The Zomato business model represents innovation and transformation in the food technology industry. The company is an Indian multinational restaurant aggregator and food delivery company. As a pioneering force in the food delivery and restaurant discovery industries, Zomato has revolutionized how people interact with dining options and culinary experiences.
Initially, Zomato started as a restaurant discovery platform, providing information about restaurants, menus, user reviews, and ratings. However, it later expanded its services to include food delivery, table reservations, and other related features. The company fuses and seamlessly integrates cutting-edge technology, robust logistics, and a user-centric approach into its business model. These factors are responsible for its success and expansion over the years.
Zomato has a multifaceted business model. It creates a comprehensive ecosystem in the food and restaurant industry by incorporating various revenue streams and services. The company faces stiff competition in the food delivery and restaurant aggregation spaces, both domestically and internationally. However, its ability to adapt, diversify its services, and leverage technology gives it a strong position in the market.
Despite Zomato’s diverse array of services, the needs of its users and restaurant partners evolve as the market dynamic changes. This article delves into the intricate workings of the Zomato business model, examining its major components and simplifying the strategies that have propelled it to become a global powerhouse in the food-tech industry.

Contents
A brief history of Zomato
Zomato was founded by Deepinder Goyal and Pankaj Chaddah in 2008. The idea for Zomato came about when Goyal and Chaddah were working as management consultants for Bain & Company in Delhi. They were frustrated with the lack of good restaurant options in their area, and they realized there was a need for a platform to help people discover new restaurants and make informed dining decisions.
Zomato was initially called “FoodieBay”. It launched as a simple online menu card for restaurants and a restaurant discovery platform in the Indian capital, New Delhi. This basic concept aimed to solve a common problem – the lack of accessible and organized restaurant information. Users could log on, search for restaurants, view menus, and make informed dining decisions.
As Zomato gained traction, the founders recognized the potential to expand beyond Delhi’s borders and provide similar services to food enthusiasts across India. This gradually expanded, encompassing more cities and a broader range of restaurant listings. The company soon expanded to offer food delivery services and has grown rapidly in recent years, and it is now one of the most popular food delivery platforms in India.
The name “Zomato” was adopted in 2010, signifying a fusion of the words “tomato” (a universally recognized food ingredient) and “zoo” (a metaphor for variety). It captured what Zomato aimed to deliver – a diverse and comprehensive selection of dining options. Zomato’s growth between 2010 and 2015 was spectacular. The company not only expanded its geographical footprint to cover multiple Indian cities but also ventured into international markets.
The company’s business model evolved to include user-generated restaurant reviews, ratings, and a social networking element that allowed users to follow their friends’ dining choices. Zomato was no longer just an information repository; it was a dynamic community of food lovers. During this phase, Zomato also embraced monetization through advertising, allowing restaurants to promote themselves on the platform. This boosted Zomato’s revenue and also helped restaurants attract a larger customer base.
The acquisition of Urbanspoon in 2015 marked a significant milestone in Zomato’s international journey, providing them with a foothold in the competitive North American market. The company was now connecting diners to restaurants on a truly global scale. This move further solidified its position as a global leader in the food-tech industry.
In recent years, Zomato has diversified its offerings beyond restaurant discovery. The acquisition of delivery startup “Runnr” in 2017 allowed Zomato to venture into food delivery, competing head-to-head with established players like Swiggy. This move proved prescient, especially in light of the increased demand for food delivery services, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In 2021, Zomato achieved a significant milestone by becoming the first Indian food delivery company to go public. Its successful IPO on the Indian stock market marked a historic moment for the Indian startup ecosystem. The company has grown from a small startup to a major player in the online food delivery market. Zomato is well-positioned to continue to grow and innovate in the future.
Who Owns Zomato
Zomato is a public company, therefore, its shares are traded on a stock exchange market. The largest shareholder in Zomato is Info Edge India, a leading Indian media and internet company. Info Edge India was one of the earliest backers of Zomato. They provided crucial initial funding and have remained a significant shareholder, owning a 23.9% stake in the company.
Other major shareholders in Zomato include Sequoia Capital India (17.8%), Alibaba Ant Financial (10.8%), Temasek Holdings (7.6%), Tiger Global Management (6.1%), and Fidelity Management & Research (5.3%). Deepinder Goyal, the co-founder and CEO of Zomato, also owns a 4.3% stake in the company. Other minor shareholders include Azim Premji Foundation (2.5%), Tiger Global Management (II) (2.1%), Baillie Gifford (1.8%), etc.
