The Merck business model focuses on developing and selling pharmaceutical products to meet global market needs. Drugs from this company are used to treat a wide range of diseases like diabetes, heart-related complications, and cancer. Merck also deals with animal health products. Some years back, the company also specialized in developing consumer healthcare products before the operations were sold in 2014 to Bayer. Merck is among the biggest pharmaceutical firms worldwide.
Contents
A brief history of Merck
Merck & Co. was first birthed in Darmstadt, Germany, in 1668. Friedrich Jacob Merck, the founder, established the company as Angel Pharmacy (Engel-Apotheke), selling codeine, cocaine, and morphine. The company transitioned into manufacturing in 1827 after Heinrich Emanuel Merck changed its operations, adopting the name E. Merck.
In 1887, the company’s inaugural sales office in the U.S. opened its doors, while its first branch in the U.S. was launched in 1891 under the name Merck & Co., with George Merck leading its operations. George is Heinrich’s grandson. The U.S. branch evolved, and the firm later opened a manufacturing plant in 1902 in Rahway, New Jersey.
Worth mentioning is that the first German-based Merck has since changed its name to Merck KGaA and has no association with the U.S.-based Merck & Co. Merck’s first commercially-used smallpox vaccine was sold in the U.S. in 1898.
The firm published a manual for pharmacists and physicians the following year (1899.) Today, the guide is available in 17 languages and is among the most used texts worldwide. 1n 1953, Merck merged with Sharp & Dohme, a Philadelphia-based pharmacy. The two firms grew to become the biggest prescription drug manufacturers in the U.S. at that time. Merck produces products for women’s health, immunology, nervous system disorders, and respiratory complications.
After stabilizing in the pharmaceutical sector, Merck started manufacturing vaccines. The company’s measles vaccine hit the market in 1963, followed by its mumps counterpart in 1967. Merck prides itself on being one of the most pharmaceutical brands globally. However, it has faced challenges along the way. For example, various lawsuits have been filed against the firm. As a result, Merck has paid colossal amounts of money in damages to patients and their families.
Who Owns Merck
70% of Merck’s overall capital is owned by the Merck family, represented by the holding company, E. Merck KG. The remaining 30% is publicly traded. The total free float shares is 129.2 million, while theoretical shares amount to 434.8 million.
Merck Mission Statement

Merck’s mission statement is “to discover, develop and provide innovative products and services that save and improve lives around the world.”
How Merck works
Merck’s operations are based on the following areas.
Oncology
This medicine branch specializes in diagnosing, offering therapy, and palliative care to patients with terminal cancers. The company also screens people for hereditary cancers, such as breast cancer, and follows up on treatment for patients in complete remission.
Vaccines
These are biological medicines that offer active obtained immunity to a specific infectious disease. Some of the firm’s vaccines include Pneumovax, Gardasil, Rota Teq, and Pneumovax.
Animal health
In this area, Merck manufactures vaccines and pharmaceutical products used to treat animals. The firm also provides health management solutions for controlling, treating, and preventing diseases in domestic and wild animals.
Diabetes
Merck manufactures drugs that patients use to regulate their blood glucose levels. Janumet and Januvia are two of the Brand’s drugs in this section.
Acute Hospital Care
Here, patients are treated for severe yet short-term illness episodes. The firm’s core products in this segment include Cubicin, Invanz, Noxafil, and Bridion.
Cardiovascular
Immuno-modulator products that change a human’s immune response by reducing or augmenting the immune system’s ability to generate antibodies fall under this section. Merck has core drugs in this section, including Simpont and Remicade.
Neuroscience and Immunology
Here, Merck diagnoses and offers treatment for neurological disorders and heart-related diseases like heart failure, coronary artery diseases, and congenital heart defects.
How Merck makes money
Merck generates most of its revenue from the following sources:
Vaccines
Vaccine development results from the collaboration between for-profit pharmaceutical companies such as Merck, public-funded research universities, and governments. Once Merck develops the vaccines, it sells them directly to physicians and veterinarians. Worth mentioning is that Merck develops vaccines for both humans and animals.
