Uber Eats is the food delivery service owned by Uber, the ride-share giant. According to Uber’s site, Uber Eats is their “food delivery platform that makes getting great food from your favorite local restaurants as easy as requesting a ride”. Just like its mother’s company, the Uber Eats Business Model is a multisided platform.
The purpose of Uber Eats, accessed mainly through its app available for iOS and Android, is to connect its users with a range of local restaurants, by displaying the food places’ menus on users’ smartphone screens, and delivering the chosen dish to their doors.
The whole service has been built off existing Uber technologies and has been quickly adopted in many cities, due to Uber’s well knows brand and driver network. Let’s check how everything works in the Uber Eats business model and how Uber Eats makes money!
Contents
Who Owns Uber Eats
Uber Eats, as presumable, is owned by Uber Technologies, Inc., and has Dara Khosrowshahi as the company’s CEO.
Uber Eats’ Mission Statement
“To make eating well effortless for everyone, everywhere”.
How Uber Eats makes money
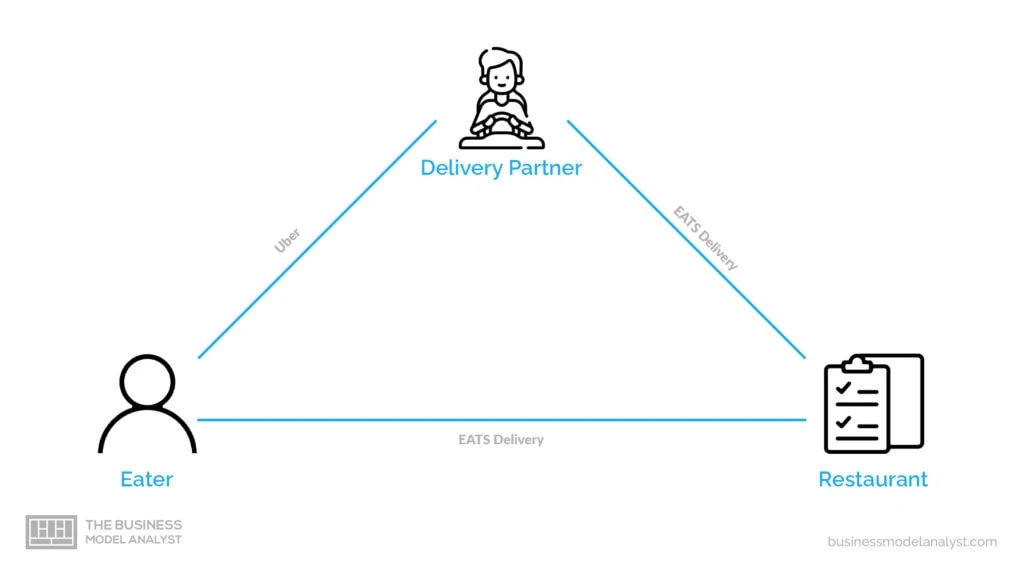
Uber Eats’ business model combines a multisided platform, aggregator, and on-demand business models. As stated previously, it involves three sides: end customers, delivery partners, and restaurant partners. Restaurants list their menus on the app, local customers check the menu and place an order, and an Uber driver/rider picks the order up from the restaurant and hands it to the customer. Uber Eats has four different revenue streams:
- Commission on orders: This is probably the main revenue stream, since Uber Eats usually earns a 30% commission from the restaurant partners, on the total cost of every order users make using its platform;
- Delivery fees: The delivery partner’s fee is divided into three parts: pickup fee, delivery fee, and distance fee (per mile). The sum of these fees will vary, according to locations, distances, and availability of drivers. And Uber Eats will take 25% of the total sum. Besides that, for orders cheaper than $12, Uber Eats will charge a $2 fee, which they call a “small orders fee”;
- Promotions: Some restaurants and food chains — such as McDonald’s — sign special contracts to offer exclusive promotions on the app, in order to get more sales. These brands will, therefore, pay special commissions and fees, according to negotiate the deal;
- Surge pricing: Uber Eats applies the same dynamic pricing algorithm that Uber does, on surge hours. This “busy fee” is calculated over demand, on the number of orders placed in the same area, at the same time, and the availability of delivery partners.
