The Snowflake business model revolves around a consumption-based pricing infrastructure complemented by its professional services. This flexible usage-based pricing strategy allows customers to pay for only what they use. This business model has taken the cloud-based data warehousing industry by storm with its innovative approach.
Snowflake is a SaaS cloud computing-based data company that offers data storage, processing, and analytic solutions that are quicker, more user-friendly, and far more versatile than traditional offerings.
Snowflake’s revolutionary approach to cloud computing has transformed the way in which organizations store, access, and analyze data. Its flexible and scalable infrastructure separates computation and storage, allowing businesses to expand each component as needed. This model, in turn, results in better performance, improved scalability, and lower costs, placing them ahead of the competition and making them a very attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
Contents
A brief history of Snowflake
In 2012, three experts in San Mateo, California; Benoît Dageville, Thierry Cruanes, and Marcin Żukowski; with a background in Oracle and large-scale data warehousing solutions, came together to create what is today known as Snowflake. The trio chose the name “snowflake” because of their immense love for snow sports and the uniqueness that can be seen in each snowflake. This reflected their company’s vision: to provide a unique and tailored approach to data management for its users.
In 2014, Snowflake officially came out of stealth mode and announced the availability of its services, allowing customers to store, access, and analyze large amounts of data in real time.
In 2015, the company raised $45 million and launched its first product to the public, the cloud data warehouse. And in 2016, they introduced a unique pricing model that allows customers to pay for only the amount of data they use, instead of the traditional fixed subscription payment.
And then, in 2019, they partnered with Microsoft Azure making it possible for customers to use Snowflake’s cloud data warehousing service on Microsoft’s cloud platform.
In 2020, Snowflake had a market valuation of over $70 billion, making it one of the biggest software IPOs in history. In addition, the company’s stock price doubled on its first day of trading, making it the most prominent software IPO in terms of first-day gains. In addition, the business announced a partnership with Salesforce that would enable users to use Snowflake’s cloud data warehouse service on Salesforce’s cloud platform, similar to what they did for Microsoft.
In 2021, Snowflake signed a partnership with Google Cloud, repeating the circuit. The company also unveiled new features and capabilities, including Snowpark, which enables developers to build unique data apps on the Snowflake platform, and Snowsight, a new data visualization tool.
Who Owns Snowflake
Snowflake was founded in 2012 by Benoit Dageville, Thierry Cruanes, and Marcin Zukowski.
Snowflake is a publicly-traded company owned by institutional and retail investors.
As of 2021, the largest shareholder in Snowflake is Sutter Hill Ventures, a venture capital firm that has invested over $1 billion in the company and has been involved with Snowflake since its early days. Other significant shareholders include Sequoia Capital, Altimeter Capital, and ICONIQ Capital. The company is also listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol SNOW.
Snowflake Mission Statement
The Snowflake mission statement is “to enable every organization to be data-driven. Our cloud-built data warehouse makes that possible by delivering instant elasticity, secure data sharing, and per-second pricing across multiple clouds.”
How Snowflake works
Snowflake is a cloud-based data warehousing technology that allows enterprises to store, manage, and analyze massive amounts of information in a highly scalable and flexible way. The platform is designed to work smoothly with cloud-based infrastructure providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, allowing users to benefit from their scalability and reliability.
The company stores data in a distributed columnar database for cloud storage and processing. The platform is based on a multi-cluster, shared-data architecture that enables numerous customers to access the same infrastructure while maintaining data isolation and security.
When customers use Snowflake, they typically start by creating one or more virtual warehouses. Each warehouse is a cluster of computing resources allocated to a single customer. The user can then input data into Snowflake using various techniques, such as bulk loading, streaming, and data replication.
After the data is loaded, customers can use Snowflake’s SQL-based query engine to run analytical queries against the data. Snowflake’s query engine is optimized for cloud-based processing and can use the distributed columnar database architecture to provide high performance and scalability.
How Snowflake makes money
Cloud Data Platform Subscription
Snowflake’s primary revenue source is its cloud data platform subscription. The subscription-based model allows customers to pay for data storage, processing power, computing, and data transfer fees. The fees are based on the platform’s usage, measured in credits.
Professional Services
Snowflake also generates revenue through professional services. The company charges customers for professional services, such as training and consulting, to its customers.
Marketplace
The Snowflake Marketplace is a platform where customers can find and purchase third-party data and applications. The marketplace provides customers with a wide range of data and tools that can be used to build their data solutions. Snowflake generates revenue by charging a commission on the sales made through its marketplace.
