The American Express Business Model is focused on providing financial and travel services to its customers. Both services are carried out through its credit and charge card offerings, which allow holders to make payments anywhere and anytime, too flexibly. Amex, as it is popularly known, generates revenue by attaching some fees to the credit cards used by the cardholders and also by accruing interests on the unpaid balance.
One way American Express stands out from other card-issuing companies is that it mainly focuses on providing high-end goods and services for customers willing to pay. It also offers travel services like reserving hotels, cars, flights, and rental cars.
Contents
A brief history of American Express
The American Express Company was founded in 1850 when Henry Wells, Williams G Fargo, and John Butterfield decided to merge their company to form an express mail dispatcher. American Express, as a company, was initially established to help consumers transport their valuable possessions from one place to the other. However, between the late 19th and early 20th century, it brought a new financial product and travel service to the market. This started in 1891 when the traveler’s check was introduced to help customers who liked to travel feel more secure about how they keep and spend their money. 1918 rolled in, and Amex left the express business, but remained in the financial and travel business. In 1958, the charge card was created to help customers conveniently pay for things they wanted; this began with the paper charge card. It was upgraded to the gold card in 1966, then in 1969, the green card. The platinum card was introduced in 1984, and finally, the centurion card was introduced in 1999. In 1862, American Express had 890 offices with about 1500 workers, currently known as one of the largest payment networks.
Who Owns American Express
Over the years, since its foundation, the ownership of American Express has changed hands numerous times to become a publicly traded company. It was first owned by Wells, Fargo, and Butterfield, plus a group of other investors, but since the first three were the ones who merged their companies, they were seen as the company’s primary owners. After the company was hit with a financial crisis between 1893 and 1915, J.P. Morgan and co took over American Express and, after some reorganization, brought it back to profitability. It became a publicly traded company, with its shares listed on New York’s Stock Exchange. From 1998, Berkshire Hathaway, which Warren Buffett owns, bought part of the company’s shares about nine times and is currently the highest shareholder of the company.
American Express Mission Statement
The American Express mission statement is “To become essential to our customers by providing differentiated products and services to help them achieve their aspirations.”
How American Express works
American Express gives its customers various offerings, including financial and travel services, and each offer works in different ways, depending on which one the customer is using.
To start with, there are credit and charge cards; a credit card given by AMEX gives customers who apply a line of credit which they can spend on purchases and get to pay later. When they have to pay back this credit is dependent on their arrangement and agreement with their lender and also the type of American Express card they use. To get a credit card, the future cardholder must first make an application, and if it is approved, the card provider gives a credit limit which has to be paid back over time before the deadline to avoid a negative mark on the credit scores.
Apart from credit cards, American Express also runs a reward program in which cardholders are given rewards for frequently using their American Express card to make purchases. These rewards can be redeemed when the cardholders travel. Also, there are travel services, like booking flights, car rentals, hotels, travel insurance, etc.
How American Express makes money
American Express generates revenue by charging fees to merchants and cardholders, as well as by earning interest on outstanding balances. The company’s focus on premium products and services also helps to differentiate it from other credit card issuers and attracts customers willing to pay higher fees for exclusive benefits. American Express makes money primarily through a few key sources, some of which are listed below.
- Merchant Discount Fees
- Interest Charges
- Annual Fees
- Foreign Exchange Fees
- Other Fees
Merchant Discount Fees
Usually, American Express has partner merchants in the form of sellers, retailers, and service providers who accept payment from AMEX cardholders through their cards. When someone purchases with an American Express cardholder, the merchant receiving the purchase pays a percentage of the transaction amount to American Express. The rate the merchant is to pay can vary, maybe depending on the type of card; however, it ranges from 2% to 3% of each payment.
Interest Charges
How the credit card works, as explained earlier, is that the cardholder is given a line of credit over a period which they can spend and then pay back at a later date. When the deadline for payment reaches, and they cannot pay back this credit in full, interest will accrue on the balance, which the cardholder will eventually have to pay. Interest charges represent a significant source of revenue for the company.
Annual Fees
Some American Express cards come with annual fees, which the cardholder must pay yearly. The annual fee could be from 100 to thousands of dollars, depending on the card type and its benefits.
Foreign Exchange Fees
One thing American Express allows its cardholders to do is purchase items in foreign currencies. So if an AMEX cardholder travels to a different country, they can still use their card to make payments in that country’s currency. However, there would be a conversion fee on each payment made. This fee could be between 2% and 3% of each payment.
Other Fees
Apart from these sources of revenue mentioned above, the other ways American Express makes its money is by charging late payment fees, balance transfer fees, and cash advance fees.
