Operating in more than 60 countries, the ExxonMobil business model is centered around providing reliable energy solutions to meet the world’s growing demand. With its extensive portfolio of exploration, production, refining, and marketing activities, ExxonMobil has become one of the largest publicly traded companies globally.
At the core of ExxonMobil’s business model is its emphasis on vertical integration. By controlling every aspect of the value chain, from upstream activities such as oil and gas exploration and production to downstream operations like refining and marketing, ExxonMobil has achieved significant cost efficiencies and maintained a competitive edge in the industry.
Moreover, ExxonMobil leverages its strong research and development capabilities to focus on technological advancements and sustainable energy solutions. The company invests heavily in R&D to improve operational efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and explore alternative energy sources.
With a diverse portfolio, ExxonMobil strives to balance its investments between high-value projects that generate substantial cash flows in the short-term and long-term growth opportunities. This strategy allows the company to adapt to market fluctuations and mitigate risks.
However, ExxonMobil also faces challenges, ranging from the impact of climate change concerns to evolving regulatory frameworks and geopolitical uncertainties. As the world transitions towards cleaner energy sources, ExxonMobil has been under pressure to decarbonize its operations and invest in renewable energy projects.
This analysis will encompass a close look at ExxonMobil’s core activities, the value it provides, revenue sources, as well as its notable strengths, weaknesses, and strategies to navigate the constantly changing energy industry.
Contents
A brief history of ExxonMobil
ExxonMobil, one of the world’s largest publicly traded international oil and gas companies, has a rich history dating back to its original predecessor companies in the late 19th century. The roots of ExxonMobil can be traced back to the founding of Standard Oil Company in 1870 by John D. Rockefeller.
Standard Oil quickly became a dominant force in the oil industry, controlling the production, refining, and distribution of petroleum products in the United States. However, in 1911, the U.S. Supreme Court ordered the breakup of Standard Oil into several smaller companies, including Standard Oil of New Jersey and Standard Oil of New York.
Standard Oil of New Jersey eventually became Exxon Corporation, while Standard Oil of New York became Mobil Oil Corporation. Throughout the early to mid-20th century, both companies continued to grow and expand their operations, building a reputation for excellence and innovation in the oil and gas industry.
In 1999, Exxon Corporation and Mobil Oil Corporation merged to form ExxonMobil Corporation. The merger created a global powerhouse in the energy sector, combining the strengths and expertise of two industry giants. The new company became the largest publicly traded oil and gas company in the world, with operations in over 200 countries and territories.
ExxonMobil’s business model is built on a solid foundation of exploration, production, refining, and marketing. The company focuses on finding and developing new oil and gas reserves, utilizing advanced technologies and expertise to extract resources safely and efficiently. ExxonMobil also operates a vast network of refineries, where crude oil is processed into a wide range of products, including gasoline, diesel, and lubricants.
In addition to its upstream and downstream operations, ExxonMobil has a robust chemicals division, which produces a variety of petrochemicals used in industries such as plastics, packaging, and automotive. The company has made significant investments in research and development to drive innovation and sustainability across its operations.
Over the years, ExxonMobil has faced many challenges and opportunities in the ever-evolving energy landscape. The company has adapted to changing market dynamics, regulatory environments, and societal expectations. It has also made significant investments in renewable and low-carbon technologies, aiming to reduce its environmental footprint and contribute to a lower-carbon future.
ExxonMobil’s commitment to excellence, innovation, and responsible operations has enabled it to maintain a leading position in the global energy industry. By leveraging its financial strength, technical expertise, and diverse portfolio of assets, the company continues to deliver value to its shareholders, customers, and communities around the world.
Who Owns ExxonMobil
ExxonMobil Corporation (US30231G1022) is a publicly owned company, with a diverse group of shareholders. As of November 6, 2023, according to MarketScreener, the largest shareholders of ExxonMobil include:
- The Vanguard Group, Inc.: The Vanguard Group owns approximately 372,212,035 shares, representing 9.298% of the company’s equity. The value of their holdings is estimated at $43,765 million;
- Fidelity Management & Research Co. LLC: Fidelity Management & Research owns approximately 97,026,072 shares, representing 2.424% of the company’s equity. The value of their holdings is estimated at $11,408 million;
- Geode Capital Management LLC: Geode Capital Management owns approximately 67,916,708 shares, representing 1.697% of the company’s equity. The value of their holdings is estimated at $7,986 million;
- Norges Bank Investment Management: Norges Bank Investment Management owns approximately 47,383,406 shares, representing 1.184% of the company’s equity. The value of their holdings is estimated at $5,571 million;
- Capital Research & Management Co.: Capital Research & Management owns approximately 36,099,525 shares, representing 0.9018% of the company’s equity. The value of their holdings is estimated at $4,245 million.
