The Chevron business model has become a cornerstone example in the oil and gas industry, rooted deep in the historical heartland of American industry. This model, created over 143 years of hard work and innovation, is a shining example of resilience, adaptability, and sustainable growth.
Known to the world for its gasoline, natural gas, and other petrochemical production, Chevron’s presence is felt globally, with operations spanning over 180 countries.
However, it’s not just about providing fuel for your car or heating for your home; it’s about the grand journey of an energy corporation that evolved with the times, expanding its operations from hydrocarbon exploration, production, and refining to chemical manufacturing, sales, and power generation.
Understanding the Chevron business model is crucial because it provides a roadmap to success in the highly competitive and ever-changing energy industry. Over its long history, Chevron has faced many challenges and controversies, including environmental concerns and inherited liabilities. Yet, the corporation’s journey provides valuable insights into resilience, strategic decision-making, and the continuous pursuit of innovation.
Contents
A brief history of Chevron
The roots of Chevron date back to 1879, when it started as Pacific Coast Oil Co., a private company specializing in the oil, gasoline, and petrochemical industries. Fast-forward to 1906, and the company became a part of the renowned Standard Oil conglomerate, transitioning from a small private firm into a public subsidiary.
Under the umbrella of Standard Oil, the company evolved and expanded, acquiring the knowledge and resources to make a significant impact in the industry. The real breakthrough came in 1911 when the company became independent from Standard Oil and took its initial steps toward becoming an industry leader.
The company, then known as the Standard Oil Company of California, initiated a period of rapid growth and expansion. It absorbed other smaller companies and built strategic partnerships inside and outside California. This aggressive growth strategy positioned Chevron as one of the Seven Sisters, the companies that dominated the global petroleum industry from the mid-1940s to the 1970s.
In 1985, another significant event reshaped the company’s future. It merged with Gulf Oil, based in Pittsburgh, leading to the creation of the Chevron brand we know today. The growth didn’t stop there; in 2001, the company merged with Texaco, further expanding its operations.
Today, Chevron is a leading name in producing fuels, lubricants, additives, and petrochemicals, with a significant presence in regions like Western North America, the U.S. Gulf Coast, Southeast Asia, South Korea, and Australia. As of 2018, the company produced an average of 791,000 barrels of net oil equivalent daily in the United States.
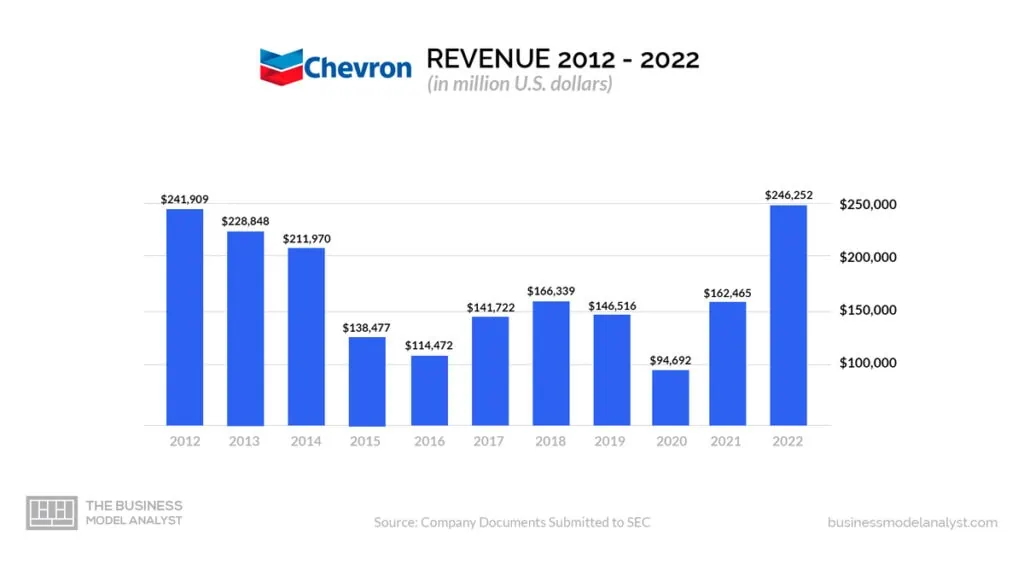
With its position as the second-largest oil company based in the United States by revenue, only behind ExxonMobil, Chevron has proven its mettle in the energy industry. In 2022, it secured the 16th spot on the Fortune 500, reporting impressive revenues of US$162.5 billion.
