Is Starbucks Profitable? Starbucks is slowly recovering from the losses it suffered following the Covid-19 pandemic. In a recently released report, Starbucks announced that its sales in the US made a fast recovery in the first three months of 2021. Same-store sales in the United States reported a 9% rise in Starbucks’ second quarter compared to the previous year’s period. Global revenue rose by 11% to hit $6.7 billion.
The company’s profit for the last quarter of 2021 was $659 million, a massive increase from $328 million the previous year. Starbucks predicted a 23% increase in same-store global sales for 2021. In 2022, Starbucks reported $32.3 billion in overall global revenues, a 13% rise compared to the previous year.
U.S. net revenues increased by 15% year-over-year to hit $6.1 billion. Starbucks’ gross profit for the year ending December 31, 2022, was $22.313 billion, marking a 5.52% increase year-over-year. The company’s gross profit increased by 7.93% in 2021 to $21.933 billion.
Contents
Timeline of Starbucks’ Financial Growth and Funding
1971-1980: The first Starbucks store opened its doors in 1971 in Seattle. On offer were spices, tea, and freshly roasted coffee beans. Gordon Bowker, Zev Sieg, and Jerry Baldwin, the founders, met at the University of San Fransisco as students. Alfred Peet, a coffee-roasting entrepreneur, motivated the founders to sell high-quality coffee beans. The business grew fast; by 1972, the founder required assistance running it.
They hired Jean Mach, who climbed the managerial ladder to eventually become the wholesale sales director, tasked with structuring Starbucks’ restaurant business. She played a core role in laying the company’s solid foundation. At some point, Siegl traveled to Berkeley, California, to learn from Alfred Peet, a Dutchman who ran Peet’s Coffee, which had thrived in the coffee industry since 1966.
Peet had a robust concept about coffee beans, which would later become synonymous with Starbucks. Starbucks purchased its coffee from Peet’s for the first nine months, giving coffee cups free of charge to hook customers. The plan succeeded, with the second Starbucks store opening in 1972.
In 1973, Starbucks stopped sourcing coffee from Peet, but he was kind enough to train Jim Reynolds, its roastmaster. Starbucks’ free-coffee strategy failed when a powerful freeze destroyed the Brazilian coffee crop in 1975. Coffee prices skyrocketed, forcing Starbucks to consider other operational tactics.
1981- 1998: In 1991, Starbucks was making massive orders from Hammarplast, a Swedish kitchen equipment manufacturer. Howard Schultz, a sales representative from the company, became curious and decided to visit Starbucks. He later landed a head of marketing job in 1982. Howard collaborated with store employees to develop excellent customer-friendly sales skills and created brochures to help customers learn about Starbucks’ products. Howard took a trip to Milan in 1983, where he learned lessons from Italy’s coffee houses. Upon return, he incorporated some of those lessons into Starbucks to improve their customer’s experience. The sixth Starbucks store opened in 1984.
It had an espresso bar and became one of the most successful coffee stores. In the same year, the founders of Starbucks acquired Peet’s Coffee. By 1986 the company has six coffee stores in Seattle. The founders sold Starbucks in 1987 to Howard Schultz. The inaugural Starbucks stores outside Seattle were opened in 1987 in Illinois, Chicago, British Columbia, and Vancouver.
By 1989 there were 46 Starbucks stores across the Pacific Midwest and Northwest, and the company was roasting over 907.185 kilograms of coffee yearly. In the same year, sales in the US grew to $500 million from $50 million in 1983. In 1989, Starbucks adopted a computer network and hired an information technology expert from McDonald’s Corporation to develop a point-of-sale system through PCs that store managers could use.
The company lost over $1 million in 1989 during its expansion phase. In 1990, Starbucks launched a new roasting plant with the expansion of its headquarters. Schultz resisted any temptation to flavor coffee beans or franchise. By this time, the company had a good reputation, eliminating the need for hugely investing in ads.
Howard leveraged his management philosophy: “hire people smarter than you are and get out of their way” to steer Starbucks in the right direction. In 1990 the company hired two executives. In 1991 Starbucks became the inaugural privately owned company in the US to render a stock option plan that included part-time employees. It also launched its first licensed store at the Seattle Sea-Tac International Airport.
