Toyota is one of the leading automakers in the world, and its strong brand recognition has assured a significant share of the worldwide market. Such a global position has made it a sustainable long-term business model. Let’s take a look at the Toyota business model.
Contents
A brief history of Toyota
The history of Toyota began in the 1920s, as a loom manufacturer founded by Sakichi Toyoda. In little time, Toyoda developed and sold the patent for an automated loom and, after that, decided to enter the automobile industry. The first vehicles were made in the early 1930s, but Toyota Motor Company would be established only in 1937.
The company started by manufacturing compact cars and, later, expanded to other types, such as pickups, SUVs, trucks, and sports cars. Nowadays, Toyota is one of the largest car manufacturers in the world, with more than 10 million vehicles sold annually. The multinational company is headquartered in Japan, but it has operations in 27 countries and sells to more than 170 countries in the world.
Who Owns Toyota
Toyota is a part of Toyota Motor Corporation, which has Takeshi Uchiyamada as the Chairman and Akio Toyoda as the President. Among many subsidiaries, the company has the following divisions: Lexus, Ranz, Scion (which had its activities suspended in February 2016), and Toyota itself.
Toyota’s Mission Statement
Toyota’s mission statement is “To attract and attain customers with high-valued products and services and the most satisfying ownership experience“.
How Toyota makes money
It is true that 90% of Toyota’s revenue comes from automotive sales, but the company also generates revenue from other operations, such as financial services, investments, and machinery.
- Toyota’s Automotive Business: Most of Toyota’s automobile sales take place in Japan and North America. Its strongest and most profitable brand is Lexus, with more than 10 million sales all over the world;
- Toyota’s Financial Services Business: Its financial services division grows faster, but it still represents only around 6% of Toyota’s business model’s revenue. It focuses on automotive sales financing, credit cards, and others, operating in 30 countries (about 90% of Toyota Motor Corporation markets);
- Toyota’s other business: Toyota holds stakes in other automotive manufacturers, such as Subaru, Isuzu, and Mazda. It also has interests in biotechnology, robotics, aerospace, etc. Lately, the company has been particularly oriented towards developing hybrid electric vehicles and related technology.
Toyota’s Business Model’s Performance
Quality
Toyota invests in development, design, production, and after-sales in order to maintain top quality. That has put the brand among the top automotive ones in terms of reliability, quality, and durability.
Speed and dependability
Toyota has managed to reorganize its production flow, by focusing on simplicity, thus increasing the speed of delivery. Now, the company has a just-in-time production system, with a controlled cost structure.
Suppliers
Toyota aims at building a strong foundation at all stages of the supply chain, from development to after-sales. In order to reach that, the company has built close and trustworthy relationships with most of its suppliers, by minimizing the number of suppliers, thus creating a long-term partnership and, this way, achieving cooperation, cost reduction, and quick response to fluctuations and innovations.
Wide range and cost
Toyota’s business model is not based on just one car, instead, it provides a wide range of products to the customers, since the company produces different models for different markets, in a well-established flexible production system. Besides, Toyota has managed to manufacture high-quality vehicles at reasonable prices. The company has tested and implemented several initiatives to reduce its operating costs and focused on local production capacities to meet the customers’ demands.
