The Tesco Business Model offers customers a wide range of products and services at competitive prices. The company achieves this through several key activities, such as product sourcing, store operations and marketing, and customer engagement. Tesco works with many suppliers to source products at the best possible prices. It also has its in-house buying team that helps to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers.
Also, Tesco operates a network of stores in the United Kingdom and worldwide. The company’s stores are designed to be convenient and easy to shop in. Tesco also offers various services, such as online grocery delivery and home shopping, to make it even easier for customers to shop with the company.
In addition, Tesco invests heavily in marketing and customer engagement. The company uses a variety of channels, including advertising, social media, and its Clubcard loyalty scheme, to reach its customers. Tesco also uses data analytics to understand its customers’ needs and preferences. Its business model has been successful in helping the company to grow into one of the largest retailers in the world.
The company’s focus on providing a wide range of products and services at competitive prices has helped to attract and retain customers. Tesco’s investment in marketing and customer engagement has also helped build the company’s brand and customer loyalty.

Contents
A brief history of Tesco
Jack Cohen, a Polish-born Jewish immigrant, founded Tesco in 1919. He started his business selling war-surplus groceries from a market stall in the East End of London. The company’s name comes from the initials of the supplier of the first tea that Cohen sold, Thomas Edward Stockwell, and the first two letters of his surname.
Tesco quickly grew from a small market stall to a major retailer. In 1924, the company opened its first self-service store, and in 1931, it opened its first supermarket. Tesco continued to expand throughout the 20th century, and by the 1990s, it had become one of the largest retailers in the world.
Cohen was a visionary entrepreneur who saw the potential of the supermarket industry. He was also a shrewd businessman who always sought ways to cut costs and improve efficiency. These factors helped Tesco to overgrow in its early years. In the 1920s, Tesco expanded its operations to include a chain of grocery stores.
The company also began to develop its private-label brands, which helped to keep prices low. In the 1930s, Tesco opened its first self-service store, a revolutionary concept.
After World War II, Tesco continued to increase — the company opened new stores across the United Kingdom and expanded into international markets. In the 1950s, Tesco introduced its Clubcard loyalty scheme, which helped to boost customer loyalty.
In the 1960s, Tesco continued to expand its international operations. The company also began to open hypermarkets, large-format stores offering a wide range of products. In the 1970s, Tesco acquired several smaller supermarket chains, which helped to strengthen its position in the market.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the company opened new stores in some new countries and began offering a more comprehensive range of services, such as home delivery and online shopping. In the 1990s, Tesco became the largest retailer in the United Kingdom.
In the 2000s and 2010s, Tesco faced increasing competition from online retailers. The company responded by investing heavily in its online business. Tesco continued expanding its international operations, opening stores in several new countries, such as China and India.
In the 2020s, Tesco faced several challenges, including the COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine. However, the company has responded to these challenges by investing in its digital capabilities and expanding its online business. Tesco also focuses on its core markets, such as the United Kingdom and China.
Tesco is a major player in the global retail industry and will likely continue to play a significant role. The company’s focus on customer service, innovation, and global expansion will help it to remain competitive in the ever-changing retail landscape.
Who Owns Tesco
Tesco is a public limited company (PLC), meaning its shares are traded on the stock exchange. This means that anyone can buy shares in Tesco, and as a result, the company has many different shareholders. The largest shareholder in Tesco is The Vanguard Group, Inc., which owns approximately 8.9% of the company’s shares.
Other significant shareholders include BlackRock, Inc., Schroders plc, and Fidelity International. Ken Murphy is the current CEO of Tesco. He was appointed in October 2020 and is the first Irish person to lead the company. Murphy has over 20 years of experience in the retail industry, and he previously worked at Boots, where he was the group managing director.
Tesco Mission Statement

Tesco’s mission statement is serving shoppers a little better every day, reflecting Tesco’s commitment to providing its customers with the best possible shopping experience.
How Tesco works
Tesco works by understanding its customer’s needs and preferences and developing a product assortment and marketing strategy that meets those needs. The company also invests heavily in its distribution network and customer service. This allows Tesco to provide a high-quality shopping experience to its customers.
First, Tesco identifies its target customers by analyzing demographics, psychographics, and buying behavior. This helps the company to understand what products and services its customers want and need. Once Tesco understands its target customers, it develops a product assortment that meets their needs. The company does this by considering price, quality, and variety.
