The Bank of America business model revolves around being a diversified financial services provider, that supplies a broad spectrum of clients, ranging from individuals and small businesses to large corporations and institutions. This model encompasses retail banking services, such as mortgages, credit cards, and savings accounts, along with commercial banking offerings like loans, cash management, and treasury solutions.
The bank also operates in investment banking, handling underwriting and mergers and acquisitions, while its wealth management arm serves high-net-worth individuals with investment and estate planning. This model uniquely positions Bank of America to navigate the intricate financial terrain with agility and precision. However, alongside its strengths, Bank of America’s business model also faces challenges that underscore the dynamic nature of the financial industry.
Contents
A brief history of Bank of America
Bank of America traces its roots back to the Bank of Italy, founded by Amadeo Peter Giannini in 1904 in San Francisco. Giannini’s vision was to provide banking services to immigrants and individuals that traditional banks often overlooked. The bank gained prominence after the 1906 San Francisco earthquake, when Giannini set up a makeshift bank on the city’s streets to provide loans to help rebuild.
Throughout the 1910s and 1920s, the Bank of Italy expanded its services, introducing savings accounts and overdraft protection. In 1928, Giannini merged his institution with the Bank of America, Los Angeles. The resulting entity was officially named the Bank of America in 1930.
The bank embarked on a journey of growth and stability despite the challenges of the Great Depression. The bank’s conservative lending practices enabled it to support public projects like the construction of the Golden Gate Bridge. The post-World War II era saw further expansion, with the introduction of BankAmericard (later Visa) and international ventures.
In 1998, the merger with NationsBank marked a turning point. The bank retained the Bank of America name, becoming a financial powerhouse and one of the largest banks in the United States. However, challenges arose during economic downturns, leading to restructuring efforts in the following years.
The bank’s resilience was tested during the 2008 global financial crisis. It responded by acquiring Merrill Lynch, thereby entering the investment banking and wealth management sectors. Bank of America embraced modern technology by investing in online banking, mobile apps, and digital services, catering to changing customer preferences.
Today, Bank of America stands as a leading global financial institution, offering a comprehensive suite of services encompassing retail and corporate banking, wealth management, investment banking, and more. Its history is one of adaptation, mergers, acquisitions, and technological advancements, shaping the bank into a key player in the modern financial landscape.
Who Owns Bank of America
Bank of America is owned by a variety of shareholders, including institutional investors, company insiders, and the public. The top five shareholders of Bank of America are BlackRock Inc., The Vanguard Group Inc., State Street Corporation, Fidelity Investments, and Rowe Price Group Inc.
Bank of America Mission Statement
Bank of America’s mission statement is “to help make financial lives better by connecting clients and communities to the resources they need to be successful.”

How Bank of America works
Bank of America is a multinational financial institution offering a wide range of banking and financial services. Here’s an overview of how it works:
Retail Banking
Bank of America’s retail banking division serves individual consumers. It offers a variety of financial services, such as savings and checking accounts. Additionally, the bank provides loans, including mortgages to buy homes, auto loans for purchasing vehicles, and personal loans for various needs. Credit cards are also available, allowing customers to make purchases on credit. The bank’s investment products, like certificates of deposit (CDs) and individual retirement accounts (IRAs), help customers grow their savings over time.
Commercial Banking
Bank of America’s commercial banking arm assists businesses of all sizes. This division offers essential services like business loans to provide necessary funds for operational expenses and growth. Lines of credit are available to help businesses manage their cash flow, and merchant services enable them to accept payments from customers through credit and debit cards. Cash management services are provided to optimize financial operations such as payments and liquidity management.
Wealth Management
Bank of America’s wealth management division caters to high-net-worth individuals and institutional clients. The bank offers personalized investment advice and portfolio management to help clients achieve their financial goals. This includes planning for retirement, guiding clients through the complex process of estate planning, and helping them manage and grow their wealth over time.
