The Abbvie business model revolves around delivering innovative healthcare solutions to improve the lives of patients around the world. As a global biopharmaceutical company, Abbvie specializes in the research, development, and commercialization of advanced therapies in multiple therapeutic areas, including immunology, oncology, neuroscience, and virology.
With a strong commitment to scientific excellence and patient-centricity, Abbvie has established itself as a leader in the healthcare industry. Their portfolio of products encompasses a wide range of treatments, from specialty drugs to targeted therapies, addressing some of the most complex and challenging diseases.
By leveraging their expertise in cutting-edge science and a deep understanding of patient needs, Abbvie strives to make a meaningful difference in healthcare. Their business model encompasses strategic collaborations, innovative research and development initiatives, and a strong commercialization strategy, all aimed at bringing transformative therapies to patients in need.
Contents
A brief history of Abbvie
Abbvie, a pharmaceutical company focused on discovering, developing, and delivering innovative medicines to improve patient care, has a rich history that dates back to its separation from Abbott Laboratories.
In January 2013, Abbott Laboratories announced the spin-off of its research-based pharmaceuticals division, which would become Abbvie. The decision to separate the pharmaceutical business was driven by a desire to allow each company to focus on its specific strengths and opportunities.
With the separation, Abbvie became an independent entity, ready to chart its own path in the industry. The company inherited a strong portfolio of products, including the blockbuster drug Humira, which was already a leading treatment for autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease.
Building on the foundation provided by Abbott Laboratories, Abbvie embarked on a journey of growth and innovation. The company focused on developing therapies in areas such as immunology, oncology, neuroscience, and virology, aiming to address unmet medical needs and improve patients’ lives.
In the ensuing years, Abbvie made strategic acquisitions and partnerships to expand its pipeline and diversify its offerings. Notable acquisitions include the 2015 acquisition of Pharmacyclics, which brought the blockbuster cancer drug Imbruvica into Abbvie’s portfolio. This addition solidified Abbvie’s position in the oncology space and provided further growth opportunities.
Continuing its commitment to innovation, Abbvie invested heavily in research and development, allocating substantial resources to discovering new treatments and advancing scientific knowledge. The company’s scientists and researchers explored new pathways and therapeutic approaches, exploring the frontiers of medical science.
In recent years, Abbvie has achieved significant milestones and successes. The company received approvals for new drugs, expanded indications for existing treatments, and continued to deliver on its mission of bringing transformative medicines to patients worldwide.
Who Owns Abbvie
AbbVie is primarily owned by institutional investors, who control a majority ownership of 71.71% of the outstanding shares. This level of interest is higher compared to most other companies in the major pharmaceutical industry.
According to CNN Money as of 8th January 2024, among institutional investors, mutual fund holders hold a significant stake in AbbVie with 39.65% ownership, followed by other institutional investors who hold 32.06% ownership. Individual stakeholders have a relatively small ownership of 0.16%.
The top 10 owners of AbbVie Inc are as follows:
- The Vanguard Group, Inc.:
- Stake: 8.67%
- Shares Owned: 152,996,305
- Total Value: $21,785,143,869
The Vanguard Group is a global investment management company, renowned for its index funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
- BlackRock Fund Advisors:
- Stake: 5.19%
- Shares Owned: 91,608,723
- Total Value: $13,044,166,068
BlackRock is a leading investment management corporation, providing asset management, risk management, and advisory services globally. BlackRock Fund Advisors specializes in managing various funds.
- SSgA Funds Management, Inc.:
- Stake: 4.42%
- Shares Owned: 77,962,930
- Total Value: $11,101,141,603
State Street Global Advisors (SSgA) is an investment management division known for managing investment funds, including mutual funds and ETFs, for institutional investors and individuals.
- Capital Research & Management Co. (International Investors):
- Stake: 2.40%
- Shares Owned: 42,445,720
- Total Value: $6,043,846,071
Capital Research & Management Co. (International Investors) is an investment management company providing diverse investment funds, including equity and fixed-income funds. It caters specifically to international investors.