Who Owns Chevron
Chevron is a publicly traded company, which means its ownership is spread across many shareholders who own its common stock. These shareholders can range from everyday individuals to large institutional investors like mutual funds, insurance companies, and retirement funds. Owning a piece of Chevron is as easy as buying its stock, which trades on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol “CVX.”
The leadership of Chevron is in the hands of its Board of Directors and its executive officers. The Board of Directors, elected by the shareholders, oversees the company’s overall direction and appoints the executive officers who manage Chevron’s daily operations.
The current CEO of Chevron is Mike Wirth, who has been with the company since 1982. Wirth became the Chairman of the Board and CEO in 2018, taking the helm of Chevron with over 35 years of experience within the company.
Chevron Mission Statement

The Chevron mission statement is “to be the global energy company most admired for its people, partnerships, and performance.”
How Chevron works
Chevron, in its most basic form, is an energy company. But when you peek under the hood, you find that it’s a lot more than that. Chevron’s work can be divided into two main areas: upstream and downstream operations.
First, the “upstream” operations are about finding and extracting oil and gas. Chevron has a bunch of scientists, engineers, and technicians working hard to discover new sources of oil and gas.
They use fancy technology like seismic imaging to peek into the earth and find places where oil and gas might be hiding. Then, they drill wells to extract these resources. Chevron’s upstream operations span the globe, from the Gulf of Mexico’s deep waters to the Middle East’s vast deserts.
Now, onto “downstream” operations. This happens after the oil and gas have been pulled out of the ground. The raw oil and gas are transported to refineries, where they’re turned into products we use daily, like gasoline for our cars, jet fuel for planes, and heating oil for homes.
Also, some of the oil and gas are used to make chemicals that end up in plastics and detergents. To make this happen, Chevron owns and operates several refineries and chemical plants worldwide.
But Chevron’s work doesn’t end there. The company sells these products to customers. Chevron runs thousands of service stations where drivers fill up their cars. Also, they sell bulk fuel and chemicals to other businesses that use them to make and power their products.
Beyond these traditional oil and gas activities, Chevron invests in renewable and sustainable energy technologies. They’re exploring stuff like biofuels, solar energy, and hydrogen power. The aim is to help meet the world’s growing energy needs while reducing the environmental impact.
How Chevron makes money
Chevron’s financial model is robust, diversified, and primarily rooted in the oil and gas industry. Their financial streams are varied and designed to optimize the monetization of the resources they extract. Below are the key areas:
Sale of Crude Oil and Natural Gas
The primary source of Chevron’s revenue comes from the sale of crude oil and natural gas. They extract these raw materials from their reserves and sell them to other companies, which refine and convert them into usable products.
Refining and Marketing
Chevron also takes part in the refinement process. They convert crude oil and natural gas into gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. The sale of these refined products, whether directly to consumers at Chevron-branded service stations or businesses, represents another significant income stream for the company.
Sale of Chemicals
Beyond fuels, Chevron’s operations extend to the chemical industry. Their subsidiary, Chevron Phillips Chemical, processes raw materials into chemicals used in various products, from plastics to cleaning agents. The sale of these chemicals contributes to the company’s overall revenue.
Power Generation
Chevron also engages in power generation, focusing on natural gas. The electricity produced at their power plants is sold to utility companies, providing another source of income, albeit a smaller one compared to their primary operations.
Exploration and Production
The sale of exploration and production rights also contributes to Chevron’s revenue. They offer other companies the rights to explore and produce oil and gas in the areas where Chevron holds licenses, which provides a different yet valuable income source.
Renewable Energy Investments
Chevron is also investing in renewable energy technologies. This includes research into biofuels, solar and wind power, and hydrogen-based solutions. While still a smaller part of their revenue structure, these renewable energy ventures could grow in importance as the global energy market continues to evolve.
