Is Instacart Profitable? Despite initial years of unprofitability, Instacart achieved its first profitable month in April 2020 during the coronavirus pandemic (eventually raking in $50 million in profit that year).
While the company is somewhat secretive concerning its profits, it did report a positive net income of over $100 in the fourth quarter of 2022, before taking into account taxes, depreciation, interest, and so on. This is strongly tied to the 39% growth the company saw in overall revenue in 2022.
While Instacart experienced significant growth and attracted substantial investment during its early years, it also struggled to achieve profitability. The company faced challenges such as high operational costs, intense competition, and the need to build and maintain a complex logistics network.
Let’s examine how these factors affected the profitability of the grocery delivery giant and how it rapidly grew to become one of the leading players in the online grocery delivery industry.
Contents
Timeline of Instacart’s Financial Growth and Funding
Here is a chronological list of significant events in Instacart’s history, arranged by year up until September 2021:
2012:
- Instacart is founded by Apoorva Mehta, Max Mullen, and Brandon Leonardo in San Francisco, California;
- The company launches its grocery delivery service, initially serving customers in the Bay Area.
2013:
- Instacart expands its services to Chicago, Boston, and Washington, D.C.;
- The company raises $8.5 million in a Series A funding round.
2014:
- Instacart expands to additional cities, including Los Angeles, New York City, and Philadelphia;
- The company raises $44 million in a Series B funding round.
2015:
- Instacart launches a new service called Instacart Express, a subscription-based membership that offers free deliveries for a monthly or annual fee;
- The company expands into Canada, starting with Toronto.
2016:
- Instacart partners with significant grocery chains, including Costco, Publix, and Wegmans, to expand its offerings and coverage;
- The company raises $220 million in a Series C funding round.
2017:
- Instacart introduces an on-demand service called Instacart Express Membership, allowing customers to order groceries without a subscription;
- The company forms partnerships with more retailers, including Albertsons, Kroger, and CVS.
2018:
- Instacart announces a partnership with Walmart to offer same-day delivery from select Walmart stores;
- The company raises $600 million in a Series E funding round, led by D1 Capital Partners.
2019:
- Instacart expands its operations internationally by launching in its first non-North American market, the United Kingdom;
- The company partners with Sephora to offer beauty and cosmetics delivery.
2020:
- The COVID-19 pandemic leads to a surge in demand for online grocery delivery services, benefiting Instacart’s business;
- Instacart becomes profitable for the first time, reportedly in April;
- The company raises $225 million in a funding round, valuing it at $13.7 billion.
2021:
- Instacart acquires the e-commerce platform Unata to enhance its digital shopping capabilities;
- The company raises $265 million in a funding round, increasing its valuation to $39 billion;
- Instacart files for an initial public offering (IPO) but delays the plan amid market volatility.
2022:
- The company cut its internal valuation to $10 billion amid widespread market volatility and uncertainty surrounding many tech startups;
- The company also further delayed its plans for an IPO due to the unfavorable market environment.
2023:
- The company’s valuations improved to $13 billion amid solid growth in terms of gross transaction volume, revenue, and gross profits.
Instacart Financial Performance: Revenues, Expenses, and Profits
Instacart has been showing strong growth in terms of gross sales, with the company posting grocery sales figures worth $26.07 billion and $30.60 billion in 2021 and 2022, respectively.
Instacart Revenue
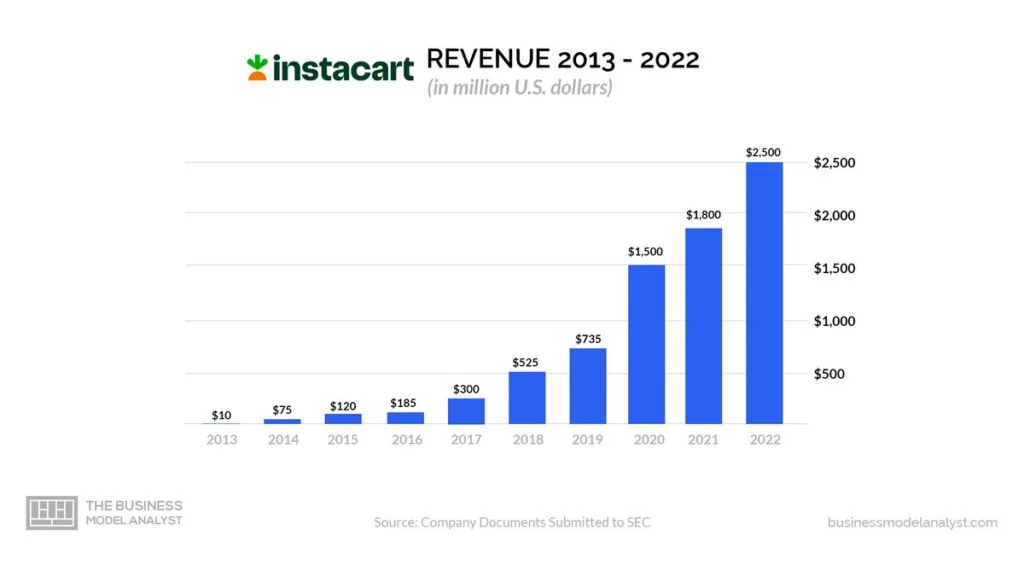
From the latest available information, Instacart reportedly generated $2.5 billion in revenue in 2022, a significant increase from the $1.8 billion and $1.5 billion it generated in revenue in 2021 and 2020, respectively. This increase in revenue is also supported by an 80% jump in Q4 profits on the back of a 50% rise in revenue during that same quarter.