- JPMorgan Investment Management, Inc.:
- Stake: 2.20%
- Shares Owned: 38,889,850
- Total Value: $5,537,525,742
JPMorgan Investment Management is part of JPMorgan Chase & Co., providing a broad array of investment products and solutions globally.
- Geode Capital Management LLC:
- Stake: 2.05%
- Shares Owned: 36,207,172
- Total Value: $5,155,539,221
Geode Capital Management specializes in quantitative and index-based investment strategies, managing portfolios for institutional investors and other clients.
- Capital Research & Management Co. (Global Investors):
- Stake: 1.81%
- Shares Owned: 31,976,144
- Total Value: $4,553,083,144
Capital Research & Management Co. (Global Investors) is another entity of the investment management company, offering a range of investment products for global investors. It operates separately from the branch serving international investors.
- Charles Schwab Investment Management:
- Stake: 1.29%
- Shares Owned: 22,749,560
- Total Value: $3,239,309,848
Charles Schwab Investment Management is a subsidiary of Charles Schwab Corporation, managing a wide range of investment products, including mutual funds and ETFs.
- Northern Trust Investments, Inc.:
- Stake: 1.10%
- Shares Owned: 19,326,109
- Total Value: $2,751,844,661
Northern Trust Investments, part of Northern Trust Corporation, offers investment management and financial services to institutional and individual investors.
- Norges Bank Investment Management:
- Stake: 1.06%
- Shares Owned: 18,769,556
- Total Value: $2,672,597,079
Norges Bank Investment Management is the investment arm of Norway’s central bank, managing the Government Pension Fund Global, one of the world’s largest sovereign wealth funds, with a global investment approach.
These institutional investors and mutual funds play a crucial role in shaping AbbVie’s ownership structure, reflecting the confidence and interest of major stakeholders in the pharmaceutical industry.
Abbvie Mission Statement
Abbvie’s mission statement is “to discover and deliver innovative medicines and solutions that address complex health issues and enhance people’s lives.”

How Abbvie works
Abbvie’s business model is centered around research and development (R&D), where they invest heavily in discovering and developing new medications. The company focuses on therapeutic areas such as immunology, oncology, neuroscience, and virology, conducting extensive clinical trials to ensure the safety and efficacy of its products.
To bring their medications to market, Abbvie collaborates with healthcare providers, regulators, and payers to secure access for patients. The company also works closely with patient advocacy groups, aiming to understand patients’ needs and improve their healthcare experience.
When it comes to commercialization, Abbvie employs a multichannel approach. They distribute their medications through various channels, including hospitals, pharmacies, and specialty clinics. Abbvie also utilizes direct-to-consumer marketing strategies to raise awareness of their products and educate patients about treatment options.
Abbvie’s products are protected by patents, which provide a period of exclusivity that allows the company to recoup its investments in R&D and generate revenue. To ensure continued growth, Abbvie actively seeks opportunities for strategic partnerships and acquisitions, aiming to expand its portfolio of treatments and enter new markets.
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in Abbvie’s business model. The company provides ongoing medical education and support to healthcare providers, fostering relationships and enabling them to make informed decisions about treatment options.
While Abbvie primarily focuses on prescription medications, they also offer patient support programs to assist individuals who have difficulty accessing their products due to financial constraints. These programs may provide financial assistance, patient education materials, or other resources to help patients access and adhere to their prescribed treatments.