Next, Tesco sets competitive prices that reflect the value of its products. The company also uses pricing strategies, such as discounts and promotions, to attract customers. It promotes its products through various channels, including advertising, social media, and a Clubcard loyalty scheme. It also uses data analytics to target its promotions to the right customers.
Tesco distributes its products through various channels, including stores, third-party retailers, and online. The company also uses data analytics to optimize its distribution network. Finally, Tesco provides excellent customer service to its customers. A dedicated customer service team is available to answer questions and resolve problems.
How Tesco makes money
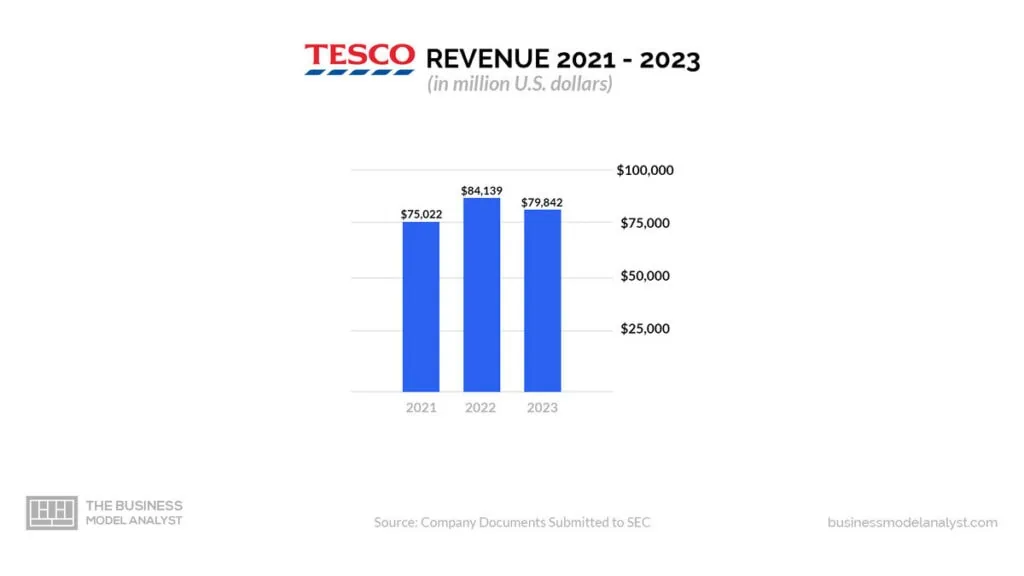
Tesco makes money through retail, primarily Clubcard and financial services. Others include rental income and advertising. Below are more details about how Tesco makes money:
Retail sales
Tesco’s primary source of income is from retail sales. The company sells various products, including groceries, clothing, and homewares. Tesco’s retail sales are driven by its extensive network of stores in the United Kingdom, Europe, and Asia. The company also sells its products online through its website and mobile app.
Clubcard
Tesco’s Clubcard loyalty scheme is a major source of revenue for the company. Members of the scheme earn points for every purchase they make, which can then be redeemed for discounts or vouchers. Tesco’s Clubcard scheme has over 19 million members, generating billions of pounds annually.
Financial services
Tesco offers various financial services, including insurance, banking, and credit cards. These services generate revenue through fees and interest payments. Tesco’s financial services business is growing rapidly and is now a significant contributor to its overall revenue.
Property
Tesco owns significant property, including its stores and distribution centers. The company generates rental income from this property. Tesco’s property portfolio is worth billions of pounds and is a major source of long-term income for the company.
Other
Tesco also generates revenue from various other sources, such as advertising and marketing. For example, Tesco sells advertising space on its website and stores. The company also generates revenue from its data analytics business, which helps Tesco to understand its customers’ needs and preferences.
