burger King’s market share;
- Chick-fil-A: While primarily concentrated in the United States, Chick-fil-A has gained substantial popularity and poses a significant threat to Burger King. Known for its chicken sandwiches and strong customer service, Chick-fil-A has cultivated a loyal following and competes directly in the fast food space;
- In-N-Out Burger: Although geographically limited primarily to the western United States, In-N-Out Burger has gained a cult-like following. Its emphasis on freshness, simplicity, and secret menu items provides unique competition to Burger King in certain regions.
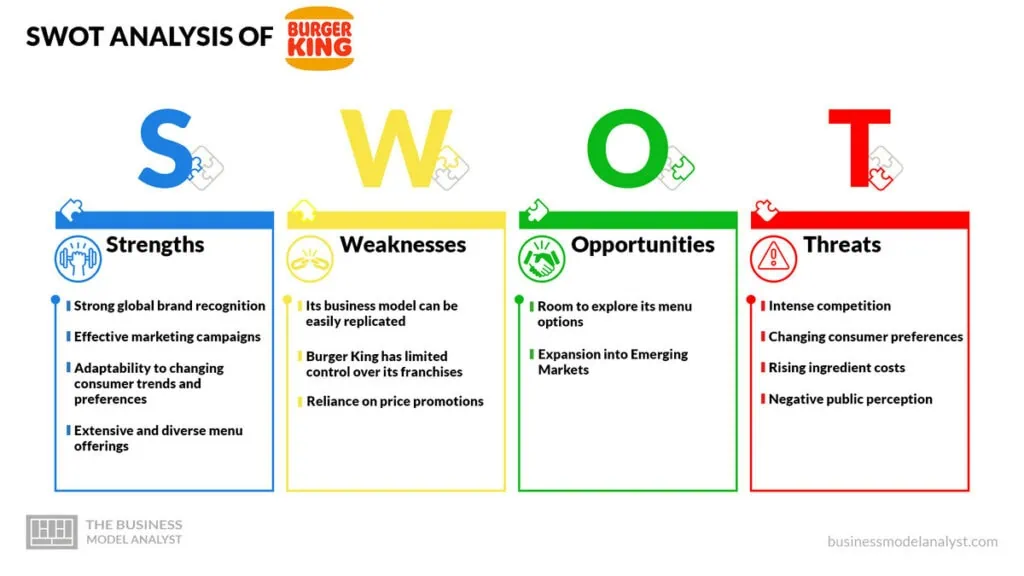
Burger King’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT analysis of Burger King:
Burger King Strengths
- Strong global brand recognition: Burger King has established a strong brand reputation that resonates with consumers around the world. The brand has successfully crafted a distinct identity that sets it apart from its competitors;
- Effective marketing campaigns: Burger King has demonstrated strength in creating effective marketing campaigns and establishing brand partnerships that generate significant consumer interest. This ability to capture the target audience’s attention and create a buzz around their products and promotions has been monumental for the brand’s success;
- Adaptability to changing consumer trends and preferences: One aspect of Burger King’s adaptability is its responsiveness to shifts in dietary preferences. In recent years, there has been a growing demand for plant-based alternatives among consumers. For instance, Burger King recognized this trend and introduced the “Impossible Whopper,” a plant-based burger option that closely mimics the taste and texture of their iconic Whopper;
- Extensive and diverse menu offerings: Burger King’s strength lies in its extensive and diverse menu offerings, a tantalizing array of options designed to cater to the varying preferences of its customers. From flame-grilled burgers to chicken sandwiches, salads, and sides, Burger King goes the extra mile to ensure there’s something for everyone.
Burger King Weaknesses
- Its business model can be easily replicated: Burger King’s business model, while successful, can be imitated by competitors. This imitability poses a weakness for the company. The fast-food industry is known for its fierce competition, with numerous players vying for market share;
- Burger King has limited control over its franchises: While franchising can be an effective business model for expansion, it also comes with specific challenges. Burger King grants considerable autonomy to its franchisees, allowing them to make local decisions and tailor their operations to the specific market. However, this decentralized approach can sometimes lead to inconsistencies in quality, service, and overall customer experience;
- Reliance on price promotions: Burger King has been known for its heavy reliance on price promotions and discounting strategies to attract customers. While these tactics can drive short-term sales, they may erode profitability and harm the brand’s image in the long run. Overdependence on such strategies may also make it challenging for the company to maintain a premium positioning or command higher product prices.
Burger King Opportunities
- Room to explore its menu options: Burger King can continue to explore menu innovation by introducing new and unique products. This includes developing plant-based options, expanding their vegetarian and vegan offerings, and incorporating global flavors to cater to diverse consumer preferences;
- Expansion into Emerging Markets: Burger King can target emerging markets with a growing middle class and an increasing appetite for fast food. This includes countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, which offer untapped opportunities for expansion.
Burger King Threats
- Intense competition: Burger King faces significant competition from fast-food chains like McDonald’s, Wendy’s, and Subway. The intense rivalry within the industry can potentially impact market share and profitability;
- Changing consumer preferences: With an increasing emphasis on healthier eating habits, consumers are shifting towards options that offer more nutritional value. This trend poses a threat to Burger King’s traditional menu, which primarily focuses on indulgent, fast-food options;
- Rising ingredient costs: Burger King heavily relies on various ingredients, including meat, vegetables, and condiments. Fluctuations in commodity prices can impact the company’s profitability and pricing strategy, leading to potential cost pressures;
- Negative public perception: Fast-food chains, including Burger King, often face criticism for their impact on public health, environmental sustainability, and labor practices. Heightened awareness and scrutiny from consumers, advocacy groups, and regulatory bodies can create reputational challenges for the company.
Conclusion
Burger King has disrupted the traditional fast food industry by reimagining the dining experience for customers while focusing on quality and affordability. By capitalizing on its strengths, Burger King has established a strong brand identity, a diverse menu, and a commitment to customer satisfaction.
Growth opportunities abound as Burger King looks to the future. The company’s focus on expanding its franchise network allows for rapid market penetration in established and emerging markets. Burger King is well-positioned to capture a growing market segment and continue to thrive in the years to come.

