The Adobe business model focuses on subscription-based services. Before 2013, Adobe used only licensing business model. However, in 2013, the company switched to a subscription-based model when it launched its Creative Cloud service. The new Adobe business model requires customers to pay an annual or monthly fee to access Adobe’s services. Adobe’s subscription model has been very successful so far and has helped the company maintain dominance in the software market. For instance, Adobe Inc was able to generate more than $17 billion in revenue for the 2022 fiscal year.
Contents
A brief history of Adobe
John Warnock and Charles Geschke founded Adobe company in 1982. Before that time, both men worked at Palo Alto Research Center (PARC), where they jointly developed a page-description programming language. They decided to create their own company to sell their invention to the public after PARC refused to sell the technology to market. Both men named the page-description language Adobe PostScript and released it to market in 1985. The company was able to generate $1.2 million in revenue in just 1985 after releasing PostScript. In 1986, the company was able to raise an additional $6.5 million to expand its product by going public.
Adobe company released another product known as Adobe Illustrator in 1986. In 1989, the company released another product called Adobe Photoshop, a graphics editor. Adobe company kept releasing new products and improving its current products throughout the 1990s. For instance, in 1993, they released a new product called Adobe Acrobat, a PDF reader and creator. Adobe began to acquire other companies starting in the 2000s.
Who Owns Adobe
Adobe’s ownership is dispersed among several shareholders of the company. The top shareholders include The Vanguard Group, Inc, BlackRock, Inc, and State Street Corporation.
Mission Statement
The Adobe mission statement is “to change the world through digital experiences.”
How Adobe works
Adobe works by providing a wide range of software products and services to the public in exchange for money. Some Adobe software products are:
Adobe Creative Cloud
Adobe Creative Cloud consists of applications for creative projects such as video editing, graphic design, and web development. Photoshop, Illustrator, Premiere Pro, and InDesign are examples of applications within this suite.
Adobe Document Cloud
This suite consists of applications for creating, viewing, managing, and sharing digital documents. Adobe Acrobat DC and Adobe Sign are examples of apps within this suite.
Adobe Fonts
Adobe Fonts consists of several thousand fonts from various designers. The fonts are readily accessible within Adobe’s creative applications like Photoshop and Illustrator.
Adobe Experience Cloud
Adobe Experience Cloud consists of tools that businesses can use to create, and monitor marketing campaigns. A few examples of tools within this suite are Adobe Campaign, Adobe Analytics, and Adobe Target.
How Adobe makes money
Adobe company makes money from the following:
Subscription
Professions who use Adobe products and services pay monthly or annual fees. Users can choose from a variety of plans they wish to subscribe to. The available plans include individual plans, education plans, and business plans. Each plan generates lots of money for Adobe company.
License
Adobe sometimes uses the license business model for some of its products rather than using the subscription model. For instance, one of Adobe’s products — Lightroom 6 — doesn’t require a subscription. Instead, it requires licensing. The one-time fee that Adobe collects from customers who buy licenses fetches significant revenue for the company.
Advertising
Adobe has an Advertising Cloud platform where it offers advertising services in exchange for money. Adobe generates money from people who use the Advertising Cloud platform.
Stock Sales
Adobe has a stock content marketplace where people can buy and sell stock images and other digital content. The company gets a certain percentage of money on every sale that occurs on the Adobe Stock marketplace.
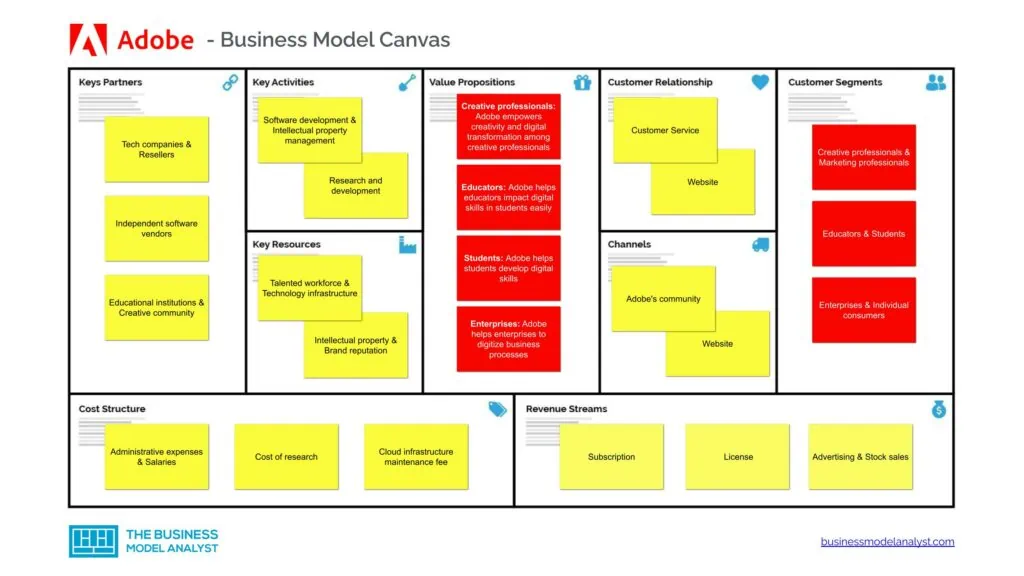
Adobe Business Model Canvas
The Adobe Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
Adobe Customer Segments
Adobe’s customer segments consist of:
- Creative professionals: Creative professionals like photographers, videographers, and graphic designers all use Adobe’s products, like Photoshop and Illustrator;
- Marketing professionals: Marketers and businesses who use Adobe Experience Cloud to create and manage creative campaigns are part of Adobe’s customer segment;
- Educators: Some educational institutions use Adobe packages to teach students digital skills;
- Students: Some students use Adobe packages while learning, especially digital skills;
- Enterprises: Organizations using Adobe products like Adobe Marketing Cloud and Adobe Document Cloud fall within this category;
- Individual consumers: Individual consumers are also part of Adobe’s customer segment.