Zomato Mission Statement

Zomato’s mission statement is “better food for more people”.
How Zomato works
Zomato works as an online food delivery and restaurant discovery platform that connects diners with restaurants. The following is a detailed explanation of how Zomato works:
Restaurant Discovery
At its core, Zomato is a platform for discovering restaurants. Users start their journey by downloading the Zomato app or visiting the website. Once logged in, they can search for restaurants based on various criteria, such as location, cuisine, budget, etc. Zomato provides a treasure trove of information, including restaurant names, addresses, contact details, and user-generated reviews and ratings.
Detailed Restaurant Listings
When users click on a restaurant of interest, they’re treated to a rich display of information. This includes the restaurant’s menu, photos of the establishment and its dishes, operating hours, and price range. User reviews and ratings are prominently featured, offering valuable insights into the quality of the dining experience.
Menu Exploration
One of Zomato’s key features is its digital menus. Users can explore a restaurant’s entire menu right on the app. This allows for a detailed examination of dishes, ingredients, and prices. Users can even filter dishes based on dietary preferences, like vegetarian or vegan.
Food Delivery
Zomato’s evolution into a food delivery service has been a game-changer. Users can order food from a vast selection of restaurants through the app. Once an order is placed, Zomato’s delivery partners, often referred to as “Zomato Delivery Executives,” pick up the order from the restaurant and deliver it to the customer’s doorstep. Users can follow their order’s progress from the moment it’s accepted by the restaurant to the time it arrives at their location.
Zomato Gold Subscription
Zomato Gold is a subscription-based loyalty program that offers members exclusive benefits such as dining and food delivery discounts. Subscribers enjoy perks like complimentary dishes, priority service, and more.
How Zomato makes money
Zomato runs a multi-faceted business model that encompasses various revenue streams and services. The company makes money in the following ways:
Food Delivery and Table Reservation Commissions
One of Zomato’s primary revenue streams is the commission it charges restaurants for each order placed through its food delivery service. When a user orders food from a restaurant via the Zomato app, the restaurant pays a percentage of the order value as a commission to Zomato. This commission varies, but is typically in the range of 15% to 25% of the order amount, depending on the restaurant’s agreement with Zomato. Also, Zomato earns a commission from the restaurant for each successful reservation made through its platform.
Delivery Fees
In addition to the commission charged to restaurants, Zomato may impose delivery fees on customers for food orders. These fees contribute to the overall revenue, with the amount often varying based on factors such as order value and location.
Advertising and Promotions
Zomato offers restaurants a variety of advertising and promotional services to enhance their visibility on the platform. Restaurants pay to feature their listings prominently, run targeted ad campaigns, and offer special deals to attract customers. These advertising services constitute a significant portion of Zomato’s revenue.
Zomato Gold
Zomato Gold is a subscription-based loyalty program that offers members exclusive discounts and perks at partner restaurants. Users pay a subscription fee to access these benefits. While a portion of this fee is passed on to the partner restaurants, Zomato retains a share, contributing to its revenue.
Data and Analytics
Zomato collects extensive data on consumer preferences, dining habits, and restaurant performance. This data is highly valuable and can be monetized by providing insights and analytics services to restaurants. Restaurants can use this data to make informed decisions about their menus, pricing, and marketing strategies.