How Abbvie makes money
Abbvie operates a revenue model based on the sale of pharmaceutical products and the licensing of its intellectual property. Let’s explore the different ways through which Abbvie generates revenue:
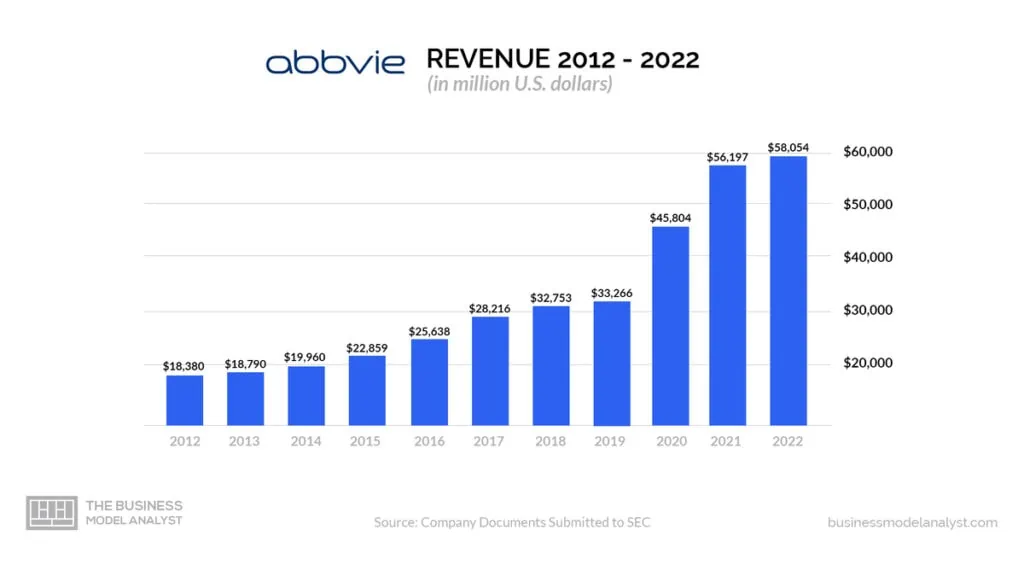
Sales of Pharmaceutical Products
Abbvie’s primary source of revenue comes from the sale of pharmaceutical products. The company develops and markets a wide range of prescription drugs across various therapeutic areas, including immunology, oncology, neuroscience, and virology. These drugs are sold to healthcare providers, hospitals, pharmacies, and other distribution channels. Abbvie invests significantly in research and development to bring innovative and effective medications to the market, which directly impacts its revenue generation.
Intellectual Property Licensing
Abbvie holds a strong portfolio of intellectual property rights, including patents and trademarks, for its pharmaceutical products. The company licenses its intellectual property to other pharmaceutical companies, allowing them to manufacture and sell generic versions of Abbvie’s drugs once the patents expire. Abbvie earns licensing fees and royalties from these agreements, providing an additional revenue stream.
Collaborations and Partnerships
Abbvie actively engages in collaborations and partnerships with other pharmaceutical companies and organizations. These partnerships may include joint research and development projects, co-marketing agreements, or licensing arrangements for specific drugs or technologies. Through these collaborations, Abbvie can leverage the expertise and resources of its partners to expand its product portfolio and reach new markets, thus generating additional revenue.
International Sales
Abbvie operates globally, with a significant portion of its revenue coming from international markets. The company sells its pharmaceutical products in various countries around the world, capitalizing on the increasing demand for healthcare and the growing prevalence of chronic diseases. International sales provide Abbvie with diversification and growth opportunities beyond its domestic market.
Specialty Pharmaceuticals and Biologics
As a specialized pharmaceutical company, Abbvie focuses on developing and commercializing specialty pharmaceuticals and biologics. These products often target patients with chronic or complex health conditions, offering specialized therapies and treatments. By focusing on niche markets and providing high-value medications, Abbvie can command premium pricing, contributing to its overall revenue generation.
Expansion into Emerging Markets
Abbvie recognizes the potential of emerging markets, both geographically and economically, with a rising demand for pharmaceutical products. The company actively expands its presence in these markets by establishing strategic partnerships, acquiring local companies, or creating distribution networks. By tapping into the growing healthcare needs of these economies, Abbvie increases its revenue and market share.
