The Tesla business model operates as a Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) business model as it sells directly, cutting out middlemen such as dealerships and offering its own charging station network. Which of these names do you recognize more easily: Tesla or Elon Musk? While, in general, we identify the author by the work — that is, it would be normal for you to know Elon Musk as the CEO of Tesla —, in the case of this visionary eccentric, in particular, it is quite common for the opposite to happen: Tesla being Elon Musk’s company.
But, anyway, in addition to its charismatic and incomparable leader, Tesla is also characterized by being a company that is basically divided into three business models: an auto-maker, a hardware supplier, and a tech company. We will know, then, how everything works in this hybrid business model, which has faced great challenges in the market. Follow up!
Contents
A brief history of Tesla
Tesla, Inc. is an American company, founded in 2003 by two engineers, Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, originally as Tesla Motors. Fourteen years later, the company would change its nomenclature, because it started to incorporate supply lifestyle products in its production.
Tesla’s first product was launched in 2008 — the Tesla Roadster, the high-performance electric sports car, whose sales ended four years later, in 2012. Instead of launching a cheaper first car, to gain in quantity, the Roadster was a luxury item. Musk, the company’s CEO, explained that, with all the technology they intended to put in the car, it would be impossible for it to reach the market at a low price. For this very reason, they chose to launch a product, above all, compelling.
In the following years, Tesla invested heavily in marketing, research, and development, prioritizing studies in safe, autopilot, and charging cars. In 2018, Tesla was already the largest seller of electric cars in the world, with more than 250,000 units sold, taking up 12% of that market.
Who Owns Tesla
As mentioned a few times, Tesla is owned by the eccentric billionaire Elon Musk. Although founded by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning back in July 2003, Elon Musk has been the CEO and chairman of the company since 2008.
Tesla’s Mission Statement
Tesla’s mission is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
Tesla’s Differentials
Currently, Tesla’s business model is based on three foundations: selling model, servicing, and charging network.
First of all, unlike other automakers that have their cars sold by dealerships worldwide, Tesla focuses on direct sales. This means that all Tesla stores are an arm of the company itself and that anyone who is served in that space will, in fact, be received by an employee of the manufacturer itself.
This allows Tesla to improve its product through direct and fast contact with the customer and guarantees them differentiated service facilities, which include the possibility of customizing a vehicle via the internet. In addition, the company has service centers in all places where it sells its cars, with personalized service, including Tesla Rangers, technicians that the company sends to people’s homes for service.
These centers also have a charging service. But, more than that, Tesla also has an extensive network of Supercharges stations, where cars can be fully recharged in up to 30 minutes — at no cost. Of course, in addition to these three factors, there is still a difference between the company’s own products. Tesla has the fastest and longest-range electric cars on the market, with unique design and brand identity.
Finally, there is still the entire research and development process promoted by the company. Tesla invests heavily in hardware and software, focusing on digital technology and even autonomous driving cars. And yet, it increasingly seeks to reduce CO2 emissions, through investment in sustainable energy, which guarantees the support of the government.
How Tesla makes money
Certainly, its most important revenue stream was and remains the sale of electric cars, representing more than 80% of its revenue, which is estimated at more than 20 billion dollars. The other 20% of income includes automotive services and vehicle leasing, but also sales of solar energy systems and storage products (about $1.5 billion).