Pharmaceutical Products
Merck’s pharmaceutical segment generates more than 80% of the company’s overall revenue. The segment includes preventive and therapeutic pharmaceuticals and medicines which it sells to health maintenance organizations, government agencies, hospitals, retailers, and wholesalers.
Veterinarian Products
Merck produces vaccines and medicines for animals. The company sells these products to retailers and wholesalers.
Oncology Franchise
Merck provides licenses to small companies, allowing them to resell their oncology drugs. The company earns from franchise fees and supplies businesses with oncology drugs at wholesale prices. Customers can then purchase drugs from small businesses at a marked-up price.
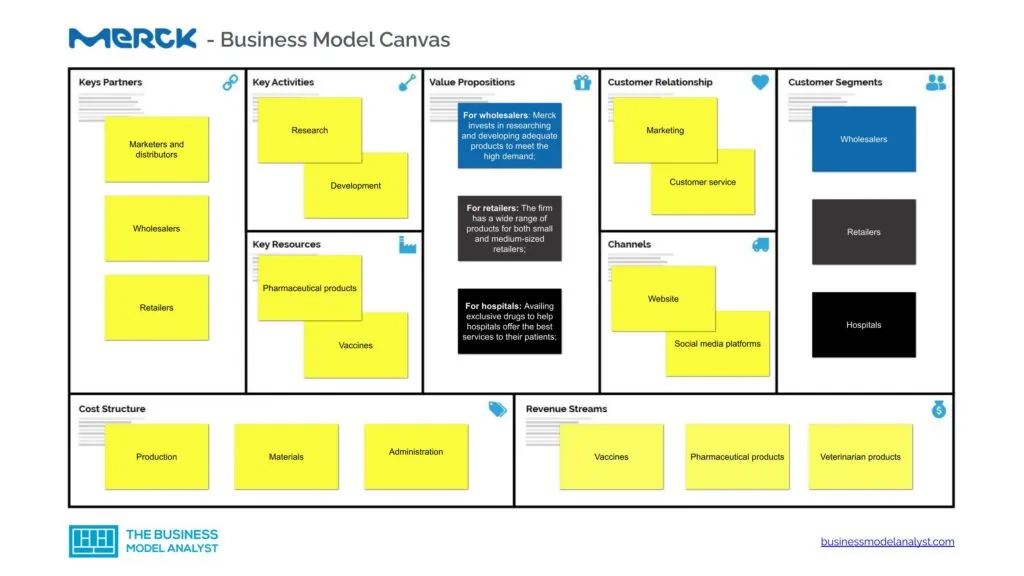
Merck Business Model Canvas
Below, there is the Merck Business Model Canvas.
Merck Customer Segments
Merck’s customer segments consist of the following:
- Wholesalers: These are either individuals or companies that purchase vaccines and pharmaceutical products in large quantities;
- Retailers: They purchase the products from the wholesalers or directly from the company and sell them to the end user;
- Hospitals: These institutions purchase vaccines and pharmaceutical products to treat their patients;
- Government agencies: Groups that purchase Merck’s products in large quantities to distribute to health-based companies;
- Physicians: Doctors who purchase vaccines and drugs to facilitate the treatment and immunization of their patients;
- Veterinarians: Specialists who research, diagnose, or treat livestock, pets, or wild animals.
- Patients: Individuals that seek healthcare services from government-owned and private hospitals.
Merck Value Propositions
Merck’s value propositions consist of the following:
- For wholesalers: Merck invests in researching and developing adequate products to meet the high demand;
- For retailers: The firm has a wide range of products for both small and medium-sized retailers;
- For hospitals: Availing exclusive drugs to help hospitals offer the best services to their patients;
- For government agencies: Provides authentic drugs with a reasonable expiration timeline to ensure products don’t go to waste in government holding centers;
- For physicians: Offers cost-friendly product packages to meet the needs of individual healthcare providers;
- For veterinarians: Provides various products to help vets offer top-tier services to domestic animal owners and wild animals;
- For patients: Allows retailers to sell over-the-counter medication to their walk-in clients.
