Since Satoshi Nakamoto published the article “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”, in 2008 (and released the open code one year later), blockchain technology seems to have gained life into businesses. More and more companies have started operating with blockchain in their business. There are successful examples of blockchain business models already in course, and innovation seems to evolve quicker and quicker. Before we move to blockchain business models, let’s take a look at the definition of blockchain itself.
Contents
What is blockchain?
Simply put, Blockchain is a series of immutable records of data, managed by groups of computers that don’t belong to any entity, company, or government. Each of these data blocks is secure and linked to each other using a cryptographic chain. Hence the name “block + chain”. The blockchain is, therefore, a fully automated and secure way of transmitting the information. A part of a transaction starts the process by creating a block. This block is verified by thousands, perhaps millions of computers distributed over the network. The verified block is added to a chain, stored on the network, creating an exclusive record with an also exclusive history. To falsify a single record, it would be necessary to falsify the entire chain in millions of instances. This is practically impossible. And all of this is completely free. Because the block is not regulated by anybody. This technology can replace all business processes and models that depend on charging one for any transaction between two parties. Blockchain is based on three pillars:
- Decentralization: as mentioned above, the data is stored inside the blockchain and shared by all of the networks. Nobody owns the records.
- Immutability: all the data is non-tamperable, through cryptography, ensuring cybersecurity.
- Transparency: the identity is hidden via complex cryptography and represented by their public address. So, although the person’s real identity is secure, all the transactions that were done by their public address can still be seen. This level of transparency has never existed before.
What is a Blockchain Business Model?
Well, in short, a business model describes a plan or strategy of a company to sell a product or service and earn profit from there. Each company will create their ways of handling business. However, there is a centralized model, composed of the owners or the shareholders, the organization, the customers, and the employees. A blockchain business model has all the three main characteristics of blockchain technology: it is decentralized, based on peer-to-peer transactions, within a trusted and reliable network.
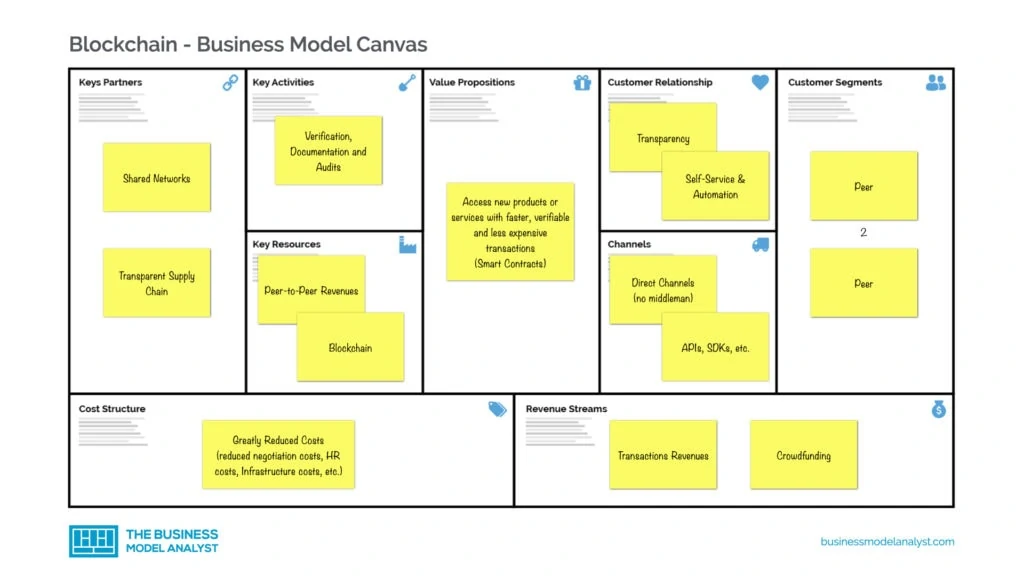
The blockchain nature alters the way a business operates in areas such as the flow of transactions, change of entities, profits, and ensuring that growth is maintained during the change. These business models eventually help improve businesses and benefit end-users.
Types of Blockchain Business models
P2P Blockchain Business Model
As said before, blockchain technology has always been peer to peer, allowing end-users to interact with each other. The profit may be made here via tokens, BaaS (Blockchain as a Service), transaction fees, and others. Filecoin and IPFS are popular examples that use this business model, by providing a platform for data storage and sharing.
Blockchain as a Service Business Model (BaaS)
Blockchain technology and ecosystem can be pretty intimidating for people in general. Nevertheless, this Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) business model permits the clients to outsource all the backend structure and focus only on the frontend.