No surprise, Uber Eats already ties with Grubhub and grows to compete with DoorDash.
Uber Eats’ Business Model Canvas
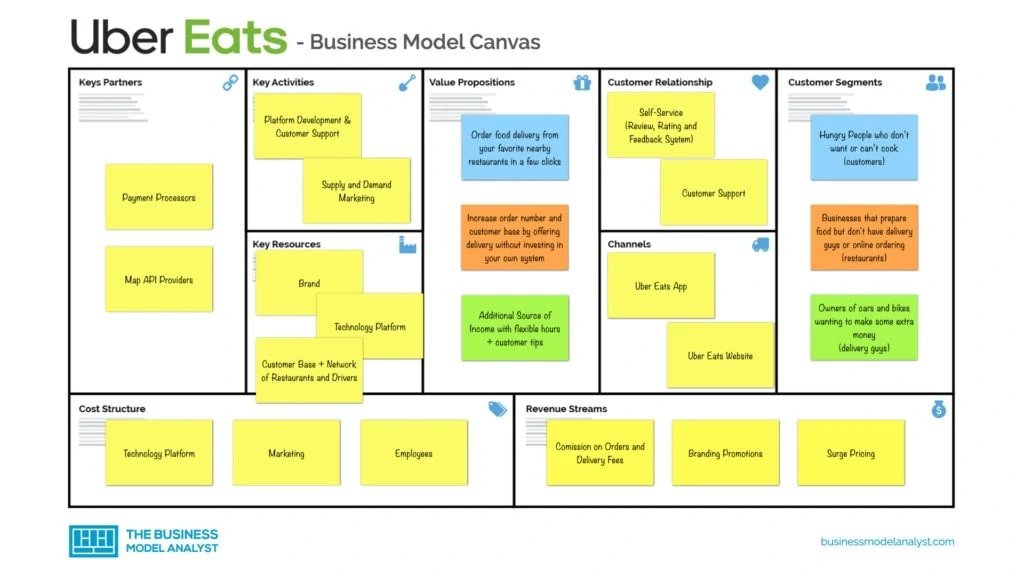
Uber Eats’ Customer Segments
The Uber Eats business model canvas is based on different transactions and customer segments: B2B between Uber Eats and restaurants, B2C between Uber Eats and end customers, and the one between Uber Eats and its delivery guys.
- The restaurants can choose the prices of the dishes they list on the app (and those can be different from the ones in their brick-and-mortar places), and they pay a commission to Uber Eats on each order;
- The end customers are the users that can create an account on the Uber Eats platform and order food from a great variety of local restaurants, just by having a device connected to the internet;
- The delivery guys are independent professionals, who pick up the orders at the restaurants and take them to the end customers. They receive information about the deliveries available, according to their location, and get paid for each service.
Uber Eats’ Value Propositions
There are different value propositions for each customer segment of Uber Eats:
- Restaurants: The restaurants can offer delivery and grow their customer base (and order numbers). Uber eats is a great marketing and advertising tool for restaurants that, by using it, don’t need to invest in a delivery team or system;
- End customers: A wide range of restaurants available within reach of a click, with updated menus and prices, information about the estimated timing, and the possibility of tracking the order. Besides, as the customer makes the order themselves, there is a smaller chance of mistakes than when they talked to a server by phone, who would take notes at the same time. Also, there are more payment options, so the user doesn’t need to have cash in hand, and can even pay through the app;
- Delivery guys: Just as with Uber, Uber Eats offer a way to increase income, and the couriers can choose where and when they will work, without having to go over complicated labor contracts with companies. In addition, the delivery guys can work by car, motorcycle, and even bicycle, depending on the location, which opens opportunities for many people to start a job.