Zomato Business Model Canvas
Zomato’s business model can be explained using the following business model canvas:
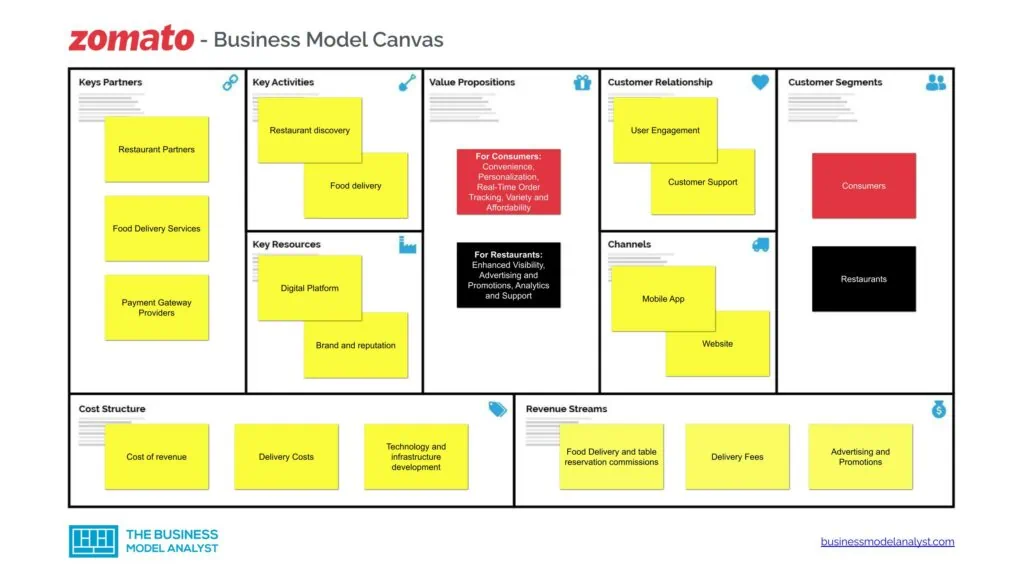
Zomato Customer Segments
Zomato’s customer segments consist of:
- Consumers: These are the people who use Zomato to find restaurants, read reviews, and order food. Zomato’s consumers are typically young, urban, and tech-savvy. They are looking for convenience and variety when it comes to food, and they are willing to use online platforms to find it;
- Restaurants: These businesses list their menus and information on Zomato. Zomato’s restaurants are typically small to medium-sized businesses that are looking to reach a wider audience. They benefit from Zomato’s platform by getting more exposure and generating more orders.
Zomato Value Propositions
Zomato’s value propositions consist of:
Value Propositions for Consumers
- Convenience: Zomato makes it easy to find restaurants, read reviews, and order food. Users can search for restaurants by cuisine, location, price, and other criteria. They can also read reviews from other users to help them decide where to eat. Once they have found a restaurant, they can place an order and track its progress in real time;
- Personalization: Zomato uses its user data to personalize the experience for each customer. This includes recommending restaurants that the user is likely to enjoy, as well as sending notifications about new restaurants and deals;
- Real-Time Order Tracking: Zomato’s food delivery service offers a unique value proposition with real-time order tracking. Consumers can monitor their order’s progress, from the restaurant kitchen to their doorstep. This transparency enhances trust and eliminates the uncertainty associated with food delivery;
- Variety: Zomato offers a wide variety of restaurants to choose from, including everything from local eateries to fine dining establishments. Users can find restaurants that serve their favorite cuisines, as well as new and exciting cuisines to try;
- Affordability: Zomato offers a variety of payment options, including cash, credit card, and debit card. Users can also find restaurants that offer discounts and promotions.
Value Propositions for Restaurants
- Enhanced Visibility: Zomato opens the doors to increased visibility in the digital age. The platform has over 100 million monthly active users, and it is available in over 24 countries. Restaurants can showcase their culinary creations to a vast and diverse audience, reaching potential customers who may have otherwise never discovered their establishment. With millions of users searching for restaurants on Zomato, it serves as a powerful marketing tool to attract new patrons;
- Advertising and Promotions: Restaurants can pay to have their listings featured prominently on the platform, run promotional campaigns, and offer special deals to attract customers. This additional exposure can lead to increased foot traffic and revenue;
- Analytics: Zomato provides restaurants with analytics data about their performance on the platform. This data can help restaurants understand their customers and improve their marketing and operations;
- Support: Zomato offers restaurant support with a variety of issues, such as customer service, payments, and logistics. This can help restaurants focus on their core operations.
