The concept of the Instacart business model has been developed around the purpose of simplifying grocery shopping for people who have a busy life because they can choose all their groceries from wherever they may be. Instacart is now the top grocery delivery service in the U.S., valued at over $17 billion.
Contents
A brief history of Instacart
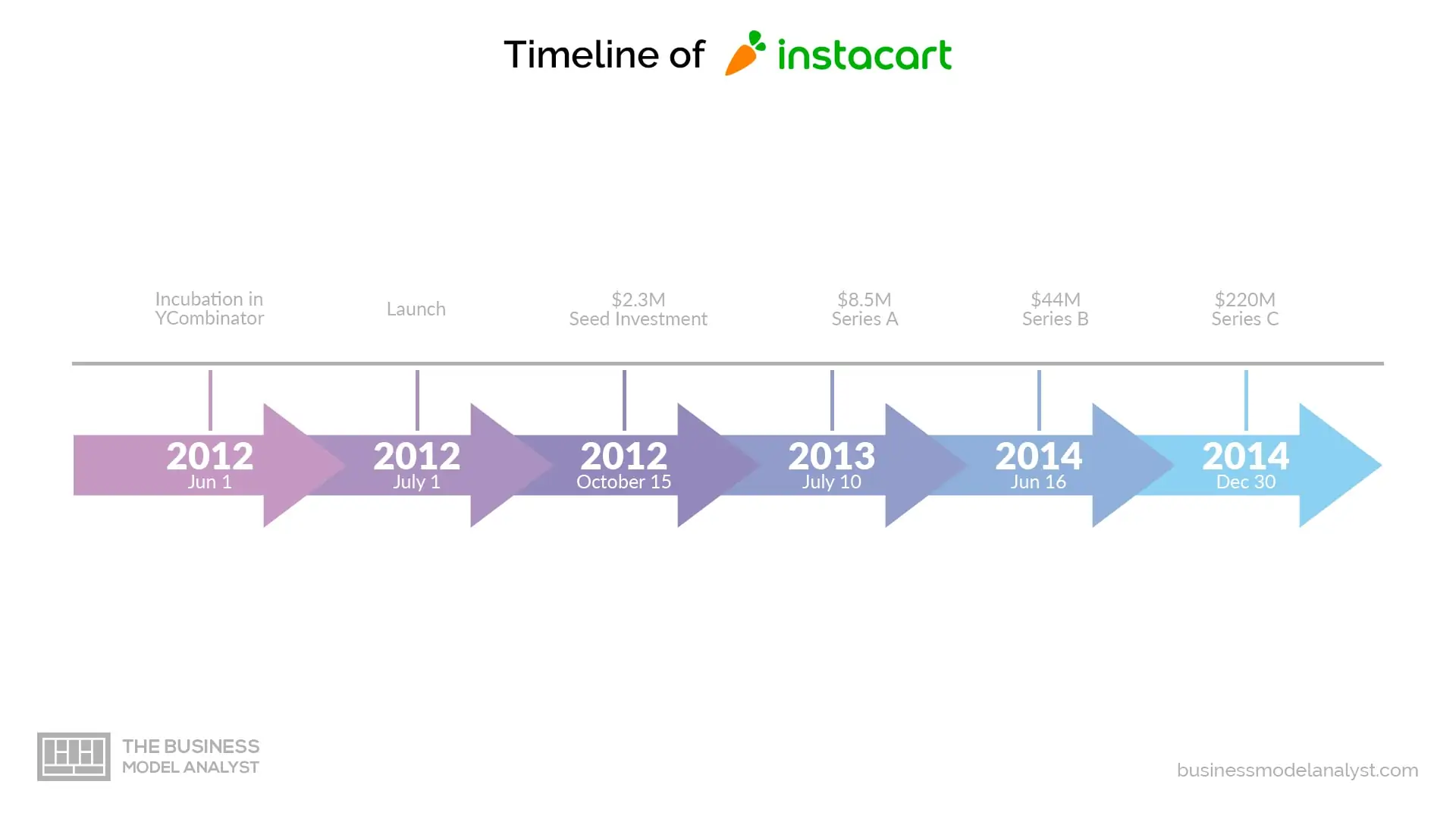
Instacart was founded in 2012 by Apoorva Mehta. Working for Amazon at that time, Mehta saw the need for an app that headed only to grocery shopping. So, that year, he joined the Y Combinator summer batch and obtained his initial funding in order to launch his startup. Five years later, Instacart has already expanded to many cities in the U.S. and arrived in Canada.
In 2018, made some important partnerships with names like Costco and Sam’s Club. The great turning point came with the COVID-19 pandemic, which increased online grocery shopping demand. As a result, 300,000 additional employees were hired. Nowadays, nine years after its foundation, Instacart is operating in over 40,000 stores in more than 5,500 cities in North America, with a network of 300 partner retailers.