By 1992 Starbucks had over 135 outlets with annual revenues of $72 million. It went public the same year. Starbucks bought The Coffee Connection in 1994 and acquired rights to make, use, advertise, and sell the “Frappuccino” beverage. In 1996 Starbucks started establishing stores outside North America, becoming the biggest coffeehouse chain globally. The same year, the company collaborated with Dreyer’s Grand Ice Cream, Inc., to produce and sell Starbucks Ice Cream.
Eight years later, the product became the leading coffee ice cream in the US. Starbucks’ market value by 1996 was approximately $271 million. Howard disposed off 12% of the firm for $25 million to raise capital for opening more stores within the next two years. By 1997, Starbucks’ sales were approaching the $1 billion mark, while its net income was $57.4 million. In 1998 Starbucks acquired Seattle Coffee Company, a UK-based firm, for $83 million.
2000-2019: Howard stepped down as the CEO in 2000 but remained the chairman. The company opened stores in Austria and Switzerland and introduced coffee-sourcing guidelines in 2001. Starbucks introduced SCTC (Starbucks Coffee Trading Company) in Lausanne in 2002 and started selling food in its stores in 2003.
It acquired Seattle’s Best Coffee and Torrefazione Italia for $72 million. In 2006, Starbucks launched its inaugural paper beverage cup and its first store in Russia in 2007. The same year, the company eliminated all artificial transfats and adopted 2% milk as the new espresso beverage standard. Starbucks bought Coffee Equipment Company, the manufacturer of the clover brewing system, in 2008 and cut massive non-retail jobs to invigorate its brand and increase profit.
Howard returned as the CEO the same year and embarked on transforming the company. The same year, they launched a community website to collect customer feedback and suggestions. Up to 300 poorly-performing stores were closed in 2009, and up to 7,000 positions were scrapped.
The same year, Starbucks communicated closures and rebranding of some of its licensed Starbucks kiosks for its US-based giant supermarkets and stop-and-shop stores. It also launched Starbucks VIA® Instant Opens Farmer Support Center in Kigali, Rwanda. The premier annual global month of service was established in 2011 to mark Starbucks’ 40th anniversary.
In 2012 the company acquired Teavana for $620 million. The company’s revenue in 2012 was more than $13 billion, with 149,000 workers worldwide. The same year, Starbucks experienced a 38% growth and introduced Starbucks® Blonde Roast. In 2017 the company bought the remaining 50% share in its Chinese venture from President Chain Store Corporation and Uni-President Enterprises Corporation for $1.3 billion. Howard stepped down as CEO again, and Kevin Johnson replaced him in 2017. However, he continued serving as executive chairman, but Myron Ullman later replaced him.
2020 to date: In 2020, at the peak of the covid pandemic, Starbucks experienced a sharp drop in sales. This forced it to negotiate reduced rent from landlords. People from 180 countries supported the company financially 1.5 million times during that challenging year. In December 2021, the Elmwood Avenue store workers became the first unionized Starbucks staff in the United States. In 2022, the company launched new stores and efficient automated machines.
Further, the company restructured its global store portfolio to create welcoming environments for all and strengthen communities. It also committed to opening 1,000 Starbucks community stores worldwide by 2030. The company is also keen to ensure that digital and physical Starbucks environments meet a high standard of accessibility for customers and partners by 2030.
Starbucks Financial Performance: Revenues, Expenses, and Profits
In 2022, Starbucks’ market share was above 37% in the United States. The company launched 1,878 new stores, bringing its total to 35,711 in more than 80 countries. Total revenue was $32.25, a 10.98% rise from the previous year. Starbucks has been recovering from the effects of the pandemic since 2021.
By the final quarter of 2021, the company’s market share was 34.74% in the United States, while revenue rose by 25% compared to the previous year. At the start of 2022, everybody expected Starbucks’ market share to rise as the economy reopened. By then, the company had accelerated the adoption of digital technology, which boosted its card reloads and activations.