Tesla’s Business Model Canvas
You can look at the Tesla Business Model designed in the Business Model Canvas below:
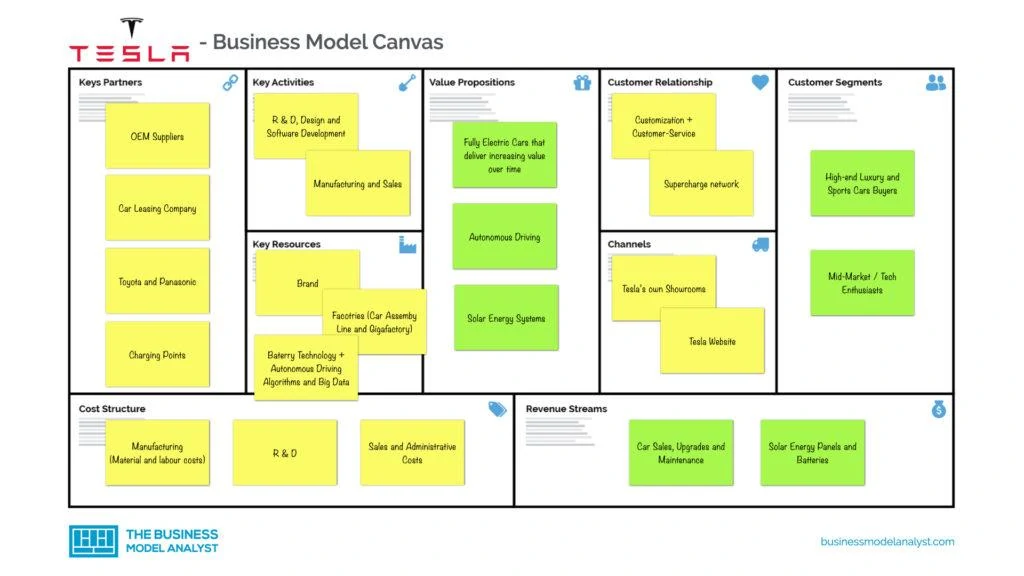
Tesla’s Customer Segments
Tesla has developed vehicles for every type of customer. From the mid-market range, with affordable pricing, to the high-end luxury and sports cars, competing with Porsche or Ferrari. In addition, Tesla is also covering the commercial vehicle sector, providing a greener option for transportation and shipping. And, of course, it’s worth remembering that Tesla’s customer segments include fast, eco-friendly car enthusiasts, with autopilot — and, surely, Elon Musk followers.
Tesla’s Value Propositions
Regarding automobiles, Tesla’s value proposition includes a greener solution that adds high performance, design, functionality, efficiency, long-range, flexible, and low-cost (or free) recharging. Aside from its own vehicles, it is worth remembering that Tesla sells home batteries and solar panels to residential and commercial customers, providing convenience when it comes to power. In addition, Tesla still sells systems and components to other auto manufacturers, as well as financial services, with loans and leases.
Tesla’s Channels
The channels that Tesla uses to reach its audience, as seen throughout this article, are its own stores, its website (self-service online store), conferences, and sales events. As stated above, the company doesn’t spend a lot on advertising. It believes in the power of its own brand and reputation, in addition to the charm produced by the CEO, Elon Musk.
Tesla’s Customer Relationships
One of Tesla’s foundations is the customer relationship, because, from the beginning, the company has focused its efforts on the customer experience. That is why the company chose, as mentioned above, to implement company-owned stores instead of dealerships, in a direct-to-customer sales model. Besides, customers can choose, order and customize their car directly via the website. In addition, Tesla is also increasingly investing in its charging network, to charge Tesla vehicles more quickly, at low or no cost. Finally, Tesla has built a very positive brand and reputation with the public, always being associated with luxury, technological and innovative vehicles, and taking into account the environmental impact.
Tesla’s Revenue Streams
- Solar energy panels and batteries;
- Car sales, upgrades, and maintenance.
Tesla’s Key Resources
Tesla’s key resources are those that allow it to fulfill its key activities in order to deliver its value proposition. Therefore, we can highlight its cutting-edge technology and engineering, its long-life battery systems, its design, and its software.
Tesla’s Key Activities
Tesla’s key activities include:
- Manufacturing Cars: Yes, Tesla’s main activity is still delivering the product it promises — electric cars. For this, it also needs to invest in the production of batteries and, still, solar energy panels;
- R&D: The company is always looking for innovative, advanced, and eco-friendly technology;
- Design: One of the differentials of the products — Elon Musk made it clear from the outset that, as its technology would prove to be costly anyway, Tesla would invest in design and not fight for price;
- Building & Maintenance: Tesla is spreading recharge stations around the world so that more people can purchase electric cars;
- Software Development: Tesla applies agile principles to develop and enhance its software;
- Sales & Marketing: The company doesn’t invest much in advertising. On the other hand, its entire operation focuses on the customer experience.