Who Owns Instacart
Instacart is owned by Maplebear Inc., its holding group. Instacart’s Founder, Apoorva Mehta, stepped down as the company’s CEO in July 2021, becoming Executive Chairman of the Board. Fidji Simo, a Board member, was appointed as the new CEO since then.
Instacart’s Mission Statement
“To build a world where everyone has access to the food they love and more time to enjoy it together.”
How Instacart makes money
To understand where the money comes from, let us check how Instacart works. First of all, customers access Instacart’s platform via website or app. Whenever an order is placed on the platform, the so-called personal shoppers in proximity will receive a notification of the request. These shoppers are independent contractors, and they receive by delivery made. Once a shopper accepts the request, they drive to the grocery store chosen, pick up the groceries and deliver them to the customer’s address. Now, we can move forward to revenues.

Commissions
Every time an item is sold through Instacart’s platform, the company receives a percentage of the price, according to the agreement made with the retailer. In some cases, Instacart even sells some products at a higher price to increase markup.
Delivery and Service Fees
Delivery fees vary from $3.99 to $9.99. Because Instacart, just like other platforms, such as Uber or Lyft, charges according to the demand and external conditions (such as the weather), the so-called surge pricing. And also due to shipment scheduling. These fees are distributed between the store and Instacart. The service fees get around 5% to 10% of the purchase. Sometimes, there are additional fees, for example, when an order surpasses a certain weight threshold or when there is a bag fee.