American Express Business Model Canvas
The American Express Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
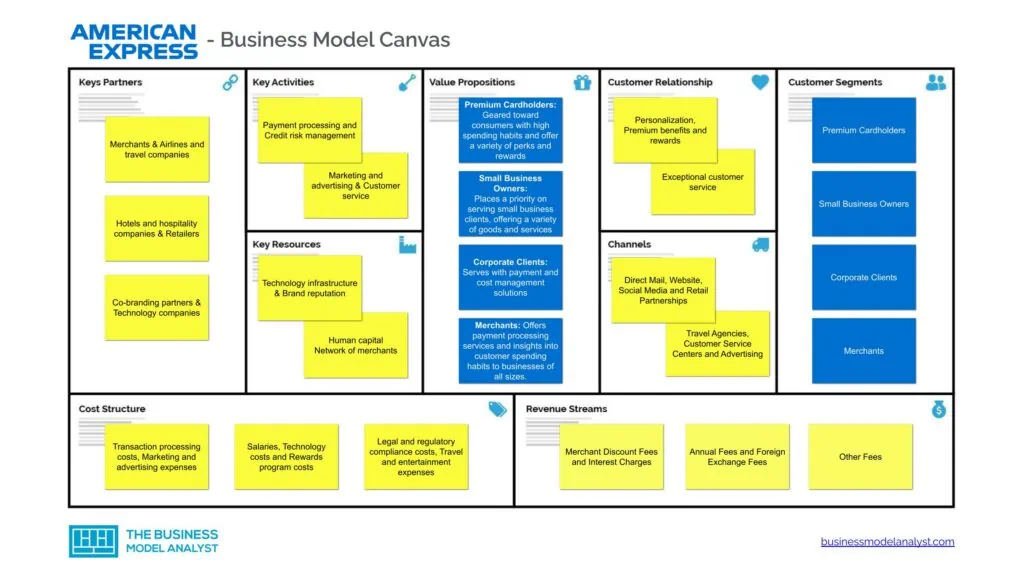
American Express Customer Segments
American Express’ customer segments consist of
- Premium Cardholders: Affluent people, business owners, and frequent travelers who enjoy special experiences, travel benefits, and individualized care make up this consumer segment of Premium Cardholders;
- Small Business Owners: Entrepreneurs, small business owners, and freelancers who value tools and resources to assist them in expanding their businesses make up this consumer category;
- Corporate Clients: Companies, international organizations, governmental bodies, and nonprofits who need sophisticated payment and expense management solutions are considered corporate clients;
- Merchants: Retailers, eateries, service providers, and other companies that value dependable payment processing and customer engagement tools are included in this customer category.
American Express Value Propositions
American Express’ value propositions consist of:
- Premium Cardholders: This market consists of people and companies ready to pay yearly fees for credit and charge cards with deluxe features, including VIP access to airport lounges, concierge services, travel perks, cashback, and rewards. The Platinum Card and The Centurion Card are two premium card choices from American Express that are geared toward consumers with high spending habits and offer a variety of perks and rewards. With collaborations with high-end travel service providers and shops, like luxury hotels, airlines, and high-end clothing lines, American Express also targets this customer segment;
- Small Business Owners: American Express places a priority on serving small business clients, offering a variety of goods and services aimed at assisting them in managing their finances and expanding their operations. This customer group values the resources and tools that can be used to keep track of costs, control cash flow, and accrue rewards. For small business owners, American Express provides several credit and charge cards and solutions for spending monitoring, invoicing, and vendor payments. To assist small company owners in overcoming obstacles and expanding their enterprises, American Express also offers resources and educational materials;
- Corporate Clients: Large enterprises, international organizations, and governmental bodies are among the corporate clients that American Express serves with payment and cost management solutions. This customer group prioritizes cost-effective cost-management systems, effective payment processing, and customized solutions. For its corporate customers, American Express provides a variety of goods and services, such as business cards, software for managing travel and expenses, and data analytics. To assist corporate clients in streamlining their operations and optimizing their spending, the organization also offers specialized account management teams and support services;
- Merchants: American Express offers payment processing services, marketing, and advertising tools, and insights into customer spending habits to businesses of all sizes. Retailers, eateries, service providers, and other companies that value dependable payment processing and customer engagement technologies make up this customer sector. Point-of-sale terminals, mobile payment apps, and internet payment choices are just a few payment processing services that American Express provides. Additionally, the company offers merchants data insights and analytics to help them better understand their consumers and run their businesses, as well as marketing and promotional tools like offers and discounts for cards.