Zomato Channels
Zomato’s channels include:
- Mobile App
- Website
- SMS and Email marketing
- Social media
- Customer Support Hotline
- Partnerships
Zomato Customer Relationships
Zomato’s customer relationships consist of:
- User Engagement
- Customer Support
- Feedback Mechanisms
- Personalized user experiences
- Sustainability Initiatives
- Personalized user experiences
- Delivery partner relationships
Zomato Revenue Streams
Zomato’s revenue streams consist of:
- Food Delivery and table reservation commissions
- Delivery Fees
- Advertising and Promotions
- Zomato Gold Subscription
- Data and Analytics
Zomato Key Resources
Zomato’s key resources consist of:
- Digital Platform
- Brand and reputation
- User Base
- Restaurant Partners
- Delivery Fleet
- Technology Infrastructure
- Financial Resources
- Employee Talent
Zomato Key Activities
Zomato’s key activities consist of:
- Restaurant discovery
- Food delivery
- Customer support
- Marketing
- Data collection and analysis
- Technology development
- Partnership management
Zomato Key Partners
Zomato’s key partners consist of:
- Restaurant Partners
- Food delivery services
- Payment Gateway Providers
- Technology partners
- Investors and Financial Partners
- Data and Analytics Partners
Zomato Cost Structure
Zomato’s cost structure consists of:
- Cost of revenue
- Delivery Costs
- Technology and infrastructure development
- Staff Salaries and Benefits
- Rent and Office Expenses
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance
- Research and Development (R&D)
- Marketing and sales
Zomato Competitors
Zomato’s competitors include:
- Swiggy: As one of Zomato’s primary rivals, Swiggy has cemented its position in the Indian market. It is known for its lightning-fast food delivery services, offering a vast array of restaurant choices to customers. Swiggy’s relentless commitment to innovation and expansion into tier-2 and tier-3 Indian cities has garnered a devoted user base, making it a powerful contender in the Indian food-tech scene;
- Uber Eats: Uber Eats is a food delivery platform that is part of Uber Technologies. The company operates in over 60 countries, and it is one of the leading food delivery platforms in the world. While Zomato has acquired Uber Eats’ India business, the company still stands as a formidable competitor to Zomato in foreign markets;
- DoorDash: This company operates primarily in the United States and Canada, DoorDash has built a reputation for its extensive restaurant partnerships and a robust delivery network. It stands as a key player, offering a diverse range of dining choices and efficient delivery options. DoorDash’s ambitious expansion strategies have propelled it to the global stage, setting the stage for international competition;
- Grubhub: Grubhub, which is now under the umbrella of Just Eat Takeaway.com, holds a strong position in the United States and Europe. It boasts an impressive portfolio of restaurant partners and a variety of delivery and pickup alternatives. The recent merger with Just Eat Takeaway.com has bolstered its presence, creating a formidable force in the food delivery industry. Therefore, this company poses a threat to Zomato in the food delivery industry;
- Delivery Hero: Originating from Germany, Delivery Hero operates in over 40 countries, solidifying its status as a global contender. With a focus on food delivery and a multitude of brands catering to diverse markets, it thrives on its adaptability to local preferences and cultural contexts. Delivery Hero’s international presence positions it as a significant player in the food delivery sector.
Zomato SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT analysis of Zomato:
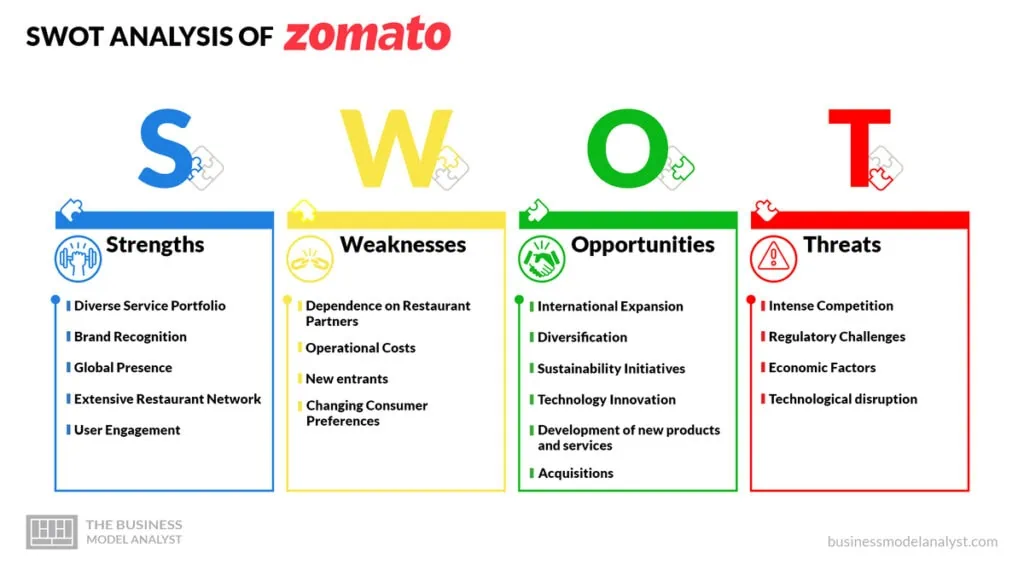
Zomato Strengths
The following are Zomato’s strengths:
- Diverse Service Portfolio: Zomato offers a wide array of services, including restaurant discovery, food delivery, table reservations, and exclusive subscription programs like Zomato Pro. This diversified portfolio allows it to cater to various customer preferences and generate multiple revenue streams;
- Brand Recognition: Zomato enjoys strong brand recognition and is known for its reliability and comprehensive restaurant information. A positive brand image attracts users and builds trust;
- Global Presence: Zomato has expanded its services to numerous countries, giving it a global footprint. This international reach provides access to diverse markets and customer segments, reducing dependency on any single region;