Subscription
The company has the Instacart Express. It is a subscription service that ensures unlimited deliveries (or orders above $35), cheaper service fees, and no surge pricing for an annual ($99) or monthly fee ($9.99).
Advertising
Sellers and brands can advertise on the platform, for additional visibility. The price will depend on the categories and search terms. Usually, advertisers set a budget previously, to avoid overspending.
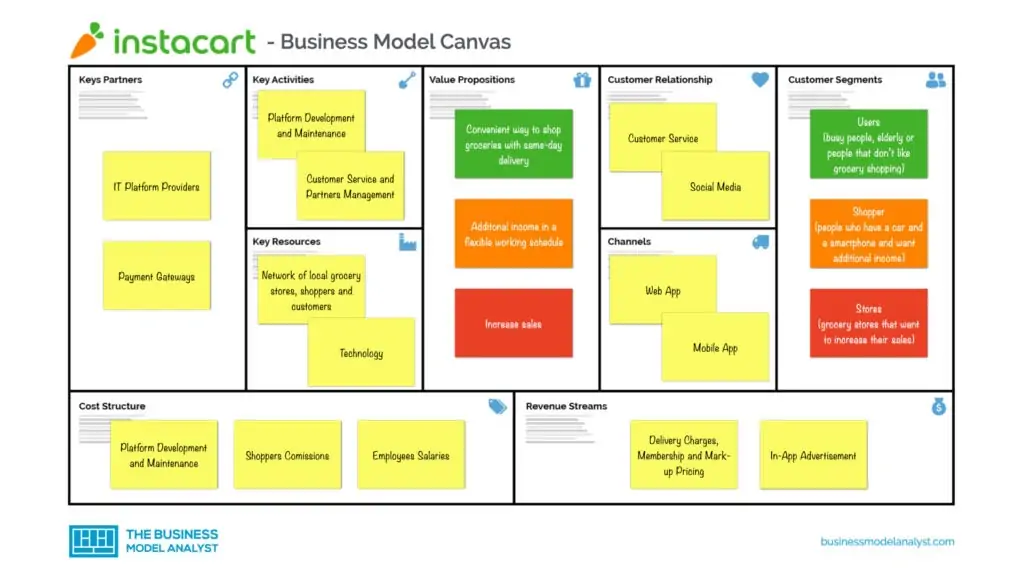
Instacart’s Business Model Canvas
The Instacart Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
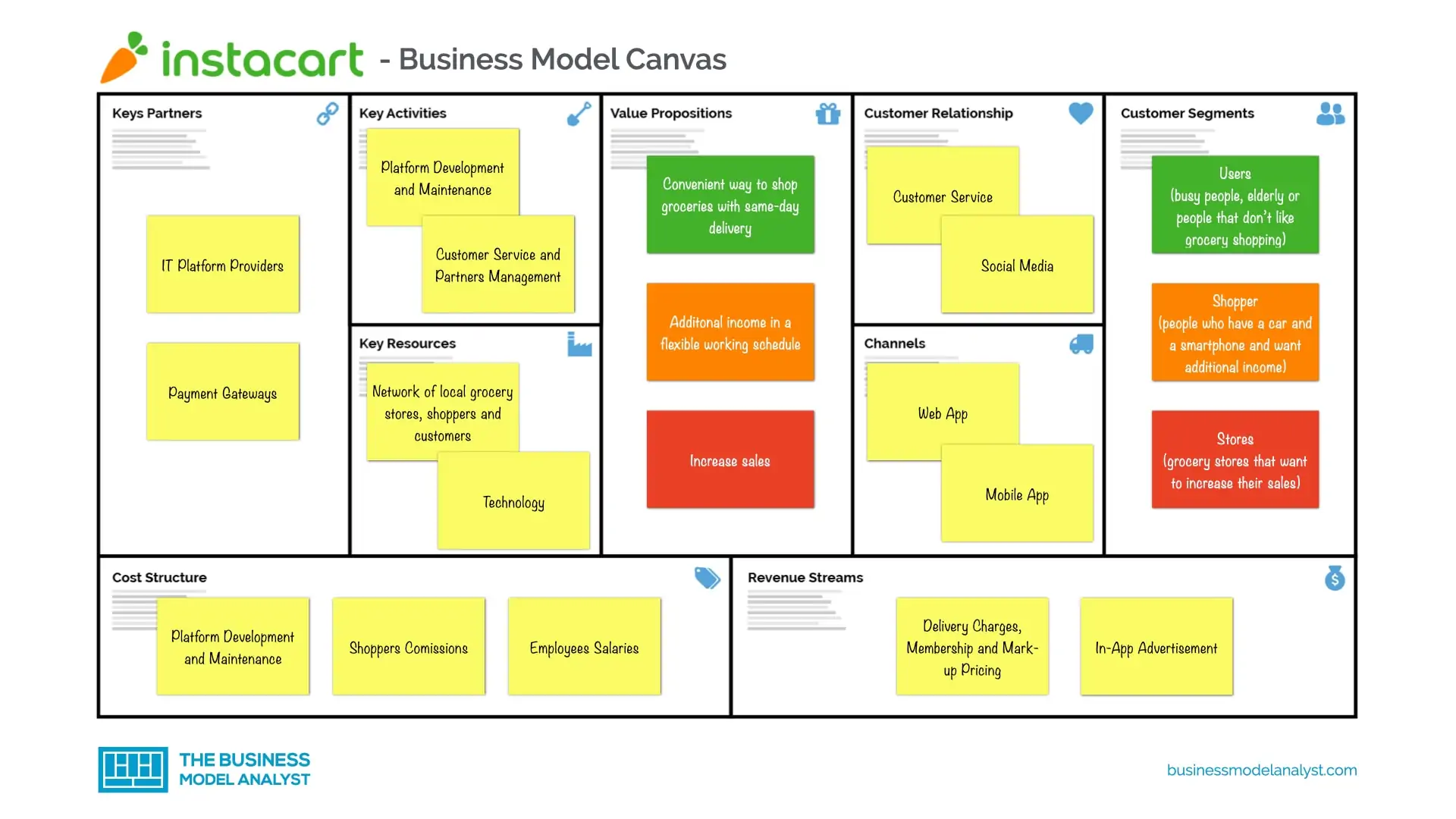
Instacart’s Customer Segments
Instacart’s customer segments consist of:
- Users: People who don’t like shopping, elderly people, people who have a tight schedule;
- Shoppers: People with a smartphone and a vehicle (car or bicycle), people who love shopping, people who need an additional income;
- Stores: The ones that want to increase their sales, and those that want to reach out to more customers.
Instacart’s Value Propositions
Instacart’s value propositions consist of:
- Users: A convenient way to shop for groceries, quick delivery, vast inventory;
- Shoppers: Flexible working schedule, additional income, part-time work;
- Stores: Additional sales, increase in the number of customers.