Other notable shareholders of ExxonMobil include State Farm Investment Management Corp., JPMorgan Investment Management, Inc., Managed Account Advisors LLC, Dimensional Fund Advisors LP, and Capital Research & Management Co. (Global Investors). These shareholders own varying stakes in the company, ranging from 0.4943% to 0.6009%.
ExxonMobil Mission Statement
ExxonMobil’s mission statement is “committed to being the world’s premier petroleum and chemical manufacturing company.”

How ExxonMobil works
As previously highlighted, ExxonMobil’s business model is based on the exploration, extraction, refining, and sale of oil and gas products, as well as the development and deployment of new technologies to improve energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact. The company operates in various segments, including Upstream, Downstream, Chemical, and Corporate.
In the Upstream segment, ExxonMobil focuses on the exploration and production of oil and gas reserves worldwide. The company invests heavily in advanced technologies and equipment to maximize production and minimize costs. ExxonMobil also enters into partnerships and joint ventures with other companies to expand its global presence and access new reserves.
Once the oil and gas are extracted, they are sent to ExxonMobil’s refineries in the Downstream segment. Here, the company processes and converts crude oil into several refined products, such as gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. ExxonMobil’s refineries are strategically located near major transportation hubs to efficiently distribute products to customers worldwide.
In addition to refining, ExxonMobil’s Downstream segment also includes marketing and distribution activities. The company operates a global network of retail stations and works with distributors and wholesalers to supply its products to customers in various sectors, including transportation, industrial, and commercial.
ExxonMobil’s Chemical segment focuses on the production and sale of petrochemicals, which are used in various industries, including packaging, automotive, and construction. The company utilizes advanced technologies and processes to develop innovative and sustainable chemical solutions.
ExxonMobil’s business model also includes investments in research and development, aimed at creating new technologies and products to address global energy challenges. The company collaborates with external partners, including universities and research institutions, to accelerate the development and deployment of cutting-edge solutions.
To ensure the efficient operation of its business model, ExxonMobil places great emphasis on safety, environmental stewardship, and community engagement. The company follows rigorous standards and practices to minimize risks and contribute positively to the communities where it operates.
Through its integrated approach and diverse portfolio of energy products and services, ExxonMobil aims to meet the world’s growing energy needs while minimizing environmental impact and creating value for its stakeholders.
How ExxonMobil makes money
ExxonMobil operates a diversified business model that encompasses various segments within the oil and gas industry. The company generates revenue through different sources, including
Upstream Operations
ExxonMobil explores and produces crude oil and natural gas resources. The company operates globally, utilizing advanced technologies and expertise to discover and extract hydrocarbon reserves. ExxonMobil generates revenue from selling crude oil, natural gas, and related products obtained from its upstream operations. This segment contributes a significant portion of the company’s overall revenue.
Refining and Marketing
ExxonMobil operates refineries where crude oil is processed into refined products such as gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and lubricants. The refined products are sold to wholesalers, retailers, and distributors worldwide. ExxonMobil’s global marketing network allows it to supply its products to various markets, meeting consumer demands and generating revenue from the sale of these refined products.
Chemical Operations
ExxonMobil also produces and markets petrochemicals and specialty chemical products. The company utilizes its integrated refining and chemical manufacturing facilities to produce a wide range of chemicals used in industries such as automotive, packaging, construction, and electronics. ExxonMobil generates revenue through the sale of these chemicals to customers worldwide.
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
ExxonMobil is involved in the production, liquefaction, and sale of LNG. The company develops and operates LNG facilities that convert natural gas into a liquid state, allowing for more accessible transportation and storage. ExxonMobil sells LNG to customers globally, including utilities, industrial companies, and other energy producers.