- Extensive Restaurant Network: Zomato has established partnerships with a vast network of restaurants worldwide. This extensive selection of dining options attracts users and provides a competitive advantage in the food-tech industry;
- User Engagement: Zomato encourages user-generated content, including reviews, ratings, and photos. This high level of engagement enhances the platform’s credibility and provides valuable information to other users.
Zomato Weaknesses
The following are Zomato’s weaknesses:
- Dependence on Restaurant Partners: A significant portion of Zomato’s revenue comes from commissions charged to restaurant partners. This dependence on restaurant partnerships can make Zomato vulnerable to fluctuations in the restaurant industry;
- Operational Costs: Managing a large delivery fleet and maintaining technology infrastructure requires substantial operational expenses. This can impact profitability, especially in markets with tight margins;
- New entrants: The food delivery and restaurant discovery market is still in its early stages of development. This means that there is a risk of new entrants entering the market and disrupting Zomato’s business;
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Shifts in consumer behavior, such as changing dining habits or the adoption of new technologies, can impact Zomato’s user base and demand for its services.
Zomato Opportunities
The following are Zomato’s opportunities:
- International Expansion: Zomato has the opportunity to further expand its global presence and tap into emerging markets, customizing its services to cater to local preferences;
- Diversification: Exploring new services or partnerships, such as grocery delivery or meal kits, can diversify revenue streams and enhance user engagement;
- Sustainability Initiatives: Zomato can capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable practices by expanding its eco-friendly initiatives and promoting responsible dining;
- Technology Innovation: Continuous investment in technology can lead to improved user experiences, enhanced delivery efficiency, and better data analytics;
- Development of new products and services: Zomato can develop new products and services to meet the needs of its customers. This could include features such as live tracking of orders or personalized recommendations;
- Acquisitions: Zomato can acquire other companies to expand its reach and capabilities. This could include companies with a strong technology platform or a large user base;
- Partnerships with other businesses: Zomato can partner with other businesses, such as grocery stores or delivery services, to offer its customers a wider range of services.
Zomato Threats
The following are the threats to Zomato’s position in the food industry:
- Intense Competition: Zomato faces fierce competition from rivals such as Swiggy, DoorDash, and Uber Eats in various markets. This competition can exert pressure on pricing and marketing expenses;
- Regulatory Challenges: The food delivery industry is subject to evolving regulations, which can pose compliance challenges and impact the cost structure. Adhering to local laws and regulations in diverse markets can be complex;
- Economic Factors: Economic downturns can affect consumer dining and food delivery spending, potentially impacting Zomato’s revenue;
- Technological disruption: The food delivery and restaurant discovery market is being disrupted by new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and blockchain. This could make it difficult for Zomato to keep up with the competition.
-> Read More About Zomato’s SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
In conclusion, Zomato’s business model is based on a combination of restaurant advertising, food delivery, and subscription services. The company has carved a niche for itself in the competitive food-tech landscape by seamlessly connecting users with an abundance of dining options, facilitating food delivery, and offering a myriad of services.
Although the company faces a number of challenges, it is constantly innovating and improving its services to stay ahead of the competition. Its relentless pursuit of innovation, global expansion, and commitment to user engagement have been instrumental to its success. Zomato is well-positioned to continue to grow and succeed in the years to come.