Tesla’s Key Partners
- Suppliers: Tesla manufactures the entire base of its cars, but there are some parts that are purchased from third parties. Therefore, Tesla’s biggest key partners are suppliers that allow the company to deliver its cars, such as windshield and brake manufacturers, just to name a few;
- Alliances: Tesla entered into an alliance with Toyota for both to develop, together, parts and systems for electric vehicles, improving this market share. Tesla and Panasonic are also together in the construction of a manufacturing plant in New York, for the development of large-scale battery and solar cells;
- Government: Due to its focus on the development of eco-friendly vehicles and energies, associated with the number of jobs the company has been creating in the U.S., Tesla receives tax incentives from the U.S. federal government;
- Charging points: Some Tesla partners include hotels, resorts, restaurants, and shopping centers, in which the company establishes its fast car recharging spaces.
Tesla’s Cost Structure
Tesla has a very broad cost structure, like any manufacturer, which includes:
- Manufacturing;
- Sales;
- Administrative costs;
- Research and Development.
Tesla’s Competitors
- Nio: Founded in 2014, the Chinese Nio manufactures premium electric vehicles for the international market. Its sales have been growing more than 100% per year, but it has fewer than 200 battery stations in China, with plenty of room to grow;
- Ford: This traditional auto company has entered the electric-powered market. Its sales of electric cars have been growing by over 70% per year, and most of the buyers are new to Ford. As one of the oldest automakers in the world, the company has a great experience advantage;
- Volkswagen: The German company launched its first electric vehicles one decade after Tesla. Nevertheless, it predicts that 50% of its sales in the U.S. will be EVs, and it is aiming to manufacture 1.5 million of those by 2025. Just like Ford, it has the strength of an old and traditional brand;
- Li Auto: One of the newest competitors, founded in 2015, this Chinese company has surprised the audience with its technology. It is growing fast and sold over 10k EVs in its first year in China;
- Nikola Corp: The company combines electric battery power with hydrogen fuel cells in its vehicles. But its focus will be on big vehicles, with electric and hydrogen fuel-powered trucks. Founded in 2014 in America, Nikola’s vehicles had zero emissions from 2016 to 2020;
- Workhorse Group: Based in the U.S., this company focuses on electric vans for delivery services. It has already fulfilled a UPS order for 950 vans. The company was founded in 1998, but the offer for EVs only began in 2015;
- Canoo Holdings: It is the latest entrant, with a different business model. Canoo’s vehicles will get on the roads in 2022, with a unique value proposition — drivers will pay a monthly subscription instead of buying or leasing the cars.
Tesla’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT Analysis of Tesla:
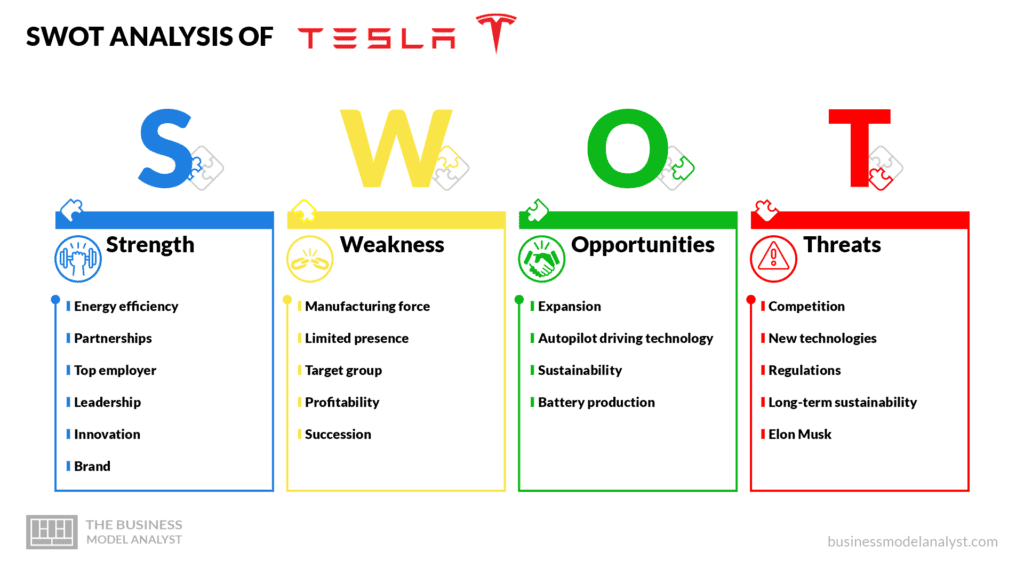
Tesla’s Strengths
- Energy efficiency: Tesla is the market leader not only in numbers of sales, but also in the use of renewable energy sources like solar power;
- Partnerships: Tesla is collaborating with giant energy companies, which help to expand its renewable energy efforts;
- Top employer: The company has been featured in Forbes as one of the best employers in 2019, and it is known as a great place for young employees due to its diversified business culture;
