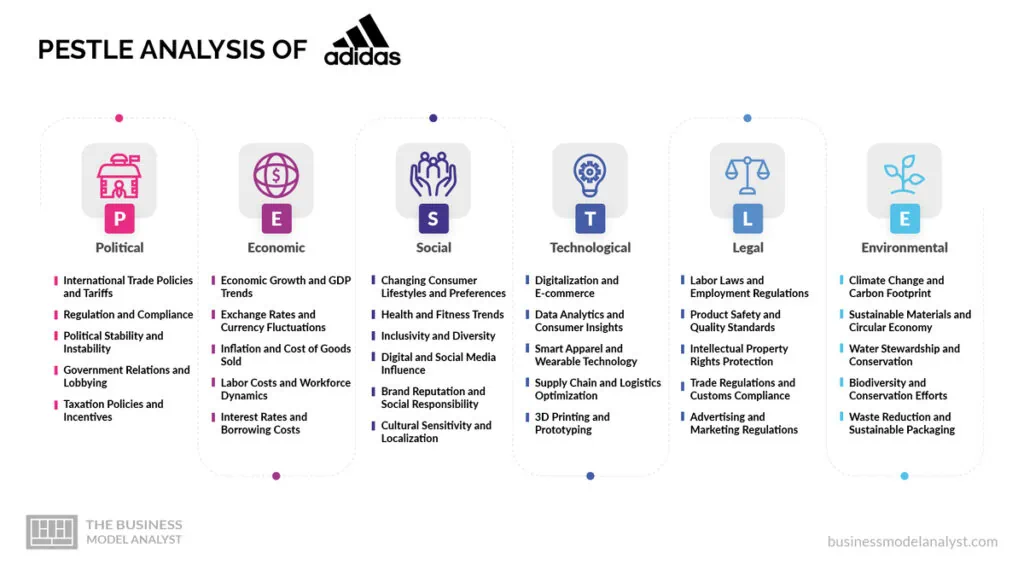
In today’s dynamic and ever-changing business landscape, organizations must continuously assess the external factors that impact their operations and strategies. One such analytical tool, asides from the SWOT analysis, that aids businesses in understanding their external environment is the PESTLE analysis.
PESTLE stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors, and it provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating the macro-environmental influences that can shape an industry or a company’s performance.
The Adidas PESTLE analysis aims to assess the key external factors that have the potential to impact the company’s strategic decisions, market position, and overall business performance.
Contents
Adidas Political Factors

Political factors play a critical role in shaping the business environment and operations of companies like Adidas. As a global sportswear brand, Adidas is impacted by various political forces in different countries where it operates.
- International Trade Policies and Tariffs
Adidas operates in multiple countries, and international trade policies significantly influence its global supply chain and distribution networks. Changes in tariffs, trade agreements, and trade barriers can impact the cost of raw materials, manufacturing, and logistics.
For instance, the imposition of tariffs on imported goods by countries where Adidas sources its materials could raise production costs and hinder competitiveness. Additionally, trade disputes between nations may lead to unpredictable disruptions in the flow of goods, affecting the timely delivery of products and customer satisfaction.
- Regulation and Compliance
As a global corporation, Adidas must comply with diverse and sometimes complex regulatory frameworks in each country of operation. These regulations encompass labor laws, environmental standards, product safety, and marketing practices.
Adhering to these laws and standards is essential for avoiding legal issues and penalties and vital to maintaining a positive brand image and reputation. Failure to comply with regulations could lead to boycotts, negative media attention, and potential financial losses.
- Political Stability and Instability
The political stability of countries where Adidas has a presence is crucial for conducting smooth and predictable operations. A stable political environment fosters investment, consumer confidence, and economic growth, which benefit the company.
On the other hand, political instability, civil unrest, or governmental changes can introduce uncertainties, disrupt supply chains, and jeopardize employee safety. Adidas must closely monitor political developments in its operating countries to assess potential risks and devise contingency plans.
- Government Relations and Lobbying
Like other multinational corporations, Adidas engages in government relations and lobbying activities to influence policies that directly impact its business. The company may collaborate with governments on initiatives related to sustainable practices, corporate social responsibility, or public health campaigns.
