As a tech giant, the Nvidia business model involves GPU sales. This graphics company gets most of its revenue from selling these specialized chips, which serve many industries, including the gaming, robotics, automotive, and professional visualization industries. According to Statista, Nvidia’s revenue from the sale of its GPUs amounted to $11.9 billion in 2023.
Another source estimates that revenue from its graphics segment accounts for approximately 87% of the company’s total revenue. However impressive these numbers may be, they are not Nvidia’s only source of income.
Traded as Nvidia Corporation(NVDA), this tech company also generates revenue from other endeavors, including professional visualization, data centers, and automotive solutions. More recently, it has moved to the mobile smartphone market, as it has developed technologies and products that apply to this field.
In this article, we’ll discuss everything you need to know about Nvidia’s business model, including how this tech giant makes money, its competition, and opportunities, among other things.
Contents
A brief history of Nvidia
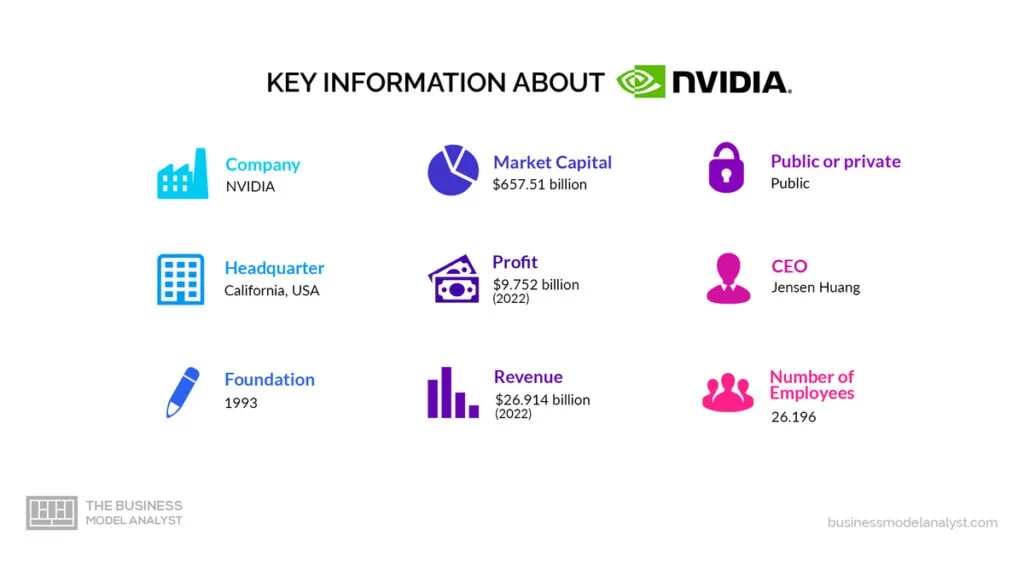
Nvidia is an American company based in Santa Clara, California. This publicly traded company designs GPUs for the gaming and professional markets and chips for the smartphone and automotive industries.
Nvidia Corporation was founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang, Chris Malachowsky, and Curtis Priem. Their innovative products and solutions have transformed various industries, including gaming, data center, automotive, healthcare, and more.
However, Nvidia’s early focus was on providing the gaming industry with advanced graphics and video solutions. The company’s first product, the NV1, was a multimedia accelerator that offered superior graphics performance for personal computers (PCs) and gaming consoles. They later introduced the GeForce 256 GPU in 1999, which put Nvidia on the map as a pioneer in the graphics industry.
In the mid-2000s, Nvidia turned its attention to the lucrative field of AI and deep learning. The company developed CUDA, a parallel computing platform and programming model that enables developers to use Nvidia GPUs for general-purpose computing, including AI and machine learning tasks.
This move proved to be a pivotal moment for NVIDIA, as the demand for GPUs in data centers and cloud computing skyrocketed, propelling the company to the forefront of the AI revolution.
Today, Nvidia has expanded its business model even further by entering the gaming console market with its Tegra processors. There are also companies such as Mellanox Technologies and ARM Holdings. Mellanox is a leading provider of high-performance networking solutions, while ARM is a semiconductor and software design company.
Such moves have seen the company rise to a market cap valuation of approximately $673 billion at the time of writing.
Although the company started to provide solutions to the computational issues relating to games, it has since evolved to offer a wide range of tech solutions in autonomous vehicles, data centers, AI, deep learning, and professional visualization spaces.