Merck Channels
Merck’s channels consist of the following:
- Website
- Social media platforms
Merck Customer Relationships
Merck’s customer relationships consist of the following:
- Marketing
- Customer service
- Joint ventures and licenses
Merck Revenue Streams
Merck’s revenue streams consist of the following:
- Vaccines
- Pharmaceutical products
- Veterinarian products
- Oncology franchise
Merck Key Resources
Merck’s key resources consist of the following:
- Pharmaceutical products
- Vaccines
- Manufacturing equipment and plant
Merck Key Activities
Merck’s key activities consist of the following:
- Research
- Development
- Production
- Distribution
- Provision of healthcare services
- Selling medical products and vaccines
Merck Key Partners
Merck’s key partners consist of:
- Marketers and distributors
- Wholesalers
- Retailers
- Governments
- Healthcare organizations
Merck Cost Structure
Merck’s cost structure consists of the following:
- Production
- Materials
- Administration
- Marketing
- Research and development
Merck Competitors
While Merck is one of the largest companies in the pharmaceutical industry, the industry is overly competitive. Some of its competitors include:
- Sanofi: This global, innovative healthcare firm specializes in science to boost people’s lives. Sanofi collaborates with professionals worldwide to transform medicine, helping patients achieve their desires. The France-based company was established in 2004;
- Johnson & Johnson: The U.S.-based multinational corporation was established in 1886. It manufactures consumer packaged products, pharmaceuticals, and medical gadgets.
It’s an American multinational corporation founded in 1886 that develops medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and consumer packaged goods.
The firm believes good health is crucial for thriving communities and vibrant lives. It strives to ensure people live healthy and fulfilling lives regardless of their stage in life or age. Johnson & Johnson is committed to enhancing the affordability and access to its products;
- Gilead Sciences: Established in California in 1987, this biopharmaceutical company would become one of the leading companies within two and a half decades. The firm strives to make the world healthy for every individual, regardless of the challenges. Gilead Sciences relies on transformative and bold science to drive innovation capable of revolutionizing the future of medicine;
- Pfizer, Inc.: One of the biggest research-based biomedical and pharmaceutical companies in the world. The company strives to discover, develop, manufacture, promote, and distribute medications for animals and humans. Headquartered in New York City, the company was founded in 1849;
Novartis: The company was founded in 1996 following a merger between Sandoz and Ciba-Geigy. The Swiss multinational pharmaceutical firm has branches in the United States. Novartis is among the leading medicine company that uses digital and science technologies to develop transformative treatments where great medication is required. It ranks as one of the best-performing firms in research and development.
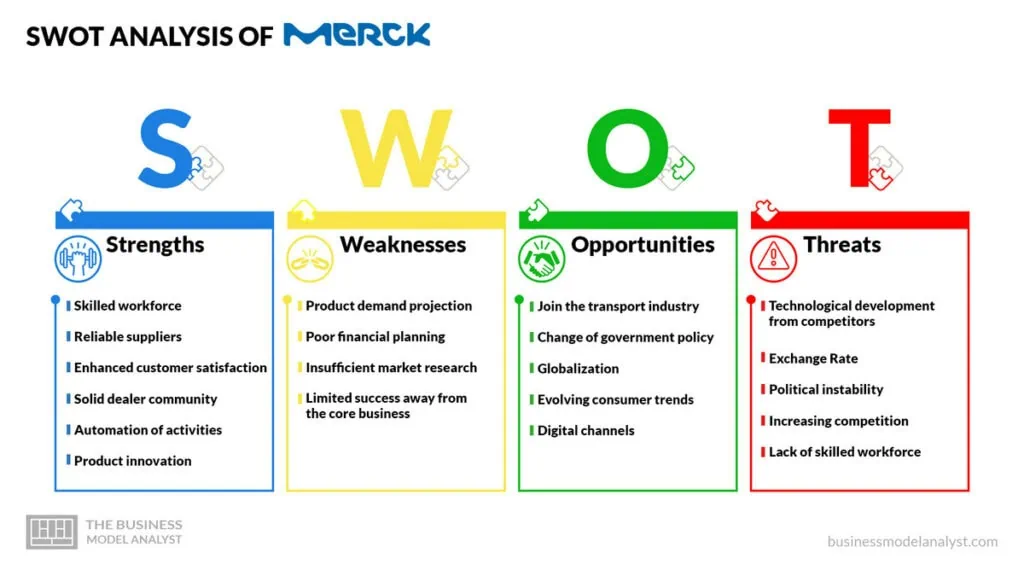
Merck SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT analysis of Merck.
