Berkshire Hathaway business model focuses on acquiring and managing varieties of companies in multiple industries. A few examples of industries where Berkshire Hathaway and its subsidiaries currently operate include the energy industry, manufacturing industry, and insurance industry. The company generates strong cash flow through the subsidiaries under its management and reinvests the profits in new opportunities. The company always analyzes risks properly to avoid losses despite having a large cash reserve. The financial statement of the company that was released publicly in 2020 revealed that the company had cash and cash equivalents of $138.3 billion in its reserve.
Contents
A brief history of Berkshire Hathaway
Berkshire Hathaway has come a very long way to become the business it is today. Its origin traces back to Valley Falls Company, which is a textile manufacturing company founded by Oliver Chace in 1839. Valley Falls Company merged with another company called Berkshire Cotton Manufacturing Company in 1929. The combined company became Berkshire Fine Spinning Associates. Berkshire Fine Spinning Associates operated for a few decades before it merged with another company called Hathaway Manufacturing Company in 1955. Horatio Hathaway created Hathaway Manufacturing Company in 1888. The merging of Berkshire Fine Spinning Associates and Hathaway Manufacturing Company gave birth to Berkshire Hathaway, though at that time, the business wasn’t diversified as it is today.
Warren Buffett started buying stocks of Berkshire Hathaway in 1962 as he assumed the value of each stock would increase eventually. Warren Buffett later decided to sell his stocks when he realized the company’s financial status wouldn’t likely improve. However, he later changed his decision to sell his stocks because he disliked the price offer he got. Instead of selling his stocks, Buffett bought more stocks of the company to become a primary controller and make significant adjustments to the company’s structure. One of the most significant changes Buffett made included venturing the textile company into the insurance business.
Who Owns Berkshire Hathaway
Warren Edward Buffett is the major owner of Berkshire Hathaway. He is also the current chairman and CEO of the company. It is important to note that some institutional investors and shareholders also own a significant percentage of the company.
Berkshire Hathaway Mission Statement
The Berkshire Hathaway mission statement is “to deliver the right parts on time and exceed all the internal and external customer requirements through continuous improvement. To provide a place for people who are hardworking, knowledgeable, dedicated, knowledgeable, and ethical who have a firm belief in the company”
How Berkshire Hathaway works
Berkshire Hathaway is a conglomerate company operating in the following industries:
Insurance industry
Berkshire’s insurance operates under the following groups:
- GEICO: GEICO became part of Berkshire Hathaway in the late 1970s, when Warren Buffett bought a very large number of GEICO’s stocks. The most common insurance GEICO offers is private passenger automobile insurance, though the company also offers other types of insurance like renter insurance, life insurance, and lots more;
- Berkshire Hathaway Reinsurance Group: This insurance group offers varieties of insurance coverages on life, casualty, and property to insurers and reinsurers in various parts of the world;
- Berkshire Hathaway Primary Group: This group consists of insurers who provide a wide range of coverage to policyholders in the U.S.
Energy Industry
Berkshire Hathaway Energy (BHE) company generates, stores, and distributes electric energy. BHE operates in various parts of the world. For instance, BHE’s distribution subsidiaries in Great Britain serve about 3.9 million end-users of electricity.
Railroad Transport Industry
One of Berkshire Hathaway’s subsidiaries owns a railway transport company known as BNSF Railway. BNSF’s railway system is one of the largest in North America. The railroad system has more than 32,500 route miles of track in 28 states.
Manufacturing Industry
Berkshire Hathaway has lots of manufacturing subsidiaries. Those subsidiaries manufacture industrial products, building products, and consumer products.
Retail
Berkshire Hathaway acts as a retailer for automotive and various other consumer products. A few examples of Berkshire Hathaway subsidiaries that serve as retailers are Berkshire Hathaway Automotive, Oriental Trading Company, and Pampered Chef.
How Berkshire Hathaway makes money
Berkshire Hathaway Makes Money from the following:
Insurance Premium
Although Berkshire Hathaway uses insurance premiums they receive from policyholders to provide coverage for claims, the company always has leftover money even after covering claims. The leftover money adds up to the company’s revenue.
Sales
Almost all the products that Berkshire Hathaway are in high demand, so the company generates a lot of money by selling its manufactured products. The subsidiaries of Berkshire Hathaway also generate vast amounts from the products they sell.
Lease
Berkshire Hathaway rents out specific properties, especially homes, to generate money.
Rail Transportation
BNSF Railways makes a lot of money from railways transportation. For instance, in 2021, BNSF Railway’s revenue was $20.7B.
Services
Berkshire Hathaway generates significant revenue from services it renders, such as power distribution.
