The Verizon business model revolves around providing a comprehensive suite of communication and technology solutions to consumers, businesses, and enterprises. As a telecommunications company, Verizon focuses on a wide range of technology domains to provide comprehensive telecommunications and digital services.
The company is a prominent player in wireless communications, offering mobile phone services, data plans, and devices, and it invests heavily in 4G LTE and 5G networks for fast and reliable wireless connectivity. Verizon has also invested significantly in its fiber-optic network infrastructure, providing high-speed internet, television, and phone services through the Fios platform.
Additionally, Verizon delivers IoT solutions and services, enabling businesses to connect and manage various devices and applications for industries like smart cities, healthcare, and manufacturing. The company offers cloud computing and storage solutions, managed security services for cybersecurity, and owns digital media properties for content distribution and advertising.
Verizon is a pioneer in 5G technology and explores edge computing, augmented reality, and virtual reality to support innovative applications and services. With a focus on these domains, Verizon aims to remain a leading telecommunications provider, catering to the diverse needs of consumers, businesses, and industries.

Contents
A brief history of Verizon
Verizon Communications, Inc. has a rich history that dates back to the 19th century, when its predecessor companies were involved in the early development of the telecommunications industry in the United States. The story began with the invention of the telephone by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876 and the subsequent formation of the Bell Telephone Company in 1877.
The Bell Telephone Company rapidly expanded its telephone network, establishing local telephone exchanges in various cities across the United States. However, operating multiple local exchanges proved challenging, and the need for a more coordinated and centralized approach became evident.
To address the challenges of managing multiple local exchanges and providing more effective long-distance communication, Gardiner Hubbard established the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1885. AT&T was incorporated as a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Bell Telephone Company.
Over time, the network of interconnected telephone exchanges and services operated and coordinated by AT&T became known as the Bell System. The Bell System consisted of various operating companies, with AT&T as the central governing entity.
However, as the Bell System grew, concerns about its monopoly power arose. In 1974, the US Department of Justice filed an antitrust lawsuit against AT&T, leading to a settlement that required AT&T to divest its local exchange service operating companies.
In 1982, due to antitrust concerns, AT&T agreed to divest its local telephone operations, creating seven regional “Baby Bell” companies. One of these “Baby Bells” was Bell Atlantic Corporation, which served the Mid-Atlantic states, providing local telephone services. Meanwhile, General Telephone & Electronics Corporation (GTE) was another telecommunications company with a national presence, offering telephone services in various regions of the country.
In 2000, Bell Atlantic Corporation merged with GTE Corporation, forming Verizon Communications, Inc. This merger brought together two significant telecommunications entities, combining their assets and resources to create a formidable player in the industry. Verizon Communications quickly became a primary provider of telecommunications services, offering a comprehensive range of communication solutions to consumers, businesses, and government agencies.
Verizon’s wireless division established itself as a leading mobile carrier, providing mobile voice and data services to millions of subscribers nationwide. The company also invested heavily in expanding its fiber-optic network, known as FIOS, to deliver high-speed internet, television, and phone services to residential and business customers.
Verizon’s commitment to growth and innovation led to strategic acquisitions and partnerships. In 2006, the company acquired MCI, a communications company with a strong business and enterprise market presence. In addition to its core telecommunications services, Verizon ventured into the media and entertainment industry. In 2015, Verizon acquired AOL, a digital media company. Later in 2017, it acquired Yahoo, an internet pioneer, to enter the digital media and online advertising markets.
Throughout its history, Verizon Communications, Inc. evolved into a diversified telecommunications company, providing a wide array of services to millions of customers while continuously embracing technological innovations and developments. The company’s dedication to connectivity, customer service, and technological progress continues to shape its legacy in the telecommunications industry.
Who Owns Verizon
Verizon is a publicly traded company, which means that a large number of investors own its shares. The largest shareholders of Verizon are The Vanguard Group, SSgA Funds Management, BlackRock, and State Street Corporation.
Verizon Mission Statement

Verizon’s mission statement is, “We deliver the promise of the digital world to our customers. We make their innovative lifestyles possible. We do it all through the most reliable network and the latest technology.”
How Verizon works
Verizon is a telecommunications company that operates a vast and complex network infrastructure to deliver a wide range of services to its customers. Here’s an overview of how Verizon works:
Network Infrastructure
Verizon’s network infrastructure consists of a vast and complex network of wired and wireless technologies. These include fiber-optic cables, copper lines, cellular towers, data centers, and other critical components. The network infrastructure is the foundation that enables Verizon to deliver its various services to customers across the United States.