Adobe Value Propositions
Adobe’s value propositions consist of:
- For Creative professionals: Adobe empowers creativity and digital transformation among creative professionals;
- For Marketing professionals: Adobe provides the tools marketing professionals need to create and manage effective campaigns;
- For Educators: Adobe helps educators impact digital skills in students easily;
- For Students: Adobe helps students develop digital skills;
- For Enterprises: Adobe helps enterprises to digitize business processes;
- For Individual consumers: Access to high-quality software products and services.
Adobe Channels
Adobe’s channels consist of:
- Adobe’s community
- Website
Adobe Customer Relationships
Adobe’s customer relationships consist of:
- Customer Service
- Website
Adobe Revenue Streams
Adobe’s revenue streams consist of:
- Subscription
- License
- Advertising
- Stock sales
Adobe Key Resources
Adobe’s key resources consist of:
- Talented workforce
- Technology infrastructure
- Intellectual property
- Brand reputation
Adobe Key Activities
Adobe’s key activities consist of:
- Software development
- Intellectual property management
- Research and development
Adobe Key Partners
Adobe’s key partners consist of:
- Tech companies
- Resellers
- Independent software vendors
- Educational institutions
- Creative community
Adobe Cost Structure
Adobe’s cost structure consists of:
- Administrative expenses
- Salaries
- Cost of research
- Cloud infrastructure maintenance fee
Adobe Competitors
- Microsoft: Microsoft is a leading tech company that creates varieties of software products and services. Some of its software products perform the same functions as Adobe software products, which is why Microsoft is Adobe’s competitor. A few examples of Microsoft’s software products that compete with Adobe’s products include digital media and marketing software;
- Google: Google is a technology company that offers internet-related services. The areas where Google competes with Adobe include analytics, cloud computing, and digital marketing;
- Oracle: Oracle is a tech company that creates software products and cloud services. The company competes with Adobe in areas like marketing automation and content management;
- International Business Machines Corporation(IBM): IBM is a tech company that provides a variety of software services to businesses and governments worldwide. The areas where the company competes with Adobe include analytics, digital marketing, and content marketing;
- Corel: Corel is among the top software companies worldwide, having over 100 million active users. The company is well known for creating high-quality creative software, just like Adobe. Some of its popular software products include CorelDRAW and VideoStudio.
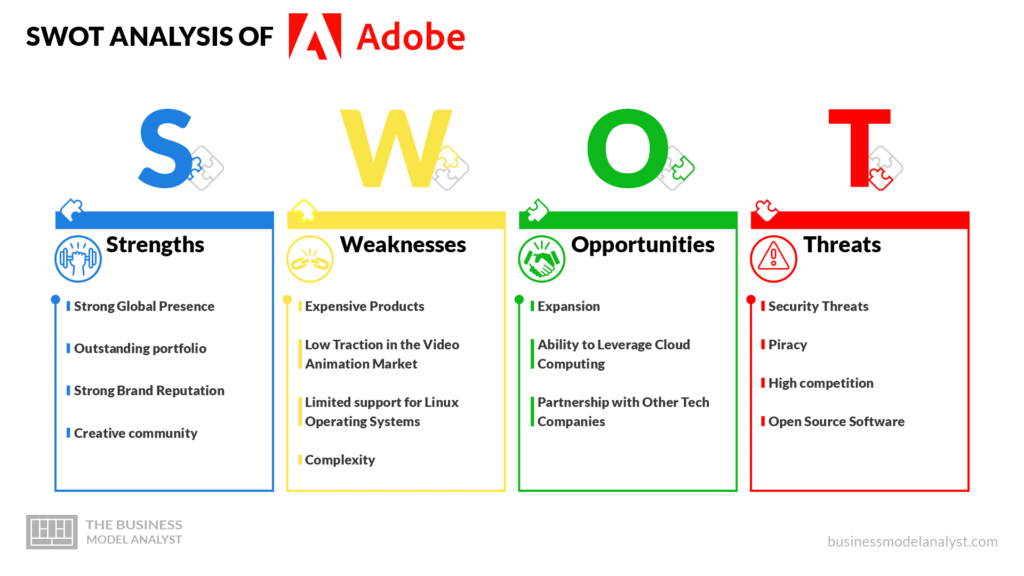
Adobe SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Adobe:
Adobe Strengths
- Strong Global Presence: Adobe’s products are widely used across the globe. The company even offers localized versions of its software in various languages like Spanish, French, Chinese, and more to reach everyone. Adobe has offices in more than 40 different countries worldwide;
- Outstanding portfolio: Adobe has a very wide range of products in media and marketing segments. The large number of dependable products in Adobe’s portfolio is one of the company’s strengths and the reason for continuous growth. While Adobe’s portfolio is very broad, the company ensures that each product within its portfolio has top-notch quality. In fact, some Adobe products seem to have no close competitors. Adobe Photoshop, for instance, is the most dominant graphic design software worldwide;
- Strong Brand Reputation: Millions of people around the world trust Adobe company to continually provide quality products and services. The company was able to gain a strong reputation for itself as a result of its focus on quality products and services;
- Creative community: Adobe’s creative community serves as one of the company’s strengths in a number of ways. The community helps Adobe get timely feedback on its products and even boosts brand loyalty.