Who Owns Nvidia
Nvidia is a publicly traded company, which means various institutional and individual shareholders own it. At the time of writing, CNN Business estimated that institutional ownership made up 67.17% of the total ownership, while individual ownership accounted for a mere 4.10% ownership of the Nvidia stock.
The Vanguard Group Inc, Fidelity Management and Research, BlackRock Fund Advisors, SSgA Funds Management, and T. Rowe Price Associates make up the largest institutional owners of Nvidia.
Huang Jen Hsun, who is the president and CEO of Nvidia, owns the most shares of any individual investor, with approximately 85 million shares of the common stock, which equate to a 3.45% stake. He holds the majority of his shares through indirect trusts.
Nvidia also has one of the best Employee Stock Purchase Plans, which allows their staff to buy Nvidia’s shares at a discounted price. The company employs over 26,000 people globally who help them achieve their organizational goals.
Nvidia Mission Statement

The Nvidia mission statement is “to transform how the world experiences computing.”
How Nvidia Works
Nvidia is a tech company specializing in designing and manufacturing graphic processing cards (GPUs) for various applications in different sectors, including gaming and professional visualization. According to Nasdaq Insights, the company generates approximately 87% of its revenue from this segment.
Nvidia’s GPUs are based on parallel processing architecture, which allows them to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, making them highly efficient for computationally-intensive tasks. Nvidia’s platform also builds the most advanced chips, systems, and software for the AI factories of the future.
This includes the NVIDIA GPU Cloud (NGC), which provides a comprehensive set of software tools, containers, and SDKs for developing and deploying AI applications in the cloud.
How Nvidia Makes Money
Nvidia’s primary source of revenue comes from the sale of GPUs, which generate the company about 87% of its revenue. However, this is not the only revenue stream that this tech giant boasts. Here’s how Nvidia makes money.
Selling GPUs for the Gaming Market
It’s no secret that Nvidia leads the market in the best gaming GPUs. Gamers around the world rely on Nvidia GPUs to power their gaming experiences. Nvidia sells its high-end GPUs to its consumers directly, thanks to the help of retailers.
OEM and IP
One of the other ways that Nvidia makes money is through licensing its intellectual property (IP) to other companies. Although this is not a mainstream revenue stream for the tech giant, it still represents a significant portion of the company’s earnings.
Remember that Nvidia is a top tech company. This means that its IP is highly sought after by companies in various industries, including gaming, data centers, automotive, and more. By licensing its IP, Nvidia generates revenue without manufacturing and selling its own products.
Royalty payments and cross-licensing agreements bring the tech giant an estimated $66 million per quarter. PC and notebook OEMs such as Dell and Toshiba pay Nvidia for the company’s GPUs.
Data Centers
Nvidia also generates revenue through its data center business. Nvidia supplies the hardware that runs most of the major cloud providers, including Amazon, Alibaba, and Microsoft. Many large companies and organizations use Nvidia’s GPUs for artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) applications.
In 2021, Nvidia’s data center revenue surpassed the company’s gaming revenue for the first time in its history. As AI and HPC continue to grow in demand across various industries, Nvidia’s data center business will continue growing, representing a significant source of revenue for the company.
Auto
One of the primary ways Nvidia makes money in the automotive industry is by providing its advanced AI and GPU technologies for autonomous vehicles. This includes in-car computer operators, autonomous technology, end-end solutions including frameworks, software toolkits, and data center infrastructures.
Professional Visualization
Nvidia’s success in the professional visualization industry is primarily driven by its success in the sale of GPUs for the gaming market. Nvidia’s graphics processing units (GPUs) are renowned for their exceptional performance, high-quality graphics, and advanced features that cater to the demands of professional workflows.
These chips are used in powerful workstations, servers, and data centers, powering a wide range of applications such as computer-aided design (CAD), virtual reality (VR), simulation, and rendering.
Quadro chips help the company generate more revenue. These chips are built to cater to the needs of high-end professional graphic users, including engineers and graphic designers, whose work requires users to utilize emerging design techniques.