Technology and Licensing
ExxonMobil also generates revenue by licensing its technologies and intellectual property to third-party companies. The company’s advanced technologies and expertise in the oil and gas industry are highly sought after, and ExxonMobil earns royalties and fees from licensing agreements.
Additionally, ExxonMobil engages in trading and hedging activities to manage price risks and optimize its operations. These activities involve buying and selling commodities, such as crude oil and petroleum products, to capture market opportunities and mitigate potential financial risks.
ExxonMobil Business Model Canvas
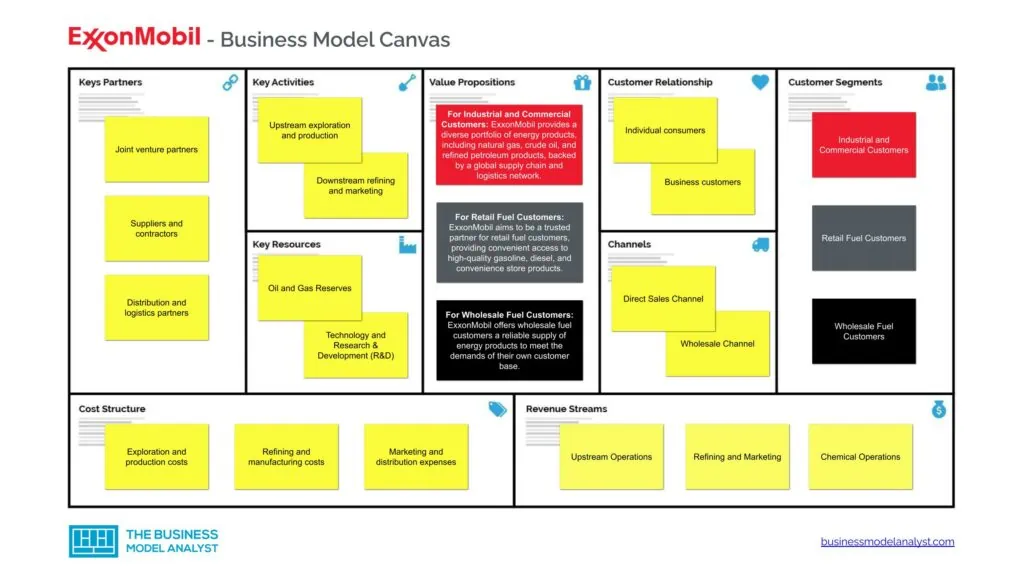
ExxonMobil Customer Segments
ExxonMobil’s customer segments are diverse and encompass various stakeholders within the energy industry. The company serves the following customer segments:
- Industrial and Commercial Customers: ExxonMobil supplies energy products such as natural gas, crude oil, and refined petroleum products to a wide range of industrial and commercial customers. This includes sectors such as manufacturing, transportation, power generation, aviation, and marine;
- Retail Fuel Customers: ExxonMobil operates a global network of retail fuel stations, serving individual customers who rely on gasoline, diesel, and convenience store products for their daily needs. These customers vary across different regions and demographics;
- Wholesale Fuel Customers: ExxonMobil provides bulk fuel supply to various distributors, wholesalers, and resellers, who then distribute fuel to their customers, including businesses in the transportation, construction, and agricultural sectors;
- Chemical and Petrochemical Customers: ExxonMobil is a leading producer of petrochemical products used in a wide range of applications, such as plastics, packaging materials, automotive components, and consumer goods. The company serves customers in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and healthcare;
- Technology and Licensing Partners: ExxonMobil has a significant presence in research and development, leveraging its expertise in technology and innovation. The company partners with technology suppliers and licenses its proprietary technologies to other companies, driving advancements in the energy sector;
- Financial Institutions and Investors: ExxonMobil’s financial performance and investment opportunities attract the interest of financial institutions and investors. These stakeholders include banks, investment funds, and individual shareholders who invest in the company’s stocks or bonds;
- Local Communities and Stakeholders: As a large multinational corporation, ExxonMobil engages with local communities, NGOs, and other stakeholders in the areas where it operates. The company prioritizes community relations, social responsibility, and environmental stewardship to build trust and foster sustainable development.