Abbvie Business Model Canvas
The Abbvie Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
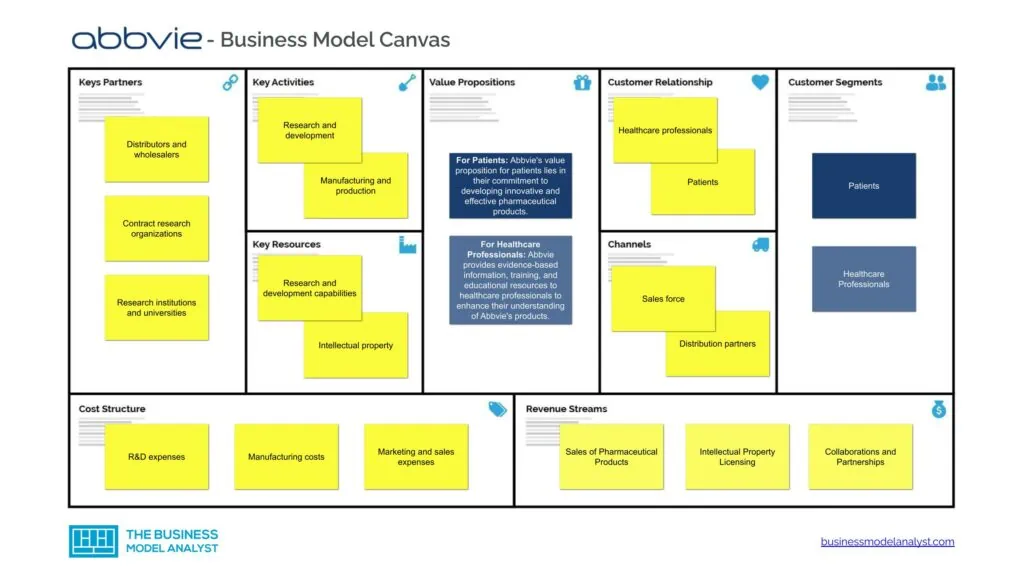
Abbvie Customer Segments
Abbvie’s customer segments can be divided into the following categories:
- Patients: Abbvie’s primary customers are patients seeking pharmaceutical products and treatments. Abbvie focuses on developing and marketing products in the fields of immunology, oncology, neuroscience, eye care, and aesthetic medicine. Their customer base includes people of all ages who are suffering from various medical conditions and need medication or healthcare solutions. Abbvie’s products range from prescription drugs to over-the-counter medications, catering to a wide range of patient needs;
- Healthcare Professionals: Abbvie also targets healthcare professionals, such as doctors, physicians, nurses, and pharmacists, who play a crucial role in the distribution and prescription of their products. Abbvie aims to build strong relationships with healthcare professionals by providing them with information, training, and support to ensure they properly prescribe and administer their medications. By targeting healthcare professionals, Abbvie aims to enhance awareness and understanding of their products within the medical community;
- Payers and Insurers: Abbvie’s customer segment also includes payers and insurers, such as government healthcare programs, private insurance companies, and pharmacy benefit managers. These organizations are critical in determining reimbursement and coverage for Abbvie’s products. Abbvie engages with payers and insurers to negotiate pricing, reimbursement rates, and formulary placements to ensure their products are accessible and affordable to patients;
- Research Institutions and Academic Partners: Research institutions and academic partners are an important customer segment for Abbvie. Abbvie collaborates with universities, research centers, and other academic institutions to conduct clinical trials, research, and development of new therapies. These partnerships help Abbvie advance scientific knowledge, explore new treatment options, and bring innovative products to the market;
- Distributors and Retailers: Abbvie works with distributors and retailers in the pharmaceutical industry to ensure the availability and distribution of their products to various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, pharmacies, and specialized medical facilities. Distributors play a crucial role in the supply chain, ensuring that Abbvie’s products reach the intended customers promptly and efficiently.