Uber Eats’ Channels
The biggest channel for Uber Eats is its mobile app. Users can also use their website. The way Uber Eats has grown its customer base has been the same as Uber itself: Word of mouth and strong monetary incentives in the form of discounts and credit for future orders.
Uber Eats’ Customer Relationships
The Uber Eats customer relationship is mostly self-service, with customer support when needed. There are different types of relationships based on each customer segment, but in order to scale, most of it is automated.
Uber Eats’ Revenue Streams
Uber Eats has four different revenue streams, as explained before:
- Commission on orders
- Delivery fees
- Branding promotions
- Surge pricing
Uber Eats’ Key Resources
- The platform, that connects restaurants and customers;
- The algorithms, that calculate all the costs and timing;
- The brand, which is used in all cities where Uber Eats operates;
- Restaurant agreements, which provide a substantial part of the transaction.
Uber Eats’ Key Activities
Uber Eats has two key activities, particularly important: Developing and maintaining the platform and its algorithms, and providing marketing for restaurants and customers, by marketing and listing their partners’ menus. Besides that, they have to work on communication with delivery partners, customer service, marketing, and management, among others.
Uber Eats’ Key Partners
The most important key partners of Uber Eats are technology providers, such as GPS systems, payment systems, cloud storage, data analytics, and more. Some argue that restaurants and delivery guys are partners, but in my opinion, they are customer segments.
Uber Eats’ Cost Structure
The whole cost structure of Uber Eats is based on maintaining the platform, and marketing to acquire new customers and staff. In addition, there are legal costs, credit card fees, research & development, customer support, etc.
How to use Uber Eats?
- Browse: Open the app and do your search. You can search for a particular restaurant, dish, or cuisine. Then, you may scroll the chosen restaurant’s menu and, when you find what you want, you simply tap to add it to the order;
- Order: When you finish adding the dishes, you’ll check the address, price (including the delivery fee), and the estimated time for delivery. If you agree with everything, you just tap “Place order”;
- Track: Now that your order is done, you’ll be able to track the whole process, from the acceptance and preparation in the restaurant to the time the food gets to your door. You can also check the delivery person’s name and vehicle, and track their ride on the map;
- Rate: At the end of every delivery trip, you will have the opportunity to rate your experience with your delivery, both about the food/restaurant and the delivery person.
Uber Eats’ Competition and Market Share
The delivery app market is very competitive with big players that compete worldwide or in specific countries. Even with so many other delivery apps, Uber Eats manages to be the top downloaded app, using mostly delivery partners’ networks and well-known brands.
Although the number of app downloads is not necessarily market share, we can see below that it has a direct relation. Uber has been the fastest-growing food delivery company and is paving its way to becoming the biggest one in the next few years.
Uber Eats’ Competitors
- DoorDash: Founded in 2013 in San Francisco, California, DoorDash is an online food ordering and delivery platform. In December 2018, it took over Uber Eats’ position and placed second in the market, only behind GrubHub;
- GrubHub: This Chicago-based company was founded in 2004 and, as mentioned, it is the most succeeded food ordering and delivery platform in the market;
- Fooda: Another Chicago-based company, Fooda was founded in 2011 and works on placing restaurant promotional popups inside several establishments, such as cafeterias, office building lobbies, and lunchrooms on a daily basis;
- Deliveroo: Founded in London, UK, in 2013, Deliveroo operates its food ordering and delivery in a massive way throughout Europe, Australia, South Asia, and Middle-East, focusing especially on dark kitchens;
- Postmates: Founded in 2011 in San Francisco, California, Postmates was focused on local delivery of restaurant-prepared meals. After its acquisition by Uber in 2020, it operated only until May 2021, before being merged with its sister company Uber Eats.