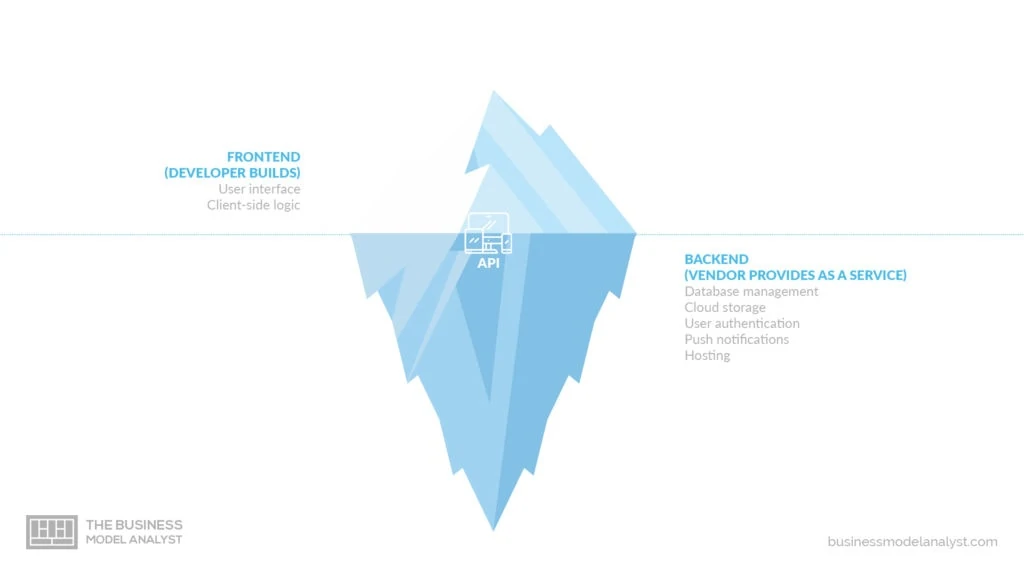
BaaS companies usually provide services such as user authentication, database management, remote updating, push notifications (for smartphone apps), cloud storage, and hosting. It is, therefore, one of the most popular blockchain business models, with famous operators such as Microsoft (Azure), Amazon (AWS), and IBM (BlueMix). The end-users, in this case, are not usually people, but other businesses and organizations. And they don’t have to worry about how blockchain works nor hardware infrastructure, thus allowing them to experiment, test, and conduct research.
Token Economy – Utility Token Business Model
The utility toke business model drives functionality into business via the use of tokens, which facilitate the network activities. Nowadays, there is plenty of startups, companies, and e-commerce websites that use the utility token business model. The token utility has three important properties: role, feature, and purpose.
Each role has its own set of features and purpose:
- Right: with a particular token, the holder gets a certain amount of rights within the ecosystem.
- Value Exchange: the tokens create an internal economic system that can help the buyers and sellers trade value within the ecosystem.
- Toll: it acts as a toll gateway to use specific functionalities of a particular system.
- Function: the token enables the holder to enrich the user experience inside a particular environment.
- Currency: it is a store of value that can be used to conduct transactions both inside and outside the given ecosystem.
- Earnings: it allows an equitable distribution of profits and benefits among investors in a particular project.
Blockchain-Based Software Products
There are blockchain companies that create solutions to be sold to bigger companies and organizations, as well as support after implementation. That usually works out fine, because the big companies don’t want to go through the process of selecting and hiring talent. It is much easier to buy a ready-made blockchain solution. Proving blockchain technology to organizations can be extremely profitable. The best example of this is the MediaChain blockchain being sold to Spotify.
Development Platforms
As blockchain technology and ecosystem is still recent, for it to grow, more developers are needed to enter the environment. Therefore, a lot of startups are creating decentralized applications (Dapps) on development platforms. To understand the relationship between development and the value of the network, we can refer to Metcalfe’s Law. According to this theory, the effect of a network is proportional to the square of the number of users connected to the system. In simple words, the more people involved, the more valuable the network is.
However, when it comes to purely business models, how can they bring value into the crypto space? There are three specific models:
- Network Fee: In this case, there is a network fee associated with the blockchain itself. They charge a small amount for the user for different activities on the network. For example, the Ethereum network charges gas fees for the use of the platform., NEO charges GAS tokens, Golem asks for golem tokens, and so on.
- Auditing: This model works in two ways: either the developers hire an auditing company to look over the smart contract for them or put up a bounty on their contract and several independent auditors and developers look up the code and search for flaws. That works out because Dapps deal with a lot of money, so it is imperative for their code to work correctly. Any little bug can lead to a large catastrophe.
- Other Services: As a blockchain business requires a lot of work, such as website, content, and frameworks, the startups may save money and time by hiring freelancers of agencies to deal with these services. It is a nice blockchain business model for talented professionals who want to use their skills to do business.
Concluding Thoughts
Just like any other business model, the blockchain ones can be a combination of ideas, and there is no hard rule on how each and every model should operate and function. At the end of the day, choosing the right one will just depend on the nature and objectives of the business.


Hi Daniel, I would be more interested to learn how blockchain can impact the Recruitment/Staffing Industry and what future business models may look like leveraging blockchain