Is WeWork profitable? As of September 2021, WeWork was not profitable. The firm has faced significant financial challenges, including large losses and a failed initial public offering (IPO) attempt in 2019. In 2020, WeWork experienced a decline in revenue following the COVID-19 pandemic. This was because many businesses shifted to remote work arrangements. And that impacted the demand for office spaces. Let’s understand what happened from the start and what the company can do to overcome its financial challenges.
Contents
Timeline of WeWork’s Financial Growth and Funding
Here is a timeline of some of the notable events related to WeWork’s financial growth and funding.
2010: Adam Neumann and Miguel McKelvey establish WeWork in New York City.
2011-2014: The company starts expanding its operations and launching new coworking spaces in various locations.
2015: WeWork raises $434 million in a funding round spearheaded by Fidelity Management and Research Company, out of which the company’s value hits $10 billion.
2016: WeWork raises an extra $690 million in a funding round led by Hony Capital and SoftBank. Out of this, its value rose to $16 billion.
2017: WeWork continues penetrating new markets to hit $20 billion in valuation.
2018: WeWork’s valuation rises to $47 billion after a $4.4 billion investment from SoftBank. This makes it one of the most valuable startups globally. But concerns about its business model and financials begin to arise.
2019: WeWork files for an initial public offering (IPO) in August. But it faces scrutiny and criticism over its governance structure, financials, and leadership. The IPO plans are ultimately deferred in September of the same year. Adam Neumann also steps down as CEO.
2019-2020: WeWork’s financial struggles worsen, with the company reporting significant losses. Its occupancy rates drop as the COVID-19 pandemic disrupts office space demand.
2020: SoftBank, WeWork’s largest investor, offers a $1.1 billion bailout package to support the company and help stabilize its operations.
2021: WeWork announces plans to go public through a merger with a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC) called BowX Acquisition Corp. The merger was expected to be completed in the first quarter of 2021.
WeWork Financial Performance: Revenues, Expenses, and Profits
WeWork was once hailed as a revolutionary disruptor in the commercial real estate industry. But the company later experienced enormous challenges on its journey to profitability. Here is a breakdown of the firm’s financial performance, highlighting its revenue sources, expenses, and profits.
WeWork Revenues
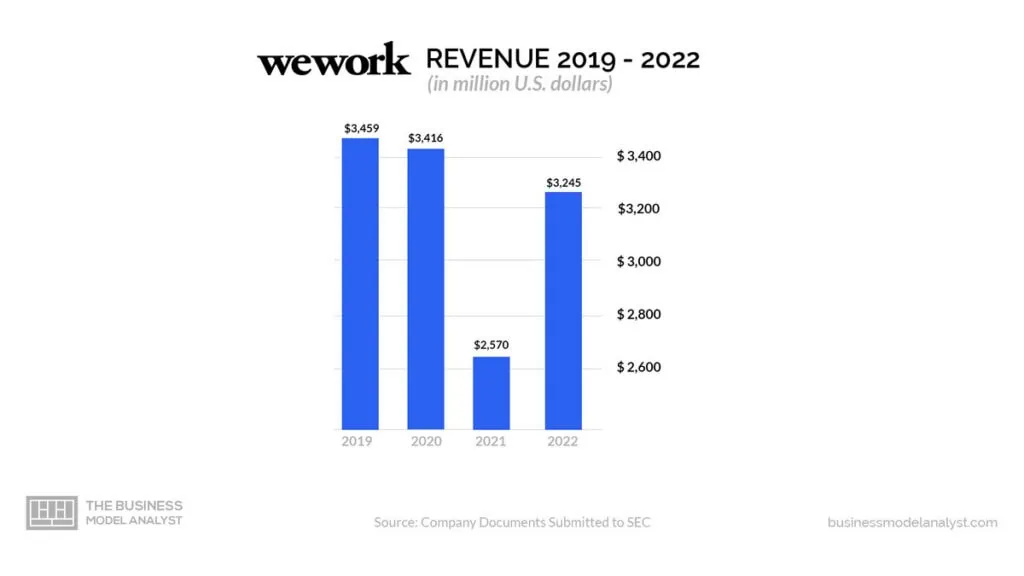
WeWork generates revenue from leasing office space to corporations, small offices, and individuals. A big chunk of WeWork’s income comes from membership fees and leasing agreements. The company offers flexible workspace solutions. And this allows individuals and businesses to rent office spaces for short-term durations or via membership plans.
