Amul business model is a cooperative business model that revolves around the three-tier structure. At the first tier are millions of milk producers, primarily farmers, who supply milk to the organization. The second tier comprises the cooperative society, represented by the Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation Ltd. (GCMMF), which handles processing, packaging, marketing, and distribution. The third tier involves retailers and consumers who receive Amul’s dairy products through a network of retail channels.
This model emphasizes cost efficiency, quality control, inclusive growth, and brand building. Amul’s cooperative structure ensures fair pricing for farmers, promotes their empowerment, and enables revenue generation through the sale of diverse dairy products.
Contents
A brief history of Amul
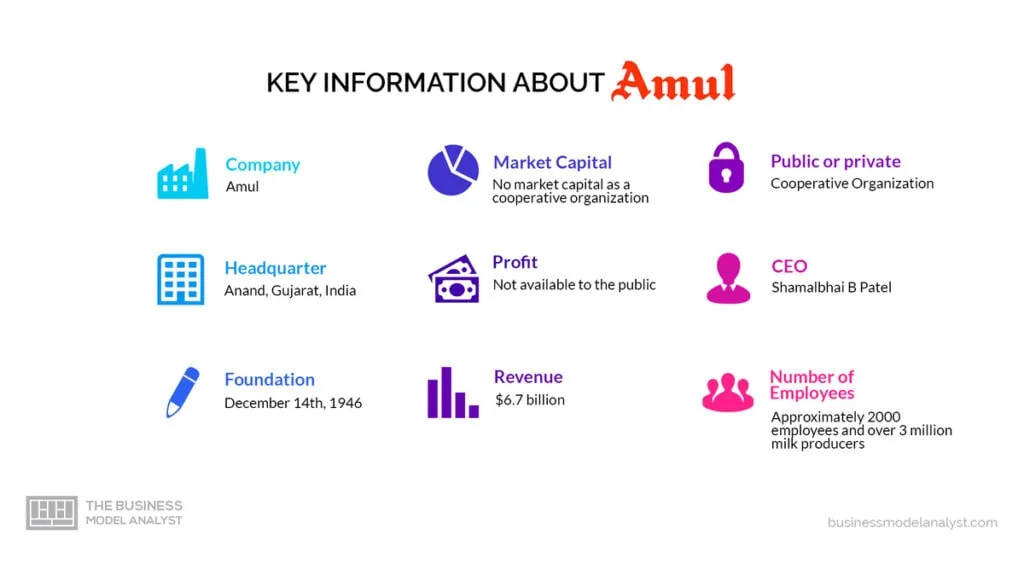
Amul, the Indian dairy cooperative, has a remarkable and continuous history that spans several decades. Founded on December 14th, 1946, in the town of Anand, Gujarat, India, Amul emerged as the Kaira District Cooperative Milk Producers’ Union Limited.
The cooperative was established by a group of farmers led by Tribhuvandas Patel, who aimed to combat the exploitation faced by local milk contractors. In 1948, Amul took a significant step forward by establishing its first milk collection and processing plant in Anand. This step marked the beginning of its journey in the dairy industry.
The year 1949 proved to be a turning point for Amul when Dr. Verghese Kurien joined as its General Manager. Known as the “Father of the White Revolution” in India, Dr. Kurien’s leadership and innovative approach revolutionized the dairy industry. His influence and vision played a crucial role in shaping Amul’s future.
One of Amul’s most recognizable aspects is its iconic advertising campaign featuring the Amul girl, which was launched in 1965. These witty and humorous advertisements, accompanied by the tagline “Utterly Butterly Delicious,” captured the nation’s imagination and significantly contributed to Amul’s brand recognition.
Over the years, Amul introduced a range of dairy products that became household favorites. In the 1970s, Amul Butter debuted, quickly becoming a staple in Indian households. Expanding its product portfolio further, Amul entered the ice cream market in 1996. Its range of Amul Ice Cream products gained significant popularity due to its quality and competitive pricing.
