Is Lyft profitable? The short answer is that, no, Lyft is not profitable. The company has never reported an annual net profit, and 2022 reversed two years of declining net losses with a $522 million higher loss than the previous year. In 2022, Lyft reported revenue of $4 billion, compared to $3.2 billion in 2021. However, the company’s net loss was $1.58 billion in 2022, compared to $1 billion in 2021.
Lyft’s losses are due to some factors, including the high cost of driver incentives, the company’s investments in new initiatives, and the competitive landscape. Despite its losses, Lyft is still growing. The company’s active ridership increased by 8.5% in 2022, and its average revenue per active rider also increased.
Lyft is hoping to become profitable in the future. The company has said that it is focused on reducing its costs and improving its efficiency. It is also hoping to benefit from the growth of the ride-hailing market. However, it is still too early to say whether Lyft will ever be profitable.
The company faces challenges, including the high cost of driver incentives and the competitive landscape. Only time will tell whether Lyft can overcome these challenges and become profitable.
Contents
Timeline of Lyft’s financial growth and funding
Lyft is a ride-hailing company founded in San Francisco, California, in 2012. The company allows users to request rides from drivers using their cars. Lyft has raised over $12 billion in funding from investors such as Andreessen Horowitz, Sequoia Capital, and Fidelity Investments. The company went public on the Nasdaq stock exchange in 2017. The timeline highlights the significant milestones of Lyft’s financial growth and funding throughout its history.
- 2012: The company was founded in San Francisco, California, and won a seed round of $500,000;
- 2013: Lyft launched its ride-hailing service in San Francisco and won a Series A round of $6 million;
- 2014: Lyft expands to Los Angeles, Chicago, and New York City. Series B round of $10 million;
- 2015: Launches its bike-sharing service, Lyft Bikes. Series C round of $15 million;
- 2016: Launches its scooter-sharing service, Lyft Scooters. Series D round of $500 million;
- 2017: Goes public on the Nasdaq stock exchange. IPO of $2.2 billion;
- 2018: Expands to 640 cities in the United States and Canada. Series E round of $1 billion;
- 2019: Launches its car-sharing service, Lyft Express Drive. Series F round of $5.5 billion;
- 2020: Launches its multimodal app, which allows users to book rides, bikes, and scooters in a single place. Series G round of $2.5 billion;
- 2021: Expands to 500 cities in the United States and Canada. Series H round of $2.4 billion;
- 2022: Reports revenue of $4 billion. Net loss of $1.58 billion.
Lyft has grown significantly since its founding in 2012. The company has raised over $12 billion in funding and expanded to over 500 cities in the United States and Canada. However, Lyft is still not profitable. The company reported a net loss of $1.58 billion in 2022 and hopes to become profitable. It has said that it is focused on reducing its costs and improving its efficiency. Lyft is also hoping to benefit from the growth of the ride-hailing market.
When did Lyft first become profitable?
Lyft first became profitable on an adjusted EBITDA basis in Q2 2021, meaning that the company could cover its operating expenses and make a profit before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. However, Lyft is still not profitable on a net basis — the company reported a net loss of $251.9 million in Q2 2021.
Lyft is hoping to become profitable on a net basis in the future. The company has said that it is focused on reducing costs and improving efficiency. Lyft is also hoping to benefit from the growth of the ride-hailing market.
Lyft’s Financial Performance: Revenues, Expenses, and Profits
Lyft Revenue
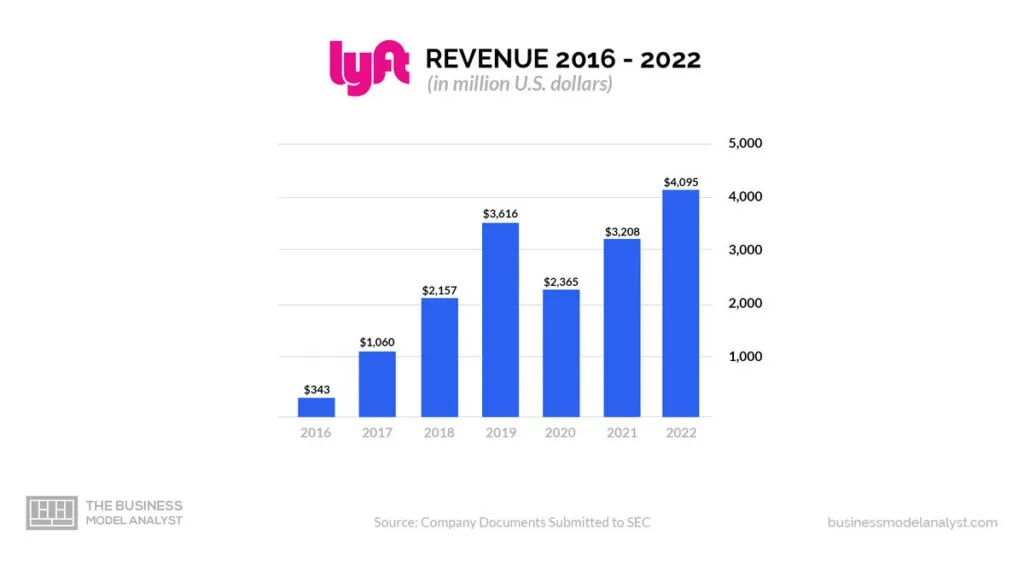
Lyft’s revenue in 2022 was $4,092.7 million, an increase of 27.8% from the previous year. In Q1 2023, Lyft’s revenue was $1,001.5 million, an increase of 14.0% year-over-year. Most of Lyft’s revenue comes from ride-share fares, which accounted for 93% of the company’s total revenue in 2022.