Fiber Optic Network (Fios)
Fios is Verizon’s advanced fiber-optic network that delivers high-speed internet, television, and phone services. Fiber-optic cables use pulses of light to transmit data, allowing for significantly faster speeds and more reliable connections compared to traditional copper lines. Fios is particularly popular in urban and suburban areas, offering fast and consistent internet speeds and a wide range of television channels.
Wireless Network
Verizon operates a nationwide wireless network that covers a vast majority of the country. This network enables customers to use their mobile phones for voice calls, text messaging, and internet access. Verizon’s wireless network supports both 4G LTE and 5G technology, offering high-speed mobile internet connectivity to millions of customers.
Internet Services
Verizon provides high-speed internet services to both residential and business customers. The company offers two main types of internet services:
- DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) Internet: DSL is delivered over traditional copper lines, DSL internet is available in areas where fiber-optic infrastructure is not yet deployed. While not as fast as fiber-optic internet, DSL provides reliable internet access for many customers;
- Fios Internet: Fios Internet is delivered over fiber-optic cables. Fios internet provides faster speeds and more bandwidth, making it ideal for customers who require higher data transfer rates and a more robust internet connection.
Television Services (Fios TV)
Fios TV is Verizon’s television service that offers subscribers a diverse range of entertainment options. It includes traditional cable TV channels, on-demand content, and access to streaming services. Customers can choose from various TV packages to suit their preferences and interests.
Phone Services
Verizon offers phone services through two main methods:
- Traditional Landline Phone: Verizon provides traditional landline phone services that use copper lines. While declining in popularity due to the rise of mobile phones and VoIP, traditional landline phone services are still available to customers who prefer this type of connection;
- Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP): Verizon also offers VoIP services, allowing customers to make phone calls over the internet, using their broadband connection. VoIP is popular for businesses and customers looking for a more flexible and cost-effective phone solution.
Business Solutions
Verizon offers a comprehensive suite of business solutions to meet the diverse needs of various industries and organizations. These solutions include:
- Cloud Services: Cloud services involve the delivery of computing resources, such as storage, servers, databases, and software applications, over the internet. Verizon offers businesses cloud computing and storage solutions, allowing them to leverage scalable and flexible IT resources without needing extensive on-premises infrastructure;
- Managed Security: Managed security services involve outsourcing security operations and monitoring to a specialized provider. Verizon’s managed security solutions include threat monitoring, incident response, security analytics, and other cybersecurity services to protect businesses from cyber threats and data breaches;
- Internet of Things (IoT) Connectivity: IoT connectivity refers to the connection and management of a vast network of devices and sensors through the internet. Verizon provides IoT connectivity solutions, enabling businesses to deploy and manage connected devices for various applications, such as smart city initiatives, industrial automation, asset tracking, and healthcare solutions;
- Enterprise Networking: Enterprise networking refers to the design, implementation, and management of advanced networking solutions for large businesses and corporations. Verizon provides various networking services, including managed network solutions, software-defined wide-area networking (SD-WAN), Ethernet connectivity, and other enterprise-grade networking services to support the communication needs of businesses.
These business solutions cater to the needs of enterprises and large organizations, providing them with advanced connectivity, data management, security, and innovative capabilities to enhance their operations and drive digital transformation.
How Verizon makes money
Service Revenues
Verizon’s primary source of revenue comes from providing telecommunications services to its customers. These services include wireless services, internet plans, television subscriptions, and phone services. Customers pay for these services monthly, contributing to Verizon’s recurring revenue stream.
Device Sales and Financing
Verizon generates revenue from selling a wide range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, and other connected devices. The company often offers device financing options, allowing customers to pay for devices over time, which can boost upfront revenues.
Roaming and Interconnection Fees
When Verizon’s customers use their devices on partner networks while traveling, Verizon earns revenue from roaming agreements with other carriers. Additionally, Verizon generates income from interconnection fees when other carriers’ traffic connects to Verizon’s network.
Enterprise and Government Contracts
Verizon provides a variety of services to large enterprise customers and government agencies. These services include network, cybersecurity, cloud, and communication solutions. Large-scale contracts with these customers contribute significantly to Verizon’s revenue.