In 1998, the cooperative made history by becoming the first Indian company to sponsor a sports event. It partnered with the Indian cricket team for the Test series against Australia, marking the beginning of Amul’s association with sports sponsorship. Amul’s success continued to soar, and in 2006, it achieved a remarkable milestone by procuring over one billion liters of milk in a single year.
This accomplishment solidified its position as one of the largest milk cooperatives in the world. By 2012, Amul had become the largest food brand in India in terms of annual turnover, surpassing multinational corporations operating in the country.
Who Owns Amul
Amul is owned by a federation of milk producers in Gujarat, India. The milk producers are organized into village-level cooperatives, which form district-level and state-level cooperative organizations. These cooperatives collectively own and control the Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation Ltd. (GCMMF), the apex marketing body responsible for marketing Amul-branded dairy products.
Amul Mission Statement

Amul mission statement is “endeavor to satisfy the taste and nutritional requirements of the customer of the world through excellence in marketing by the committed team.”
How Amul Works
Amul operates through a cooperative model involving various stakeholders’ collaboration and follows a systematic process. Here is a comprehensive explanation of how Amul operates:
Milk Procurement
Amul sources milk from dairy farmers who are members of village-level milk cooperatives or societies. These cooperatives collect the milk from their members, maintaining records of the quantity and quality of the milk supplied.
Milk Collection and Testing
District-level cooperative milk unions further aggregate the milk collected by the village-level cooperatives. These unions have collection centers where the milk is received, and it undergoes testing for various quality parameters such as fat content, SNF (Solid-Not-Fat) content, and overall cleanliness.
Milk Processing
Once the milk meets the quality standards, it is transported to Amul’s processing plants in specially designed tankers to ensure hygiene and freshness. At the processing plants, the milk undergoes various processes, including pasteurization (heating to eliminate harmful bacteria), homogenization (ensuring uniform distribution of fat globules), and cream separation.
Product Manufacturing
Based on processed milk, Amul manufactures a wide range of dairy products. These products include milk, butter, cheese, ice cream, yogurt, and more. Additional ingredients and flavors are added as necessary to create the desired products.
Packaging and Labeling
The manufactured dairy products are packaged in appropriate containers, such as cartons, pouches, tubs, or bottles. Each package is labeled with essential information, including product details, nutritional facts, manufacturing date, and expiry date. Proper packaging and labeling ensure product integrity and consumer safety.
Distribution and Marketing
Amul has an extensive distribution network that includes retail outlets, supermarkets, and exclusive Amul stores. The products are delivered to these locations for sale to consumers. Amul employs various marketing strategies, utilizing print, television, digital media, and outdoor advertising to promote its brand and products.
Consumer Engagement
Amul actively engages with consumers to understand their preferences and expectations. The company values consumer feedback and conducts market research to stay attuned to changing consumer needs. Amul maintains an online presence and interacts with consumers through social media platforms to build strong relationships and address their queries and concerns.
Cooperative Governance
The decision-making process at Amul involves elected representatives from the milk societies and district unions. These representatives form the board of directors for the Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation Ltd. (GCMMF), which is the apex marketing body overseeing Amul’s operations. The cooperative governance structure ensures that the milk producers have a say in the organization’s management, policies, and strategic decisions.
How Amul Makes Money
The Amul company makes money from the following:
Sales of Dairy Products
The primary revenue source for Amul is the sale of its diverse range of dairy products. These products include milk, butter, cheese, ice cream, yogurt, and more. Amul distributes its products through various channels like retail outlets, supermarkets, Amul exclusive stores, and online platforms. When customers purchase these dairy products, it generates revenue for Amul.
Licensing and Franchise
Amul operates a licensing and franchising model, allowing other companies or individuals to use the Amul brand name and sell Amul products under specific agreements and conditions. Amul receives licensing fees and royalties in these arrangements, contributing to its revenue. This model expands Amul’s reach by leveraging the marketing and distribution capabilities of its licensees and franchisees.