Due to this, store traffic increased, and same-store sales reported an 18% rise in the US. The Starbucks loyalty program hit 26.4 million active members, marking a 21% growth. In-store sales in China dropped by 14% due to the outbreak of the Omicron variant and lockdowns in key cities.
Net global value hit $8.1 billion, a 19% growth compared to the first quarter of 2021. Despite the company’s growth, supply chain costs increased due to the virus outbreak. In the April 2022 quarter, Starbucks’ net consolidated net revenue was $7.6% billion, while earnings per share were 59 cents.
While the net revenue dropped from the previous quarter, it marked a 15% growth compared to the 2021-second quarter. Starbucks recorded a 17% revenue growth in the United States, hitting $5.4 billion. This was attributed to a 12% comparable store sales growth. Operating profit in the US rose from $896.4 in the previous year’s second quarter to $931.5 million. In the final quarter that ended in October 2022, Starbucks expected its consolidated sales to hit $8.3 billion. However, it rose by 3.3% from the previous $8.41 billion. The company opened the newest stores in the last quarter.
Starbucks Revenue
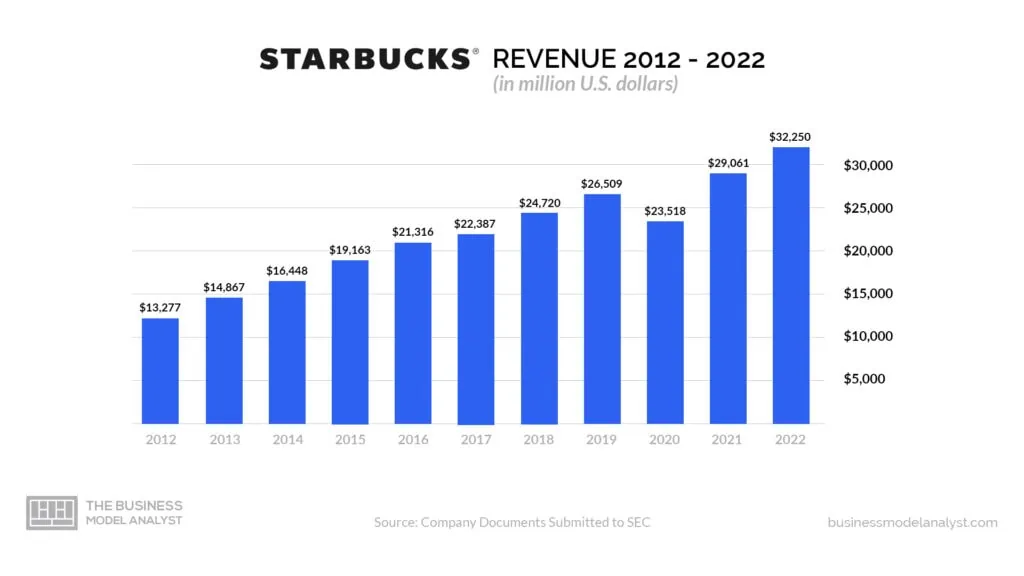
In 2021, Starbucks’ net revenue was $29 billion, a 24% and $5.5 billion increase, respectively, compared to the previous year’s performance. An increase in company-operated store revenue was attributed to a 20% rise in comparable store sales. 524 new stores were opened during that period.
The company’s after-tax earnings were $4.1 billion, but the net earnings from the divestiture of some operations were $865 million. The company’s annual revenue for 2020 was $23.5 billion, an 11.28% increase from the previous year. Peak quarterly revenue in 2022 was $8.2 billion, while revenue for the December Quarter was $8.714 billion, an 8.24% rise year over year. Annual revenue for December 31, 2022, increased by 8.41% year-over-year to $32.914 billion.
Starbucks Expenses
Starbucks’ December 31, 2022, operating expenses increased by 11.88% year-over-year to $28.221 billion. The company’s 2022 annual operating expenses rose 14.24% from the previous year to $27.633 billion. 2021’s annual operating expenses were $24.189 billion, a 10.17% increase from the previous year.