Advertising and Media Revenue
Verizon owns media properties, such as Yahoo, AOL, and Verizon Media Group. These platforms generate revenue through advertising and digital media services. Advertisers pay to display ads on Verizon’s media properties, providing an additional revenue stream.
Verizon Business Model
Let’s take a look at the Verizon Business Model Canvas below:
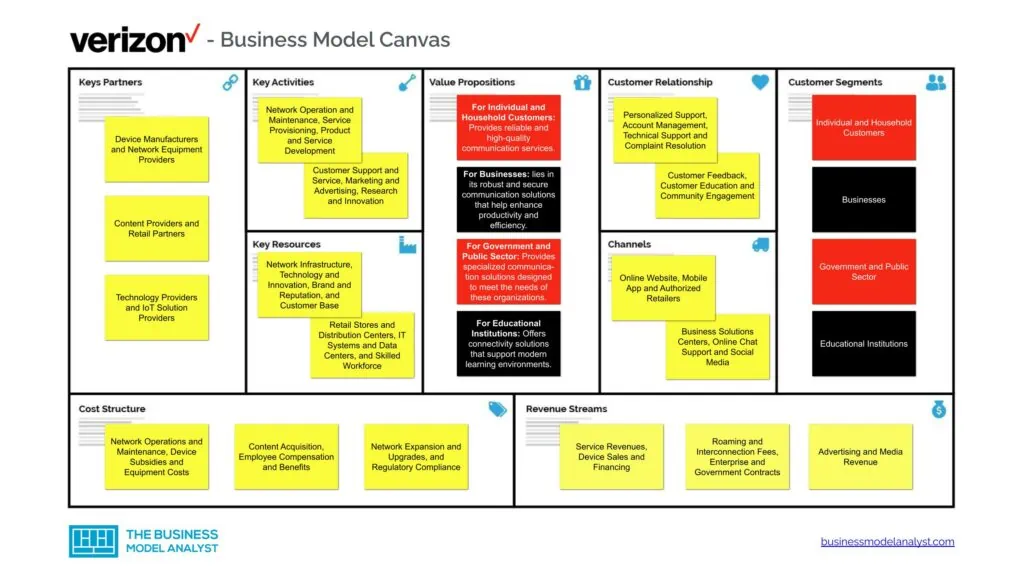
Verizon Customer Segments
Verizon’s customer segments consist of:
- Individual and Household Customers: Individual and household customers refer to private consumers who purchase goods or services for personal use and consumption. These customers can be anyone from various age groups and backgrounds who buy products for their homes;
- Businesses: Businesses, also known as corporations or companies, are organizations that produce, sell, or provide goods and services in exchange for money. They can range from small local enterprises to large multinational corporations;
- Government and Public Sector: The government and public sector encompass various governmental entities and organizations responsible for governing and providing public services to citizens. These include local, regional, and national governments, as well as agencies, departments, and public institutions that manage services such as education, healthcare, transportation, law enforcement, and public infrastructure;
- Educational Institutions: Educational institutions are organizations dedicated to providing formal education and academic instruction. This category includes schools, colleges, universities, and other learning centers. Educational institutions aim to impart knowledge and skills to students and facilitate their intellectual and personal development;
- Healthcare Providers: Healthcare providers refer to organizations and professionals involved in offering medical services and healthcare to patients. This category encompasses hospitals, clinics, doctors, nurses, pharmacists, therapists, and other healthcare professionals who diagnose, treat, and care for individuals with medical needs;
- Financial Services Industry: The financial services industry comprises businesses and institutions that offer various financial products and services to individuals, businesses, and governments. This sector includes banks, credit unions, insurance companies, investment firms, brokerage houses, and other financial intermediaries that facilitate monetary transactions, investment opportunities, and risk management;
- Media and Entertainment Industry: The media and entertainment industry encompasses businesses and organizations creating, producing, and distributing various media and entertainment content. Examples include film and television studios, music labels, publishing houses, news outlets, streaming platforms, video game developers, and other entities that cater to the entertainment and information needs of the public.