Snowpark
Snowpark is a feature that enables developers to write custom code in Java or Scala to query, transform and analyze data within Snowflake. In addition, this paid add-on feature allows customers to use their own custom code in Snowflake.
Partnerships
Snowflake also generates revenue through its partnerships. The company partners with various software vendors and system integrators to offer its customers integrated solutions and charges a commission on the sales generated through its partner network.
Snowflake Business Model Canvas
The Snowflake Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
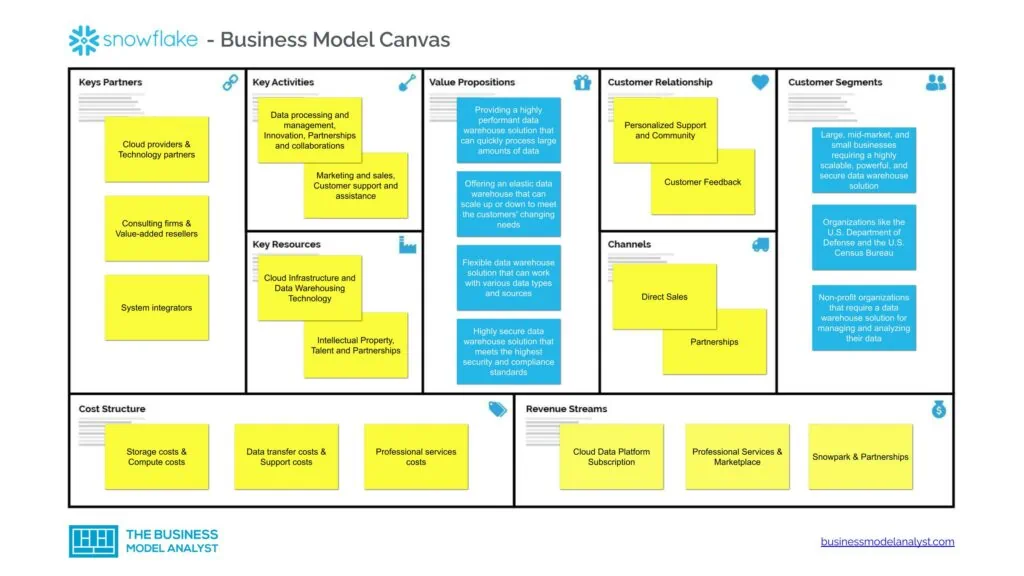
Snowflake Customer Segments
Snowflake customer segments consist of:
- Companies: Snowflake’s primary customer segment is large, mid-market, and small businesses requiring a highly scalable, powerful, and secure data warehouse solution to manage and analyze vast amounts of data;
- Government organizations: Snowflake also provides services to organizations like the U.S. Department of Defense and the U.S. Census Bureau;
- Non-profit organizations: Snowflake also serves non-profit organizations that require a data warehouse solution for managing and analyzing their data.
Snowflake Value Propositions
Snowflake value propositions consist of:
- Providing a highly performant data warehouse solution that can quickly process large amounts of data. Snowflake’s data warehouse solution is designed with a unique architecture that separates storage from computing. This separation allows for massively parallel processing over a large number of virtual compute instances, enabling Snowflake to process large amounts of data at high speeds.
Also, It uses a technique called query optimization to quicken query performance. This requires analyzing each query and automatically generating an execution plan that makes the best use of the available resources. This allows fast query execution times, even when working with complex questions and large datasets.
Overall, Snowflake’s structure is designed to scale with the customers’ needs, ensuring that their workloads are always running smoothly.
- Offering an elastic data warehouse that can scale up or down to meet the customers’ changing needs. Snowflake’s flexible data warehouse is designed to handle data workloads of any size or complexity. Considering its cloud-native architecture and built-in auto-scaling capabilities, Snowflake can automatically and dynamically adjust the number of computing resources required for handling a given workload based on the amount of data being processed, the number of concurrent users, and other factors.
This also ensures that the customers pay only for what they use, rather than having to pay for fixed capacity that may go underutilized or be insufficient during peak periods.
- Flexible data warehouse solution that can work with various data types and sources. Snowflake’s flexibility refers to its ability to handle multiple data types and sources, such as structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, including CSV, JSON, Avro, Parquet, and more. It can handle both batch and streaming data and is compatible with multiple programming languages, including Python, R, and Java.
It can also integrate with other tools and platforms, including Informatica, Talend, and Matillion, allowing customers to build customized data pipelines that fit their needs.