Global Markets
Bank of America engages in trading, sales, and research of financial instruments. Traders buy and sell assets like stocks, bonds, currencies, and commodities to generate profits. Sales teams work with institutional clients to provide them with insights and opportunities related to these assets. Research analysts provide market insights and recommendations to help clients make informed investment decisions.
Investment Banking
Bank of America’s investment banking arm assists corporations, governments, and financial institutions in strategic financial matters. This includes advising on mergers and acquisitions, where companies combine or acquire others. They also help clients raise capital by issuing stocks or bonds, allowing them to fund their operations and expansion plans. Investment bankers provide guidance on various financial strategies and transactions.
Online and Mobile Banking
Bank of America’s online and mobile platforms provide convenient access to accounts and transactions. Customers can check their account balances, transfer money between accounts, and pay bills using mobile devices. Digital payment options enable customers to make electronic payments to merchants and individuals, reducing their reliance on physical cash.
Branch Network
Bank of America maintains a network of physical branches across various locations. These branches offer face-to-face assistance for customers who prefer in-person interactions. Services include opening new accounts, discussing financial needs with bank representatives, and accessing ATMs for withdrawing cash or checking balances.
Technology and Security
The bank utilizes advanced technology to ensure secure transactions and safeguard customer information. Encryption methods are employed to encode sensitive data, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to access it. Multifactor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring customers to provide multiple forms of verification before accessing their accounts.
Regulatory Compliance
As a financial institution, Bank of America operates within the legal and regulatory framework established by government agencies. Compliance with regulations helps ensure fair practices, protect customer interests, and maintain the financial system’s stability.
How Bank of America Makes Money
Here are the key ways Bank of America generates revenue:
Interest Income
One of the primary sources of revenue for Bank of America is the interest it earns on loans and credit products it provides to customers. This includes interest on mortgages, auto loans, personal loans, credit card balances, and other types of loans. The bank charges borrowers interest on the funds they borrow, and this interest income contributes significantly to its revenue.
Fees and Service Charges
Bank of America charges various fees for its services, such as account maintenance, overdrafts, wire transfers, foreign transactions, and ATM fees for non-customers using their ATMs. These fees add up and contribute to the bank’s revenue.
Investment and Wealth Management Fees
Bank of America provides investment advisory services through its wealth management division and manages client investment portfolios. The bank charges fees based on the assets under management or for specific investment services it provides.
Trading and Market Activities Revenue
Bank of America engages in trading activities through its global markets’ division. It earns revenue by buying and selling financial instruments like stocks, bonds, currencies, and commodities, aiming to profit from market price fluctuations.
Credit Card Revenue
Bank of America issues credit cards to customers and earns revenue through merchant fees, interchange fees, and annual credit card fees. The bank also earns interest on outstanding credit card balances that customers carry from month to month.
Investment Banking Fees
Bank of America’s investment banking division earns fees for providing advisory services in mergers and acquisitions (M&A), underwriting securities offerings (such as initial public offerings), and facilitating other corporate finance transactions.
Treasury and Cash Management Service Fees
The bank offers cash management services to businesses, helping them manage their cash flow and liquidity. Bank of America charges fees for services like managing payments, handling deposits, and optimizing working capital.
Asset Management Fees
Through its asset management services, Bank of America earns fees for managing investment portfolios for institutional clients and individuals. These fees are based on a percentage of the assets under management.
Wealth Management and Financial Planning Fees
The bank’s wealth management division charges fees for providing personalized financial planning and advisory services to high-net-worth individuals and institutional clients.
Insurance Services Revenue
Bank of America offers various insurance products, such as life insurance, homeowners insurance, and auto insurance. The bank earns revenue from selling these insurance products to customers.
Foreign Exchange and International Transactions
Bank of America earns revenue from foreign exchange services, including currency conversion and facilitating international transactions for its clients.