Verizon Value Propositions
Verizon’s value propositions consist of:
- For Individual and Household Customers: Verizon’s value proposition to individual and household customers revolves around providing reliable and high-quality communication services. They include mobile phone plans with extensive coverage, fast and stable internet connectivity through fiber-optic or DSL services, as well as home phone and TV packages. Verizon also offers entertainment options such as streaming services and exclusive content, giving customers access to a variety of media and entertainment content;
- For Businesses: Verizon’s value proposition lies in its robust and secure communication solutions that help enhance productivity and efficiency. The solutions include scalable and customizable business internet plans, reliable voice services, cloud-based data storage, and management solutions, and advanced business phone systems. Verizon also offers network security and data protection services to safeguard businesses from cyber threats;
- For Government and Public Sector: Verizon provides government and public sector entities with specialized communication solutions designed to meet the unique needs of these organizations. The value propositions include secure and reliable network infrastructure, tailored data and voice plans for public safety agencies, and advanced emergency response and disaster recovery solutions. Verizon also offers smart city solutions;
- For Educational Institutions: Verizon offers connectivity solutions that support modern learning environments. The solutions include high-speed internet for schools and universities, enabling online learning and collaboration. Verizon also provides devices and tablets with educational content, empowering educators to deliver engaging digital lessons. Additionally, Verizon offers cybersecurity solutions to protect educational institutions’ sensitive data and information;
- For Healthcare Providers: Verizon’s value proposition to healthcare providers centers around enabling efficient and secure healthcare delivery. This includes connectivity solutions that support telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, enhancing access to healthcare services. Verizon offers secure cloud storage for patient records, facilitating seamless data sharing and accessibility. Additionally, the company provides robust cybersecurity solutions to safeguard healthcare institutions’ sensitive patient data;
- For Financial Services Industry: For the financial services industry, Verizon offers reliable and secure communication services critical for data-intensive operations. This includes high-speed internet and private networks for secure data transmission and communication. Verizon also provides data centers and cloud services to support financial institutions’ data storage and processing needs, ensuring compliance with industry regulations and data security standards;
- For Media and Entertainment Industry: To the media and entertainment industry, Verizon offers content delivery solutions and high-speed networks to ensure seamless streaming and distribution of media content. The company also collaborates with media partners to offer its customers exclusive content and entertainment experiences.
Verizon Channels
Verizon’s channels consist of:
- Online Website
- Mobile App
- Authorized Retailers
- Business Solutions Centers
- Online Chat Support
- Social Media
Verizon Customer Relationships
Verizon’s customer relationships consist of:
- Personalized Support
- Account Management
- Technical Support
- Complaint Resolution
- Customer Feedback
- Customer Education
- Community Engagement
Verizon Revenue Streams
Verizon’s revenue streams consist of:
- Service Revenues
- Device Sales and Financing
- Roaming and Interconnection Fees
- Enterprise and Government Contracts
- Advertising and Media Revenue
Verizon Key Resources
Verizon’s key resources consist of:
- Network Infrastructure
- Technology and Innovation
- Brand and Reputation
- Customer Base
- Retail Stores and Distribution Centers
- IT Systems and Data Centers
- Skilled Workforce
- Partnerships and Alliances
Verizon Key Activities
Verizon’s key activities consist of:
- Network Operation and Maintenance
- Service Provisioning
- Product and Service Development
- Customer Support and Service
- Marketing and Advertising
- Research and Innovation
- Retail Operations
- Strategic Partnerships
- Regulatory Compliance
Verizon Key Partners
Verizon’s key partners consist of:
- Device Manufacturers
- Network Equipment Providers
- Content Providers
- Retail Partners
- Technology Providers
- IoT Solution Providers
Verizon Cost Structure
Verizon’s cost structure consists of:
- Network Operations and Maintenance