Chevron Business Model Canvas
The Chevron Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
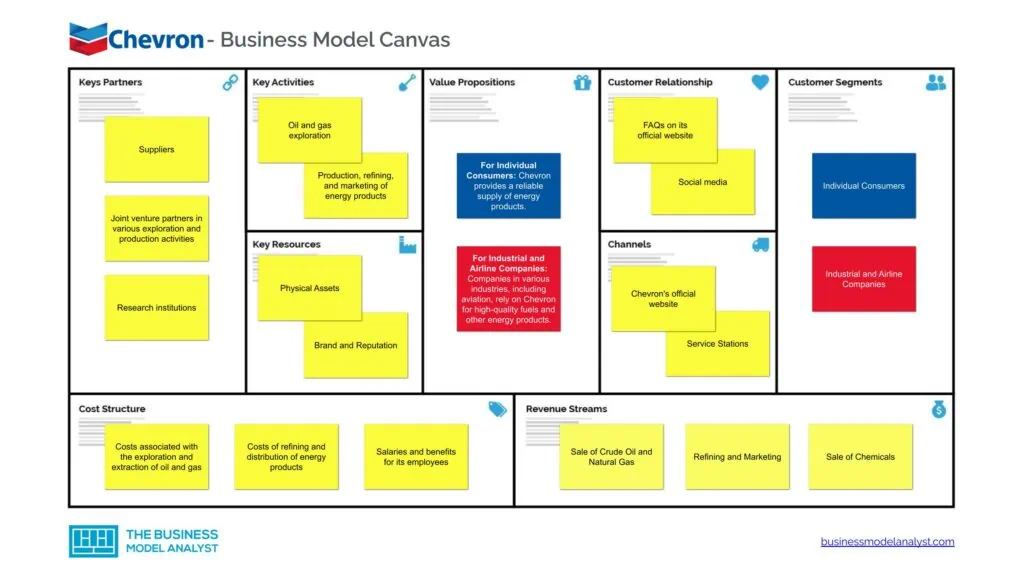
Chevron Customer Segments
Chevron customer segments consist of:
- Individual Consumers: Chevron serves individual consumers who need fuel for their cars, homes, and businesses. These consumers purchase Chevron’s products, like gasoline and heating oil, mainly at service stations;
- Industrial and Airline Companies: Manufacturing, transportation, and construction firms that need large amounts of fuel for their operations. Chevron provides them with fuel and other petroleum-based products. Airlines need jet fuel to operate, and Chevron, as a leading energy company, supplies this jet fuel;
- Government Entities: Chevron works with governments worldwide, supplying them with various energy needs. This could be fuel for government vehicles, heating oil for government buildings, or power generation;
- Utility Companies: Chevron generates electricity, which it sells to utility companies. These companies then distribute this electricity to homes and businesses;
- Chemical Industry: Through its subsidiary, Chevron Phillips Chemical, Chevron sells chemicals used in various industries, from plastics to cleaning agents.
- Sustainable Energy Users: Chevron is also providing to a growing segment of customers who are looking for greener and more sustainable energy solutions. These include corporations seeking to reduce their carbon footprint, municipalities aiming for green power generation, and individual consumers investing in clean energy for their homes.
Chevron Value Propositions
Chevron value propositions consist of:
- For Individual Consumers: Chevron provides a reliable supply of energy products. Its global network of service stations means that consumers can trust that they’ll be able to find Chevron fuel wherever they are. The quality of Chevron’s gasoline and other products ensures that consumers get the best performance from their vehicles and equipment;
- For Industrial and Airline Companies: Companies in various industries, including aviation, rely on Chevron for high-quality fuels and other energy products. They trust Chevron’s dependable supply and excellent product quality to keep their operations running smoothly;
- For Government Entities: For government entities, working with a trusted company like Chevron ensures reliable energy supplies for their operations. They also benefit from Chevron’s investments in cleaner energy sources, which align with governmental goals of reducing carbon emissions;
- For Utility Companies: Chevron provides a consistent source of electricity to utility companies. By using Chevron’s power generation services, these companies can provide homes and businesses with the necessary electricity;
- For Chemical Manufacturers: Chevron’s value to chemical manufacturers lies in its ability to supply high-quality raw materials for various products. Through Chevron Phillips Chemical, it delivers chemicals used in everything from plastics to cleaning agents.
- Sustainable Energy: Chevron is investing in sustainable and renewable energy sources. This commitment to sustainability appeals to customers who are conscious of the environment and looking for greener energy options.
Chevron Channels
Chevron channels consist of:
- Chevron’s official website (https://www.chevron.com/)
- Service Stations
- Direct Sales to large industrial customers, utilities, and airlines
- Wholesalers and retailers
Chevron Customer Relationships
Chevron customer relationships consist of:
- FAQs on its official website
- Social media
- Company’s sales teams
- Email and telephone support.