Toyota’s Business Model Canvas
Let’s take a look at the Toyota Business Model Canvas below:
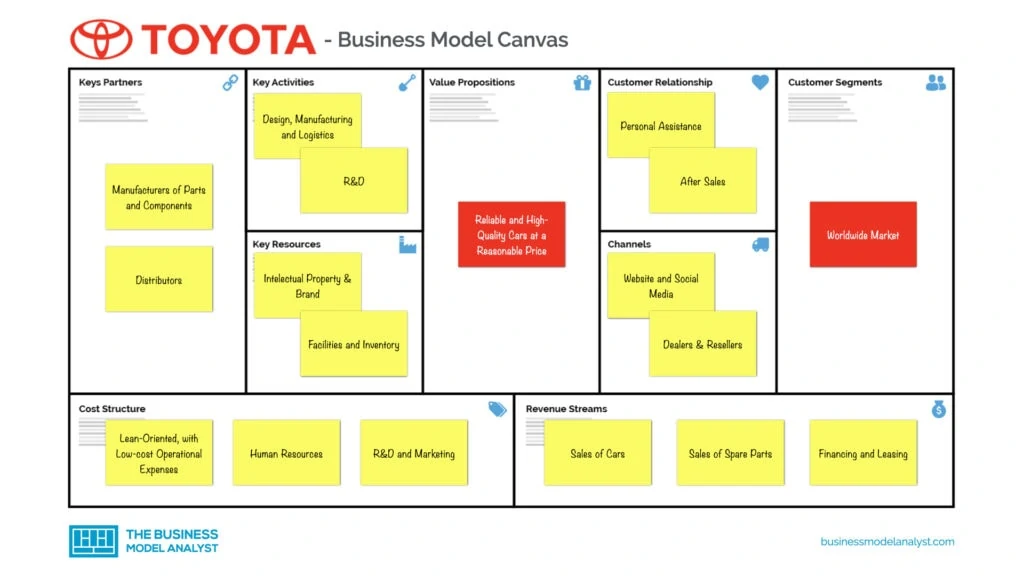
Toyota’s Customer Segments
Toyota’s customer segments consist of:
- General worldwide public
- Freight companies
Toyota’s Value Propositions
Regarding Toyota’s value propositions, it can be described as reliable and high-quality cars at a reasonable price.
Toyota’s Channels
Toyota’s channels consist of:
- Dealers
- Resellers
- Service Centers
- Branches
- Showrooms
- Website
- Social media
Toyota’s Customer Relationships
Toyota’s customer relationships consist of:
- Reputation
- Quality
- Footprint
- Delivery time
- Personal assistance
- After-sales
Toyota’s Revenue Streams
Toyota’s revenue streams consist of:
- Sales of products (automobiles, commercial vehicles, and engines)
- Sales of spare parts
- Services of banking
- Financing, leasing
- Commissions
- Sales from non-automotive businesses
Toyota’s Key Resources
Toyota’s key resources consist of:
- Human resources
- Intellectual property
- Partners
- Facilities
- Brand
- Inventory
Toyota’s Key Activities
Toyota’s key activities consist of:
- Manufacturing
- Engineering
- Design
- Assembling
- Supply chain
- R&D
- Logistics
Toyota’s Key Partners
Toyota’s key partners consist of:
- Manufacturers of parts and components
- Suppliers
- Dealers
- Distributors
Toyota’s Cost Structure
Toyota’s cost structure can be described as lean-oriented, with low-cost operational expenses, which include:
- Manufacturing facilities and operations
- Raw materials and components
- Distribution and logistics
- Staff compensation
- Investments in technology and R&D
- Maintenance
- Marketing and advertising
Toyota’s Competitors
- Ford: Founded in 1903 by Henry Ford, Ford Motor Company is a multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Michigan. With an impressive number of 4.2 million sold units in 2020, it has a revenue of around US$ 136.3 billion;
- Chevrolet: The automobile division of the manufacturer General Motors (GM) was founded in 1911, in Michigan, just like its rival Ford. Chevrolet had around 2.4 million vehicles sold worldwide in 2021;
- Nissan: It is a Japanese multinational automobile manufacturer, based in Yokohama, Japan, and accounts for an impressive number of 4.75 million sold units in 2020, with revenue of around US$ 90.8 billion;
- Honda: Another Japanese multinational automobile manufacturer, Honda is headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, and it is also responsible for designing, manufacturing, and selling motorcycles and power equipment;
- Mercedes-Benz: Headquartered in Stuttgart, Germany, Mercedes-Benz is a luxury and commercial vehicle automotive manufacturer founded in 1926. Although it competes in the luxury segment, Mercedes was has sold over 2.1 million units globally in 2020, making it the largest brand of premium vehicles in the world;
- BMW: Another German luxury and commercial vehicle automotive manufacturer, BMW is headquartered in Munich, Germany, and it is also responsible for designing, manufacturing, and selling motorcycles, which — same as its vehicles — compete in the luxury sector of the market;
- Tesla: Last but not least, Elon Musk’s automotive and clean energy company aims exclusively at electric vehicles — but not just that. It also works with battery energy storage, solar panels, solar roof tiles, and related services. As far as it concerns Toyota, Tesla sold over 930,400 vehicles in the year 2021, and over 295,300 units of Tesla’s Model 3 and Model Y were sold in the first quarter of 2022, according to Tesla itself.