Nvidia Business Model Canvas
The Nvidia Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
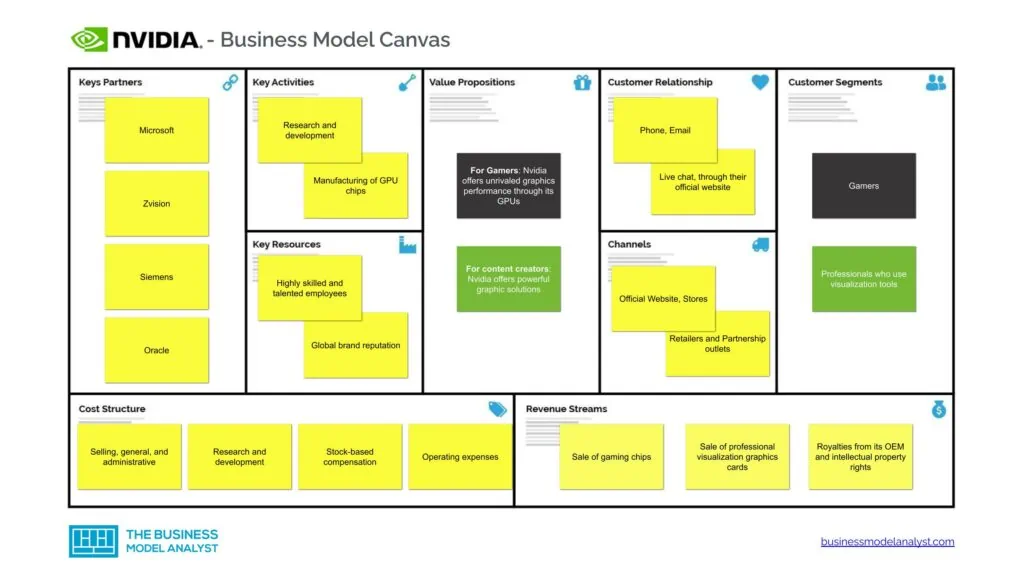
Nvidia Customer Segments
Nvidia’s customer segments is largely dominated by gamers and professionals who use visualization tools in their line of work. However, there are plenty of other professionals who use Nvidia’s solutions, as explained below.
- Gamers: Gamers form the largest and most significant customer segment for Nvidia. Gamers, especially professional ones, demand top-of-the-line hardware, including GPUs, to deliver stunning graphics and a smooth gaming experience.
And not only that, but this company’s gaming customers go beyond individual gamers as gaming events organizers, esports teams, and content creators use Nvidia’s graphics solutions for live-streaming, video editing, and content creation;
- Professionals who use visualization tools, including engineers and artists: Professionals from diverse domains, such as engineers and artists, also rely on Nvidia’s powerful graphic tools to give them advanced visual computing solutions, bringing their creative work to life;
- Data Centers: Nvidia’s hardware and chip-based solutions have become an essential technology for data centers. The company is a trusted partner for data centers, providing highly scalable technologies that give data center operators the ability to achieve new heights of computing excellence;
- Automakers: Nvidia has emerged as a key player in the automotive industry. The tech giant provides solutions that power advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), autonomous vehicles, and in-car infotainment systems. Automakers rely on Nvidia’s expertise and solutions in artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) to develop safer, smarter, and more connected vehicles that redefine the driving experience;
- Professionals in the AI industry: Professionals in the AI industry, including data scientists, researchers, and developers, form a critical customer segment for Nvidia. As a leading provider of high-performance GPUs and AI computing solutions, Nvidia has become an indispensable partner for professionals in the AI field who require powerful and scalable hardware for their complex computational needs.
Nvidia Value Propositions
Nvidia value propositions consist of:
- For Gamers, Nvidia offers unrivaled graphics performance through its GPUs: One of Nvidia’s key strengths is its ability to deliver stunning graphics in real-time. Advancements like ray tracing have enabled Nvidia GPUs to accurately simulate the behavior of light. Realistic reflections, shadows, and lighting effects in virtual environments are some of the immersive results that gamers are looking for;
- For content creators, Nvidia offers powerful graphic solutions, like powerful rendering capabilities that enhance the delivery of content: Nvidia offers a range of powerful graphics solutions that are especially useful for content creators who need to render videos with complex graphics;
- For Event Organizers and E-sports Teams, Nvidia offers world-class and scalable solutions for gaming events: Nvidia’s solutions include high-performance graphics cards, GPUs, and software tools that can help event organizers and e-sports teams deliver enhanced gaming experiences to their audiences;
- For automakers, Nvidia offers in-car computer operators, autonomous technology, end-end solutions including frameworks, software toolkits, data center infrastructures: Nvidia’s in-car computer platforms, such as the Nvidia DRIVE platform, provide automakers with the processing power and software capabilities they need to create advanced infotainment systems, driver assistance features, and autonomous driving capabilities.