Tesco Business Model Canvas
The Tesco Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
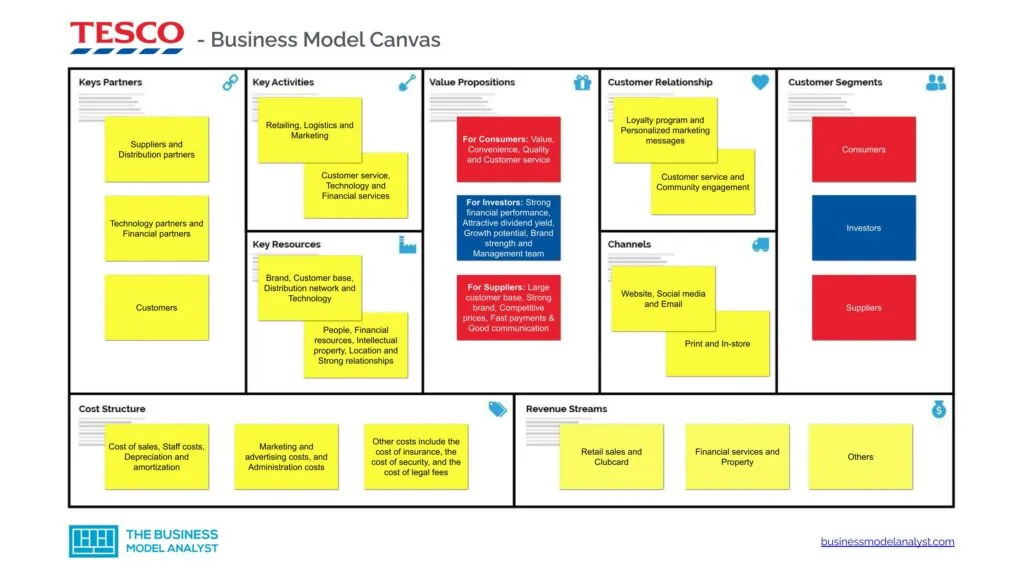
Tesco Customer Segments
Tesco’s customer segments consist of:
- Consumers
- Investors
- Suppliers
Tesco Value Propositions
Tesco’s value propositions consist of:
Value Propositions for Consumers
- Value: Tesco’s Clubcard loyalty scheme offers consumer benefits, such as discounts on groceries and other products;
- Convenience: Tesco’s online shopping service allows consumers to shop from home and have their groceries delivered to their door;
- Quality: Tesco’s own-brand products are often considered high quality, and the company offers some guarantees;
- Customer service: Tesco’s customer service team is known for being helpful and responsive. The company also offers some ways for consumers to contact customer service, which makes it easy to get help when needed.
Value Propositions for Investors
- Strong financial performance: Tesco’s revenue has grown by an average of 4% per year over the past five years. The company’s profit margin has also been consistently high;
- Attractive dividend yield: Tesco’s dividend yield has been consistently above 4% for many years. The company has a history of increasing its dividend payments, which is a good sign for investors;
- Growth potential: Tesco is expanding its international operations. The company also invests in new technologies, such as online grocery delivery. This growth potential could benefit investors in the long term;
- Brand strength: Tesco is a well-known and respected brand. The company has a strong brand presence in the United Kingdom and is gaining market share in other countries;
- Management team: Tesco has a strong management team. The team has a proven track record of success and is committed to delivering shareholder value. The team is led by Ken Murphy, who has been CEO of Tesco since 2020.
Value propositions for suppliers:
- Large customer base: Tesco is a large retailer with a global customer base. This allows suppliers to reach a large number of customers through Tesco’s stores;
- Strong brand: Tesco is a well-known and respected brand. This allows suppliers to associate their products with Tesco’s brand, which can help increase sales;
- Competitive prices: Tesco is a price-competitive retailer. This means that suppliers can expect to receive competitive prices for their products;
- Fast payments: Tesco pays its suppliers quickly. This gives suppliers the confidence that they will be paid for their products promptly;
- Good communication: Tesco has a sound communication system with its suppliers. This allows suppliers to communicate with Tesco about their products and any issues;
- Support for innovation: Tesco is supportive of innovation. This means that suppliers can approach Tesco with new product ideas, and Tesco is open to working with suppliers to develop these ideas.
Tesco Channels
Tesco’s channels consist of:
- Website
- Social media
- In-store
Tesco Customer Relationships
Tesco’s customer relationships consist of:
- Loyalty program
- Personalized marketing messages
- Customer service
- Community engagement
Tesco Revenue Streams
Tesco’s revenue streams consist of:
- Retail sales
- Clubcard
- Financial services
- Property
- Other
Tesco Key Resources
Tesco’s key resources consist of:
- Brand
- Customer base
- Distribution network
- Technology
- People
- Financial resources
- Intellectual property
- Location
- Strong relationships
Tesco Key Activities
Tesco’s key activities consist of:
- Retailing
- Logistics
- Marketing
- Customer service
- Technology
- Financial services:
Tesco Key Partners
Tesco’s key partners consist of:
- Suppliers
- Distribution partners
- Technology partners
- Financial partners
- Customers
Tesco Cost Structure
Tesco’s cost structure consists of
- Cost of sales
- Staff costs
- Depreciation and amortization
- Marketing and advertising costs
- Administration costs
- Other costs include the cost of insurance, the cost of security, and the cost of legal fees.