Bank of America Business Model
Let’s take a look at the Bank of America Business Model Canvas below:
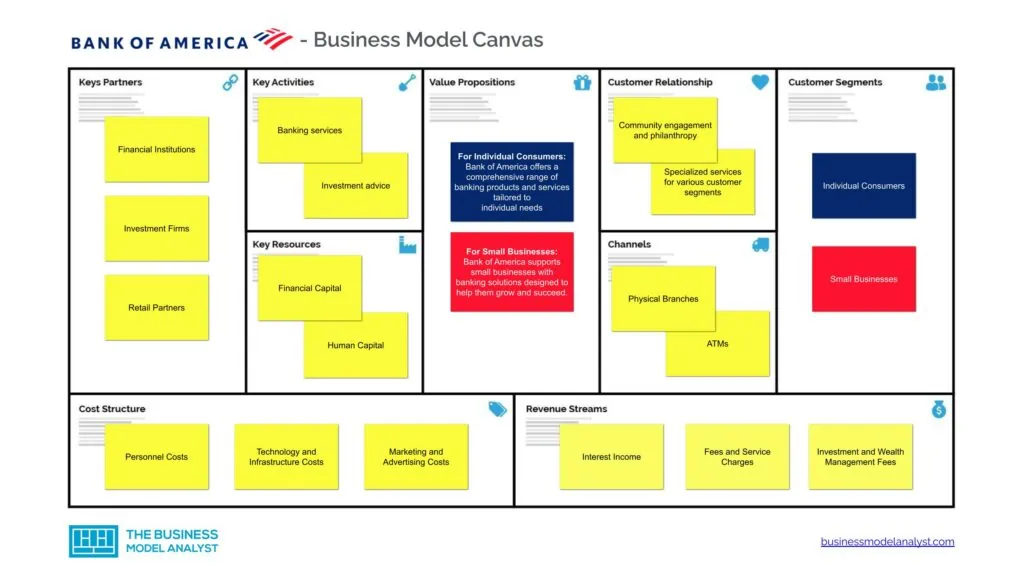
Bank of America Customer Segments
Bank of America’s customer segments consist of:
- Individual Consumers: These are private individuals who utilize Bank of America’s services for personal financial needs. They could be using the bank for their savings accounts, checking accounts, credit cards, and personal loans;
- Small Businesses: Small businesses are privately owned enterprises with relatively few employees and a modest level of revenue. They can range from local shops and restaurants to small consulting firms. An example could be a family-owned bakery or a boutique clothing store;
- Mid-Sized and Large Corporations: These organizations have grown beyond the small business phase and have a significant number of employees and higher revenue. They often operate in multiple locations or even globally. Companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Coca-Cola fall into this category;
- Institutional Clients: Institutional Clients are large entities that engage in substantial financial activities and investments, managing extensive portfolios and assets that impact various sectors of the economy. Examples include government agencies, pension funds, insurance companies, and universities;
- High-Net-Worth Individuals: These are individuals with substantial financial assets and net worth. They typically have investible assets exceeding a certain threshold (such as several million dollars). High-net-worth individuals often have more complex financial needs and may seek specialized financial planning and investment services;
- Investors and Traders: These are individuals or entities that engage in buying and selling financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies to generate profits. Investors usually have a longer-term perspective, while traders focus on shorter-term price movements;
- Digital Banking Users: These are individuals or businesses that conduct their banking activities primarily through digital channels, such as online platforms and mobile apps;
- Mortgage and Homebuying Customers: These are individuals or families seeking to purchase homes and need financing in the form of mortgages. They work with lenders to secure loans for buying real estate;
- Community and Non-Profit Organizations: These groups operate for the betterment of society rather than for profit. They include charities, NGOs, religious organizations, and community development groups. Examples range from organizations providing disaster relief to those promoting environmental conservation.