Toyota’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Toyota:
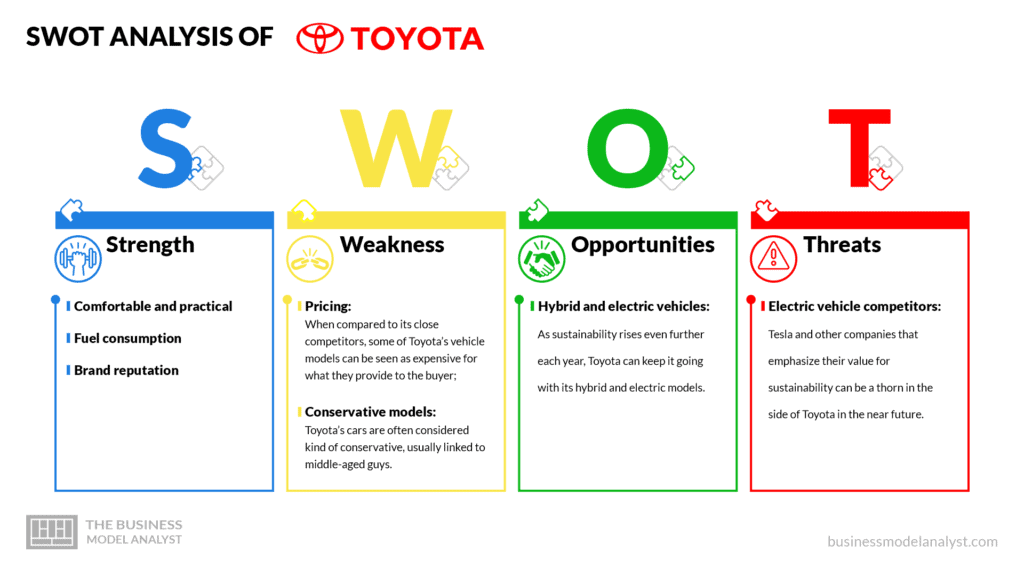
Toyota’s Strengths
- Comfortable and practical: Most of Toyota’s cars are well-equipped, with a spacious trunk and yet greatly comfortable, practical, and with technological interior space;
- Fuel consumption: Toyota’s vehicles usually present very relatively efficient results in terms of fuel consumption;
- Brand reputation: Toyota’s brand is a strong one worldwide.
Toyota’s Weaknesses
- Pricing: When compared to its close competitors, some of Toyota’s vehicle models can be seen as expensive for what they provide to the buyer;
- Conservative models: Toyota’s cars are often considered kind of conservative, usually linked to middle-aged guys.
Toyota’s Opportunities
- Hybrid and electric vehicles: As sustainability rises even further each year, Toyota can keep it going with its hybrid and electric models.
Toyota’s Threats
- Electric vehicle competitors: Tesla and other companies that emphasize their value for sustainability can be a thorn in the side of Toyota in the near future.
-> Read More About Toyota’s SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
Toyota has always followed its “Five Main Principles” since its foundation. They have been revised and, nowadays, the company has a set of values and guidelines that actually guide all of its decisions and operations. Besides, according to its Corporate Governance Report from 2019, Toyota has been focusing on innovative technology, especially in robotics and artificial intelligence, in order to follow any tendencies and to create new mobility services. Moreover, the company has been a leader in environmentally friendly vehicle technologies and has set a goal of killing off carbon dioxide emissions from its automobiles by the year 2050.
As to the challenges Toyota may face, its biggest one should probably remain competition from many well-established brands around the world, particularly because the company competes in all classes of vehicles, all over the globe. That’s why the company is always investing in innovation and in developing new products and tools, in order to keep adapting and anticipating how the automotive industry might change, react accordingly, and avoid losses.