Membership fees provide recurring revenue since clients pay monthly or annually for access to WeWork’s coworking spaces, amenities, and services. Leasing agreements involve longer-term commitments, often signed by enterprise clients or larger organizations seeking dedicated office spaces within WeWork locations.
Besides contributing to WeWork’s revenue stability, these lease agreements provide a solid foundation for financial planning. WeWork’s revenue also comes from upselling opportunities like access to meeting rooms, event spaces, IT support, networking events, and professional development programs. The company has also explored partnerships and enterprise solutions to diversify its revenue streams.
By collaborating with organizations, WeWork offers tailored workspace solutions to meet specific business requirements. For example, white-labeling WeWork spaces or providing custom-built office environments for corporate clients. These partnerships enable the company to tap into the demand for flexible workspaces from larger enterprises, generating substantial revenue through customized arrangements and long-term contracts.
WeWork’s revenue growth has been propelled by its ambitious global expansion strategy. The company has entered numerous markets worldwide, targeting key cities and business hubs. By establishing a strong presence in diverse locations, WeWork has attracted a broad customer base and diversified its revenue streams.
This approach allows the company to benefit from the demand for coworking spaces across different regions. And this minimizes its reliance on specific markets and reduces revenue volatility. To cope with evolving market dynamics, WeWork has embraced digital transformation and virtual offerings.
When remote work gained prominence, WeWork introduced virtual memberships. These provide access to its global network of professionals, virtual events, and online collaboration platforms. These virtual offerings have contributed to WeWork’s revenue diversification. And also provided for the changing needs of remote workers and distributed teams.
WeWork Expenses
WeWork incurs various expenses, and these include lease payments for the properties it rents, employee salaries, marketing costs, and administrative fees. Other significant costs are associated with renovating and furnishing its office spaces to provide a coworking environment.
Lease payments take up the most significant percentage of expenses. The company operates coworking spaces in prime locations worldwide. As a result, it incurs substantial costs in securing and maintaining these properties. Long-term lease commitments, often ranging from several years to a decade, form a large portion of WeWork’s expenses.
These lease payments remain constant, even with changes in occupancy rates or short-term fluctuations in demand. Consequently, the company also bears the financial burden of lease expenses, even during periods of low utilization or economic downturns.
WeWork invests in renovating and furnishing its coworking spaces to create attractive and functional work environments. It aims to offer modern, amenity-rich rooms that meet the needs of its diverse clientele.
Renovation and maintenance costs include expenses related to interior design, construction, furniture, fixtures, and ongoing repairs. WeWork’s commitment to maintaining high-quality workspaces contributes significantly to its costs because it must ensure the spaces remain attractive and meet the evolving demands of its members.
Employee salaries and benefits also consume a considerable portion of WeWork’s expenses. As a global organization, the company employs a large workforce to help with managing its coworking spaces, sales and marketing, customer support, and operational activities. These expenses include wages, bonuses, healthcare, retirement contributions, and other perks. The cost of maintaining a large workforce in various regions and ensuring employee satisfaction contributes to WeWork’s expenses.
To attract new clients and maintain brand visibility, WeWork invests in marketing and advertising activities. The company uses different marketing strategies, such as digital campaigns, events, sponsorships, and partnerships.
These initiatives aim to increase awareness of WeWork’s offerings and differentiate it from competitors. Marketing and advertising expenses consume a large part of the company’s cost structure as it seeks to capture a larger market share and sustain its growth trajectory.
Administrative and general expenses help support WeWork’s day-to-day operations. These expenses incorporate overhead costs like rent for corporate offices, utilities, technology infrastructure, software licenses, legal and professional services, insurance, and administrative staff salaries. These expenses help facilitate smooth operations, maintain compliance with regulations, and support the broader organizational framework.