These partnerships can enhance Adidas’ reputation and foster a positive image among consumers and stakeholders. However, improper lobbying or allegations of undue influence can lead to negative publicity and damage the company’s credibility.
- Taxation Policies and Incentives
Taxation policies in various countries can significantly affect Adidas’ financial performance. Different tax rates, incentives, and regulations on profits, import/export duties, and intellectual property rights can influence the company’s profitability and competitiveness.
Governments may offer tax incentives for investing in certain regions, which could influence Adidas’ decisions on manufacturing facilities, distribution centers, and marketing efforts.
- Global Political Relations
Adidas operates in a highly interconnected world where geopolitical relations can impact its business. Tensions between nations or trade blocs may lead to changes in import/export regulations, affecting cross-border logistics and supply chains.
Additionally, geopolitical events like sanctions, conflicts, or diplomatic disputes can alter consumer behavior and brand perception in specific regions.
- Intellectual Property Rights Protection
The enforcement of intellectual property rights is critical for Adidas, given its innovative designs and brand reputation. Political factors that influence the strength of intellectual property laws, patent protection, and trademark regulations can impact Adidas’ ability to defend its products against counterfeiting and unauthorized imitations.
Robust protection ensures that Adidas can maintain a competitive advantage and continue investing in research and development.
Adidas Economic Factors
Economic factors have a profound impact on Adidas. Economic conditions influence consumer behavior, purchasing power, production costs, and overall business performance.
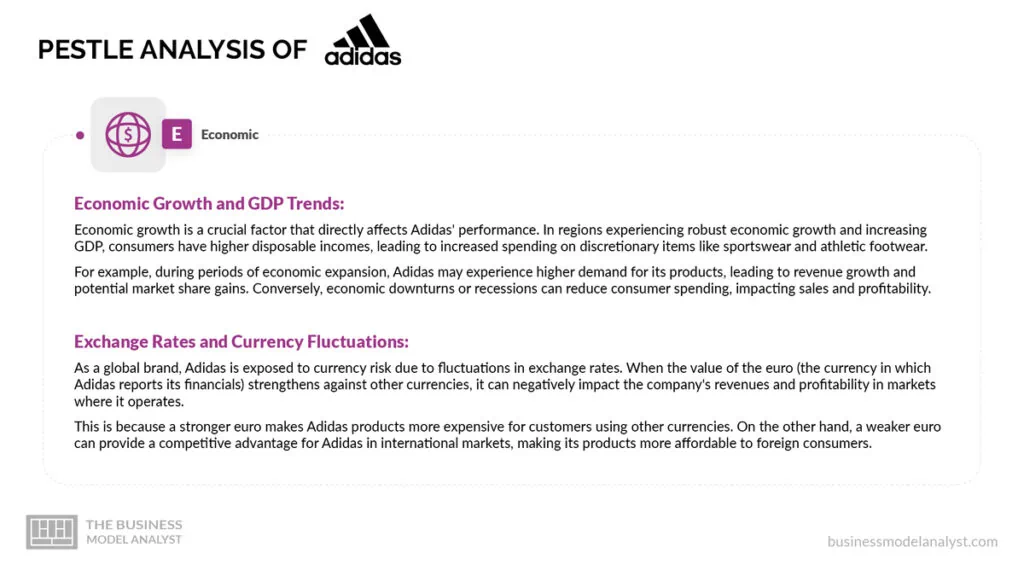
- Economic Growth and GDP Trends
Economic growth is a crucial factor that directly affects Adidas’ performance. In regions experiencing robust economic growth and increasing GDP, consumers have higher disposable incomes, leading to increased spending on discretionary items like sportswear and athletic footwear.
For example, during periods of economic expansion, Adidas may experience higher demand for its products, leading to revenue growth and potential market share gains. Conversely, economic downturns or recessions can reduce consumer spending, impacting sales and profitability.
- Exchange Rates and Currency Fluctuations
As a global brand, Adidas is exposed to currency risk due to fluctuations in exchange rates. When the value of the euro (the currency in which Adidas reports its financials) strengthens against other currencies, it can negatively impact the company’s revenues and profitability in markets where it operates.
This is because a stronger euro makes Adidas products more expensive for customers using other currencies. On the other hand, a weaker euro can provide a competitive advantage for Adidas in international markets, making its products more affordable to foreign consumers.