By serving a diverse range of customer segments, ExxonMobil strategically positions itself as a key player in the global energy market, catering to the evolving needs and demands of different stakeholders.
ExxonMobil Value Propositions
ExxonMobil’s value propositions consist of:
- For Industrial and Commercial Customers: Here, ExxonMobil provides a diverse portfolio of energy products, including natural gas, crude oil, and refined petroleum products, backed by a global supply chain and logistics network. Their value proposition centers around reliable energy supply, competitive pricing, and customized solutions that optimize efficiency and support business growth;
- For Retail Fuel Customers: ExxonMobil aims to be a trusted partner for retail fuel customers, providing convenient access to high-quality gasoline, diesel, and convenience store products. Their value proposition focuses on providing a seamless refueling experience, competitive pricing, and loyalty programs that reward customer loyalty;
- For Wholesale Fuel Customers: ExxonMobil offers wholesale fuel customers a reliable supply of energy products to meet the demands of their own customer base. The value proposition to wholesale fuel customers centers around ensuring a consistent and cost-effective fuel supply that enables their customers’ success;
- For Chemical and Petrochemical Customers: ExxonMobil serves chemical and petrochemical customers by offering a wide range of high-quality petrochemical products, innovative solutions, and technical support. Their value proposition lies in providing reliable and sustainable inputs for their customers’ manufacturing processes, helping them enhance product performance, reduce costs, and optimize efficiency;
- For Technology and Licensing Partners: ExxonMobil’s value proposition includes providing partners with innovative solutions that improve operational efficiency, reduce environmental impacts, and enable competitive advantages. They offer comprehensive support throughout the technology transfer process, helping partners capitalize on ExxonMobil’s extensive research and development capabilities;
- For Financial Institutions and Investors: ExxonMobil’s value proposition to financial institutions and investors revolves around delivering long-term value and returns on investment. They strive to maintain strong financial performance, robust governance practices, and transparent reporting;
- For Local Communities and Stakeholders: ExxonMobil’s value proposition to local communities and stakeholders focuses on responsible corporate citizenship, social engagement, and environmental stewardship. Their value proposition includes transparency, open communication, and proactive measures to mitigate environmental impacts and ensure the well-being of local communities.
ExxonMobil Channels
ExxonMobil’s channels consist of:
- Direct Sales Channel: ExxonMobil uses its extensive network of company-owned and franchise fuel stations to directly sell petroleum products to end consumers;
- Wholesale Channel: ExxonMobil distributes its products to wholesalers and bulk purchasers like industrial customers, gas stations, and airlines through bulk sales and terminal operations;
- Business-to-Business (B2B) Channel: ExxonMobil utilizes a B2B channel to sell lubricants, petrochemicals, and refining products directly to other businesses, such as automotive, manufacturing, and chemical industries.
ExxonMobil Customer Relationships
ExxonMobil’s customer relationships consist of:
- Individual consumers: ExxonMobil maintains customer relationships with individual consumers through its fuel stations. It focuses on providing quality fuel, convenience store offerings, rewards programs, and loyalty initiatives to enhance customer experience and loyalty;
- Business customers: For B2B customers, ExxonMobil builds and maintains relationships through direct sales representatives, corporate contracts, and tailored product offerings. They provide technical support and supply chain management, as well as offer sustainable solutions to meet specific client requirements.