Uber Eats’ SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Uber:
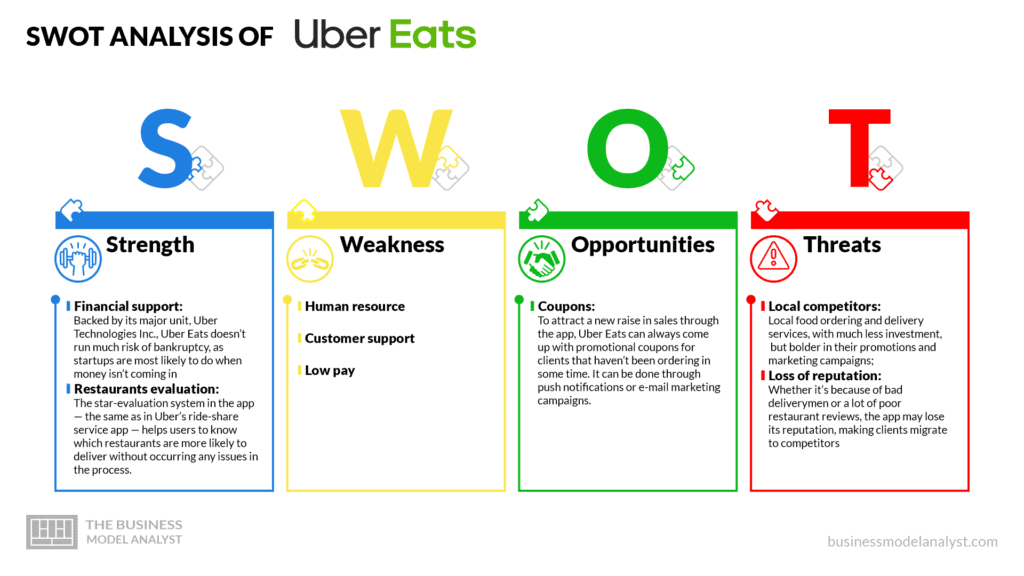
Uber Eats’ Strengths
- Financial support: Backed by its major unit, Uber Technologies Inc., Uber Eats doesn’t run much risk of bankruptcy, as startups are most likely to do when money isn’t coming in;
- Restaurants evaluation: The star-evaluation system in the app — the same as in Uber’s ride-share service app — helps users to know which restaurants are more likely to deliver without occurring any issues in the process.
Uber Eats’ Weaknesses
- Human resource: As it is a human-dependent service, Uber Eats is vulnerable to bad, inattentive, and/or reckless deliverymen, which may result in poorly rated deliveries;
- Customer support: Although the spent money on flawed deliveries is usually refunded to the client — most of the time, naturally, depending on the situation —, customer support in the app could be improved. Often, clients complain about the response time of Uber Eats’ customer support team;
- Low pay: The same issue as Uber’s ride-share service app, deliverymen working for Uber Eats often complain about the high percentage of the fee that Uber receives from each delivery separately.
Uber Eats’ Opportunities
- Coupons: To attract a new raise in sales through the app, Uber Eats can always come up with promotional coupons for clients that haven’t been ordering in some time. It can be done through push notifications or e-mail marketing campaigns.
Uber Eats’ Threats
- Local competitors: Local food ordering and delivery services, with much less investment, but bolder in their promotions and marketing campaigns;
- Loss of reputation: Whether it’s because of bad deliverymen or a lot of poor restaurant reviews, the app may lose its reputation, making clients migrate to competitors
Conclusion
As mentioned above, Uber Eats already has a significant market share and kept growing over the past years. With the Covid-19 pandemic of 2020, the food delivery service has excelled to grow even further, as people stayed home all over the world and ordered meals to have at home, not just at the dinner time, but also for the lunch break. Now, in the post-vaccine period, the company needs to maintain its high rhythm, backed up by Uber, to catch a bigger slide in the food delivery market.