Other sources of revenue include bike-share and scooter-share fees, advertising, and subscriptions. In Q1 2023, Lyft’s revenue from ride-share fares increased by 14.0% year-over-year, driven by solid demand for ride-share services.
Lyft’s revenue from bike-share and scooter-share fees also increased by 14.0% year-over-year, driven by the continued growth of these businesses. Lyft’s revenue from advertising and subscriptions increased by 17.0% year-over-year, driven by the company’s investments in new advertising products and services, as well as the growth of its subscription business.
Lyft’s revenue growth in Q1 2023 was driven by strong demand for ride-share services and the continued growth of its bike-share and scooter-share businesses. The company also saw growth in its advertising and subscription businesses.
Lyft Expenses
The majority of Lyft’s expenses are related to its ride-share business. The cost of goods sold includes the cost of paying drivers for their rides, as well as the cost of providing insurance and other benefits to drivers. Operating expenses include marketing and sales, general and administrative, and research and development.
In Q1 2023, Lyft’s expenses were $849.8 million. This was an increase of 19.7% from the same period in the previous year. The increase in expenses was driven by the growth of Lyft’s business and the company’s investments in research and development. The cost of goods sold was the most considerable expense for Lyft in Q1 2023, at $486.1 million. This was followed by operating expenses, which totaled $310.2 million.
Driver incentives were the most significant component of operating expenses, at $203.0 million. Marketing and sales expenses were $68.7 million, and general and administrative expenses were $38.5 million. Lyft’s research and development expenses are relatively low compared to other technology companies because Lyft’s ride-share business is less complex than other technology businesses.
Lyft Profit
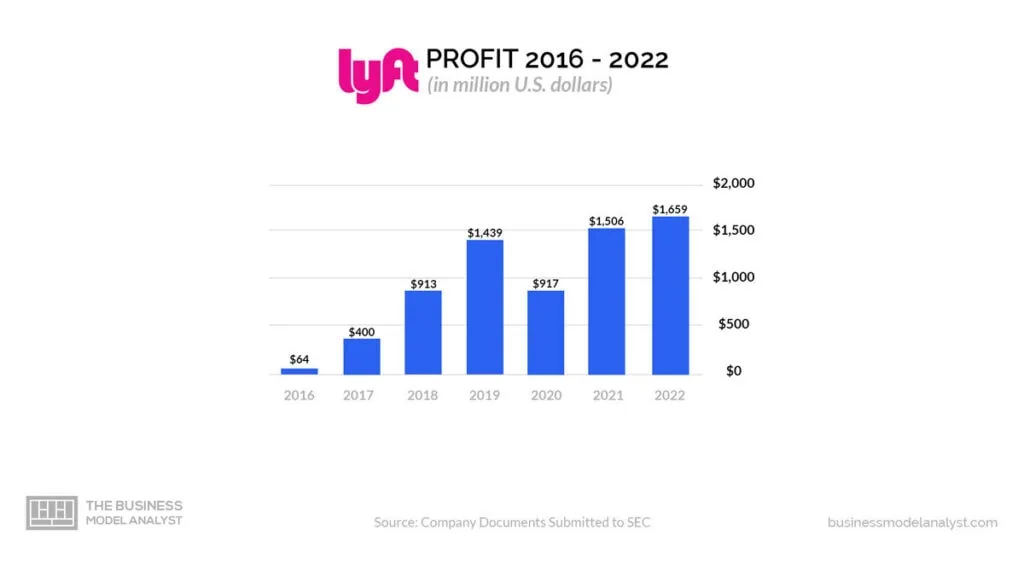
Lyft has never reported an annual net profit. In 2022, the company reported a net loss of $1.58 billion, compared to a net loss of $1 billion in 2021. In 2022, Lyft reported revenue of $4 billion, compared to $3.2 billion in 2021.