Contract Manufacturing
Amul engages in contract manufacturing, wherein it produces dairy products on behalf of other companies or brands. Through these agreements, Amul utilizes its production capabilities and facilities to manufacture dairy products for external entities. This provides an additional revenue stream for Amul and helps maximize the utilization of its production infrastructure.
Ancillary Services
Amul offers ancillary services to support the dairy industry stakeholders. These services include providing packaging materials, equipment, and technical support to milk cooperatives and other entities involved in the dairy sector. By offering these services, Amul generates revenue beyond its core dairy product sales
Amul Business Model
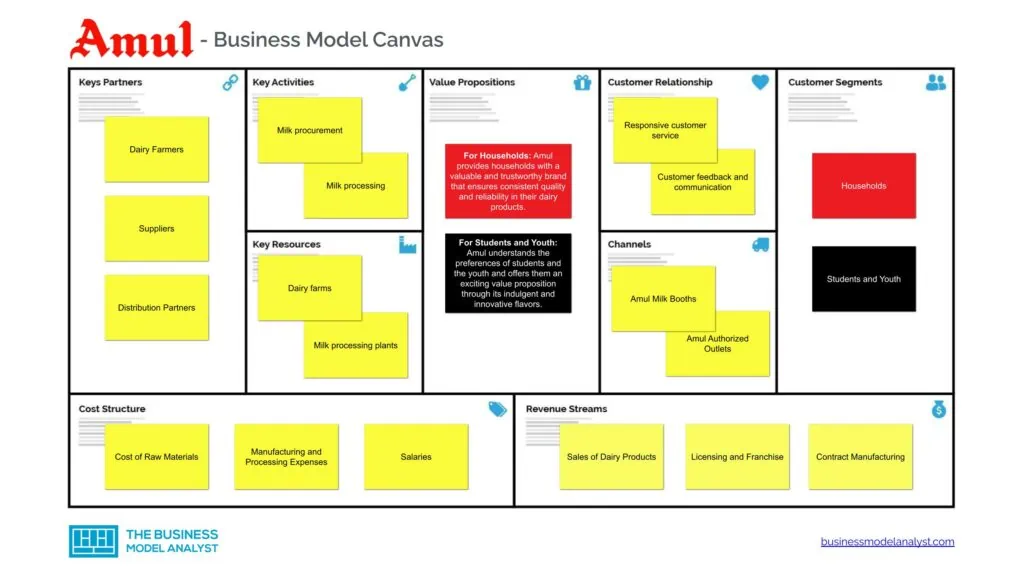
Let’s take a look at the Amul Business Model Canvas below:
Amul Customer Segments
Amul’s customer segments consist of:
- Households: Households refer to groups of people living together in a shared dwelling, typically a residential home. They can be composed of family members, roommates, or individuals living alone. Households manage their domestic affairs, including finances, household chores, and day-to-day activities. They often make purchasing decisions related to groceries, household goods, and services;
- Students and Youth: Students and youth refer to individuals who are pursuing education or are in their younger years. They are typically enrolled in educational institutions such as schools, colleges, or universities. They have specific needs related to education, career development, social activities, and personal growth;
- Health-conscious Consumers: Health-conscious consumers prioritize their physical and mental well-being and actively seek products and services that promote good health. They focus on maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and adopting a holistic approach to wellness. Health-conscious consumers often prefer organic or natural food products, fitness-related gadgets, and wellness services;
- Retailers and Small Businesses: Retailers and small businesses are entities engaged in the sale of goods or services to consumers. Retailers can range from small local stores to large chains, while small businesses can encompass a variety of sectors, including retail, hospitality, consulting, or manufacturing. These entities typically interact directly with customers and are involved in sourcing products, marketing, sales, and customer service;
- Food Service Industry: The food service industry encompasses establishments involved in preparing and selling food and beverages to customers. These establishments include restaurants, cafés, fast food chains, catering services, and food trucks.