- Highly secure data warehouse solution that meets the highest security and compliance standards. Snowflake provides end-to-end encryption for all data in transit, and at rest, including backups and metadata; its access control policies are based on roles, and it is compliant with various industry standards and regulations, such as (SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR), it also provides detailed auditing and monitoring capabilities. With all these features, Snowflake ensures that customer data is always protected and meets the highest security and regulatory compliance standards.
Snowflake Channels
Snowflake’s channels consist of the following:
- Direct Sales: Snowflake’s direct sales team sells its data warehousing solutions directly to customers;
- Partnerships: Snowflake partners with various technology companies, including cloud providers, software vendors, and system integrators;
- Online: Snowflake provides a platform where customers can sign up for its data warehousing services, access resources, and manage their accounts.
Snowflake Customer Relationships
Snowflake’s customer relationships consist of the following:
- Personalized Support: Snowflake provides customized support to customers, helping them with everything from initial onboarding to ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting. This includes dedicated account managers, customer success teams, and technical support;
- Community: Snowflake has an active community of users who share information, best practices, and solutions to common problems. This community helps to foster customer relationships by enabling customers to learn from each other, share experiences, and work together to solve challenges;
- Customer Feedback: Snowflake values customer feedback and uses it to improve its products and services continually. The company regularly surveys customers to understand their needs, challenges, and pain points and incorporates this feedback into its product roadmap.
Snowflake Revenue Streams
Snowflake’s revenue streams consist of:
- Cloud Data Platform Subscription
- Professional Services
- Marketplace
- Snowpark
- Partnerships
Snowflake Key Resources
Snowflake’s key resources consist of the following:
- Cloud Infrastructure: Snowflake leverages cloud infrastructure provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) to deliver its data warehousing services;
- Data Warehousing Technology: Snowflake’s proprietary technology is a crucial resource for the company. The technology enables the company to separate storage and computing, providing a scalable, flexible, and efficient data warehousing service;
- Intellectual Property: Snowflake’s intellectual property, including patents, trademarks, and copyrights, is a valuable resource for the company as It helps the company protect its technology and prevent competitors from copying its services;
- Talent: Snowflake’s team of experienced data warehousing and cloud computing experts is another crucial resource for the company. The group includes software engineers, data scientists, and cloud infrastructure experts with deep industry knowledge;
- Partnerships: Snowflake has partnered with leading cloud providers, technology vendors, and consulting firms to expand its reach and offer additional services to its customers. These partnerships are a vital resource for the company in terms of driving customer acquisition and revenue growth.
Snowflake Key Activities
Snowflake’s key activities consist of the following:
- Data processing and management: Snowflake offers a cloud-based data warehouse technology that enables customers to securely and scalably store and manage enormous amounts of data;
- Innovation: The company invests heavily in research and development to continuously improve its platform and services;
- Partnerships and collaborations: Snowflake collaborates with several partners and technology companies to integrate and augment its platform with new features and capabilities;
- Marketing and sales: The company markets its services to potential customers and works to close deals to generate revenue;
- Customer support and assistance: Snowflake provides customer support to ensure customers have a seamless experience with its platform and services.
Snowflake Key Partners
Snowflake’s key partners consist of:
- Cloud providers: Snowflake works with leading cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform to host and operate its platform;
- Technology partners: The company partners with a range of technology providers to enhance its platform and services, including companies like Tableau, Looker, and Databricks;
- Consulting firms: Snowflake collaborates with consulting firms to help clients integrate and implement its platform and services;
- Value-added resellers: The company partners with value-added resellers to distribute and sell its services to a broader range of customers;
- System integrators: Snowflake partners with system integrators to provide end-to-end data management and analytics solutions.
Snowflake Cost Structure
Snowflake’s cost structure consists of:
- Storage costs: Snowflake charges customers for the amount of data stored in its cloud-based data warehouse. Storage pricing varies depending on the region, with prices typically ranging from $23 to $40 per terabyte per month;
- Compute costs: The company also charges customers for the amount of processing power used to analyze data. Compute pricing also varies depending on the performance level, with prices ranging from $0.00056 to $1.50 per credit per hour;
- Data transfer costs: Customers are charged by Snowflake for data transported in and out of its warehouse. Prices for data transfer range from $0.04 to $0.16 per gigabyte, depending on the region and the amount of data transmitted;
- Support costs: Customers can select from various service plans, each tailored to their specific requirements, provided by Snowflake. Different support tiers are available, from basic to premium, including round-the-clock access to technical specialists. Plans for technical assistance begin at $5,000 annually;
- Professional services costs: Snowflake offers professional services to help customers integrate and optimize their data warehouse. Prices for professional services vary depending on the scope of the project.