Abbvie Value Propositions
Abbvie’s value propositions consist of:
- For Patients: Abbvie’s value proposition for patients lies in their commitment to developing innovative and effective pharmaceutical products. They strive to improve the quality of life for patients by offering a wide range of medications and therapies that address various medical conditions. Abbvie’s products are designed to provide relief, manage symptoms, and potentially cure diseases, ensuring patients have access to the best possible treatments;
- For Healthcare Professionals: Abbvie provides evidence-based information, training, and educational resources to healthcare professionals to enhance their understanding of Abbvie’s products. This empowers healthcare professionals to make informed treatment decisions and provide optimal patient care. Abbvie’s value proposition to healthcare professionals also includes ongoing support, such as access to medical experts and assistance with patient management;
- For Payers and Insurers: Abbvie understands the financial aspect of healthcare and works closely with payers and insurers to provide value-based solutions. They collaborate to ensure that their products are cost-effective and aligned with the demands of payers and insurers. Abbvie’s value proposition to this customer segment includes reliable and affordable medication options, as well as transparent pricing and reimbursement structures. By demonstrating their products’ clinical and economic benefits, Abbvie aims to gain coverage and reimbursement while delivering value to payers and insurers;
- For Research Institutions and Academic Partners: Abbvie’s value proposition to research institutions and academic partners is centered around collaboration and innovation. They actively engage with these institutions to conduct clinical trials, research studies, and collaborative projects that advance medical science and contribute to developing new and improved therapies. Abbvie provides funding, expertise, and resources to support research initiatives, fostering a mutually beneficial relationship. By partnering with research institutions, Abbvie aims to bring cutting-edge treatments to patients and contribute to scientific advancements in their therapeutic areas;
- For Distributors and Retailers: Abbvie’s value proposition to distributors and retailers is founded on a strong supply chain and reliable product availability. They ensure their products are efficiently distributed and accessible to healthcare professionals and patients. Abbvie maintains a robust network of distributors and retailers, collaborating closely with them to optimize inventory management, product delivery, and customer support. Their value proposition includes consistent product supply, reliable logistics, and responsive customer service, enabling distributors and retailers to efficiently meet the needs of their customers.
Abbvie Channels
Abbvie’s channels consist of:
- Sales force: Abbvie relies on its dedicated sales force to promote and distribute its products to healthcare professionals, hospitals, and pharmacies;
- Distribution partners: The company also collaborates with various distributors, wholesalers, and retailers to ensure the availability of its medications across different markets;
- Digital platforms: Abbvie utilizes digital channels, such as websites and social media, to provide information about its products and connect with patients and healthcare professionals;
- Collaborations and partnerships: Abbvie establishes strategic alliances with other pharmaceutical companies or healthcare organizations to expand the distribution and reach of its offerings.
Abbvie Customer Relationships
Abbvie’s customer relationships consist of:
- Healthcare professionals: Abbvie maintains strong relationships with doctors, physicians, and other healthcare professionals who prescribe or recommend its products;
- Patients: The company focuses on building patient-centric relationships by providing education, support programs, and direct engagement to enhance treatment experiences;
- Advocacy groups: Abbvie collaborates with patient advocacy organizations to gain insights, address unmet needs, and create awareness about diseases and therapeutic options;
- Key opinion leaders: Abbvie maintains relationships with influential experts in the medical community who can act as brand ambassadors and contribute to the development of new products.
Abbvie Revenue Streams
Abbvie’s revenue streams consist of:
- Sales of Pharmaceutical Products
- Intellectual Property Licensing
- Collaborations and Partnerships
- International Sales
- Specialty Pharmaceuticals and Biologics
- Expansion into Emerging Markets
Abbvie Key Resources
Abbvie’s key resources consist of:
- Research and development capabilities: Abbvie heavily invests in research and development to create innovative therapies and expand its product portfolio;
- Intellectual property: The company holds a significant number of patents, trademarks, and licenses that protect its drug formulations, manufacturing processes, and brand reputation;
- Manufacturing facilities: Abbvie operates multiple manufacturing facilities globally to ensure a consistent supply of its drugs;
- Talent and expertise: The company’s key resources include a skilled workforce comprising scientists, researchers, sales representatives, and other professionals who contribute to the company’s success;
- Brand reputation: Abbvie’s strong brand reputation, built on its high-quality products and commitment to patient care, serves as a valuable resource in attracting customers and differentiating itself from competitors.