Berkshire Hathaway Business Model Canvas
Let’s take a look at the Berkshire Hathaway Business Model Canvas below:
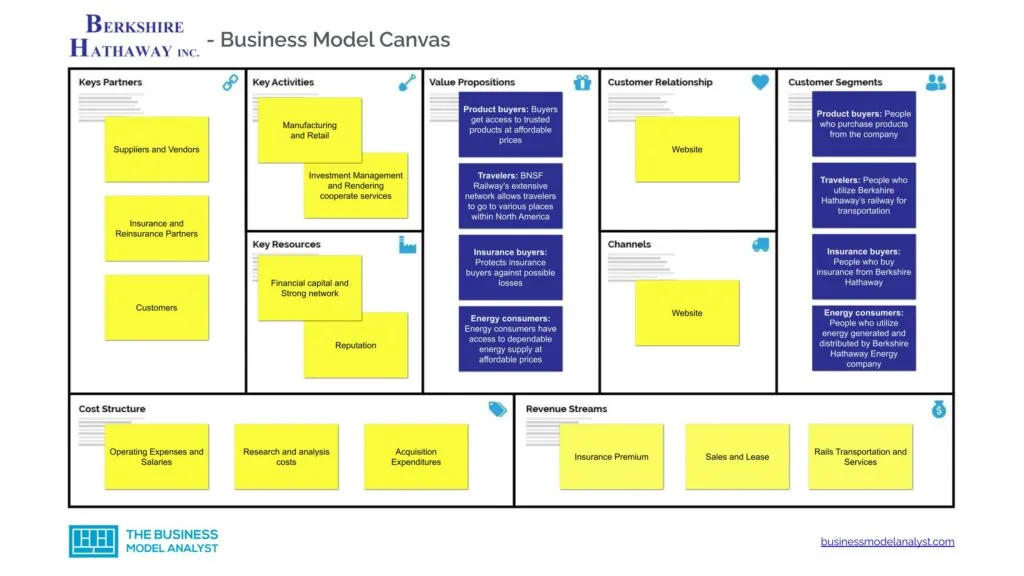
Berkshire Hathaway Customer Segments
The Berkshire Hathaway customer segments consist of:
- Product buyers: This category comprises people who purchase products from the company;
- Travelers: This category comprises people who utilize Berkshire Hathaway’s railway for transportation;
- Insurance buyers: This category comprises people who buy insurance from Berkshire Hathaway;
- Energy consumers: This category comprises people who utilize energy generated and distributed by Berkshire Hathaway Energy company;
- Investors: This category comprises individual and institutional investors who buy Berkshire Hathaway’s shares to get returns on their investments.
Berkshire Hathaway Value Propositions
The Berkshire Hathaway value propositions consist of:
- Product buyers: Buyers get access to trusted products at affordable prices;
- Travelers: BNSF Railway’s extensive network allows travelers to go to various places within North America;
- Insurance buyers: Protects insurance buyers against possible losses;
- Energy consumers: Energy consumers have access to dependable energy supply at affordable prices;
- Investors: The company generates attractive returns for its investors.
Berkshire Hathaway Channels
The Berkshire Hathaway channels consist of:
- Website
Berkshire Hathaway Customer Relationships
The Berkshire Hathaway customer relationships consist of:
- Website
Berkshire Hathaway Revenue Streams
The Berkshire Hathaway revenue streams consist of:
- Insurance Premium
- Sales
- Lease
- Rails Transportation
- Services
Berkshire Hathaway Key Resources
The Berkshire Hathaway key resources consist of:
- Financial capital
- Strong network
- Reputation
Berkshire Hathaway Key Activities
The Berkshire Hathaway key activities consist of:
- Manufacturing
- Retail
- Investment Management
- Rendering cooperate services
Berkshire Hathaway Key Partners
The Berkshire Hathaway key partners consist of:
- Suppliers and Vendors
- Insurance and Reinsurance Partners
- Customers
Berkshire Hathaway Cost Structure
The Berkshire Hathaway cost structure consists of:
- Operating Expenses
- Salaries
- Research and analysis costs
- Acquisition Expenditures
Berkshire Hathaway Competitors
- BlackRock: Just like Berkshire Hathaway, BlackRock company manages a large number of assets. In fact, BlackRock is the largest asset manager in the world, with more than $9 trillion in assets under its management. In terms of property management and investment, BlackRock competes with Berkshire Hathaway;
- JPMorgan Chase: JPMorgan Chase is a financial institution in the US with a diversified business portfolio. Some of the businesses in its portfolio compete with Berkshire Hathaway. For instance, JPMorgan Chase engages in asset management and insurance, which Berkshire Hathaway also engages in;
- The Carlyle Group: The Carlyle Group is a multinational company in the U.S. that manages assets and renders financial services. The company has investments across various industries like the energy and power sector, technology, retail, and aerospace;
- Allianz: Allianz is a European multinational financial services company. The company operates insurance and investment businesses. These two businesses make Allianz one of Berkshire Hathaway’s competitors. Allianz also has a strong reputation and large financial capital, just like Berkshire Hathaway;
- Allstate: Allstate is an American insurance company. It competes keenly with the insurance business of Berkshire Hathaway within the US.