Bank of America Value Propositions
Bank of America’s value propositions consist of:
- For Individual Consumers: Bank of America offers a comprehensive range of banking products and services tailored to individual needs, including convenient digital banking options, credit cards, personal loans, mortgages, and investment opportunities. The bank focuses on providing accessible and reliable financial solutions to help individuals manage and improve their financial well-being;
- For Small Businesses: Bank of America supports small businesses with banking solutions designed to help them grow and succeed. This includes business banking accounts, lending options, merchant services, cash management tools, and resources for financial management and planning;
- For Mid-Sized and Large Corporations: The bank provides mid-sized and large corporations with a suite of commercial banking services, including loans, treasury solutions, cash management, and global trade services. Bank of America’s value proposition lies in helping corporations manage their finances, optimize cash flow, and navigate complex financial challenges;
- For Institutional Clients: Institutional clients benefit from Bank of America’s global markets division, which offers trading and sales services across various asset classes. The bank’s investment banking arm provides underwriting, mergers and acquisitions advisory, and capital raising services, catering to the financial needs of institutional clients;
- For High-Net-Worth Individuals: Through Merrill Lynch, Bank of America offers high-net-worth individuals personalized wealth management and financial advisory services. The value proposition includes tailored investment strategies, retirement planning, estate planning, and access to a wide range of financial expertise;
- For Investors and Traders: Bank of America’s global markets division serves investors and traders by offering access to trading opportunities in equities, fixed income, currencies, and commodities. The bank’s deep market expertise and trading capabilities are its key value propositions to this segment;
- Digital Banking Users: Bank of America provides digital banking users with convenient and secure online and mobile banking services. The value proposition includes easy access to account information, convenient fund transfers, bill payment options, and the ability to manage finances on the go;
- Mortgage and Homebuying Customers: Bank of America offers mortgage and homebuying customers a wide range of mortgage products, refinancing options, and personalized guidance throughout the homebuying process. The bank’s value proposition lies in helping customers find suitable financing solutions for their homeownership goals;
- Community and Non-Profit Organizations: Bank of America engages with community and non-profit organizations through initiatives, grants, and programs to support social and economic causes. The bank’s value proposition to this segment is centered around fostering positive impact and contributing to the well-being of communities.
Bank of America Channels
Bank of America’s channels consist of:
- Physical Branches
- ATMs
- Online Banking
- Mobile Banking
- Merrill Edge (Online Investment Platform)
- Bank of America Financial Centers
- Business Banking Platforms
Bank of America Customer Relationships
Bank of America’s customer relationships consist of:
- Community engagement and philanthropy
- Specialized services for various customer segments
- Credit and lending services
Bank of America Revenue Streams
Bank of America’s revenue streams consist of:
- Interest Income
- Fees and Service Charges
- Investment and Wealth Management Fees
- Trading and Market Activities Revenue
- Credit Card Revenue
- Investment Banking Fees
- Treasury and Cash Management Service Fees
- Asset Management Fees
- Wealth Management and Financial Planning Fees
- Insurance Services Revenue
- Foreign Exchange and International Transactions
Bank of America Key Resources
Bank of America’s key resources consist of:
- Financial Capital
- Human Capital
- Technological Infrastructure
- Customer Base
- Branch Networks and ATMs
- Brand Reputation
- Data and Analytics
- Intellectual Property
- Market Presence
Bank of America Key Activities
Bank of America’s key activities consist of:
- Banking services
- Investment advice
- Wealth management
- Trading expertise
- Lending support
- Digital innovation
- Tech advancements
- Customer care
- Regulatory adherence
- Brand building
Bank of America Key Partners
Bank of America’s key partners consist of:
- Financial Institutions
- Investment Firms
- Retail Partners
- Payment Networks
- Technology Providers
- Real Estate Partners
- Government Agencies