Abbvie Key Activities
Abbvie’s key activities consist of:
- Research and development
- Manufacturing and production
- Marketing and sales
- Licensing and acquisitions
- Clinical trials
- Corporate strategy
Abbvie Key Partners
Abbvie’s key partners consist of:
- Distributors and wholesalers
- Contract research organizations
- Research institutions and universities
- Healthcare providers and hospitals
- Licensing and collaboration partners
- Government agencies and regulatory bodies
Abbvie Cost Structure
Abbvie’s cost structure consists of:
- R&D expenses
- Manufacturing costs
- Marketing and sales expenses
- Distribution and logistics costs
- Clinical trial expenses
- Administrative overhead
- Royalties and licensing fees
- Regulatory and legal costs
Abbvie Competitors
Abbvie faces intense competition in the pharmaceutical industry. Here are some of its key competitors and their respective areas of focus:
- Johnson & Johnson (J&J): J&J operates in multiple segments, including pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and consumer health products. It competes with Abbvie in areas such as immunology, oncology, and infectious diseases;
- Pfizer: Pfizer is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies globally. It competes with Abbvie in various therapeutic areas, including immunology, inflammation, and oncology. Notably, Pfizer’s subsidiary, Upjohn, recently merged with Mylan to establish Viatris, which will also compete in the same market segments;
- Merck & Co.: Merck, also known as MSD outside the United States, is focused on developing innovative therapies in various therapeutic areas such as oncology, infectious diseases, and immunology. Abbvie competes with Merck in areas like immunology, hepatitis C, and cancer;
- Amgen: Amgen is a significant player in the biotechnology industry, primarily known for its expertise in developing novel therapies for various diseases, including cancer and autoimmune disorders. Abbvie competes with Amgen in segments related to oncology, inflammation, and immunology;
- Roche: Roche is a leading global pharmaceutical company, specializing in oncology, immunology, infectious diseases, and neuroscience. Abbvie competes with Roche in areas like immunology and oncology, particularly in the blood cancer field.
Abbvie SWOT Analysis
To understand Abbvie’s strategic position and potential growth prospects, a SWOT analysis is essential. By examining Abbvie’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats, we can gain insights into the company’s business model.
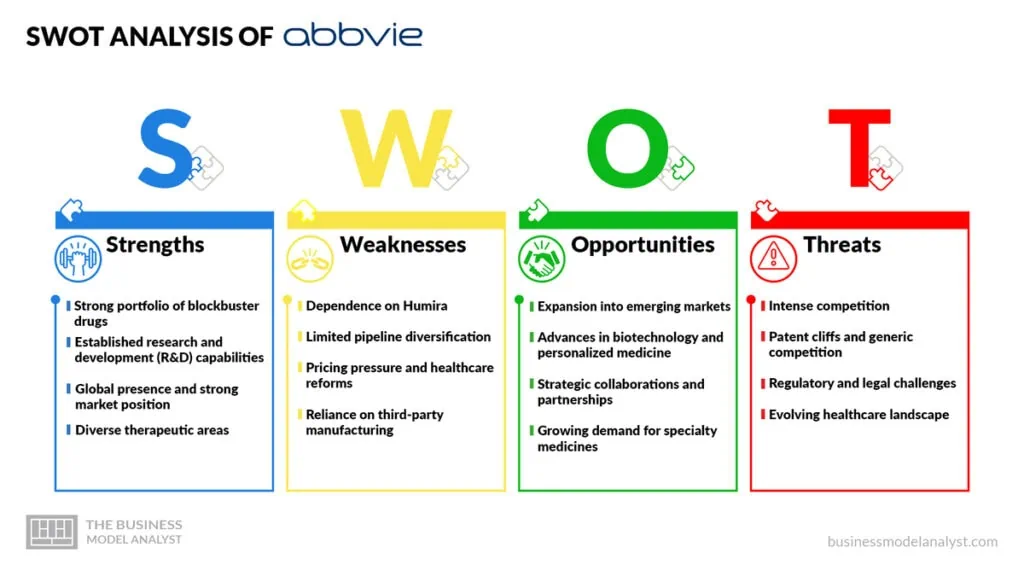
Abbvie Strengths
- Strong portfolio of blockbuster drugs: Abbvie’s strength lies in its portfolio of successful drugs, including Humira, which is one of the highest-grossing drugs in the world;
- Established research and development (R&D) capabilities: Abbvie invests significantly in R&D, enabling the company to develop innovative therapies and expand its product pipeline;
- Global presence and strong market position: Abbvie has a well-established presence in key pharmaceutical markets worldwide, giving it a competitive advantage over its peers;
- Diverse therapeutic areas: Abbvie operates in multiple therapeutic areas, including immunology, oncology, and neuroscience, which diversifies its revenue streams and reduces dependency on a single product.