Berkshire Hathaway SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Berkshire Hathaway:
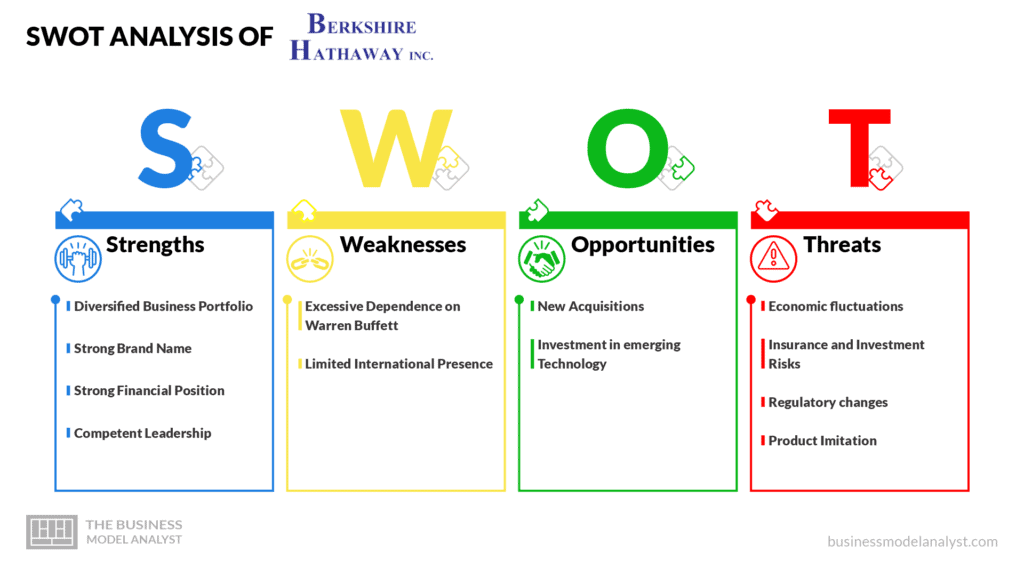
Berkshire Hathaway Strengths
- Diversified Business Portfolio: The diverse businesses in Berkshire Hathaway’s portfolio strengthen the company. The diversity allows the company to quickly expand to new products and generate revenue from various sources. Even if one of its industries experiences a decline, the company will still generate significant revenue from its other industries;
- Strong Brand Name: Berkshire Hathaway’s good reputation is one of its major strengths. For instance, the company’s reputation helps it attract investors;
- Strong Financial Position: Berkshire Hathaway’s financial position is one of the company’s top strengths. The company uses its financial positions to make acquisitions when necessary and operate its diverse businesses;
- Competent Leadership: Warren Buffett, the company’s CEO, is a very experienced leader. Buffett has been managing investments successfully for more than five decades. His competence as a leader strengthens the company.
Berkshire Hathaway Weaknesses
- Excessive Dependence on Warren Buffett: Buffett makes almost all major decisions for the company. This may have significant consequences for the company when Buffett steps down as the CEO;
- Limited International Presence: Berkshire Hathaway isn’t operational in some parts of the world. The company needs to expand well into the global market rather than focusing excessively on North America.
Berkshire Hathaway Opportunities
- New Acquisitions: Berkshire Hathaway has made lots of acquisitions in the past, and it has the potential to continue making more acquisitions. New acquisitions will help the company grow even further than it has already;
- Investment in emerging Technology: While Berkshire Hathaway has invested in a few tech companies like Apple, it can still increase its investment in emerging technology in the near future to get more significant returns;
Berkshire Hathaway Threats
- Economic fluctuations: Just like all other typical businesses, a general decline in the economic situation will threaten Berkshire Hathaway. Even when the general economy seems stable, some mistakes in the company’s decision-making can destabilize the company’s economic status.
- Insurance and Investment Risks: The risks associated with the insurance business and investments pose some threats to Berkshire Hathaway. Great losses may arise from those risks if Berkshire Hathaway doesn’t analyze risks properly;
- Regulatory changes: Changes in government regulations can pose some threats to Berkshire Hathaway. For instance, if tax laws in the US become highly unfavorable, the company’s financial position may decline significantly;
- Product Imitation: Some substandard companies are very likely to produce counterfeit products of Berkshire Hathaway just to benefit from the company’s reputation. However, such counterfeit products may eventually tarnish Berkshire Hathaway’s reputation.
Conclusion
Berkshire Hathaway is a very successful company. The company has made an outstanding contribution to humanity through its various subsidiaries. The company emphasizes quality when manufacturing, rendering services, and investing in businesses.