- Corporate Clients
- Insurance Companies
Bank of America Cost Structure
Bank of America’s cost structure consists of:
- Personnel Costs
- Technology and Infrastructure Costs
- Marketing and Advertising Costs
- Occupancy and Facilities Costs
- Regulatory and Compliance Costs
- Depreciation and Amortization
- Interest Expenses
- Loss Provisions
- Acquisition and Merger Costs
- Employee Training and Development Costs
Bank of America Competitors
- JPMorgan Chase & Co.: JPMorgan Chase is one of the largest and most prominent financial institutions in the United States. It operates as a diversified financial services company, providing a wide range of services, including consumer banking, commercial banking, investment banking, asset management, and more. JPMorgan Chase serves millions of customers globally and has a significant market presence. The bank is known for its substantial investment banking operations, asset management services through its subsidiary J.P. Morgan Asset Management, and its robust consumer banking division;
- Wells Fargo & Co.: Wells Fargo is another central U.S. bank with many financial services. It operates across consumer banking, commercial banking, investment banking, and wealth management. Wells Fargo was historically known for its extensive branch network and retail banking operations, but it also offers mortgage services, investment solutions, and other financial products. The bank has faced significant regulatory and public scrutiny due to past controversies, which impacted its reputation;
- Citigroup Inc.: Citigroup is a global financial services company with operations spanning retail banking, corporate banking, investment banking, and wealth management. It operates in numerous countries, making it one of the largest international banks. Citigroup’s consumer banking division serves millions of customers worldwide, while its investment banking arm, Citibank, is recognized for its global presence and diverse financial services;
- Goldman Sachs Group Inc.: Goldman Sachs is a renowned investment bank and financial services company. It’s known for its solid presence in investment banking, securities trading, asset management, and financial advisory services. Goldman Sachs caters to a wide range of clients, including corporations, governments, and high-net-worth individuals. The company’s prominence in the financial industry is often associated with its involvement in mergers and acquisitions, trading, and capital market activities;
- Morgan Stanley: Morgan Stanley is another major investment bank and financial services provider. Like Goldman Sachs, it offers investment banking, trading, and wealth management services. Morgan Stanley’s wealth management division, often referred to as Morgan Stanley Wealth Management, is a key driver of its revenues. The company focuses on providing financial advice, asset management, and investment solutions to individuals, institutions, and corporations.
Bank of America SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT analysis of Bank of America:
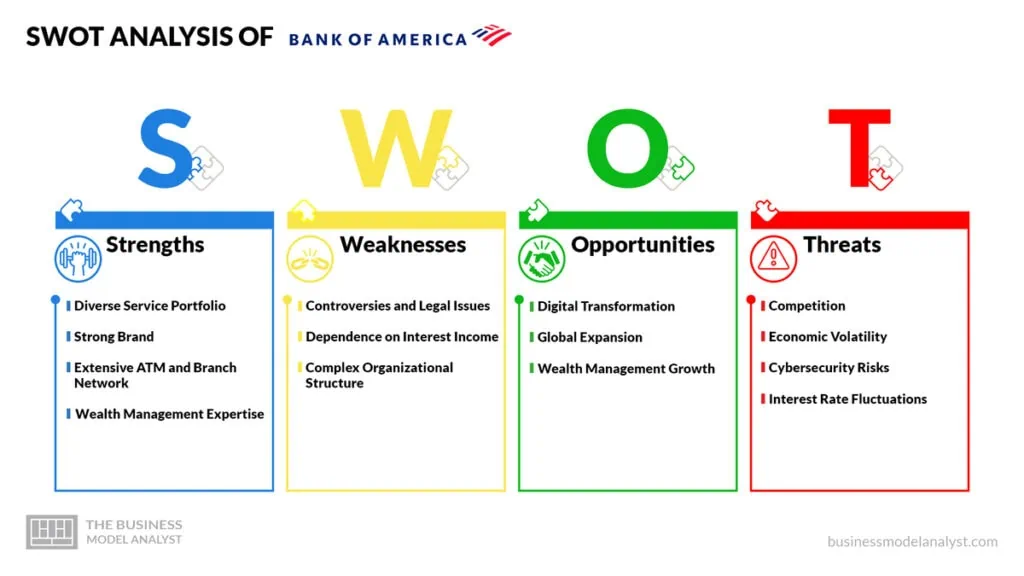
Bank of America Strengths
- Diverse Service Portfolio: Bank of America’s strength lies in its ability to offer a diverse array of financial services. From retail banking to investment banking, wealth management to corporate banking, the bank serves a broad spectrum of customers with various financial needs. This diversity allows Bank of America to capture different segments of the market and generate revenue through a wide range of products and services;
- Strong Brand: Bank of America’s strong brand recognition is a significant advantage. Its long history, extensive presence, and reputation for stability contribute to customer trust and loyalty. The recognizable brand not only attracts new customers but also retains existing ones, enhancing the bank’s competitive edge in the industry;
- Extensive ATM and Branch Network: The bank’s vast network of branches and ATMs contributes to its accessibility and customer convenience. The physical presence allows customers to conduct in-person transactions, seek assistance, and access financial services in various locations. This network can be a critical factor in attracting and retaining customers who prefer face-to-face interactions;
- Wealth Management Expertise: Bank of America’s wealth management division, led by Merrill Lynch, is a strength that caters to high-net-worth individuals and institutional clients. This segment offers personalized financial advisory services, investment management, and tailored solutions. The bank’s ability to provide comprehensive wealth management services adds another layer of revenue diversification.