Snowflake Competitors
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Redshift: Launched in 2012, Redshift is a cloud-based data warehousing solution that enables customers to analyze large data sets quickly. It offers seamless integration with other AWS services and supports SQL-based queries;
- Google BigQuery: Launched in 2010, BigQuery is a fully managed, cloud-native data warehouse that provides fast and cost-effective analysis of large datasets. It is designed to handle the demands of businesses of all sizes, and its integration with the Google Cloud Platform makes it easy to use alongside other tools and services;
- Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics: Formerly known as Azure SQL Data Warehouse, Synapse Analytics is a cloud-based analytics service that provides enterprises with the ability to store and analyze large amounts of structured and unstructured data;
- Oracle Autonomous Data Warehouse: It is a cloud-based solution that automates many of the tasks associated with data warehousing, including security, backup, and performance tuning;
- Teradata Vantage: Founded in 1979 in California, United States. It is an analytics platform that provides customers with a range of tools and capabilities to store, process, and analyze large data sets;
- IBM Cloud Pak for Data: Launched on April 7, 2011. IBM Cloud Pak for Data is an end-to-end data and AI platform that enables businesses to collect, analyze, and manage data across multiple clouds and on-premise environments.
Despite the competition, Snowflake has differentiated itself by offering a unique cloud-based data warehousing and analytics platform designed for simplicity, speed, and performance.
Snowflake SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Snowflake:
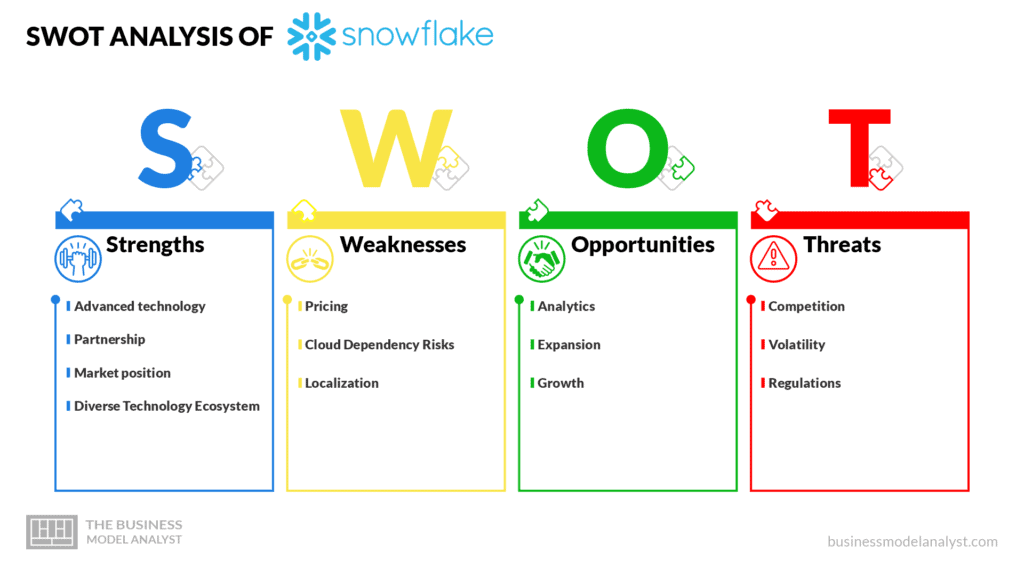
Snowflake Strengths
- Advanced technology: This provides the company with a notable advantage in the cloud-based data warehousing industry. Its high-performance capabilities, robust security features, and ease of use make it a go-to option for customers yearning for a comprehensive and powerful data warehousing solution;
- Partnership: By collaborating with cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Snowflake can offer its customers easy integration with their existing cloud infrastructure. Through these partnerships and Snowflake’s integration with the cloud providers’ infrastructure, customers can easily access Snowflake’s services without having to go through complex setup and installation processes;
- Market position: Snowflake enjoys a strong market position and brand recognition. In fact, it is currently ranked first in Forbes Cloud 100, a list of the top 100 private cloud companies in the world. This ranking is a testament to the company’s innovative approach and the value it provides to its customers. Its growing customer base also serves as a validation of Snowflake’s ability to offer a comprehensive and streamlined solution for managing data that attract new customers who are seeking a more efficient and scalable solution to their data-related needs;
- Diverse Technology Ecosystem: Snowflake benefits from a large, diverse ecosystem of technology partners, which is an excellent advantage for the company and its customers. By collaborating with other technology providers, it can expand its offerings and provide a more comprehensive solution to its customers.