- Inflation and Cost of Goods Sold
Inflation affects both the cost of raw materials and the cost of production for Adidas. When inflation rates rise, the cost of sourcing materials and manufacturing products may increase, leading to higher production costs.
Moreover, inflation can also affect consumer purchasing power and demand for Adidas products. The company must manage cost inflation effectively through strategic sourcing, supply chain optimization, and pricing strategies to maintain profitability without compromising product quality.
- Labor Costs and Workforce Dynamics
Adidas operates production facilities and sourcing networks in various countries, each with its labor market dynamics. Labor costs, wages, and workforce availability influence the company’s production decisions and overall operational efficiency.
For instance, in countries where labor costs are relatively low, Adidas may choose to establish manufacturing facilities to take advantage of cost savings. However, labor rights issues or inadequate labor conditions can lead to negative publicity and reputational risks for the company.
- Interest Rates and Borrowing Costs
Fluctuations in interest rates can significantly impact Adidas’ borrowing costs and financial decisions. High-interest rates can increase the company’s debt burden, making it more expensive to finance investments or expansion.
Conversely, low-interest rates can provide Adidas with opportunities to access affordable credit for capital projects, acquisitions, or research and development initiatives. Careful financial planning and risk management are essential for Adidas to navigate interest rate changes effectively.
- Consumer Confidence and Spending Patterns
The level of consumer confidence in the economy influences consumer spending behavior. During periods of economic uncertainty or recession, consumers may cut back on non-essential purchases, impacting Adidas’ sales.
On the other hand, during economic upturns, increased consumer confidence can drive higher demand for sportswear and athletic footwear. Adidas must monitor consumer sentiment and adapt its marketing and product strategies accordingly to stay attuned to changing spending patterns.
- Trade Agreements and Economic Integration
Trade agreements and economic blocs, such as the European Union or the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), can significantly impact Adidas’ global supply chain and market access.
Participation in these agreements can lead to reduced trade barriers, streamlined customs procedures, and increased market opportunities. For example, preferential trade agreements can facilitate easier access to markets, enhancing Adidas’ competitive advantage and profitability in those regions.
- Urbanization and Emerging Markets
The ongoing trend of urbanization, particularly in emerging markets, presents both opportunities and challenges for Adidas. As more people move to cities, there is an increased focus on fitness, health, and lifestyle, leading to higher demand for sportswear and athletic apparel. By strategically targeting emerging markets with urbanization trends, Adidas can tap into new consumer bases and grow its market share.
Adidas Social Factors

Social factors are vital in shaping the success and reputation of a global brand like Adidas. Understanding the social landscape and consumer preferences is critical for the company’s marketing, product development, and corporate social responsibility efforts.
- Changing Consumer Lifestyles and Preferences
Consumer lifestyles and preferences continually evolve, influenced by factors such as fashion trends, health consciousness, and cultural influences. Adidas must adapt its product offerings to provide these changing preferences.
For instance, the growing popularity of athleisure wear has driven demand for stylish and comfortable sportswear that can be worn both during workouts and in everyday life. To stay relevant and appealing to consumers, Adidas needs to anticipate and respond to shifting lifestyle trends.
- Health and Fitness Trends
The increasing emphasis on health and fitness globally has led to a surge in demand for sportswear and athletic footwear. Consumers are now more health-conscious and engaged in various physical activities, from gym workouts to outdoor sports.
Adidas has capitalized on this trend by aligning its marketing campaigns with active lifestyles and emphasizing the performance aspects of its products. The company’s partnership with athletes and fitness influencers further enhances its brand appeal in the fitness community.
- Inclusivity and Diversity
In today’s socially conscious world, brands are expected to embrace inclusivity and diversity in their marketing and product representation. Consumers increasingly seek products that reflect their values and identities.
Adidas has made efforts to promote diversity in its advertising campaigns and product designs, including partnerships with athletes from diverse backgrounds and the introduction of inclusive sizing. For example, their collaboration with Parley for the Oceans, which uses recycled plastic to create sustainable footwear, reflects their commitment to environmental and social responsibility.
- Digital and Social Media Influence
The rise of social media and digital platforms has transformed how consumers interact with brands. Social media platforms serve as powerful channels for brand communication, customer engagement, and influencer marketing.
