Turo is a peer-to-peer (P2P) car-sharing service based in San Francisco, California, which allows users to temporarily rent out their cars to other members for a rental fee. Let’s take a look at the Turo business model as well as how the company makes money.
Contents
A brief history of Turo
Turo started in 2010 as RelayRides and was the brainchild of Harvard Business School student Shelby Clark, along with assistance from her classmates Nabeel Al-Kady and Tara Reeves. Envisioning itself as the “Airbnb for cars”, it allowed users to rent out their vehicles to other members on the platform for a short period. After several rounds of funding from prominent venture capitalists like Shasta Ventures, Canaan Partners, Google Ventures, August Capital, and Trinity Ventures, the platform relaunched in 2015 as Turo.
This rebranding was said to represent their commitment to a shift from short-term car-sharing services to more long-term arrangements. In 2017 the company expanded its services to include several provinces within Canada. As of 2021, Turo had over 14 million users and 450,000 vehicles in over 56 countries worldwide.
Who Owns Turo
Currently, the platform is owned by InterActiveCorp (IAC), which owns the largest shares in the company. However, there are plans to introduce the company as a publicly traded firm in 2022 which means the company will then be owned by the public shareholders who own its stock.
Turo’s Mission Statement
Turk’s mission statement is “to reinvent the car rental experience and put the world’s one billion cars to better use”.
How Turo makes money
Let’s take a look at how Turo makes money.
Commission from Rental Fees
Turo is a significant part of the sharing and tourism community and allows vehicle owners (referred to as hosts by the platform) to rent out their automobiles to interested renters for a fixed period using their platform. In return for this service (as well as covering the cost of insurance, background checks, and GPS tracking) the company takes a percentage of the estimated cost of the trip. This may range anywhere from 15 to 45 percent but is usually 25 percent.
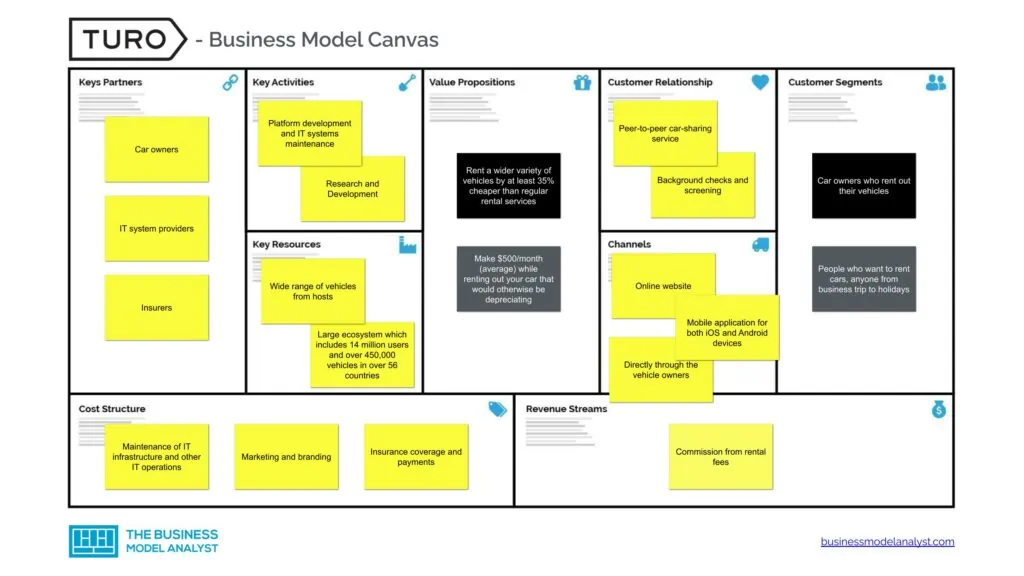
Turo’s Business Model Canvas
Turo Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
Turo’s Customer Segments
Turo customer segments consist of:
- Hosts: Car owners who rent out their vehicles are referred to as hosts. Turo allows them to put their vehicle to good use by helping them generate revenue by renting out the vehicle;
- Renters: This may include anyone from those on business trips to holiday travelers to people who require vehicles for specific purposes, such as moving vans. This offers them a greater deal of convenience, safety, and variety to choose from, as well as being cheaper than traditional rental services.
Turo’s Value Propositions
Turo value propositions consist of:
- The platform asserts that its services are up to 35% cheaper than regular rental services;
- Turo also offers renters a wider variety of vehicles. This is because they have a wide range of less conventional vehicles under their service such as trucks, moving vans, sports cars, and so on;
- Using Turo offers both hosts and renters a greater degree of convenience since they can choose the vehicle of their choice online, agree on the price, period, and mileage and then pick up the vehicle at an agreed location;
- The platform offers hosts greater control over their vehicles, as well as how they are used. It also allows the hosts to advertise their vehicles for a fee;
- Turo provides insurance coverage to both hosts and renters for claims up to $750,000.