ExxonMobil Revenue Streams
ExxonMobil’s revenue streams consist of:
- Upstream Operations
- Refining and Marketing
- Chemical Operations
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
- Technology and Licensing
ExxonMobil Key Resources
ExxonMobil’s key resources consist of:
- Oil and Gas Reserves: ExxonMobil’s key resource is its extensive portfolio of oil and gas reserves worldwide. These reserves provide the raw materials necessary to produce petroleum products and generate revenue;
- Technology and Research & Development (R&D): The company invests heavily in technology and R&D to explore new oil fields, develop innovative extraction techniques, and improve refining processes. This allows ExxonMobil to maximize extraction and production efficiency, ensuring a competitive edge in the industry;
- Distribution and Supply Chain Infrastructure: ExxonMobil has an extensive distribution and supply chain infrastructure, including pipelines, terminals, refineries, storage facilities, and a network of fuel stations. These resources enable efficient transportation and distribution of products to customers;
- Brand and Reputation: ExxonMobil’s brand and reputation are key resources contributing to customer trust and loyalty. The company’s established brand name, reliability, and commitment to sustainability help maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
ExxonMobil Key Activities
ExxonMobil’s key activities consist of:
- Upstream exploration and production
- Downstream refining and marketing
- Chemical manufacturing
- Natural gas and power marketing
- Research and development
ExxonMobil Key Partners
ExxonMobil’s key partners consist of:
- Joint venture partners
- Suppliers and contractors
- Distribution and logistics partners
- Research and academic institutions
- Governments and regulatory bodies
ExxonMobil Cost Structure
ExxonMobil’s cost structure consists of:
- Exploration and production costs
- Refining and manufacturing costs
- Marketing and distribution expenses
- Research and development expenses
- Employee salaries and benefits
- Taxes and royalties
- Capital expenditures
- Environmental and regulatory compliance costs
- Advertising and promotional expenses
ExxonMobil Competitors
In the highly competitive global energy market, ExxonMobil faces stiff competition from these major players. The competition revolves around resource access, technological capabilities, operational efficiency, environmental performance, and market positioning. Their competitors include
- Royal Dutch Shell: Shell is one of ExxonMobil’s main competitors in the global energy market. With a strong presence in both the upstream and downstream segments, Shell competes with ExxonMobil in terms of oil and gas exploration, production, refining, and retailing;
- Chevron Corporation: Chevron is another major competitor that operates in similar segments as ExxonMobil. Both companies are engaged in upstream activities, such as exploration and drilling, as well as downstream operations involving refining, marketing, and distributing petroleum products;
- BP P.L.C.: BP is a global energy company that competes directly with ExxonMobil in the oil and gas industry. Like ExxonMobil, BP has a diverse portfolio of assets in exploration, production, refining, and retailing. Both companies also face similar challenges in terms of environmental regulations and public perception;
- TotalEnergies: TotalEnergies is a French multinational energy company and one of ExxonMobil’s competitors. It operates in various segments, including upstream activities such as exploration and production, downstream operations involving refining and marketing, as well as renewable energy sources;
- ConocoPhillips: ConocoPhillips is an American energy company that competes with ExxonMobil primarily in the upstream segment. Both companies are involved in oil and gas exploration, development, and production, although ConocoPhillips has a smaller downstream presence;
- PetroChina: As one of the largest oil and gas companies in the world, PetroChina is a significant competitor for ExxonMobil, particularly in the Asian market. Both companies are engaged in various energy-related activities, including exploration, production, refining, and marketing;
- ENI S.p.A.: ENI, an Italian multinational energy company, is also a competitor to ExxonMobil. Its operations span across the entire energy value chain, including activities in exploration, production, refining, and retailing. ENI has been expanding its renewable energy portfolio, competing with ExxonMobil in this growing sector as well.
ExxonMobil SWOT Analysis
Understanding ExxonMobil’s SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis is essential for gaining insights into its strategic positioning and potential avenues for growth and improvement.