Adidas has actively embraced social media, collaborating with popular influencers and leveraging user-generated content to enhance brand visibility and foster a sense of community among its followers. Social media also allows Adidas to receive real-time feedback from customers, enabling the company to improve its products and services based on consumer preferences.
- Brand Reputation and Social Responsibility
A brand’s reputation is intrinsically linked to its social responsibility efforts. Consumers increasingly expect companies to address social and environmental issues proactively. Adidas has committed to sustainable and ethical practices in its supply chain, striving to reduce its carbon footprint and ensure fair labor practices.
For instance, the “Adidas Better Cotton Initiative” promotes the use of sustainable cotton in their products, contributing to the improvement of cotton farming practices and farmers’ livelihoods.
- Cultural Sensitivity and Localization
Adidas operates in diverse cultural contexts globally, and cultural sensitivity is crucial for its success. The company must be mindful of cultural nuances when designing products and marketing campaigns.
For example, specific designs or color choices may be considered offensive in some cultures, which could lead to negative publicity and reputational damage. By adopting a localized approach and understanding the specific preferences and sensitivities of each market, Adidas can effectively connect with consumers on a deeper level.
- Fashion Collaboration and Influencer Marketing
Collaborations with fashion designers, celebrities, and influencers have become a prominent marketing strategy for Adidas. These partnerships enable the brand to tap into new markets and attract consumers who follow the style choices of these influencers.
Notable collaborations with celebrities like Kanye West (Adidas Yeezy line) and fashion designers like Stella McCartney have helped Adidas gain popularity in the fashion-forward consumer segment.
- Evolving Retail Landscape and E-commerce
The retail landscape is rapidly evolving, with a significant shift towards e-commerce and online shopping. Social factors such as convenience, digital experiences, and contactless transactions influence consumer behavior.
Adidas has invested in its e-commerce platform and embraced digital innovation to offer a seamless shopping experience to customers worldwide. Moreover, the company has adapted its marketing strategies to engage with consumers through social media platforms and influencer partnerships, fostering a sense of community and loyalty.
Adidas Technological Factors

Technological advancements and innovation play a pivotal role in shaping the competitive landscape and growth trajectory of companies like Adidas. As a leading sportswear brand, Adidas continually faces the impact of technological factors on its product development, manufacturing processes, marketing strategies, and overall business operations.
- Digitalization and E-commerce
The retail industry’s rapid digitalization has revolutionized how consumers shop for sportswear. E-commerce platforms offer a convenient and seamless shopping experience, enabling consumers to browse, compare, and purchase Adidas products from the comfort of their homes.
Adidas has invested heavily in its e-commerce platform, optimizing user experience and expanding its online presence to provide a global customer base. The company’s online store and partnerships with major e-commerce platforms have contributed to increased sales and brand visibility.
- Data Analytics and Consumer Insights
Advancements in data analytics have enabled companies to gain valuable insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. Adidas leverages data analytics to understand its customer base better, identify emerging market trends, and make informed decisions on product design and marketing campaigns.
For instance, data analysis of customer feedback and social media engagement helps Adidas refine its product offerings and tailor its marketing messages to resonate with target audiences.
- Smart Apparel and Wearable Technology
Integrating technology into sportswear has given rise to smart apparel and wearable devices. Adidas has embraced this trend by launching products like miCoach, a wearable device that tracks and analyzes athletic performance.
Additionally, the brand has collaborated with tech companies to incorporate sensors and smart fabrics into its products, enabling athletes to monitor their performance metrics in real time. Smart apparel not only enhances customer engagement but also opens up new revenue streams and opportunities for Adidas in the health and fitness market.
- Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization
Technological advancements have facilitated significant improvements in supply chain management and logistics. Adidas employs technologies like RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) to track and manage inventory efficiently.
RFID tags provide real-time visibility into product movements, allowing Adidas to optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and streamline distribution processes. Enhanced logistics capabilities contribute to improved customer satisfaction by ensuring timely deliveries and efficient order fulfillment.
- 3D Printing and Prototyping
The adoption of 3D printing technology has revolutionized the prototyping and product development process in the sportswear industry. Adidas leverages 3D printing to create rapid prototypes, allowing designers to visualize and refine product designs quickly.