Chevron Revenue Streams
Chevron revenue streams consist of:
- Sale of Crude Oil and Natural Gas
- Refining and Marketing
- Sale of Chemicals
- Power Generation
- Exploration and Production
- Renewable Energy Investments
Chevron Key Resources
Chevron key resources consist of:
- Physical Assets (oil and gas reserves, refineries, service stations, distribution networks)
- Brand and Reputation
- Intellectual Property (Patents and proprietary technology)
- Financial Resource
- Sales administrators
- Human Capital (engineers, geoscientists, and other professionals)
Chevron Key Activities
Chevron key activities consist of:
- Oil and gas exploration
- Production, refining, and marketing of energy products
- Research and development in energy technology
Chevron Key Partners
Chevron key partners consist of:
- Suppliers
- Joint venture partners in various exploration and production activities
- Research institutions
- Governmental and non-governmental organisations for environmental and sustainability initiatives
Chevron Cost Structure
Chevron cost structure consists of:
- Costs associated with the exploration and extraction of oil and gas
- Costs of refining and distribution of energy products
- Salaries and benefits for its employees
- Maintenance of physical assets
- Costs related to research and development
- Costs of regulatory compliance and environmental remediation efforts
Chevron Competitors
- ExxonMobil: It’s one of the biggest names in the energy business and a tough competitor for Chevron. Established in 1999, ExxonMobil is involved in oil and gas exploration, production, and sales, just like Chevron. These two companies often compete head-to-head for the same markets and resources;
- BP: British Petroleum, or BP, is another heavy hitter in the energy field. This company, established in 1909, also deals with oil and gas. They work worldwide and have a reputation for investing in alternative energy sources. BP is known for its eco-friendly initiatives, making it a strong competitor for Chevron;
- Royal Dutch Shell: Shell is another global player in the energy sector. They were founded in 1907 and have grown into one of the world’s largest companies. Shell deals in oil, gas, and renewable energy, offering stiff competition to Chevron in multiple areas;
- TotalEnergies: Based in France, TotalEnergies is a major energy company that’s been around since 1924. They are involved in everything from oil and gas to renewable energy. They are well-known for their research and development efforts, particularly in alternative energy;
- ConocoPhillips: This American energy corporation, established in 1917, is a direct competitor of Chevron in the exploration and production of oil and gas. ConocoPhillips focuses on finding and producing oil and gas globally, offering a significant challenge to Chevron.
Chevron SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Chevron:
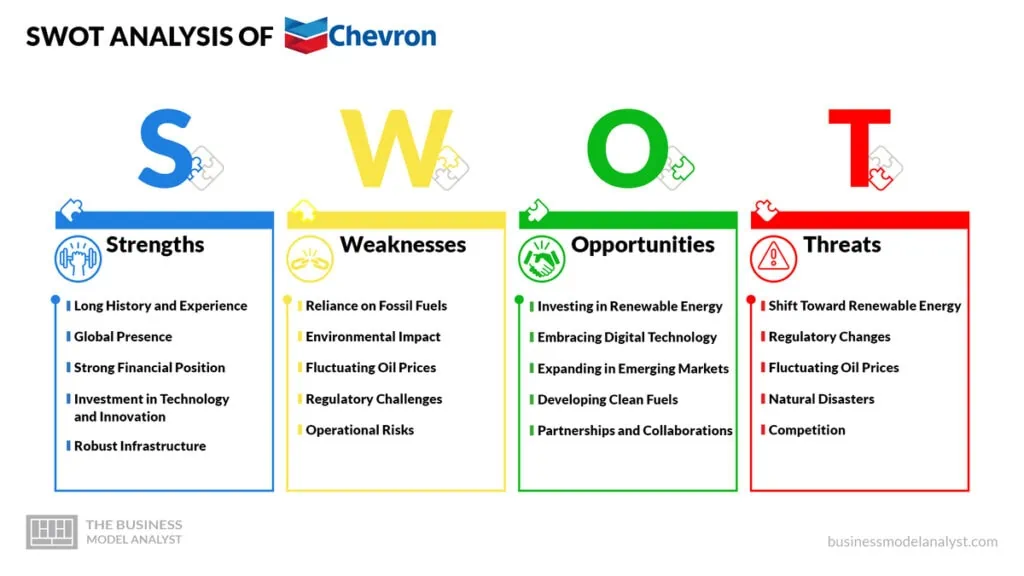
Chevron Strengths
- Long History and Experience: Chevron has been around for over a century, and that’s a lot of time to learn the ropes. Their experience in the oil and gas industry is one of their biggest strengths. They know the market well and have learned how to navigate its ups and downs;
- Global Presence: Chevron has operations in many parts of the world. This broad reach gives them access to numerous markets and diverse resources. It also means they can serve various customers, from big corporations to everyday consumers;
- Strong Financial Position: Chevron is one of the most prominent players in the energy sector. They’ve got a solid financial backbone that allows them to invest in new projects, research and development, and more. This financial strength also means they can weather more challenging times when they come along;
- Investment in Technology and Innovation: Chevron is not just about oil and gas. They’re also investing in new tech and innovation. This includes everything from improving their operations to exploring renewable energy. It shows they’re not stuck in the past, but are looking forward to the future;
- Robust Infrastructure: Chevron has an extensive infrastructure network, including pipelines, refineries, and more. This infrastructure allows them to transport and process their products efficiently. It also provides a competitive edge, as building such a network takes time, resources, and expertise.