Nvidia Channels
Nvidia channels consist of:
- Official Website
- Stores
- Retailers and Partnership outlets
Nvidia Customer Relationships
Nvidia customer relationships consist of:
- Phone
- Live chat, through their official website
Nvidia Revenue Streams
Nvidia revenue streams consist of:
- Sale of gaming chips
- Sale of professional visualization graphics cards
- Royalties from its OEM and intellectual property rights
- Supply of cloud-based hardware and data centers
- Provision of solutions in the automotive industry, including frameworks, software toolkits
Nvidia Key Resources
Nvidia key resources consist of:
- Highly skilled and talented employees;
- Global brand reputation, especially among gamers and professional using visualization tools;
- Strong research and development (R&D) capabilities;
- Intellectual Property (IP) — Nvidia has a wide variety of patents and trademarks, which it uses to protect its technology and intellectual property rights.
- Industry-leading GPU Technology.
Nvidia Key Activities
Nvidia key activities consist of:
- Research and development, which includes high-performance graphics processing; units for gaming, AI, data centers, autonomous vehicles, and professional visualization
- Manufacturing of GPU chips;
- Collaboration with partners and customers in various industries.
Nvidia Key Partners
Nvidia key partners consist of:
- Microsoft
- Zvision
- Siemens
- Oracle
- Foxconn
- Volvo
- Intel
Nvidia Cost Structure
Nvidia cost structure consists of:
- Selling, general, and administrative;
- Research and development;
- Stock-based compensation;
- Taxes;
- Operating expenses, including licensing fees, intellectual property royalties.
Nvidia Competitors
- AMD: AMD, also known as Advanced Micro Devices, is a huge player in the tech industry and a major competitor to Nvidia. AMD has established itself as a formidable rival to Nvidia, particularly in the field of GPUs for gaming and high-performance computing;
- Intel: Intel is an American multinational tech company based in California. Much like Nvidia, Intel is one of the largest chip designers and manufacturers. While NVIDIA primarily focuses on developing high-performance computing and artificial intelligence technologies, Intel features a wide range of computing products, including desktop and laptop CPUs, server processors, and FPGA accelerators;
- Qualcomm: Qualcomm is a leading American semiconductor and telecommunications equipment company. They design and market wireless telecommunications products and services. Qualcomm focuses primarily on developing processors for mobile devices, while Nvidia’s core operations include high-performance computing and artificial intelligence. Both companies are at the forefront of developing technology in the semiconductor industry.
Nvidia SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Nvidia:
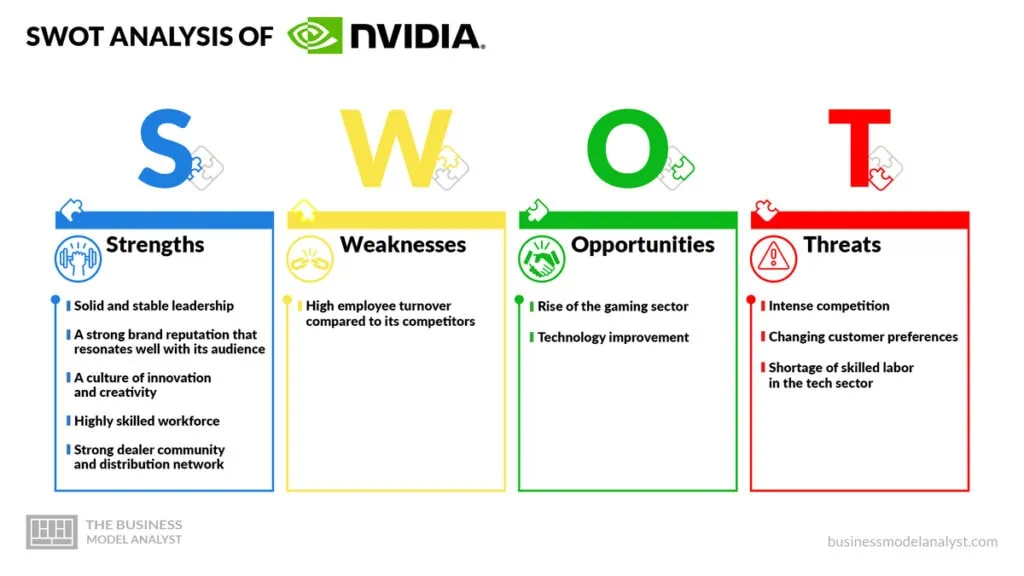
Nvidia Strengths
- Solid and stable leadership: Unlike most tech companies, Nvidia has been led by its CEO, Jensen Huang, for over two decades. Although he went public with the company, he still retains a significant portion of the company as an individual shareholder.