- Leadership: As a result of its extraordinary growth and its leadership in EV sales, Tesla became the most valuable automotive company in 2020;
- Innovation: Tesla invests heavily in research and development in order to build new technologies and deliver top-class design and comfort, thus increasing its popularity among its customers;
- Brand: When Tesla was founded to build electric cars, it did not have any competition, thus becoming the top of mind when it comes to EVs. Besides, the market trusts the company to develop clean energy as well as profitable products.
Tesla’s Weaknesses
- Manufacturing force: When compared to other automobile companies, Tesla has a smaller structure for manufacturing, resulting in limited production and delays in distribution;
- Limited presence: Despite its growth, Tesla’s market core is still the U.S., with over 70% of its revenues, and it struggles on establishing itself around the world;
- Target group: Tesla is a premium clean energy brand, so despite its significant growth, it still has a small target group due to its high prices;
- Profitability: Tesla still burns cash because of its high operational costs, which threatens its profitability and, consequently, the investors’ opinions;
- Succession: Elon Musk is the face of Tesla, and its name has become inseparable from the brand.
Tesla’s Opportunities
- Expansion: The U.S. and China generate most of Tesla’s sales, especially in America, accounting for about 70% of them. The brand has plenty of capacity for expanding globally, mainly in Asian markets like China and India;
- Autopilot driving technology: That is the technology that the whole world has been waiting for, and Tesla’s autonomous driving technology gained fame as safe and convenient, and it keeps evolving;
- Sustainability: As people get more environmentally conscious, the demand for sustainable products has been growing quickly, thus increasing its potential growth;
- Battery production: Tesla is working on manufacturing its battery cell in-house, which will lower the production cost and create many new jobs at the same time.
Tesla’s Threats
- Competition: Tesla’s competitors have been in the market for hundreds of years and are rapidly investing in electric car technology, even being able to offer more affordable products;
- New technologies: Vehicles are using more and more innovative technology and new ways of energy, and that demand can increase operational costs and decrease margins;
- Regulations: There are no adequate regulations for autonomous cars yet, which can jeopardize Tesla’s future;
- Long-term sustainability: Clean energy companies demand long-term sustainability strategies, and Tesla’s limited infrastructure may not support that;
- Elon Musk: Although he may be considered a genius and visionary, Musk has been building a controversial image due to his erratic behavior, which is often not aligned with social expectations.
-> Read more about Tesla’s SWOT Analysis.
Conclusion
Tesla did not invent the electric car, but possibly it was largely responsible for shedding new light on this product on the market, by producing cars with differentiated design, long-lasting batteries, and a whole technological support and servicing network. In addition, it implemented a business model practically unique in its area, by selling directly to the consumer, without middlemen. It can, therefore, be said, without fear of making a mistake, that Tesla is one of the most successful automobile industries today and certainly Elon Musk and his peers continue to seek new and original methods of transportation.