Amul Value Propositions
Amul’s value propositions consist of:
- For Households: Amul provides households with a valuable and trustworthy brand that ensures consistent quality and reliability in their dairy products. Families can rely on Amul’s extensive range of high-quality and nutritious dairy products, such as milk, butter, cheese, and yogurt, to meet their daily needs. Amul’s commitment to maintaining its trusted brand image is a unique and essential value proposition for households;
- For Students and Youth: Amul understands the preferences of students and the youth and offers them an exciting value proposition through its indulgent and innovative flavors. With a wide range of ice cream flavors and other products, Amul provides to the taste preferences of this customer segment, providing them with delicious and enjoyable dairy treats. Amul’s ability to consistently introduce new and unique flavors makes it a popular choice among students and the youth;
- For Health-conscious Consumers: Amul recognizes the growing importance of health-conscious consumers and offers them a significant value proposition through its range of low-fat and low-sugar options. These healthier alternatives, which include low-fat milk, low-fat cheese, and low-sugar yogurt, allow health-conscious individuals to make nutritious choices without compromising on taste. Amul’s commitment to providing healthier dairy options sets it apart in the market;
- For Retailers and Small Businesses: Amul provides retailers and small businesses with a competitive edge through its attractive pricing and strong brand support. By offering its dairy products at competitive prices, Amul enables retailers and small businesses to generate profit margins while providing to the demands of their customers. Additionally, Amul’s marketing and brand support empower retailers to effectively promote and sell Amul products, enhancing their business success;
- For Food Service Industry: Amul’s consistent quality and reliable bulk supplies make it a preferred choice for the food service industry. With a reputation for providing high-quality dairy products, Amul meets the stringent requirements of food service establishments. Furthermore, Amul’s ability to efficiently supply bulk quantities of its dairy products ensures that the food service industry can effectively meet its customers’ demands.
Amul Channels
Amul’s channels consist of:
- Amul Milk Booths
- Amul Authorized Outlets
- Amul Ice Cream Scooping Parlors
- Amul Online Store
Amul Customer Relationships
Amul’s customer relationships consist of:
- Responsive customer service
- Customer feedback and communication
- Loyalty programs and incentives
- Community involvement and social initiatives
Amul Revenue Streams
Amul’s revenue streams consist of:
- Sales of Dairy Products
- Licensing and Franchise
- Contract Manufacturing
- Ancillary Services
Amul Key Resources
Amul’s key resources consist of:
- Dairy farms
- Milk processing plants
- Manufacturing facilities
- Distribution network
- Technological infrastructure
- Brand and intellectual property
- Skilled workforce
Amul Key Activities
Amul’s key activities consist of:
- Milk procurement
- Milk processing
- Product manufacturing
- Quality control
- Distribution and logistics
- Marketing and advertising
- Farmer support and training
Amul Key Partners
Amul’s key partners consist of:
- Dairy Farmers
- Suppliers
- Distribution Partners
- Technology Providers
- Financial Institutions
- Advertising and Marketing Agencies
Amul Cost Structure
Amul’s cost structure consists of:
- Cost of Raw Materials
- Manufacturing and Processing Expenses
- Salaries
- Distribution and Logistics Expenses
- Marketing and Advertising Expenses
- Overhead and Administrative Costs
- Compliance and Regulatory Expenses
Amul Competitors
- Mother Dairy: Mother Dairy is a well-known dairy brand in India, established in 1974 by the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) under the Operation Flood program. It started as a small milk booth in Delhi and gradually expanded its product range to include milk, ice cream, yogurt, butter, cheese, and other dairy products. Mother Dairy operates mainly in northern and eastern India and has become a popular choice for consumers;
- Britannia: Britannia Industries Limited is a renowned food processing company in India that produces a wide range of dairy products, including cheese, butter, milk, and flavored milk. Although Britannia is primarily known for its biscuits, it has established a strong presence in the dairy sector. The company has a rich history dating back to 1892 and has diversified its product offerings over the years to supply the evolving consumer demands;
- Nestlé: Nestlé is a multinational food and beverage company that operates globally, including in India. It has a significant presence in the Indian dairy market with a wide range of dairy products, such as milk, milk powder, infant nutrition, and dairy-based beverages. Nestlé’s history traces back to 1866, when it was founded in Switzerland, and it has since expanded its product portfolio to encompass various food and beverage categories;
- Parag Milk Foods: Parag Milk Foods Ltd. is an Indian dairy company that specializes in the production and marketing of milk and milk-based products. It was established in 1992 and has grown steadily since then. Parag Milk Foods operates under various brand names like Gowardhan and Go, offering a diverse range of products such as milk, ghee, butter, cheese, paneer (cottage cheese), and yogurt. The company primarily operates in western and northern India;
- Kwality: Kwality Limited is one of India’s oldest and most reputed dairy companies, with a history dating back to 1992. It produces and markets a wide range of dairy products, including milk, butter, cheese, ghee, and flavored milk. Kwality has a strong presence in northern India and has expanded its operations over the years to become a significant player in the Indian dairy industry.