But more relevant to this point, Nvidia has been led by one person for a long time. This brings an element of stability to the company. And not only that, but Huang’s leadership style has been described as visionary and innovative;
- A strong brand reputation that resonates well with its audience: Nvidia has a long history of flooding the market with high-quality graphics cards that many professionals, including gamers, use. These products are known for their exceptional performance and reliability, which has helped the company earn the trust of its customers;
- A culture of innovation and creativity: For decades now, Nvidia has created high-performance graphics processors that have revolutionized the gaming industry. But beyond gaming, Nvidia’s innovations have also helped advance other industries, including AI, robotics, and autonomous vehicles;
- Highly skilled workforce: Nvidia’s workforce is one of the most talented and knowledgeable in the tech industry. And not only that, but the tech giant has a reputation for hiring and retaining top talent. This is reflected in the quality of its products and services;
- Strong dealer community and distribution network: Nvidia’s dealer community includes a mix of large multinational corporations and smaller, specialized resellers. This allows Nvidia to tap into different market segments and customer niches.
The company also has established relationships with key retailers, including Amazon, Best Buy, and Newegg, which help to increase the visibility and availability of Nvidia products;
- Intellectual Property Rights: Nvidia has a strong portfolio of patents, trademarks, and copyrights that protect its intellectual property. This portfolio includes key technologies that are critical to the company’s success, such as graphics processing units (GPUs), artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, and software tools. They give Nvidia a competitive advantage, making it challenging for its competitors to replicate or imitate its products and services.
Nvidia Weaknesses
- High employee turnover compared to its competitors: Nvidia has struggled with high employee turnover compared to its competitors. This weakness can be a significant hurdle for the company as it tries to stay competitive in an increasingly crowded marketplace.
When employees leave a company, it can cause a ripple effect that impacts the entire organization. High employee turnover can result in a loss of institutional knowledge and experience, decreased morale, and increased recruiting and training costs. This can have a significant impact on a company’s bottom line, as well as its ability to innovate and grow.
Nvidia Opportunities
- Rise of the gaming sector: Recently, the gaming sector has experienced significant growth, and this presents a tremendous opportunity for Nvidia. One of the key factors driving the growth of the gaming industry is the increasing accessibility of gaming technology.
The company’s powerful graphics cards and other gaming hardware are among the best in the industry.
This makes them a popular choice among gamers and esports professionals alike. In addition, Nvidia has been actively investing in VR technology, working to create powerful VR-ready hardware that can deliver a truly immersive experience;
- Technology improvement: Advancements in tech are a common occurrence today, and this presents a lucrative opportunity for Nvidia. Advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data science, present Nvidia in a ripe position to take advantage of these trends.
Nvidia Threats
- Intense competition: Nvidia has enjoyed a huge slice of the market share for decades. However, the rise of other GPU manufacturers has posed a pivotal threat to Nvidia’s continued success.
While Nvidia has traditionally faced competition from AMD, the rise of other players like Intel and Qualcomm has further intensified this competition. This has led to price wars and decreased profit margins, which can make it difficult for Nvidia to maintain its market share;
- Changing customer preferences: Customer preferences are constantly evolving, and this can pose a significant threat to Nvidia’s business operations. One example of changing customer preferences in the gaming industry is the shift toward mobile gaming;
- Shortage of skilled labor in the tech sector: The shortage of skilled labor is a crucial threat to Nvidia’s continued success, as it can limit the company’s ability to innovate and expand. Without a steady supply of talented and experienced workers, Nvidia could struggle to keep pace with its competitors and could fall behind in the rapidly evolving tech landscape.
Conclusion
Nvidia has long been known for its top-of-the-line graphics cards, which has enabled the company to base its business model around the sale of such. However, with revenue from its data centers slowly creeping and overtaking revenue from gaming, it’s evident that Nvidia is diversifying its portfolio and revenue streams.
Nvidia is no longer a gaming graphics company, but a computing company. While gaming remains a significant part of their business, Nvidia has expanded its product portfolio and market reach to encompass a wide range of computing applications.
The company’s innovative approach to GPU development, strategic partnerships, and customer-centric focus have positioned it as an industry leader in providing world-class technology solutions.

