The Vine business model was groundbreaking in the realm of digital media, having significantly altered the practices of both production and consumption. Twitter’s Vine was a video-sharing platform that allowed users to make and share looping 6-second clips. When it was first introduced in 2013, Vine quickly became an extremely popular social media app. On it, Viners could upload, share, and watch short videos. It grew into a major outlet for arts and entertainment until it was discontinued in late 2016.
Vine was a platform for sharing short, looping videos up to six seconds in length. It was founded in June 2012 by Dom Hofmann, Rus Yusupov, and Colin Kroll. In October 2012, Twitter reportedly spent $30 million to acquire the startup.
It was launched in January 2013 and immediately rose to prominence as a leading social networking software. The platform pioneered the distribution of user-made short films on social media. As of June 2013, Vine already had more than 13 million active users on iOS.
User engagement was the core of Vine’s business model. Users could like and comment on videos, as well as produce and post their own. Additionally, the platform enabled users to embed their films on other websites, which increased the platform’s exposure.
Following an adult content scandal, Vine released Vine Kids in January 2015 as a version of the app for children under the age of 13. Later, in the same year, Vine introduced Vine Music, a feature that lets users create and share music videos.
Close to its shutdown in October 2016, Vine started losing users to other services like YouTube and Instagram that had come to compete with its video platform offering. The application was officially shut down a few months later.
Contents
Who Owns Vine
Twitter still owns Vine after its acquisition in October 2012. Vine was developed by Colin Kroll, Dom Hofmann, and Rus Yusupov and released in January 2013. Prior to Twitter purchasing Vine, these three were its primary owners. Although Twitter officially discontinued the app in 2016, the company continues to own the name and website. After Twitter’s acquisition by Elon Musk, there have been talks about bringing back the platform.
Vine Mission Statement
Vine’s mission statement is “to create innovative, cost-effective cybersecurity solutions that make a measurable impact.”
How Did Vine Work?
Vine was a short-form video-sharing platform where users could create and share 6-second looping videos with their friends and followers. The videos could be shared across several social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, etc.
Vine’s For You channel was launched in 2015 and worked very much like TikTok’s For You page. Vine’s For You channel included a selection of Vine videos from its users, according to an individual user’s preferences. Its primary purpose was to facilitate the discovery of new content. However, its algorithm was not as optimized for user retention as TikTok’s.
How Vine Makes Money?
Before it was shut down, Vine was unable to generate revenue via advertisements or sponsored content. Vine put more effort into expanding its user base and creating new features. Twitter probably had intentions to monetize Vine via sponsored content or advertising. Still, these plans were never carried out, since the service failed to retain its user base when new competitors like Instagram arrived. While the platform had acquired as many as 200 million users in its first three years, it was shut down almost as quickly as it had gained them. Find out what happened to Vine.