Amul SWOT Analysis
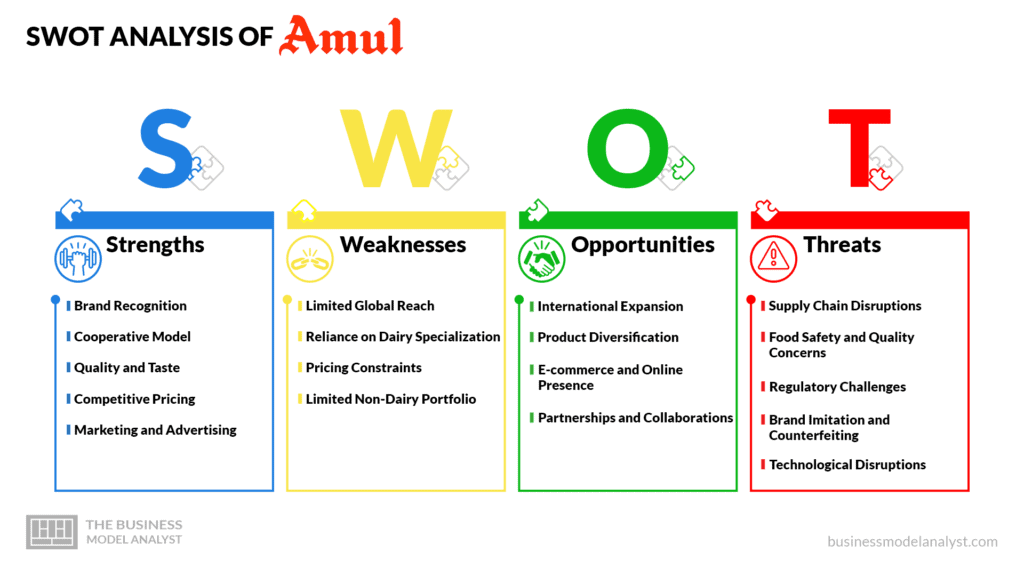
Below, there is a detailed SWOT analysis of Amul:
Amul Strengths
- Brand Recognition: Amul has built a strong brand image and is widely recognized across India. The brand has become synonymous with quality dairy products and enjoys high levels of trust among consumers;
- Cooperative Model: Amul operates on a cooperative model, which means it is owned and governed by several dairy farmers. This model helps in ensuring a steady supply of high-quality milk and provides livelihood opportunities to farmers;
- Quality and Taste: Amul products are known for their consistent quality and delicious taste. The company follows stringent quality control measures at every stage of production to ensure that consumers receive the best dairy products;
- Competitive Pricing: Amul adopts a competitive pricing strategy, offering its products at affordable prices compared to many of its competitors. This approach has helped them attract a large customer base, including both urban and rural consumers;
- Marketing and Advertising: Amul is known for its creative and memorable advertising campaigns. The brand often uses topical and humorous advertisements featuring its iconic mascot, the Amul girl. These campaigns have helped build brand recall and establish an emotional connection with consumers.