American Express Channels
American Express’ channels consist of:
- Direct Mail
- Website
- Social Media
- Retail Partnerships
- Travel Agencies
- Customer Service Centers
- Advertising
American Express Customer relationships
American Express’ customer relationships consist of:
- Personalization
- Premium benefits and rewards
- Exceptional customer service
- Soliciting feedback and conducting surveys
- Community building through social media and online forums
American Express Revenue Streams
American Express’ revenue streams consist of:
- Merchant Discount Fees
- Interest Charges
- Annual Fees
- Foreign Exchange Fees
- Other Fees
American Express Key Resources
American Express’ key resources consist of:
- Technology infrastructure
- Brand reputation
- Human capital
- Network of merchants
- Partnerships
- Data and analytics
- Regulatory compliance
American Express Key Activities
American Express’ key activities include:
- Payment processing
- Credit risk management
- Marketing and advertising
- Customer service
- Technology development
- Data analysis and insights
- Compliance and risk management
American Express Key Partners
American Express’ key partners consist of:
- Merchants
- Airlines and travel companies
- Hotels and hospitality companies
- Retailers
- Co-branding partners
- Technology companies
- Financial institutions
American Express Cost Structure
American Express’ cost structure consists of:
- Transaction processing costs
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Salaries
- Technology costs
- Rewards program costs
- Legal and regulatory compliance costs
- Travel and entertainment expenses
American Express Competitors
- Visa Inc: Being one of the leaders in card issuance and also a leader in payment technology, the Visa business model focuses on offering a lot of services to individuals, organizations, and governments around the world. By enabling electronic transactions during buying and selling, it is recognized as one of the most extensive payment processing networks. Besides having credit card offerings, Visa also issues debit and prepaid cards. Apart from giving cards, Visa provides a variety of additional goods and services in addition to its basic payment processing services, such as fraud prevention tools, loyalty programs, and data analytics services;
- Mastercard, Inc.: Like Visa and Amex, Mastercard runs a sizable and highly effective infrastructure for processing payments. Cardholders can choose to use either credit, debit, or prepaid cards issued by Mastercard, thanks to a network that processes payments on behalf of the firm. In addition, it provides its customers with various other goods and services, such as data analytics, loyalty programs, and tools for preventing fraud;
- JPMorgan Chase & Co: Leading provider of financial services, JPMorgan Chase provides a variety of goods and services to individuals and companies worldwide. One of the biggest in the sector, Chase Card Services, the company’s credit card division, offers several well-known cards, such as the Chase Sapphire Reserve and the Chase Freedom Flex. JPMorgan Chase provides various other financial services, such as investment banking, asset management, and commercial banking, in addition to its credit card operation;
- Capital One Financial Corporation: Financial services provider Capital One provides both individuals and companies with a variety of goods and services. One of the biggest in the sector, the company’s credit card division offers well-known cards, including the Capital One Venture Rewards Credit Card and the Capital One Quicksilver Cash Rewards Credit Card. Capital One provides various other financial services and products besides its credit card operations, such as auto loans, mortgages, and savings accounts.
American Express SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of American Express:
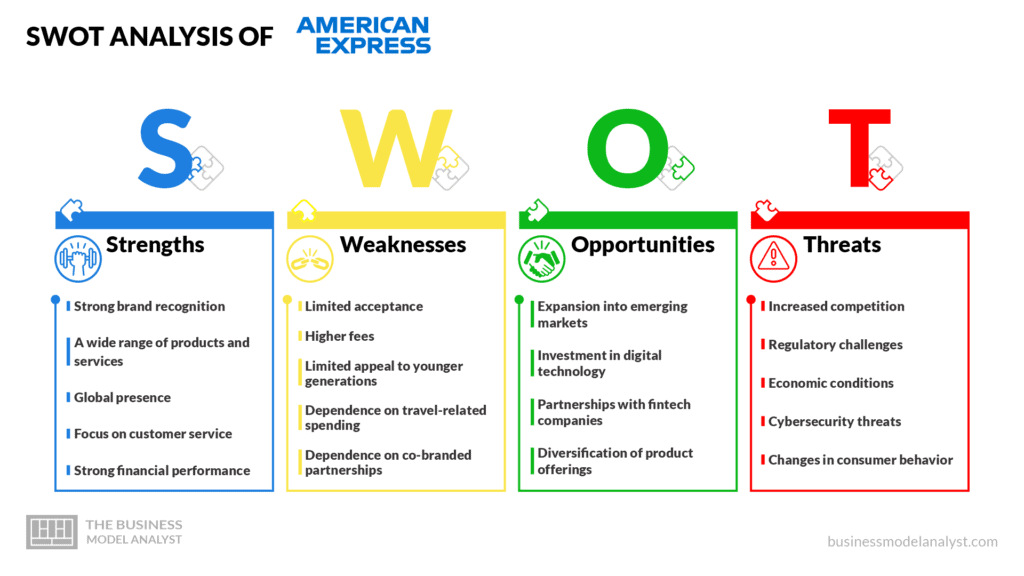
American Express Strengths
- Strong brand recognition: In the financial sector, American Express is a well-known brand that is associated with prestige, luxury, and high-quality service. High net-worth individuals are drawn to the organization because of its distinctive brand identity, which also helps it stand out from rivals;
- A wide range of products and services: Credit cards, charge cards, savings accounts, investment products, insurance, travel services, and more are just a few of the goods and services that American Express provides. With such a varied portfolio, the business can meet the needs of various consumer segments and bring in money from multiple sources;
- Global presence: Another strength is that American Express currently operates in more than 130 countries. So it helps the company access new markets and reach out to consumers of different demographics. This also supports an increment in Amex’s generated revenue;