Vine Business Model Canvas
The Vine Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
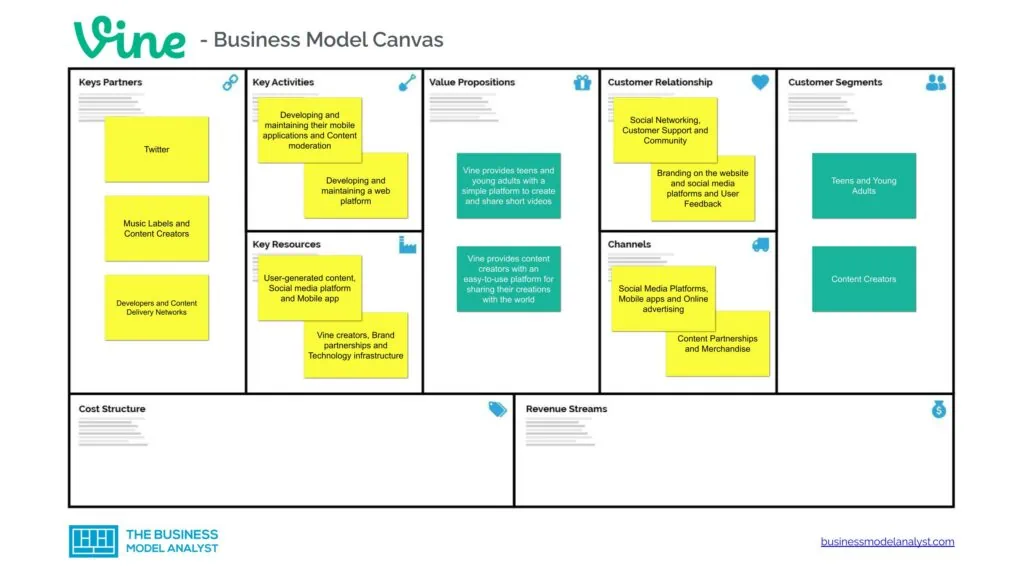
Vine Customer Segments
Vine customer segments consist of:
- Teens and Young Adults: Users in their teens and early 20s who short-form and engaging videos appealed to made up the majority of Vine’s user base;
- Content Creators: Content creators, including brands, used Vine to create and share videos with their followers, often to become famous and/or make money.
Vine Value Propositions
Vine value propositions consist of:
- Vine provides teens and young adults with a simple platform to create and share short videos. They had easy access to a broad range of content — comedy, music, DIY projects, etc. — and could easily interact with content creators, which gave them a sense of community;
- Vine provides content creators with an easy-to-use platform for sharing their creations with the world. By collaborating with businesses, content creators could easily monetize their videos and earn money from them. Vine offered brands a practical way to connect with a wide range of individuals, including teenagers and young adults, who were quite engaged on the platform.
Vine Channels
Vine channels consist of:
- Social Media Platforms
- Mobile apps
- Online advertising
- Content Partnerships
- Merchandise
Vine Customer Relationships
Vine customer relationships consist of:
- Social Networking
- Customer Support
- Community
- Branding on the website and social media platforms
- User Feedback
Vine Key Resources
Vine key resources consist of:
- User-generated content
- Social media platform
- Mobile app
- Vine creators
- Brand partnerships
- Technology infrastructure
- Human resources
Vine Key Activities
Vine key activities consist of:
- Developing and maintaining their mobile applications
- Content moderation
- Developing and maintaining a web platform
- Developing an API to facilitate integration with other platforms
- User Acquisition
- Managing relationships with content creators
- Analyzing user data
Vine Key Partners
Vine key partners consist of:
- Music Labels
- Content Creators
- Developers
- Content Delivery Networks
Vine Competitors
- Instagram: Seeing the success of Vine, Instagram added a new feature to their platform that allowed users to publish 15-second videos that could be shared with friends and followers;
- YouTube: Among the top visited websites today, YouTube has been around since 2005 and is one of the most popular video-sharing platforms. It allows users to upload videos of any length;
- Viddy: Viddy was a video-sharing website that debuted in 2012 and immediately established itself as a direct competitor to Vine. It was dubbed the Instagram of videos, since it allowed users to create, edit, and share 15-second videos. It was pulled from app stores in November 2014 and was officially canceled the following month;
- Keek: Keek was a video-sharing platform that launched in 2011, dubbed a “micro version of YouTube,” that let users share video status updates called keeks. It allowed users to upload 36-second videos and share them with their followers;
- Mobli: Mobli was a photo- and video-sharing platform that launched in 2010, but failed to garner a reliable user base as Vine had amassed. It allowed users to post short videos and photos, and share them with their friends and family. It was shut down in 2016 when the company declared bankruptcy;
- Socialcam: Socialcam was a mobile social video app launched in 2011. It lasted for four years before being shut down in October 2015. It allowed users to create and share videos online and across other social media platforms.