WeWork is a technology-based company, so it allocates resources to technology and innovation investments. The firm leverages technology to improve member experiences, streamline operations, and develop proprietary tools and platforms. Investments in technology and innovation contribute to WeWork’s expenses as it continuously seeks to enhance its offerings, optimize processes, and remain at the forefront of the coworking industry.
WeWork Profits
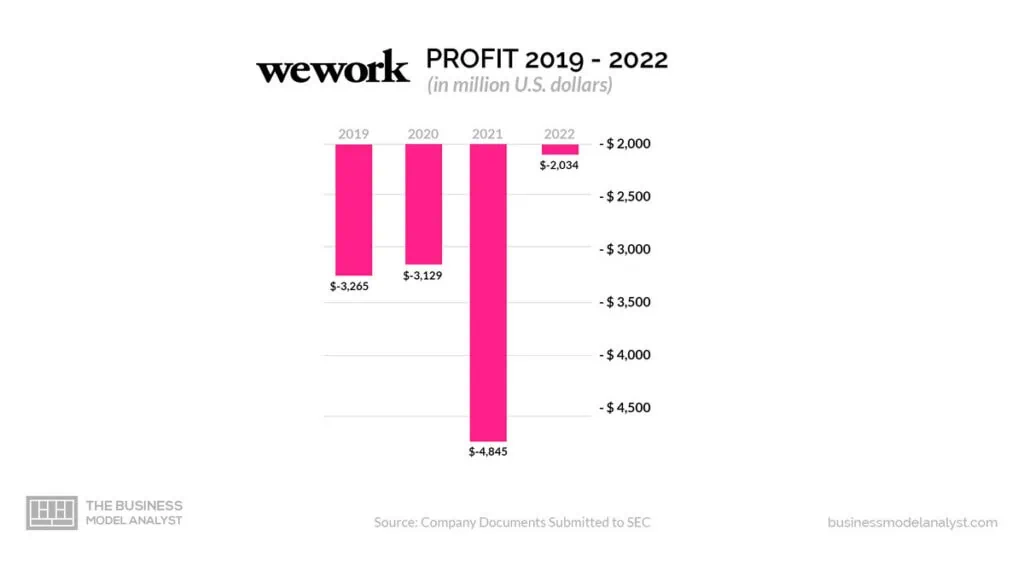
WeWork has experienced losses in its financial performance. Its rapid expansion, coupled with high operating costs and aggressive leasing commitments, has weighed down on its financial challenges. In 2019 alone, WeWork reported a net loss of $1.9 billion.
WeWork’s profit is highly influenced by its revenue growth and stability. The company generates revenue primarily from leasing office spaces to individuals, small businesses, and corporations.
A core component of profit is the ability to consistently attract clients, maintain high occupancy rates, and generate substantial revenue from membership fees and leasing agreements. Sustainable revenue growth and stability lay the foundation for the company to achieve profitability and cover its expenses.
The ability to manage expenses effectively also plays a significant role in a company’s ability to make a profit. WeWork incurs various expenses, as we’ve previously mentioned. These include lease payments, property renovations, employee salaries, marketing costs, administrative fees, and technology investments. Managing these expenses efficiently, optimizing operational processes, and implementing cost-cutting measures can help WeWork improve its profit margin and edge closer to making a profit.
Occupancy rates and space utilization can also impact WeWork’s profit significantly. Higher occupancy rates mean more rented spaces and increased revenue potential. By using available office spaces efficiently, WeWork can maximize its profit margins. But, the COVID-19 pandemic has presented challenges because remote work and economic uncertainties have led to lower occupancy rates and reduced use. Restoring and maintaining high occupancy rates are crucial for WeWork to improve its profit position.
The company’s ability to adapt to changing market demands offers flexible workspace solutions, and scaling its operations is critical in its profit generation efforts. The company’s business model provides agility and the potential to adjust to evolving customer preferences and market trends. Expanding into new markets and establishing partnerships can help the company tap into a broader client base, enhance its revenue streams, and ultimately improve its profit performance.
WeWork’s profit is also influenced by its ability to provide value-added services and effectively upsell to its clients. WeWork can generate extra revenue by offering additional amenities, like access to meeting rooms, event spaces, IT support, and professional development programs. Upselling to clients through upgraded membership plans or customized solutions for enterprise customers is an opportunity to increase profit per customer.