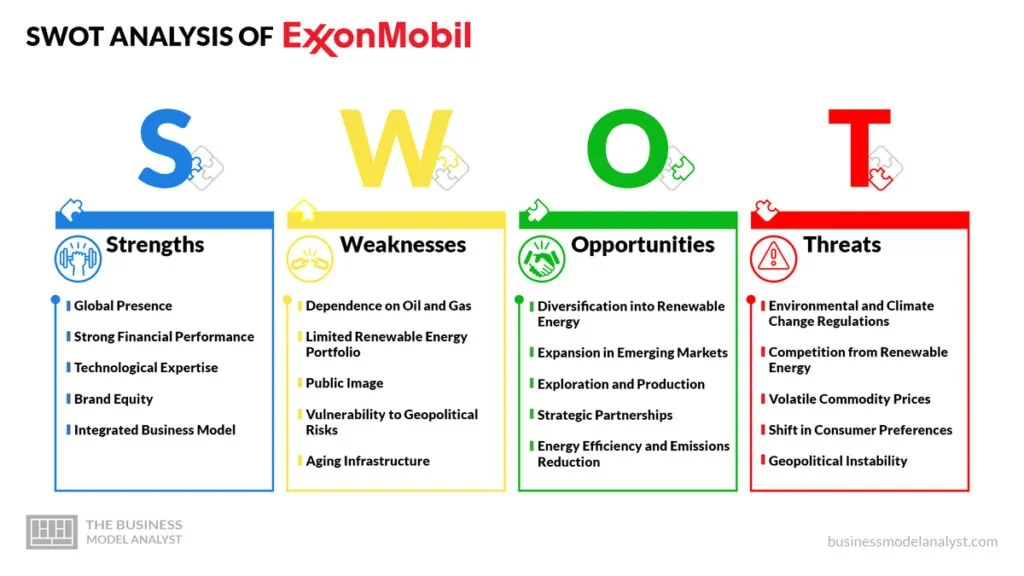
ExxonMobil Strengths
- Global Presence: ExxonMobil operates in over 200 countries, which gives them a robust global footprint and diversified revenue streams;
- Strong Financial Performance: The company consistently generates significant revenue and maintains a solid financial position in the industry;
- Technological Expertise: ExxonMobil has a history of investing in research and development, allowing it to stay at the forefront of technological advancements in the energy sector;
- Brand Equity: The ExxonMobil brand is widely recognized and trusted, which gives the company a competitive advantage in the market;
- Integrated Business Model: ExxonMobil’s vertically integrated model, from exploration to distribution, allows them to control the entire value chain.
ExxonMobil Weaknesses
- Dependence on Oil and Gas: The company’s heavy reliance on oil and gas products makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in commodity prices, regulatory changes, and growing concerns about climate change;
- Limited Renewable Energy Portfolio: Although ExxonMobil has started to invest in renewable energy, its portfolio in this sector is comparatively small, which limits its exposure to growing green energy trends;
- Public Image: ExxonMobil has faced criticism for its perceived lack of action on climate change and other environmental issues, which can impact its reputation and brand image;
- Vulnerability to Geopolitical Risks: Operating in multiple countries exposes ExxonMobil to geopolitical uncertainties, including political instability and regulatory changes;
- Aging Infrastructure: The company’s extensive infrastructure may require significant investments in maintenance and upgrades, leading to increased costs.
ExxonMobil Opportunities
- Diversification into Renewable Energy: Shifting towards renewable energy sources and investing in clean technologies can help ExxonMobil adapt to the changing energy landscape and reduce its carbon footprint;
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: Increasing energy demand in emerging markets presents opportunities for ExxonMobil to expand its operations and tap into growing markets;
- Exploration and Production: The exploration and production of unconventional resources, such as shale gas and oil, can provide new growth opportunities for the company;
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with other industry players, technology firms, or governments can help ExxonMobil access new markets, leverage expertise, and drive innovation;
- Energy Efficiency and Emissions Reduction: Implementing energy-efficient practices and reducing emissions can help ExxonMobil meet regulatory requirements and address environmental concerns.
ExxonMobil Threats
- Environmental and Climate Change Regulations: Increasing public and regulatory pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition to cleaner energy sources can impact ExxonMobil’s operations and require costly compliance measures;
- Competition from Renewable Energy: The growth of renewable energy sources and rapidly declining costs threaten ExxonMobil’s core business, as they may face competition from alternative energy providers;
- Volatile Commodity Prices: Fluctuations in oil and gas prices can significantly impact ExxonMobil’s revenue and profitability;
- Shift in Consumer Preferences: Changing consumer preferences towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly products can influence demand for ExxonMobil’s traditional energy offerings;
- Geopolitical Instability: Political conflicts, trade disputes, and economic uncertainties can disrupt ExxonMobil’s operations, particularly in regions with a significant presence.
Conclusion
ExxonMobil’s business model is rooted in its vertically integrated approach and relentless focus on the exploration, production, refining, and marketing of petroleum and petrochemical products. The company leverages its size, scale, and global presence to mitigate risks, optimize operations, and maximize profits.
Despite facing numerous challenges, such as volatile oil prices, increasing environmental concerns, and shifting toward renewable energy sources, ExxonMobil demonstrates resilience and adaptability.
By investing in technology, diversifying its energy portfolio, and embracing sustainability initiatives, the company is well-positioned to navigate the evolving energy landscape and maintain its position as a leader in the industry.