Vine SWOT Analysis
Let’s take a look at Vine SWOT Analysis:
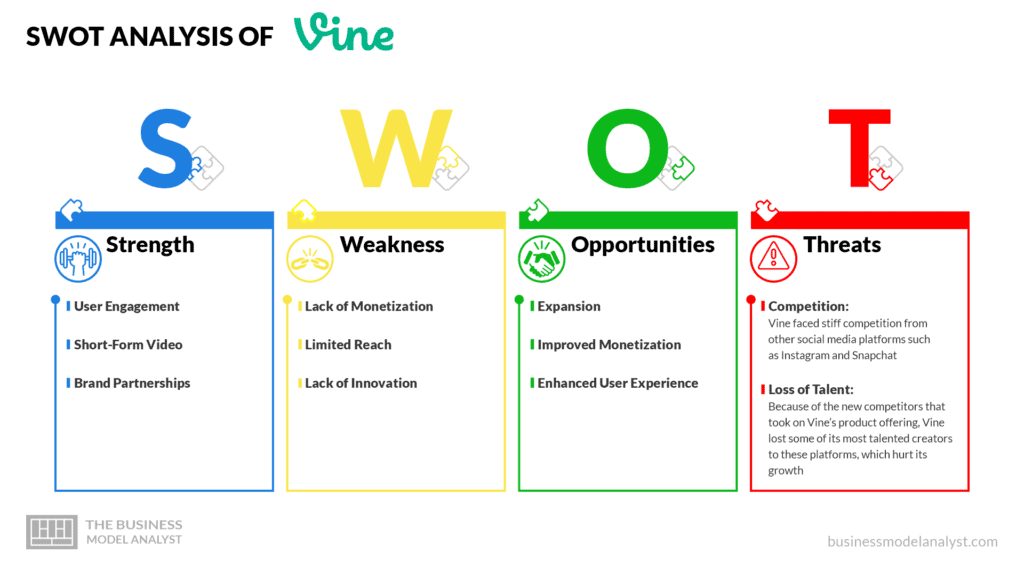
Vine Strengths
- User Engagement: Vine had a very engaged user base that was passionate about creating and sharing content;
- Short-Form Video: Vine was the first platform to popularize short-form video content, and it was successful in doing so;
- Brand Partnerships: Vine had a good relationship with brands and was able to create successful partnerships.
Vine Weaknesses
- Lack of Monetization: Although Vine had a large user base, it struggled to monetize its platform, which eventually led to its demise;
- Limited Reach: When compared to other social media platforms at the time, Vine had a limited reach, which hindered its growth;
- Lack of Innovation: Although Vine was innovative at launch, no new features were added. As other more popular social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram added more video features, Vine started losing its users to these platforms.
Vine Opportunities
- Expansion: Adding more features, such as live-streaming or podcasts, could have allowed Vine to grow its user base and/or retain previous users;
- Improved Monetization: Vine could have improved its monetization strategies to make the platform more profitable.
Sponsored content is one way Vine could have made money. Brands and companies could have paid Vine to feature their short-form video ads on the app. Vine missed out on a great opportunity to monetize its platform while also providing its users with more engaging content.
The addition of advertisements was another way Vine could have generated revenue from its audience. This could have been an excellent way for Vine to improve its platform as well as generate revenue.
- Enhanced User Experience: Making improvements and adding features such as video editing tools and filters might have allowed Vine to last longer than it.
Vine Threats
- Competition: Vine faced stiff competition from other social media platforms such as Instagram and Snapchat;
- Loss of Talent: Because of the new competitors that took on Vine’s product offering, Vine lost some of its most talented creators to these platforms, which hurt its growth.
Conclusion
The Vine business model was a very successful one for the purpose it served: building a loyal user base. With it, Vine was able to develop a strong brand by utilizing the platform’s reach and the strength of user-generated content. If new features had been added — and with a sustainable revenue model —, Vine might have become a significant player in the social media space. Today, Vine represents a lesson for startups and established businesses on the importance of continuously adding new features and engaging innovatively with competitors.