Partners in this ecosystem range from cloud service providers to data integration specialists to suppliers of Business Intelligence and analytics tools. These companies provide integrations and services that enhance Snowflake’s offering and benefit the company’s clientele.
Snowflake Weaknesses
- Pricing: One of the main drawbacks of Snowflake’s business model is its high pricing. The company’s pricing model is based on a consumption-based subscription model, which charges customers based on what they do on Snowflake. While this pricing model can be attractive to larger enterprises with high data processing needs, it can be less accessible for smaller companies and startups with limited budgets.
Snowflake’s pricing is generally higher than its competitors in the cloud-based data warehousing industry, making it less accessible for smaller companies and startups.
- Cloud Dependency Risks: As a fully managed SaaS platform, Snowflake relies on cloud infrastructure providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) to host and deliver its services. While this allows Snowflake to benefit from the scalability and reliability of these cloud providers, it also means that the company is dependent on them for its operations. And this dependency on cloud infrastructure providers can limit Snowflake’s control over its platform and potentially increase its costs.
- Localization: Another potential limitation of Snowflake’s business model is its limited geographic reach. Presently, Snowflake is primarily focused on serving customers in North America and Europe, and this can limit its growth potential in other regions.
While Snowflake has a growing customer base in these regions, it has a limited presence in other markets, which could make it difficult to expand its customer base and compete with other cloud-based data warehousing providers that have a more global presence.
Snowflake Opportunities
- Analytics: The demand for data-driven insights and analytics has been growing rapidly in recent years, fueled by the proliferation of data and the increased importance of making data-driven decisions in business. This trend has created a large potential market for Snowflake, which offers cloud-based data warehousing solutions.
Snowflake’s platform is well-suited to meet this growing demand for analytics. Its advanced technology and unique architecture allow organizations to easily store, manage and analyze large volumes of data while also providing the scalability, performance, and security required to support mission-critical analytics applications.
- Expansion: Expansion into new industries and markets, including emerging technology fields such as AI and ML (artificial intelligence and machine learning), represents an essential opportunity for Snowflake to continue its growth trajectory to meet the evolving needs of its clientele. Maintaining its position as a market leader in cloud-based data warehousing will be possible. It will fuel further expansion in the coming years if the company keeps pushing the boundaries of innovation and developing new solutions to meet the complex data requirements of various industries.
- Growth: Continued development and improvement of technology and architecture, coupled with strong partnerships and a focus on meeting the evolving needs of its customers, are key factors driving Snowflake’s growth and success. As the demand for data-driven insights and analytics continues to grow, Snowflake’s ability to innovate and provide flexible, high-performance data warehousing solutions will be critical to its ongoing success in the years ahead.
Snowflake Threats
- Competition: Snowflake faces intense rivalry from various players in the market. These competitors are providers that also offer data warehousing and analytics services that can be used in conjunction with their other cloud services to offer customers a more all-encompassing cloud solution.
Snowflake also battles with emerging data analytics and warehousing startups that are looking to change the market. These startups offer innovative approaches to data management and analytics, sometimes at a lower price point, which can attract customers who are looking for cost-effective solutions.
- Volatility: Like any other business, Snowflake is vulnerable to economic downturns and shifts in technology trends that can affect its demand and market growth. In times of economic uncertainty or recession, companies may cut back on their IT spending, including cloud-based data warehousing and analytics services. Also, the rapid pace of technological innovation can cause market disruption and changes in customer demand.
- Regulations: Any security breach or data leak can significantly damage Snowflake’s reputation and customer trust, leading to financial losses and legal liabilities.
Moreover, Snowflake must comply with various regulations related to data privacy and security, such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines and legal penalties, further harming its reputation and financial performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, since its founding in 2012, Snowflake has been a dominant innovation in the data warehousing market. The company’s business model differentiates it from more traditional data warehousing services. Snowflake’s ability to attract a wide range of customers, from solo entrepreneurs to multinational corporations, directly results from its focus on its customers and their needs.
While cloud-based data warehousing accounts for most of Snowflake’s revenue, the company also benefits from selling professional services and a marketplace. Snowflakes’ most valuable assets are the cloud infrastructure, cutting-edge data warehousing technologies, and talented staff. Also, the company has formed significant partnerships with industry-leading cloud services like AWS and Azure.
Snowflake’s unique business model, innovative technology, and customer-focused approach have made it a significant player in the data warehousing industry. As the demand for advanced data management solutions grows, Snowflake is well-positioned to capitalize on this trend and drive innovation.