Abbvie Weaknesses
- Dependence on Humira: Abbvie heavily relies on Humira for a significant portion of its revenue, making the company vulnerable to patent expiration and the entry of biosimilar competitors;
- Limited pipeline diversification: Despite ongoing R&D efforts, Abbvie’s pipeline is primarily focused on specialties related to its existing therapeutic areas, which may limit its ability to tap into emerging markets and areas of unmet medical need;
- Pricing pressure and healthcare reforms: Abbvie, along with the entire pharmaceutical industry, faces challenges related to pricing pressure, healthcare reforms, and government regulations, which can impact profitability and market access;
- Reliance on third-party manufacturing: Abbvie relies on third-party manufacturers for some of its products, which exposes it to risks associated with supply chain disruptions and quality control issues.
Abbvie Opportunities
- Expansion into emerging markets: Abbvie has the opportunity to tap into the growing demand for healthcare in emerging markets, particularly in Asia and Latin America, by introducing its existing portfolio and developing drugs tailored to specific regional needs;
- Advances in biotechnology and personalized medicine: With breakthroughs in biotechnology and an increasing focus on personalized medicine, Abbvie can leverage its R&D capabilities to develop targeted therapies and gain a competitive advantage;
- Strategic collaborations and partnerships: Abbvie can explore strategic collaborations and partnerships with other pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, and research organizations to access new technologies, expand its product pipeline, and accelerate drug development;
- Growing demand for specialty medicines: The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and aging populations worldwide presents opportunities for Abbvie to expand its offering of specialty drugs and meet the evolving needs of patients.
Abbvie Threats
- Intense competition: Abbvie operates in a highly competitive pharmaceutical market, facing intense competition from both established players and emerging biotech companies. This competition can put pressure on pricing and market share;
- Patent cliffs and generic competition: The expiration of patents for key drugs exposes Abbvie to the risk of generic competitors entering the market, causing a decline in revenue and market share;
- Regulatory and legal challenges: Abbvie faces regulatory scrutiny and potential legal disputes related to marketing practices, drug safety, and intellectual property rights, which can impact its reputation and financial performance;
- Evolving healthcare landscape: Changes in healthcare policies, reimbursement models, and customer preferences can significantly impact Abbvie’s business model and profitability, requiring the company to adapt and innovate continuously.
Conclusion
Abbvie’s business model focuses on innovation and diversification within the pharmaceutical industry. The company’s strong emphasis on research and development, coupled with strategic partnerships and acquisitions, positions it as a leader in the market.
Abbvie’s core product portfolio, anchored by its flagship drug Humira, provides a steady revenue stream while the company explores new therapeutic areas. In addition, Abbvie’s commitment to patient-centricity and its efforts to expand globally exemplify its long-term growth strategy.
Despite potential challenges such as patent expirations and regulatory hurdles, Abbvie’s well-rounded business model positions it for continued success in the ever-evolving healthcare landscape.