Bank of America Weaknesses
- Controversies and Legal Issues: Bank of America has faced some legal and regulatory challenges over the years, leading to reputational damage and substantial financial penalties. These controversies can erode customer trust and investor confidence, affecting the bank’s overall image and profitability;
- Dependence on Interest Income: A significant portion of Bank of America’s revenue comes from interest income, including lending and interest rate spreads. This dependence on interest income makes the bank vulnerable to changes in interest rates and economic conditions. In a low-interest-rate environment, the bank’s profitability can be adversely affected;
- Complex Organizational Structure: Being a large and diversified financial institution, Bank of America’s organizational structure can become complex and challenging to manage efficiently. This complexity might lead to slower decision-making processes, increased bureaucracy, and difficulties in coordination across different business units.
Bank of America Opportunities
- Digital Transformation: The ongoing shift towards digital banking presents Bank of America with an opportunity to enhance customer experiences and streamline operations. By investing in advanced online banking platforms, mobile apps, and digital solutions, the bank can attract tech-savvy customers and offer more convenient services;
- Global Expansion: Bank of America’s global presence positions it well for further expansion into new international markets. By strategically entering regions with growing economies, the bank can reach untapped customer segments and diversify its revenue streams;
- Wealth Management Growth: The increasing demand for personalized financial advisory services presents an opportunity for Bank of America to further grow its wealth management division. By expanding its offerings and catering to high-net-worth individuals and institutional clients, the bank can capture a larger share of the wealth management market.
Bank of America Threats
- Competition: The banking and financial services sector is highly competitive, with numerous large institutions, regional banks, fintech startups, and emerging players vying for market share. Intense competition can put pressure on fees, interest rates, and margins, potentially impacting the bank’s revenue;
- Economic Volatility: Economic downturns and financial market fluctuations can impact credit quality, asset values, and demand for banking services. Economic challenges can lead to higher loan defaults, reduced borrowing, and decreased investment activities, affecting the bank’s profitability;
- Cybersecurity Risks: As digital banking evolves, the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches becomes more prominent. Cybersecurity threats can result in financial losses, reputational damage, regulatory fines, and legal liabilities, impacting the bank’s operations and trust among customers;
- Interest Rate Fluctuations: Interest rate changes can directly impact Bank of America’s net interest margin, the difference between what it earns from lending and what it pays on deposits. The impacts of interest rate fluctuations can grow even more significant if the bank cannot adjust its lending and deposit rates effectively.
Conclusion
Bank of America’s business model stands as a testament to its unique ability to seamlessly adapt and serve a vast spectrum of clients in the realm of financial services. The diversity of its offerings, ranging from retail banking to investment solutions, underscores its commitment to meeting the multifaceted needs of individuals, small businesses, and large corporations.
However, this versatility doesn’t come without challenges. The ever-evolving landscape of finance demands that Bank of America constantly overcome obstacles, from regulatory complexities and economic fluctuations to the perpetual pursuit of technological innovation. Yet, these challenges serve as catalysts for growth and evolution, prompting the bank to refine its strategies and offerings in order to remain at the forefront of the industry.