Turo’s Channels
Turo channels consist of:
- Online website
- Mobile application for both iOS and Android devices
- Directly through the vehicle owners
- Social media
- Customer support
- Advertising
Turo’s Customer Relationships
Turo customer relationships consist of:
- Peer-to-peer car-sharing service;
- Background checks and screening;
- Allowing renters to negotiate and pay for the right to temporarily utilize a host’s vehicle, as well as facilitating the collection of the vehicle.
Turo’s Revenue Streams
Turo revenue streams consist of:
- Commission from rental fees
Turo’s Key Resources
Turo key resources consist of:
- Wide range of vehicles from hosts
- Large ecosystem which includes 14 million users and over 450,000 vehicles in over 56 countries
- IT staff
- Brand image, as a pioneer in the sharing and tourism industry
- Strong investor support
Turo’s Key Activities
Turo key activities consist of:
- Platform development and IT systems maintenance
- Research and Development
- Marketing and advertising
- Legal services
- Customer support
Turo’s Key Partners
Turo key partners consist of:
- Car owners
- IT support staff
- Various investor
- Insurance partners
Turo’s Cost Structure
Turo cost structure consists of:
- Maintenance of IT infrastructure and other IT operations
- Marketing and branding
- Insurance coverage and payments
- Research and Development
- Administrative expenses
- Operating costs (rent, utilities, wages, legal fees, etc.)
Turo’s Competitors
- Uber Rentals: Uber Rentals is the car-sharing service offered by the ride-hailing company Uber. The service debuted in 2019 and does not operate a P2P system but rather works as third-party connecting users to other rental services;
- Getaround: Getaround is an American car-sharing company that operates a peer-to-peer car-sharing service that is quite similar to Turo. It was founded in 2009 and is seen by many as Turo’s closest competitor;
- Zipcar: Zipcar is a car rental service that was launched in 2000 and allows users to choose from the fleet of over 12,000 cars that the company maintains;
- The Hertz Corporation: The Hertz Corporation is one of the oldest and largest car rental services in the world. They offer over 12,000 vehicles and operate as a traditional rental service where customers are allowed access to the vehicles for a fee.
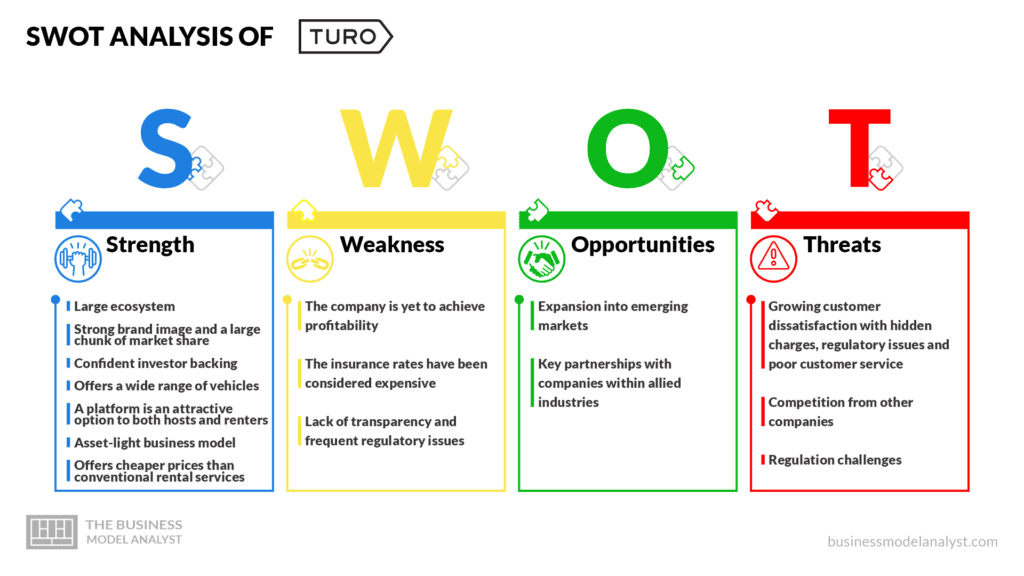
Turo’s SWOT Analysis
Let’s take a look at the swot analysis of Turo.
Turo’s Strengths
- Large ecosystem;
- Strong brand image and a large chunk of market share;
- Confident investor backing;
- Offers a wide range of vehicles;
- A platform is an attractive option to both hosts and renters;
- Asset-light business model;
- Offers cheaper prices than conventional rental services.
Turo’s Weaknesses
- The company is yet to achieve profitability;
- The insurance rates have been considered expensive;
- Lack of transparency and frequent regulatory issues.
Turo Opportunities
- Expansion into emerging markets;
- Key partnerships with companies within allied industries.
Turo’s Threats
- Growing customer dissatisfaction with hidden charges, regulatory issues and poor customer service;
- Competition from other companies;
- Regulation challenges.
Conclusion
Turo is a pioneer in the emerging Car sharing ecosystem. Even though the company has not achieved profitability and proven itself as a viable business model, its large market share, dedicated following and widely innovative business model are all strong indicators that you may prove to be one of the most influential car-sharing tech companies for the last few decades.