Instacart’s Channels
Instacart’s channels consist of:
- Website
- App for Android and iOS
- Shoppers
- Press
- Internet marketing
Instacart’s Customer Relationships
Instacart’s customer relationships consist of:
- Customer service
- Social media
- Local stores
- Community
Instacart’s Revenue Streams
Instacart’s revenue streams consist of:
- Commissions,
- Markup overprices
- Delivery fees
- Service fees
- Membership fee
- Ads
Instacart’s Key Resources
Instacart’s key resources consist of:
- Partnership with stores
- Shoppers
- Platform
- Human Resources
Instacart’s Key Activities
Instacart’s key activities consist of:
- Software development
- Platform maintenance
- Payment processing
- Delivery
- Customer service
- Training
- Shoppers management
- Local market management
Instacart’s Key Partners
Instacart’s key partners consist of:
- Shoppers
- Local grocery stores and supermarkets
- IT platform providers
Instacart’s Cost Structure
Instacart’s cost structure consists of:
- Technological maintenance
- Salaries
- Commissions
- Shoppers payment
- Payment processing fees
- Administration and operations
- Marketing
Instacart’s Competitors
- Shipt: Owned by Target, it is available in 300 cities in the USA and partners with great grocery stores such as Costco, CVS, Jewel, Kroger, Office Depot, and Publix;
- Amazon Fresh: Provided by the biggest retailer in the world, but it is available in only 15 cities and just for Amazon Prime members;
- Walmart+: One of the greatest retailers on the planet, perks, and discounts are given uniquely to Walmart members;
- Fresh Direct: Founded in 1999, specialized in delivering goods directly from farmers, artisans, and fishermen. It also delivers beverages, flowers, health and beauty products, and baby items. But the service is limited to six cities;
- Blue Apron: Grocery delivery company focused on providing customers with ingredients and recipes to prepare meals at home.
Instacart’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Instacart:
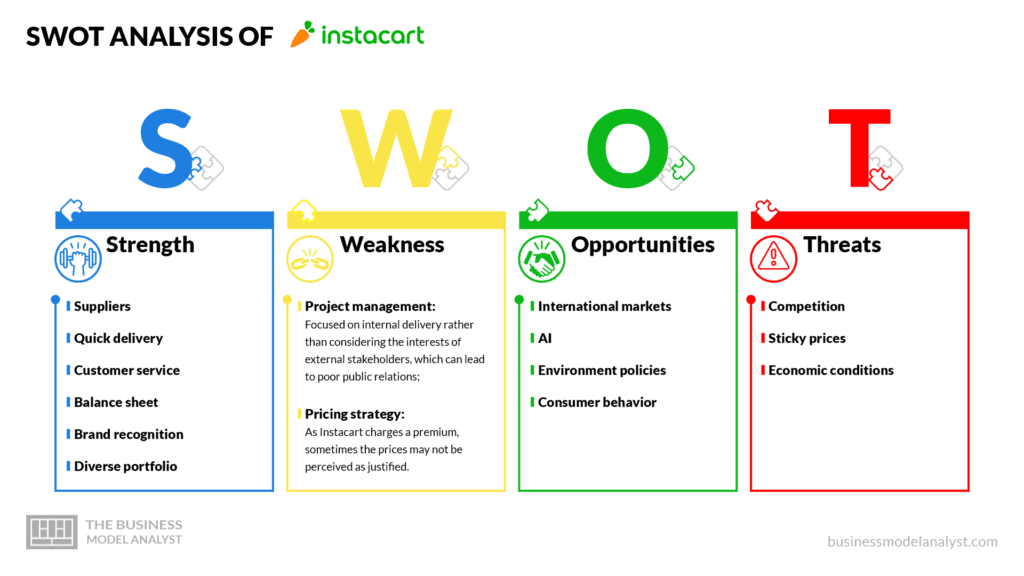
Instacart’s Strengths
- Suppliers: Instacart partners are reliable and trustworthy since they are established stores, including some of the greatest retailers in the country;
- Quick delivery: One can get one’s groceries as quickly as in one hour;
- Customer service: Social media managers provide 24/7 help on the site and social network;
- Balance sheet: The financial situation allows the company to invest in new and diverse projects;
- Brand recognition: Instacart has a brand strong enough to attract new customers regularly;
- Diverse portfolio: The brand portfolio enables to target different segments.
Instacart’s Weaknesses
- Project management: Focused on internal delivery rather than considering the interests of external stakeholders, which can lead to poor public relations;
- Pricing strategy: As Instacart charges a premium, sometimes the prices may not be perceived as justified.
Instacart’s Opportunities
- International markets: Instacart can grow its market share through globalization and the internet;
- AI: Developments in artificial intelligence can help predict consumer demand, making better recommendation engines;
- Environment policies: New policies can ensure more benefits from technology;
- Consumer behavior: Just like it happened with the COVID-19 pandemic, new trends, and consumer habits can promote app usage.
Instacart’s Threats
- Competition: Not only does the amount of competitors keep growing, but also there are names such as Amazon and Walmart, some of the greatest retailers in the world;
- Sticky prices: Instacart operates in an industry where there is a culture of sticky prices, which can jeopardize the pricing that its premium service deserves;
- Economic conditions: Economic issues can affect customers’ spending patterns and purchasing power.
Conclusion
The Instacart business model is based on bringing convenience to people, which is something that may always be present in this field of action. Besides, although the number of competitors keeps growing more and more, as mentioned before, Instacart is still the predominant company in the market of online grocery shopping, and it looks like the rivals are going to eat dust for a while if things keep the way they are.