Amul Weaknesses
- Limited Global Reach: Amul has a strong presence in the Indian market but lacks significant international penetration. Expanding its operations and establishing a stronger foothold in global markets is challenging due to competition from local brands and the need for adaptation to diverse consumer preferences;
- Reliance on Dairy Specialization: Amul is primarily known for its dairy products, such as milk, butter, and cheese. While this specialization has been a source of strength, it also poses a weakness in terms of brand diversification. Relying heavily on a single product category makes the company vulnerable to shifts in consumer preferences or industry trends;
- Pricing Constraints: Amul has positioned itself as an affordable brand supplying the masses. While this strategy has helped capture a significant market share, it may limit the company’s ability to compete in premium segments or offer higher-margin products. Balancing competitive pricing with the introduction of premium offerings could be an area for improvement;
- Limited Non-Dairy Portfolio: While Amul has expanded its product portfolio over the years, its range of non-dairy products is relatively limited. Diversifying into non-dairy segments, such as snacks, beverages, or plant-based alternatives, can provide new growth opportunities and reduce dependence on the dairy sector.
Amul Opportunities
- International Expansion: Amul has the potential to expand its operations and distribution network beyond India’s borders. By entering new international markets, Amul can leverage its brand reputation and capitalize on the growing demand for Indian dairy products in various countries;
- Product Diversification: Amul can explore opportunities to diversify its product portfolio beyond dairy. By introducing new product lines such as snacks, beverages, desserts, or plant-based alternatives, Amul can provide to evolving consumer preferences and capture a broader market share;
- E-commerce and Online Presence: The rise of e-commerce and digital platforms presents an opportunity for Amul to strengthen its online presence. By enhancing its e-commerce capabilities, optimizing digital marketing strategies, and establishing partnerships with online retailers, Amul can reach a broader customer base and improve convenience for consumers;
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Forming strategic partnerships or collaborations with other food and beverage companies, retailers, or technology providers can open up new avenues for growth and enable Amul to access new markets, distribution channels, or technological advancements.
Amul Threats
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Amul relies on a complex supply chain to source raw materials and distribute its products. Disruptions in the supply chain, such as natural disasters, transportation issues, or political instability, can impact production, lead to shortages, and affect customer satisfaction. Ensuring a robust and resilient supply chain is crucial;
- Food Safety and Quality Concerns: Maintaining high standards of food safety and quality is of utmost importance in the dairy industry. Any incidents related to contamination, product recalls, or quality issues can severely damage Amul’s reputation and erode customer trust. Vigilance in quality control and adherence to strict food safety standards are essential to mitigate this threat;
- Regulatory Challenges: The dairy industry is subject to various regulations and compliance requirements, including those related to food safety, labeling, packaging, and advertising. Changes in regulations or non-compliance can create challenges for Amul and impact its operations. Staying abreast of regulatory changes and ensuring compliance is crucial to avoid penalties and maintain business continuity;
- Brand Imitation and Counterfeiting: Amul’s strong brand reputation and recognition make it susceptible to brand imitation and counterfeiting. Unauthorized use of the Amul brand or counterfeit products can lead to revenue loss and harm the brand’s image and consumer trust. Implementing robust brand protection measures and taking legal action against infringers is crucial;
- Technological Disruptions: Rapid advancements in technology, such as automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics, can disrupt traditional business models. Amul needs to continuously invest in technology and innovation to remain competitive, improve operational efficiency, and deliver superior customer experiences.
-> Read More About Amul’s SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
The Amul business model stands as a shining example of the power of cooperative efforts and inclusive growth. Amul has achieved remarkable success in the dairy industry with its three-tier structure and emphasis on cost efficiency, quality control, and brand building. Through this model, millions of milk producers, primarily farmers, have found fair pricing, empowerment, and a sustainable source of income.
One of the key strengths of the Amul business model is its focus on collaboration. By bringing together farmers and the Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation Ltd. (GCMMF), Amul has created a strong network that ensures the steady supply of high-quality milk and the efficient processing, packaging, marketing, and distribution of dairy products. This collaboration has benefited the farmers, the cooperative society, and the end consumers.