Market position and economies of scale also affect the company’s profit level. As one of the most prominent players in the coworking industry, WeWork has the advantage of scale. WeWork can leverage its size to negotiate favorable lease terms, streamline operations, and optimize costs. As the market leader, WeWork also benefits from brand recognition and customer trust. And this enables it to attract a more extensive customer base, which can help it achieve higher profit margins.
Potential for Profitability
Various factors can influence WeWork’s ability to achieve financial success and reshape its trajectory in the coworking market. Diversifying revenue streams is one of the core factors.
Of course, the company’s primary revenue comes from leasing office spaces. But the company can expand into adjacent markets and offer additional services.
By leveraging its extensive network and brand recognition, the company can explore partnerships, introduce value-added services, and tap into emerging trends like remote work solutions or enterprise-focused offerings. Diversification can eliminate or even reduce the risks associated with a heavy reliance on traditional coworking revenue.
And this can create new avenues for profit generation. To become profitable, WeWork must prioritize operational efficiency and cost optimization. The company was criticized for its high operating expenses, particularly lease commitments and property renovation costs.
Streamlining operations, renegotiating lease terms, and implementing stringent cost management measures can help improve profitability. WeWork can also leverage technology and data analytics to optimize space utilization, energy consumption, and overall operational effectiveness, reducing unnecessary expenditures and improving profit margins.
WeWork’s potential for profitability lies in its ability to expand and penetrate new markets effectively. While the company has a global presence, there are still untapped markets and regions where the demand for flexible workspaces is rising.
WeWork can capture new customers, increase occupancy rates, and drive revenue growth by targeting these markets strategically. Worth mentioning is that successful market expansion requires a deep understanding of local dynamics, cultural nuances, and customization of offerings to meet specific market needs.
WeWork’s ability to enhance member experiences and foster long-term client relationships is critical for its profitability. The company can attract and retain a loyal customer base by improving the quality of its coworking spaces, amenities, and services continuously. Happy and satisfied members are more likely to renew their memberships, upgrade to higher-tier plans, and recommend WeWork to their networks. This can lead to higher revenue, improved profitability, and reduced customer acquisition costs.
WeWork’s potential for profitability can be amplified via strategic partnerships and alliances. Collaborating with established organizations, technology providers, or industry experts can unlock new growth opportunities.
For example, partnering with companies offering complementary services or expertise can enable WeWork to deliver integrated solutions and attract larger enterprise clients. Further, strategic alliances can provide access to new markets, strengthen WeWork’s value proposition, and enhance its overall competitive advantage.
WeWork’s ability to adapt to changing work trends can boost its profitability. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift towards remote work and flexible work arrangements. WeWork can capitalize on these evolving trends by offering hybrid work solutions, virtual memberships, and workspace customization options. The company can remain relevant and seize new profit opportunities in the dynamic work environment by aligning its offerings with the changing needs of the workforce.
Conclusion
WeWork’s revenue breakdown highlights the multi-faceted nature of its business model. Membership fees and leasing agreements form the core revenue sources, while additional services, partnerships, enterprise solutions, and global expansion provide avenues for growth and revenue diversification.
As the company continues to adapt to market demands and explore innovative solutions, understanding the dynamics of its revenue breakdown is paramount in assessing its financial performance and long-term viability in the coworking industry.
WeWork can become profitable by focusing on cost management, diversifying revenue streams, enhancing member experiences, strategically expanding into new markets, forging partnerships, embracing technology, adapting to changing work trends, and maintaining financial discipline. Implementing these measures can help the company improve its financial performance, increase profitability, and secure its position as a leader in the coworking industry.
WeWork’s profit breakdown comprises various core components that impact its financial performance. Revenue growth and stability, effective expense management, occupancy rates, flexibility, value-added services, economies of scale, and market positioning all contribute to the company’s profit generation.
As WeWork continues its journey towards profitability, a strategic focus on these factors is vital to navigate the challenges of the coworking industry and improve its financial outlook.