This technology accelerates the product development cycle, reducing the time to market for new designs and innovations. Additionally, 3D printing enables Adidas to customize products for individual customers, offering personalized options that provide unique preferences and requirements.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Product Design
AI technologies are increasingly utilized in sportswear design and development. Adidas employs AI algorithms to analyze consumer data and market trends, informing the design process to create products that align with customer preferences.
AI-driven design tools can generate innovative patterns, materials, and color combinations, leading to novel product offerings that resonate with fashion-forward consumers. By incorporating AI into its design process, Adidas can continuously innovate and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
- Virtual Try-On and Augmented Reality (AR) Retail
Virtual try-on and AR technologies have transformed the retail experience for customers. Adidas has integrated AR features into its mobile apps, allowing users to virtually try on shoes and apparel before making a purchase.
This enhances the online shopping experience and reduces the likelihood of returns, improving customer satisfaction. Moreover, Adidas has experimented with interactive AR displays in brick-and-mortar stores, providing engaging and immersive experiences to shoppers.
- Sustainability and Eco-Innovations
Technological advancements play a significant role in Adidas’ sustainability efforts. The company actively invests in eco-innovations and sustainable materials research. For example, it explores new technologies to create environmentally friendly materials like recycled polyester and biodegradable fabrics.
Adidas’ partnership with Parley for the Oceans demonstrates its commitment to combating plastic pollution by incorporating recycled ocean plastic into its products, exemplifying how technology can drive positive environmental impact.
Adidas Legislative Factors

Legislative/legal factors encompass the laws, regulations, and policies enacted by governments that directly impact Adidas’ business operations and compliance requirements. As a global sportswear brand, Adidas operates in various countries, each with its unique legislative landscape.
- Labor Laws and Employment Regulations
Labor laws and employment regulations profoundly influence Adidas’ operations, particularly in countries where the company manufactures its products. These laws govern aspects such as working hours, wages, occupational health and safety, child labor, and workers’ rights.
Adidas must comply with these regulations to ensure fair treatment of workers and avoid legal penalties or negative publicity related to labor rights violations. For instance, adherence to minimum wage laws and providing safe working conditions are crucial aspects of the company’s ethical and responsible business practices.
- Product Safety and Quality Standards
Legislative requirements for product safety and quality standards vary across countries and regions. Adidas must ensure its products meet all applicable safety regulations to protect consumers and avoid product recalls or legal liabilities.
Complying with standards such as the Consumer Product Safety Act in the United States or the European Union’s General Product Safety Directive is essential for maintaining the company’s reputation and consumer trust.
- Intellectual Property Rights Protection
Intellectual property (IP) rights legislation is critical for protecting Adidas’ brand identity, trademarks, patents, and designs. The company invests heavily in research and development to create innovative products, and IP protection is crucial to prevent unauthorized use or imitation of its designs and technologies.
Adidas must actively monitor and enforce its IP rights through legal measures to safeguard its market position and prevent counterfeit products from entering the market.
- Trade Regulations and Customs Compliance
Adidas operates in a global market, necessitating compliance with international trade regulations and customs requirements. The company must navigate complex import and export regulations, tariffs, and trade agreements between countries.
Non-compliance with these regulations can result in delays in shipments, customs duties, and potential trade disputes. For example, changes in trade policies, such as the imposition of new tariffs or trade sanctions, may impact Adidas’ supply chain and sourcing decisions.
- Advertising and Marketing Regulations
Legislation related to advertising and marketing practices varies from country to country, influencing how Adidas promotes its products and engages with consumers. The company must adhere to regulations regarding truth in advertising, endorsements, and the use of misleading claims. For example, certain countries may have strict rules on the use of celebrity endorsements or require clear disclosures when using digital marketing channels.
- Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Standards
Increasing global concerns about environmental sustainability have led to the enactment of various environmental regulations. As a responsible corporate entity, Adidas must comply with environmental laws related to waste management, emissions, and sustainable practices.
The company’s commitment to sustainability is evident through initiatives like the Science-Based Targets initiative, where it sets ambitious carbon reduction goals aligned with the Paris Agreement.
- Taxation and Corporate Governance
Taxation policies and corporate governance regulations significantly impact Adidas’ financial performance and transparency. The company operates in various tax jurisdictions, and it must comply with tax laws and report financial information accurately.