- Device Subsidies and Equipment Costs
- Content Acquisition
- Employee Compensation and Benefits
- Network Expansion and Upgrades
- Regulatory Compliance
- Customer Service and Support
- Corporate Overhead and Administrative Expenses
Verizon Competitors
- AT&T Inc: AT&T is one of the largest telecommunications companies globally, with a diverse portfolio of services, including wireless, internet, TV, and media. It operates an extensive wireless network covering a significant portion of the United States. AT&T’s mobile plans cater to various customer segments, offering both unlimited and tiered data options. The company’s emphasis on content ownership led to its acquisition of WarnerMedia, giving it access to a wide range of media properties, including HBO, CNN, and Warner Bros. This acquisition has allowed AT&T to bundle its services and offer unique packages that include wireless, internet, and premium content;
- Vodafone Group: Vodafone is a multinational telecommunications company headquartered in the United Kingdom. It operates in multiple countries across Europe, Africa, Asia, and Oceania. Vodafone provides a comprehensive range of telecommunications services, including mobile voice and data services, fixed-line services, broadband internet, and enterprise solutions. With its global presence, Vodafone caters to millions of individual and business customers. The company’s extensive international footprint and diverse service offerings make it a significant global competitor in the telecommunications market;
- T-Mobile U.S., Inc.: T-Mobile is known for its innovative and disruptive approach to the wireless industry. Under the leadership of its outspoken CEO, John Legere (until May 2020), the company introduced various “Un-carrier” initiatives, such as eliminating contracts, offering transparent pricing, and introducing unlimited data plans without overage charges. T-Mobile has focused on expanding its network coverage and capacity, particularly in rural areas, to compete more effectively with Verizon and AT&T. The merger with Sprint, which was completed in April 2020, significantly boosted T-Mobile’s spectrum holdings and network capabilities, positioning it as a formidable competitor in the market;
- Orange S.A.: Orange S.A., commonly known as Orange, is a French multinational telecommunications company operating in various regions worldwide. The company has a strong presence in Europe, particularly in countries such as France, Spain, Poland, Belgium, Romania, and Slovakia. It also has a significant market share in various African countries, including Egypt, Senegal, Mali, and Ivory Coast. Orange competes with Verizon by focusing on its core European and African markets, delivering tailored solutions for individual consumers and businesses, and continuously investing in infrastructure, innovation, and customer satisfaction. These efforts position Orange as a formidable global competitor in the dynamic and ever-evolving telecommunications landscape.
Verizon SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT analysis of Verizon:
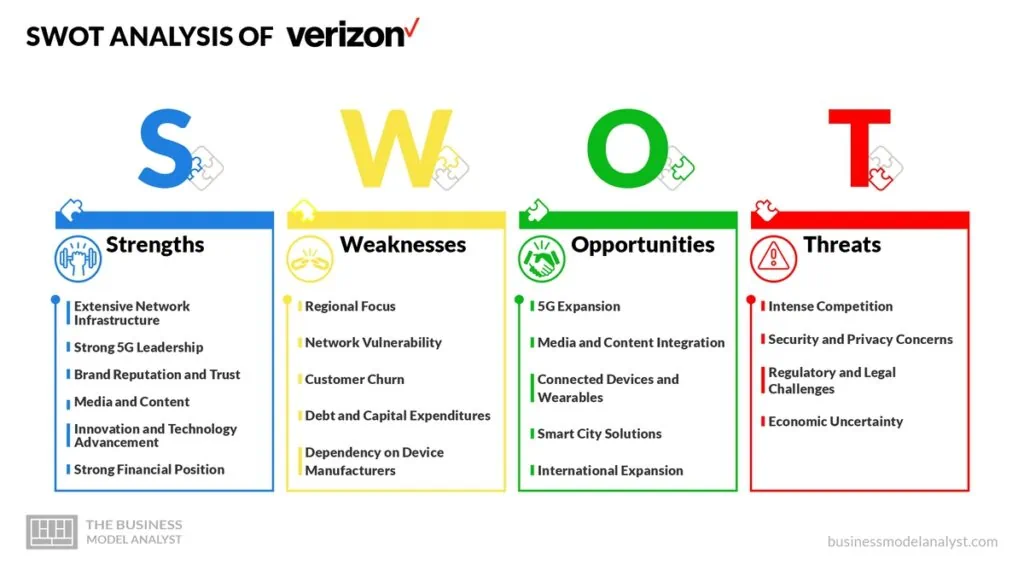
Verizon Strengths
- Extensive Network Infrastructure: Verizon operates a robust and expansive network infrastructure, encompassing wireless and wired networks. The company’s nationwide coverage provides reliable voice and data services to millions of customers across the United States;
- Strong 5G Leadership: Verizon has been at the forefront of 5G deployment, investing heavily in developing and expanding its 5G network. As one of the first carriers to introduce 5G services, Verizon has gained an edge in offering faster data speeds and improved connectivity to customers;
- Brand Reputation and Trust: Verizon has built a strong brand reputation over the years, earning the trust of its customers for its reliable service and network performance. The company’s commitment to quality and customer service has contributed to high customer loyalty;
- Media and Content: With acquisitions such as AOL and Yahoo, Verizon has entered the media and content space. The company leverages its content properties to offer unique entertainment options to its customers, differentiating its services from traditional telecommunications providers;
- Innovation and Technology Advancement: As a technology-driven company, Verizon continues to invest in research, innovation, and the development of new solutions. A few of them are emerging technologies like 5G applications, edge computing, and IoT innovations;
- Strong Financial Position: Verizon’s financial strength and stability allow it to make strategic investments in network expansion, technology upgrades, and acquisitions, positioning the company for future growth and competitiveness.