Merck Strengths
- Skilled workforce: Merck invests in training its employees to improve their skills and motivate them to be productive;
- Reliable suppliers: Merck has dependable raw material suppliers, enabling it to counter supply chain barriers;
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: Merck’s effective customer relationship department ensures its customers are happy while attracting potential customers through word of mouth;
- Solid dealer community: The company has developed a strong culture among dealers and distributors. Dealers promote the company’s products and train their sales teams to improve customer interactions;
- Automation of activities: By adopting advanced services, Merck can scale up or down based on market demand;
- Product innovation: Merck has invested in research and development. It has a wide range of products to meet the different demands of its diverse customers.
Merck Weaknesses
- Product demand projection: The company is yet to master the art of estimating market demand. Eventually, it misses opportunities or surpasses expectations, incurring losses and holding a higher inventory for a more extended period;
- Poor financial planning: Merck’s financial planning and strategy are often unmanageable. With insufficient financial resources, growing the company becomes difficult. In such circumstances, a company hardly meets market demand;
- Insufficient market research: Market research is a critical part of developing a company. However, Merck hardly conducts regular market research. This means a significant percentage of the company decisions are based on outdated data that barely meets consumer demands. The industry is evolving fast, and companies can’t overlook the importance of proper and regular research;
- Limited success away from the core business: While Merck is among the leading firms in the pharmaceutical industry, diversifying its product range has been challenging.
Merck Opportunities
- Join the transport industry: By venturing into the transport industry, Merck will meet its transportation needs while cutting costs. The industry has been growing rapidly, and the market demand is high. Penetrating and offering transportation services will help the company increase its revenue streams;
- Change of government policy: Merck can leverage the green government initiative to sell its products to state and federal government contractors. Tax reductions by the government will help the firm increase its profits. It can invest the savings in development projects;
- Globalization: Expanding to other countries will help Merck uncover new markets and opportunities. Eventually, the company will use advanced technology and execute innovative experiments with other countries, increasing its conversance in the industry;
- Evolving consumer trends: These habits can present Merck with a new market. It will allow the firm to diversify its products and create new revenue streams;
- Digital channels: With more people using digital media today, companies have no choice but to adopt different online pages. Merck can increase its investment to study consumer behavior and leverage data analytics to fulfill their needs.
Merck Threats
- Technological development from competitors: Merck’s competitors use advanced tools and technology to improve their operations. This places the firm in a risky position of reduced productivity and losing consumers to more effective companies. Adopting advanced technology is a must-do activity for companies wishing to stay ahead of their competitors in the modern age;
- Exchange Rate: International exchange rates have been shaky, with the global economy slumping, especially after the pandemic. This is a global problem, and for Merck, it’s a wait-and-see whether the economy improves;
- Political instability: Political unrest in the country and poor government policies can hinder a company’s plans while derailing its growth and success. Merck must beware of the effects of political turmoil and establish ways to wade through them for the company’s sake;
- Increasing competition: The pharmaceutical market is overly competitive, with each player striving to be the best. This can affect a company’s sales and overall profitability;
- Lack of skilled workforce: When a company can’t find the right staff for its operations, it’s unable to meet customer demands. This affects its overall sales and takes a toll on the profitability levels.
Conclusion
Merck is still a successful company, even though a few challenges threaten its position on the leaderboard. Fortunately, Merck and its stakeholders can lay down proper plans to adopt advanced technology and advance to other regions. Doing that, in addition to listening to its customers and doing everything possible to meet demands, will ensure Merck remains ahead of its competitors.