Lyft’s losses are due to several factors, including the high cost of acquiring and retaining drivers, the high cost of marketing and advertising, and the need to invest in new technologies, such as self-driving cars. Here are the steps Lyft is taking to become profitable.
Reducing marketing spending
Lyft has been reducing its marketing spending in recent years. This is because the company believes it can attract new riders and retain existing riders without spending as much on marketing. In 2022, Lyft spent $540 million on marketing, down from $640 million in 2021.
Streamlining operations
Lyft has been streamlining its operations to reduce costs. This includes closing some offices and laying off employees. The company believes that by streamlining its operations, it can become more efficient and save money.
Expanding into new markets
Lyft is expanding into new markets to increase its revenue. The company has recently launched operations in India and Mexico. Lyft believes that by expanding into new markets, it can reach a wider audience and generate more revenue.
Offering new services
Lyft is offering new services to increase its revenue. The company has recently launched a food delivery service and a car rental service. Lyft believes that providing new services can attract new customers and generate more revenue.
Investing in self-driving cars
Lyft is investing in self-driving cars to reduce costs in the long term. The company believes that self-driving cars will eventually eliminate the need for drivers, significantly reducing the company’s costs.
Potential for Profitability
Lyft’s potential for profitability is uncertain. The company has been losing money for several years, and it is unclear when it will be able to turn a profit. However, the company is taking steps to improve its financial performance and has a strong track record of growth. One of Lyft’s most significant expenses is acquiring and retaining drivers. The company pays drivers a commission on each ride and provides them with benefits such as health insurance and paid time off. If Lyft can reduce the cost of drivers, it will be more profitable.
Lyft also spends a lot of money on marketing and advertising. The company needs to spend money on marketing to attract new riders and retain existing riders. However, if Lyft can reduce its marketing spending, it will be more profitable. The ride-hailing market is growing rapidly, and Lyft is well-positioned to benefit from this growth. However, if the ride-hailing market slows down, it could impact Lyft’s profitability.
Lyft is investing in self-driving cars, and if self-driving cars become widely adopted, it could significantly reduce Lyft’s costs. This would make Lyft more profitable. Here are some of the opportunities that could contribute to Lyft’s profitability:
Increase fares
Lyft could increase fares to generate more revenue. However, this could lead to decreased ridership, so it would need to be done carefully. The company would need to consider factors such as the current state of the ride-hailing market, the level of competition from other ride-hailing companies, and the willingness of riders to pay higher fares.
Charge for wait time
Lyft could charge riders for wait time, which would help offset the cost of drivers waiting for rides. This would be a relatively easy change to implement, and it could generate additional revenue for the company. However, it is essential to note that this could also lead to decreased ridership, as some riders may be less likely to use the service if they have to pay for wait time.
Improve driver satisfaction
The company could also improve driver satisfaction by increasing driver pay and providing more support, helping to reduce driver turnover, which would save the company money in the long run. The company could also implement programs to help drivers with car maintenance and insurance. Additionally, Lyft could provide drivers with more opportunities for training and professional development.
Expand into new markets
Lyft could expand into new markets to increase its revenue. This would require the company to invest in marketing and advertising, but it could be a profitable move in the long run. Lyft could focus on expanding into markets where there is a high demand for ride-hailing services or where there is less competition from other ride-hailing companies.
Offer new services
Lyft could offer new services, such as food delivery or car rentals, to increase its revenue. This would require the company to invest in new technology and infrastructure, but it could be a profitable move if the new services are thriving. Lyft could partner with other companies to offer these new services, or it could develop the services in-house.
Invest in self-driving cars
Lyft is already investing in self-driving cars, and if this technology becomes widely adopted, it could significantly reduce the company’s costs. This would make Lyft more profitable in the long run. Lyft could continue to invest in self-driving car technology, or it could partner with other companies that are developing self-driving cars.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Lyft has emerged as a pioneering force in the ride-sharing industry, revolutionizing how people commute and enhancing urban mobility. Through its innovative platform and user-friendly app, Lyft has created a seamless experience for both passengers and drivers, fostering a sense of community and trust in the process.
The company’s commitment to safety, accessibility, and environmental sustainability has set a benchmark for the transportation sector, inspiring positive changes and promoting shared responsibility. Lyft can improve its profitability by offering new services, expanding into new markets, charging for wait time, and increasing its fares.