Furthermore, corporate governance regulations, such as those governing executive compensation and board structures, play a role in shaping the company’s corporate culture and management practices.
- Privacy and Data Protection Laws
In an increasingly digital world, data privacy and protection have become critical legislative concerns. Adidas collects and processes customer data for various purposes, such as marketing and product customization. The company must comply with data protection laws, like the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), to safeguard customer information and respect individuals’ privacy rights.
Adidas Environmental Factors

Environmental factors are of utmost importance for a company like Adidas, as sustainability and responsible practices are critical to maintaining its brand reputation and long-term success. As a global sportswear brand, Adidas faces various environmental challenges and opportunities in its operations, supply chain, and product development. In this extensive analysis, we delve into the environmental factors affecting Adidas and explore the company’s efforts to mitigate its environmental impact.
- Climate Change and Carbon Footprint
As a major player in the sportswear industry, Adidas recognizes its responsibility in addressing climate change. The company has set ambitious targets to reduce its carbon footprint and transition to renewable energy sources.
For example, Adidas aims to achieve carbon neutrality in its own operations by 2025 and reduce greenhouse gas emissions across its entire value chain. The company’s “Adidas x Parley” collaboration is a prominent example of its commitment to sustainability and combating climate change.
- Sustainable Materials and Circular Economy
Adidas is actively exploring sustainable materials to reduce its reliance on virgin resources and promote a circular economy. The company incorporates recycled polyester, organic cotton, and other eco-friendly materials into its products.
By embracing circularity principles, Adidas seeks to design products with longer lifespans and improve end-of-life recycling options for its products. This approach helps minimize waste and extends the useful life of materials, contributing to a more sustainable fashion industry.
- Water Stewardship and Conservation
The sportswear manufacturing process requires a significant amount of water. Adidas acknowledges the importance of responsible water management and has established water stewardship programs to reduce water consumption and improve water quality in its supply chain.
The company collaborates with suppliers and local communities to implement water-saving technologies and practices. Furthermore, Adidas participates in the “Zero Discharge of Hazardous Chemicals” initiative, aiming to eliminate harmful substances from its supply chain and protect water resources.
- Biodiversity and Conservation Efforts
Adidas recognizes the impact of its operations on biodiversity and natural habitats. The company is committed to reducing deforestation and conserving biodiversity through sustainable sourcing practices.
For example, it supports the protection of high conservation value areas and promotes responsible forest management in its supply chain. Adidas also collaborates with conservation organizations to raise awareness of biodiversity issues and promote sustainable practices within the sportswear industry.
- Waste Reduction and Sustainable Packaging
Adidas is dedicated to reducing waste generation throughout its supply chain and retail operations. The company aims to eliminate single-use plastics from its offices, retail stores, and events.
It explores innovative packaging solutions to minimize environmental impacts. Adidas’ “End Plastic Waste” initiative aims to create a closed-loop system where plastic waste is recycled and reused, preventing it from entering landfills or polluting oceans.
- Environmental Compliance and Certifications
Adidas adheres to environmental regulations in the countries where it operates and strives to surpass minimum compliance requirements. The company maintains environmental management systems to continually monitor and improve its environmental performance.
Additionally, Adidas seeks third-party certifications such as ISO 14001, demonstrating its commitment to environmental best practices.
- Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Adidas strongly emphasizes supply chain transparency and traceability to ensure responsible sourcing practices. The company collaborates with suppliers to improve visibility into their operations and identify potential environmental risks.
Initiatives like the “Sustainable Apparel Coalition’s Higg Index” enable Adidas to assess the environmental impacts of its products and supply chain partners.
Conclusion
The PESTLE analysis demonstrates that Adidas operates in a dynamic and challenging global business environment. While the company faces political and economic uncertainties, it has shown resilience and adaptability throughout its history.
By capitalizing on social trends, technological innovations, and a solid commitment to sustainability, Adidas can maintain its competitive edge in the sportswear market. Navigating legal complexities and maintaining a positive public image will be critical in safeguarding the brand’s reputation and growth prospects.
To remain successful in the future, Adidas should continue to monitor the external environment closely, anticipate emerging trends and challenges, and proactively adjust its strategies accordingly.
Furthermore, fostering innovation, embracing diversity, and fostering a customer-centric approach will be essential in cementing Adidas’ position as a global leader in the sportswear industry.