- Focus on customer service: In addition to providing its clients with a variety of privileges and rewards, such as access to private events, savings on travel and entertainment, and more, American Express places a high priority on providing excellent customer service. This strategy has helped the business retain high levels of customer satisfaction while cultivating a loyal client base;
- Strong financial performance: American Express has a history of producing solid financial results, including steady revenue growth and profitability. This shows how well the business can manage risks, keep expenses under control, and produce ongoing profits.
American Express Weaknesses
- Limited acceptance: Amex is not as extensively recognized by merchants and shops around the world as other credit cards are. This might reduce the number of customers it attracts and influence some customers to use other, more extensively used credit cards;
- Higher fees: Amex has more fees for businesses than other credit cards, which can deter some companies from accepting it and reduce the number of firms that do;
- Limited appeal to younger generations: Younger generations may not find Amex’s traditional emphasis on high-end clients and rewards programs as appealing as they once did, since they place a higher value on financial products’ simplicity, flexibility, and sustainability;
- Dependence on travel-related spending: The COVID-19 epidemic has affected travel and related spending, which may have a detrimental effect on the company’s revenue and profitability. Amex has historically been strong in the travel and entertainment sectors;
- Dependence on co-branded partnerships: Amex depends significantly on co-branded alliances with businesses like Delta, Marriott, and Hilton, which may be risky if these alliances end or if competition in the co-branding market increases.
American Express Opportunities
- Expansion into emerging markets: In rising regions like India, China, and other Asian nations, where the middle class is expanding quickly, and there is an increasing demand for credit cards and other financial products, Amex may look for prospects to boost its business;
- Investment in digital technology: Amex might spend more on digital technology to provide its customers with cutting-edge goods and services. To enhance its payment processing, fraud detection, and customer service, the business could investigate advanced technology like blockchain, artificial intelligence, and machine learning;
- Partnerships with fintech companies: Amex might collaborate with fintech firms to provide its clients with fresh goods and services. Partnerships with businesses focusing on lending, financial management, or digital payments may fall under this category;
- Diversification of product offerings: Amex may develop other product lines besides its current credit cards, such as providing its clients with banking, insurance, or investing services.
American Express Threats
- Increased competition: Amex is up against fierce competition from Visa, Mastercard, and other credit card issuers, as well as emerging players, including fintech startups, digital payment providers, and significant technology firms;
- Regulatory challenges: Like many providers of financial services, Amex faces regulatory obstacles that might affect its operations. Law and rule modifications, such as new data privacy rules, may raise compliance costs and effectiveness practices;
- Economic conditions: Global economic changes like inflation, recession, or other downturns could have effectiveness pending, decrease the use of credit cards, and affect Amex’s revenue and profitability;
- Cybersecurity threats: Amex is a provider of financial services; therefore, it is constantly concerned about cyber-attacks and data breaches, which could harm its brand and cause losses in money and legal repercussions;
- Changes in consumer behavior: Consumer behavior shifts, including a decrease in credit card use or a preference for other payment options, could affect Amex’s operations and necessitate the corporation making changes to its business strategy and product line to stay competitive.
Conclusion
American Express is a well-known provider of financial services and has been around since 1850. Although it was initially formed to provide express mail services, it has become a prominent provider of banking and travel services. The company has a long history and is credited with inventing products, including traveler’s checks, charge cards, and incentive programs. Clients of American Express have a selection of credit and charge cards to choose from, each with its terms and benefits. American Express remains a significant player in the financial and travel services industries to become a client’s go-to source by providing unique goods and services.