Chevron Weaknesses
- Reliance on Fossil Fuels: Chevron’s core business is centered around oil and gas. But as more people are concerned about climate change, there’s a shift towards cleaner and renewable energy sources. Chevron’s heavy dependence on fossil fuels could be a big drawback in this changing energy landscape;
- Environmental Impact: The oil and gas industry is often linked to environmental damage, from oil spills to greenhouse gas emissions. Chevron has had its share of environmental issues in the past. These problems harm the planet and can damage Chevron’s reputation and lead to costly lawsuits;
- Fluctuating Oil Prices: Oil prices can go up and down significantly, affecting Chevron’s revenues. Chevron makes less money from oil sales when oil prices are low. This dependence on unpredictable oil prices is a significant weakness;
- Regulatory Challenges: Chevron, like other energy companies, faces a lot of regulations. These rules can change, especially with an increasing focus on climate change and environmental protection. Dealing with these changes can be challenging and costly for Chevron;
- Operational Risks: Chevron’s operations, which include drilling and transporting oil, come with risks. Accidents can happen, leading to human and environmental harm. These incidents can also disrupt Chevron’s business and lead to financial losses.
Chevron Opportunities
- Investing in Renewable Energy: The world is shifting to cleaner, more sustainable energy sources, and Chevron could grab this chance. By putting more money and effort into renewable energy like wind and solar power, Chevron could set itself up for the future and attract environmentally conscious consumers;
- Embracing Digital Technology: The energy sector is becoming more digital. New ways of finding and extracting oil and gas often rely on advanced technology. Chevron can use this technology to improve its operations, save money, and reduce its environmental impact;
- Expanding in Emerging Markets: As economies grow in Asia and Africa, so does energy demand. Chevron could see this as an opportunity to expand its business in these growing markets. This could bring in new customers and boost Chevron’s revenues;
- Developing Clean Fuels: Aside from renewables, there’s a lot of interest in cleaner fuels like hydrogen and biofuels. These fuels could be prominent in the future, especially for transport and heating. Chevron could get ahead of the game by investing in these clean fuels;
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Chevron could partner up with other companies or organizations. These partnerships could lead to new projects, shared knowledge, and innovation. It’s an excellent chance for Chevron to strengthen its position in the energy sector.
Chevron Threats
- Shift Toward Renewable Energy: The world is moving more and more toward renewable energy. While this is a good thing for the planet, it can be a threat to a company like Chevron that’s mainly focused on oil and gas. If they don’t adapt quickly enough, they could lose out;
- Regulatory Changes: Governments are getting stricter about pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. These regulations could mean higher costs and more challenges for an oil and gas company like Chevron. They could even lead to penalties if Chevron doesn’t meet the standards;
- Fluctuating Oil Prices: The price of oil can go up and down a lot. Many factors, such as political events, changes in supply and demand, and natural disasters, influence it. If oil prices drop, it can hurt Chevron’s profits;
- Natural Disasters: Natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods can affect Chevron’s operations. These events can damage Chevron’s equipment and facilities, disrupt their supply chains, and lead to costly repairs and delays;
- Competition: The energy market is very competitive. Chevron is up against other big oil and gas companies and companies in the renewable energy sector. Keeping up with these competitors can be a constant challenge.
Conclusion
Chevron’s steady and enduring commitment to fueling the world has made it a giant in the energy industry. Their broad range of activities, from digging up oil and gas to refining and selling them, has made them a key player in our daily lives.
Even as the world wrestles with climate change, Chevron’s role cannot be ignored. Their resources power our vehicles, generate electricity, heat our homes, and much more. Their widespread reach and consistent performance are testaments to their hard work.
Chevron’s challenge will be adapting to a world moving toward renewable energy. It’s a tall order, but their expertise and resources make them more than capable of rising to the occasion. They can remain a leading energy provider with a push toward more sustainable practices and investment in alternative energy sources.