Adobe Weaknesses
- Expensive Products: The cost of Adobe’s products is unattractive to customers, as they are widely considered to be very expensive. Software products from other companies performing similar jobs as Adobe are quite affordable compared to Adobe products. The rate at which customers patronize Adobe might reduce significantly in the future if alternative software products with cheaper licensing fees or monthly subscription fees continue to come into the market;
- Low Traction in the Video Animation Market: One would expect Adobe to have a strong presence in the video animation market, just as it does in the graphic design market. However, the company has a very low presence in the video animation market despite having software products for creating 3D animation. Animator creators prefer to use software products from other companies since other products seem to offer better features compared to Adobe Premiere Pro;
- Limited support for Linux Operating Systems: Adobe’s failure to officially release most of its applications for Linus OS is widely considered to be a major weakness for the company. For instance, Photoshop isn’t officially compatible with Linux OS. While Some Linux users can still use Photoshop on their computer via virtual machines, only a few Linux users will choose to go through the complex processes required to set up Photoshop on Linux. They will instead use alternative image editing software;
- Complexity: Almost all Adobe software packages have several advanced features that require significant effort and time commitment to master. The advanced features are usually overwhelming for starters. The complexity of Adobe packages might discourage beginners from testing Adobe packages, but rather try out other beginner-friendly software packages.
Adobe Opportunities
- Expansion: Adobe can use its strong position in the market to expand its products, either by acquiring other promising tech companies or creating new products. The company may even expand the capabilities of its existing products, especially in the video animation market. A few examples of segments where Adobe has the opportunity to expand include Artificial Intelligence (AI), Augmented Reality (AR), and Virtual Reality (VR);
- Ability to Leverage Cloud Computing: Cloud computing gives Adobe a significant number of opportunities that the company can utilize to grow. For instance, Adobe can create AI-powered tools using cloud computing;
- Partnership with Other Tech Companies: As a reputable brand, Adobe has the opportunity to partner with other great tech companies like Microsoft to achieve bigger goals. For instance, a partnership between Adobe and another top tech company can help Adobe access new markets and integrate its technology with top hardware manufacturers.
Adobe Threats
- Security Threats: As a leading software provider, Adobe is one of the top targets for cybercriminals. In the past, hackers have developed various kinds of malware and viruses for Adobe packages just to gain unauthorized access to the devices of people who use Adobe packages. Cybercriminals aren’t the only people who pose security threats to Adobe and its users. Adobe’s contractors and even employees also pose some level of threat as they have access to very sensitive user data, and they may wish to exploit the data if they lack integrity;
- Piracy: Piracy is one of Adobe’s major threats. Piracy harms the company by significantly reducing the revenue Adobe gets from subscriptions. If pirated versions of Adobe products continue to increase excessively, the company may no longer have enough financial resources to invest in research and expand;
- High competition: Adobe is one of the tech companies facing the highest level of competition. Adobe faces increased competition in areas like video editing, marketing, graphic design, marketing, and more. If the company fails to keep improving its product, its competitor may succeed in making Adobe irrelevant in the market;
- Open Source Software: Open source software like Blender, GIMP, and Inkscape perform almost the same function as Adobe packages like Photoshop and Illustrator. These open-source software serve as threats to Adobe, since some people will prefer them to Expensive Adobe software packages.
Conclusion
Adobe’s business model allows customers to access software products and services after paying monthly or yearly fees rather than buying the software. The company also generates additional revenue from sales of some services like consulting, training, and support. The company is very likely to increase its revenue streams in the future as it diversifies into new markets.