Relation Year/Revenue in USD millions:
- 2013: $10
- 2014: $75
- 2015: $120
- 2016: $185
- 2017: $300
- 2018: $525
- 2019: $735
- 2020: $1,500
- 2021: $1,800
- 2022: $2,500
Advertising accounted for 30% of their revenue in 2022, totaling about $740 million and representing a 30% year-on-year increase from 2021. Instacart charges customers a delivery fee and service fee for each order placed through its platform.
Instacart also offers a subscription-based membership program called Instacart Express. Members pay a monthly or annual fee to receive free delivery on eligible orders over a certain amount.
Instacart partners with various retailers, such as grocery stores and other businesses, to provide their customers with online shopping and delivery services. These partnerships involve revenue-sharing arrangements, where Instacart earns a percentage of each transaction processed through its platform.
Instacart collects extensive data on consumer behavior, purchase patterns, and preferences. It analyzes this data to provide insights and analytics to its retail partners. Instacart monetizes this service by charging for access to its data and analytics tools.
Instacart Expenses
Instacart is a privately listed company and does not openly disclose its expenses. However, Instacart incurs significant expenses in workforce costs, technology and infrastructure, marketing and advertising, logistics, customer support, insurance and liability, regulatory compliance, research and development, and administrative overhead.
Efficiently managing these expenses is crucial for profitability. Balancing fair compensation for the workforce while optimizing costs is essential. Strategic investments in technology and infrastructure ensure seamless user experiences.
Effective marketing strategies should be balanced with return on investment. Efficient logistics management minimizes costs.
Investments in customer support enhance satisfaction and loyalty. Adhering to regulations protects the company’s reputation. Research and development efforts drive continuous improvement. Managing administrative and overhead costs efficiently helps optimize resources.
By analyzing and optimizing these expenses, Instacart can meet customer expectations, adapt to market dynamics, and maintain profitability as a leading online grocery delivery service.
Instacart Profit
While Instacart regularly publishes its profits and losses, the company did report generating $100 million in gross earnings in the fourth quarter of 2022. This was attributed to an overall growth in gross transaction volume to $29 billion, representing a 16% increase from the preceding year.
Potential for Profitability
Strategies to Profitability
To maintain profitability, Instacart can adopt several strategies that focus on improving operational efficiency, expanding revenue streams, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Firstly, optimizing its logistics and delivery operations can reduce costs by streamlining routes and improving resource allocation. This can be achieved by using advanced algorithms and machine learning to enhance route planning and minimize delivery times.
Secondly, Instacart can diversify its revenue streams by offering additional services such as advertising and partnerships with local businesses. By providing targeted advertising opportunities to brands and collaborating with neighborhood stores for last-mile deliveries, Instacart can generate additional income while leveraging its existing infrastructure.
Thirdly, investing in data analytics and customer relationship management tools can help Instacart better understand customer preferences and behavior. This enables personalized recommendations and targeted promotions, leading to increased customer loyalty and repeat business.
Lastly, fostering strong relationships with its shoppers and incentivizing their performance can improve efficiency and customer satisfaction. Providing training programs, performance bonuses, and recognition can enhance shopper loyalty and productivity, resulting in faster and more accurate deliveries.
Challenges that Instacart faces as a business
Despite its recent success and strong positive growth trend, Instacart still faces some significant challenges to its continued success.
For instance, the online grocery delivery market is highly competitive, with established players like Amazon, Walmart, and local grocery chains launching their delivery services. Increased competition poses a threat to Instacart’s market share and requires the company to continuously innovate and differentiate itself to maintain its competitive edge.
Also, rapidly changing consumer preferences and behaviors means Instacart must adapt to these changes to avoid consumers opting for alternative shopping methods. Likewise, if the demand for online grocery delivery diminishes, Instacart’s growth and profitability could be negatively impacted.
Managing a complex logistics network, coordinating with multiple retailers, and ensuring timely delivery pose operational challenges for Instacart.
Instacart heavily relies on a network of gig economy workers to fulfill customer orders. The classification of these workers as independent contractors has faced scrutiny and legal challenges in some jurisdictions. As Instacart expands its operations, it may encounter regulatory challenges and legal complexities in different jurisdictions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Instacart has made significant strides towards profitability in recent years, culminating in its first profitable month in April 2020 and reporting positive net income in the fourth quarter of 2022.
The company has experienced remarkable revenue growth, with 2022 figures reaching $2.5 billion, driven by increased demand for online grocery delivery services during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Instacart has diversified its revenue streams through advertising partnerships and subscription-based memberships. However, it faces challenges such as intense competition, changing consumer preferences, and managing a complex logistics network.
By implementing strategies to optimize operations, expand revenue streams, and enhance customer satisfaction, Instacart aims to maintain its profitability and continue as a leading player in the online grocery delivery industry.