Tesco Competitors
- Asda is a British supermarket chain founded in 1949 by Jack Cohen. Asda is the second-largest supermarket chain in the United Kingdom, after Tesco, and is owned by Walmart. Asda is known for its low prices and wide range of products, including groceries, clothing, and homewares. It has over 630 stores in the United Kingdom and operates some online stores. Asda’s headquarters are located in Leeds, United Kingdom. It employs over 320,000 people and has an annual revenue of over £50 billion. Asda is a major competitor to Tesco, Sainsbury’s, and Morrisons;
- Sainsbury’s is a British supermarket chain founded in 1869 by John James Sainsbury. Sainsbury’s is the third-largest supermarket chain in the United Kingdom, after Tesco and Asda. The company is known for its high-quality products and its commitment to sustainability. It is committed to reducing its environmental impact, and it has some initiatives to reduce food waste, such as donating surplus food to charity and composting food waste. Sainsbury’s has also pledged to reduce its carbon emissions by 50% by 2030 and to use 100% sustainable packaging by 2025. It is a significant player in the retail industry, and it is likely to continue to be a significant competitor to Tesco in the years to come;
- Aldi is a German discount supermarket chain that has been expanding rapidly in the United Kingdom in recent years. The company was founded in 1961 by Theo Albrecht and headquartered in Essen, Germany, with over 900 stores in the United Kingdom. Aldi’s annual revenue is over £10 billion. It is known for its low prices and limited range of products, and its stores are typically smaller than traditional supermarkets, offering a limited selection of products. This allows Aldi to keep its prices low. Aldi is a major competitor to Tesco in the discount supermarket segment;
- Morrisons is a British multinational retail company that operates a chain of supermarkets in the United Kingdom and Ireland. It is the fifth-largest grocery retailer in the UK, with a market share of around 10%. Morrisons is known for its fresh food and its focus on local produce. It also offers many other products, including groceries, household goods, and clothing. It was founded in 1899 by William Morrison. The company began as a small grocery store in Bradford, West Yorkshire. Over the years, Morrisons has become one of the largest retailers in the UK. It operates over 490 supermarkets and employs over 130,000 people. Morrisons is known for its fresh food, including its own-brand products. It has a strong focus on local produce, and many of its products are sourced from farms in the UK. Its prices are competitive, and it often runs promotional offers;
- Lidl is a German discount supermarket chain that operates stores in over 20 countries. Known for its low prices and wide range of products, including groceries, household goods, and clothing, Lidl was founded in 1973 by Dieter Schwarz and has since grown to become one of the largest supermarket chains in the world. Lidl also offers some private-label products, often cheaper than name-brand products. The company is also known for its high-quality products and excellent customer service.
Tesco SWOT Analysis
Below, there are Tesco’s swot analysis.

Tesco Strengths
Here are Tesco’s strengths.’
- Strong brand image: Tesco is one of the most well-known and trusted brands in the UK. The company has been operating for over 90 years and has a long history of providing quality products and services. Tesco’s brand is synonymous with convenience and value, one of the most popular brands in the UK;
- Extensive store network: Tesco has a vast network of stores across the UK, including supermarkets, convenience stores, and online stores. This gives the company a significant reach and allows it to serve a wide range of customers. Tesco’s store network is constantly expanding, and the company is now in over ten countries worldwide;
- Efficient supply chain: Tesco has a very efficient supply chain, which allows it to keep its prices low. The company works closely with its suppliers to ensure a steady supply of products at competitive prices. Tesco’s supply chain is one of the most efficient in the world, and it is a critical factor in the company’s success;
- Innovative technology: Tesco is constantly investing in new technologies, such as online shopping and self-checkout. This allows the company to provide customers with a more convenient and personalized shopping experience. Tesco is one of the most innovative retailers in the world, and its use of technology is helping it to stay ahead of the competition.