The company’s pre-paid expenses for December 31, 2022, quarter declined by 29.54% to hit $0.374 billion year over year. 2022’s pre-paid expenses dropped by 18.65% from the previous year to $0.484 billion. Pre-paid expenses for 2021 dropped by 19.59% from the previous year, hitting $0.595 billion.
Starbucks Profit
80% of the total Starbucks revenue is from its 15,000 company-owned coffee shops worldwide. This amounts to $3,800 every day and $520 for each store. One cup of Starbucks coffee generates a 6% profit. Starbucks’ coffee shops sell a big percentage of its coffee to people on the go, generating high sales and profit.
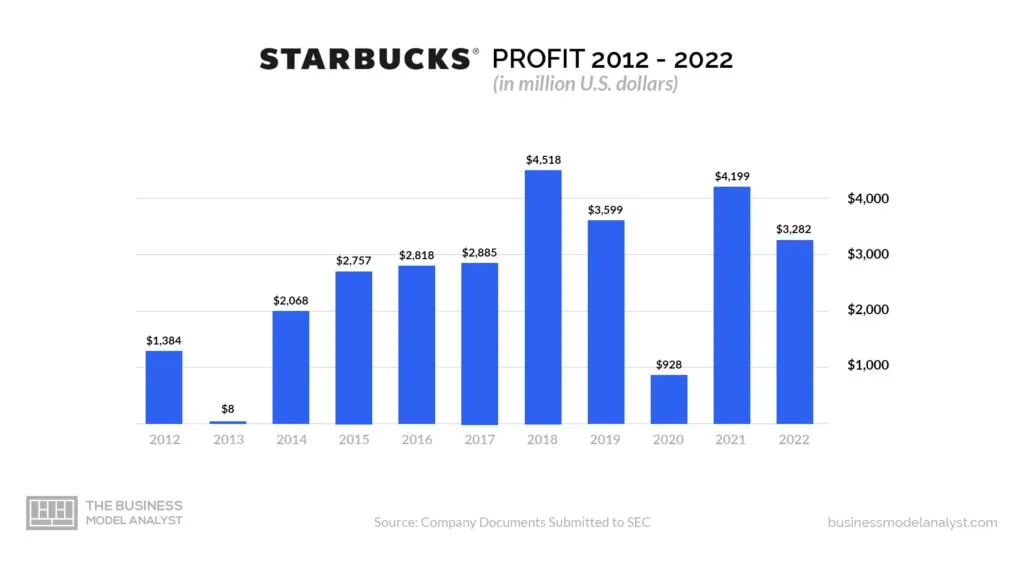
The company’s profit for the December 31, 2022 quarter rose by 6.88% year-over-year to hit $5.904 billion, while gross profit for the entire year ending December 31, 2022, was $22.313 billion, marking a 5.52% rise in year-over-year. Annual gross profit for 2022 increased by 7.93% from the previous year, hitting $21.933 billion.
Potential for Profitability
Starbucks can increase its profits by expanding to new regions. Currently, the company’s leading coffee shops are in the United States. Expanding to emerging markets like China, India, and some parts of Africa can be a strategic move. Further, Starbucks can expand its business operations to maximize revenue generation opportunities.
Moreover, developing products based on the target customer’s preferences can increase the company’s sales and profits in the long term. Starbucks is already a household name. The company can leverage its popularity to introduce new products in its stores to maximize profitability.
The world is evolving fast, and new technologies and trends are emerging in different sectors. While Starbucks is a leader in the coffee world, a lot can be done. Starbucks can adopt the latest coffee trends, such as RSI-reducing gizmos, the ultimate foam technology, snap-chilling, and back-to-black. Starbucks is committed to owning 55,000 coffee shops by 2030, and while that can be a massive investment, it may also increase the company’s profitability.
Conclusion
Even after closing down its stores during the COVID-19 pandemic, Starbucks returned bigger and better. The company’s sales, revenue, and profits started stabilizing slowly from the beginning of 2021 and have not relented. As we have seen in this article, there is still more Starbucks can do to boost profits. With Starbucks’s measures to improve its operations while giving its customers the best, the future can only be brighter.