Verizon Weaknesses
- Regional Focus: While Verizon is a major player in the United States, it does not have a global presence comparable to some of its competitors. Its operations are primarily concentrated in the US, which limits its exposure to international markets and potential growth opportunities in other regions;
- Network Vulnerability: The continuous expansion of the 5G network and growing reliance on digital infrastructure expose Verizon to potential cybersecurity threats and network vulnerabilities. Safeguarding customer data and maintaining network security is crucial;
- Customer Churn: Retaining customers in a competitive market is challenging. Verizon faces the risk of customer churn as customers switch carriers based on pricing, service quality, or promotional offers;
- Debt and Capital Expenditures: Verizon’s significant capital investments in network expansion, 5G deployment, and acquisitions have resulted in a substantial debt burden. The company’s ability to manage its debt levels is an ongoing concern;
- Dependency on Device Manufacturers: Verizon’s device offerings are dependent on agreements with device manufacturers. Changes in these partnerships or supply chain disruptions could impact device availability and customer choices.
Verizon Opportunities
- 5G Expansion: As a leader in 5G technology, Verizon has the opportunity to further expand its 5G network coverage and capabilities. Rolling out 5G to more cities and regions can attract new customers and businesses seeking faster and more reliable connectivity;
- Media and Content Integration: Verizon can explore opportunities to leverage its media properties, such as AOL and Yahoo, to offer its customers unique content bundles and entertainment services. Integrating media offerings with its telecom services can differentiate Verizon from its competitors;
- Connected Devices and Wearables: The increasing popularity of connected devices and wearables presents an opportunity for Verizon to provide data plans and connectivity for these devices. Expanding into this market can drive additional revenue and strengthen customer engagement;
- Smart City Solutions: Verizon can explore partnerships and initiatives related to smart city solutions, leveraging its 5G capabilities to support smart infrastructure, IoT deployments, and digital services in urban areas;
- International Expansion: While Verizon’s primary focus has been the US market, there may be opportunities for strategic international expansion, either through partnerships or acquisitions, to enter new markets and tap into global growth potential.
Verizon Threats
- Intense Competition: Verizon faces fierce competition from other major carriers, such as AT&T and T-Mobile, as well as regional and niche players. Intense competition can lead to price wars and erode profit margins. To remain competitive, Verizon must continuously invest in its network infrastructure, customer service, and innovative offerings;
- Security and Privacy Concerns: With increasing reliance on digital infrastructure and data-driven services, cybersecurity threats and data breaches pose a significant risk to Verizon and its customers. Any security breach can damage the company’s reputation and result in financial losses. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is critical to safeguarding customer data and maintaining trust;
- Regulatory and Legal Challenges: The telecommunications industry is subject to extensive regulations, including net neutrality, privacy laws, and spectrum allocation rules. Changes in regulatory policies or legal challenges can impact Verizon’s operations, pricing, and ability to offer specialized services. Adhering to regulations and advocating for favorable policies is essential;
- Economic Uncertainty: Economic downturns or uncertainties can lead to reduced consumer spending and business investments in telecommunications services. Customers may prioritize cost-saving options or delay upgrading devices or plans during such periods, affecting Verizon’s revenue and growth prospects.
Conclusion
As a significant player in the telecommunications industry, Verizon faces both opportunities and challenges as it moves into the future. One of the significant challenges is the highly competitive nature of the telecommunications market, with intense competition from other major carriers in the United States. Additionally, the emergence of new technologies and non-traditional competitors poses a threat to its market position.
On the positive side, Verizon’s focus on 5G deployment and technological advancements presents exciting opportunities. The transformative potential of 5G, particularly in areas like IoT applications and augmented reality, can open up new revenue streams and innovative service offerings.
To thrive in the future, Verizon must maintain a customer-centric approach and focus on delivering tailored solutions to meet the changing demands of individual consumers and enterprise customers.
Being agile and adaptable to emerging trends will be crucial to retain and attract customers in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. The future for Verizon looks promising due to its established brand reputation, extensive network infrastructure, and commitment to innovation.