Tesco Weaknesses
Below, there are Tesco’s weaknesses
- Over-Reliance on the UK market: Tesco’s revenue heavily relies on the UK market. In 2021, 91% of Tesco’s revenue came from the UK. This makes the company vulnerable to changes in the UK economy, such as the Brexit vote. If the UK economy were to experience a recession, Tesco’s revenue would likely decline;
- Price competition: Tesco faces intense competition from discount retailers like Aldi and Lidl. These retailers can offer lower prices because they operate with more negligible overhead. This has put pressure on Tesco’s profit margins. To compete with these discount retailers, Tesco may need to lower its prices, which could further reduce its profit margins;
- Food quality scandals: Tesco has been involved in some food quality scandals, such as the horse meat scandal in 2013. These scandals have damaged the company’s reputation and have led to customer losses. To regain the trust of its customers, Tesco needs to ensure that its food is of the highest quality;
- Slow adoption of new technologies: Tesco has been slow to adopt new technologies, such as online shopping. This has put the company at a disadvantage to its competitors, who have been more successful in the online market. To compete with these competitors, Tesco needs to invest in new technologies and improve its online presence.
Tesco Opportunities
Below, there are Tesco’s opportunities:
- Focus on customer experience: Tesco can focus on improving the customer experience by offering more personalized services and by making it easier for customers to shop. For example, Tesco could offer a loyalty program that rewards customers for their purchases. The company could also make it easier for customers to shop online by providing a more comprehensive range of products and improving its website;
- Invest in new technologies: Tesco can invest in new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, to improve its operations and provide customers with new services. For example, Tesco could use artificial intelligence to predict customer demand and optimize its supply chain. The company could also use blockchain to track the provenance of its products and to ensure that they are sustainable;
- Expand into new product categories: Tesco can expand into new product categories, such as clothing and home goods, to reach a broader range of customers. For example, Tesco could open a chain of clothing stores or a home goods store. The company could also partner with other companies to offer these products, such as Amazon or Alibaba;
- Partner with other companies: Tesco can partner with other companies, such as tech companies and food delivery companies, to offer new services to customers. For example, Tesco could partner with a tech company to develop a new mobile app that makes shopping easier for customers. The company could also partner with a food delivery company to offer grocery delivery services.
Tesco Threats
Below, there are Tesco’s threats:
- Rising competition: The grocery retail industry is highly competitive, and Tesco faces competition from other large retailers, including Sainsbury’s, Asda, and Aldi. These retailers constantly innovate and expand their product offerings, which pressures Tesco to keep up. For example, Aldi has been very successful in the UK by offering low prices on a limited range of products. Tesco needs to find ways to compete with Aldi without sacrificing its quality or its range of products;
- Economic uncertainty: The global economy is uncertain, which could harm Tesco’s business. For example, if there is a recession, consumers may have less money to spend on groceries, which could lead to a decline in Tesco’s sales. Tesco needs to have a solid financial position to weather any economic downturns;
- Changing consumer preferences: Consumer preferences are changing, and Tesco needs to adapt its business to meet these changes. For example, consumers are increasingly demanding healthier and more sustainable food options. Tesco needs to ensure that its product offerings reflect these changes to remain competitive. Tesco could do this by expanding its range of healthy and sustainable products or partnering with companies offering these products;
- Technological disruption: The retail industry is being disrupted by technology, and Tesco needs to adapt its business to meet these changes. For example, online grocery shopping is becoming increasingly popular, and Tesco needs to ensure a strong online presence to compete with other retailers. Tesco could do this by investing in its online platform or partnering with online grocery delivery companies.
-> Read More About Tesco’s SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
Tesco is a leading multinational retailer that has been serving customers for over 100 years. The company is firmly committed to providing affordable, healthy, and sustainable food. Tesco also aims to help customers enjoy a better quality of life and an easier way of living. In recent years, Tesco has faced challenges, such as increased competition from online retailers and changing consumer habits.
However, the company has responded to these challenges by investing in its digital infrastructure and expanding its product offerings. Tesco is also committed to reducing its environmental impact and becoming a more sustainable business. Overall, Tesco is a well-established retailer with a strong track record. The company is well-positioned to continue to grow and succeed in the future. Its commitment to sustainability is evident in its recent efforts to reduce food waste and packaging.
The company is also investing in new technologies, such as self-checkout and online grocery delivery, to make shopping more convenient for customers. Tesco is a major employer in many countries, and it is committed to providing its employees with an excellent work-life balance.

