Shopify is an e-commerce platform that allows merchants to create an online store and sell their products for a monthly subscription fee. The Shopify business model is also known as Software as a Service. However, in the year 2018, Shopify obtained more than 50% of its income through another source, which they call “Merchant Solutions”.
According to Shopify itself, that is part of its mission, which consists of improving commerce for all, and helping entrepreneurs of all sizes to reach their greatest potential in business. So, let us check out what Shopify’s business model really is.
Contents
How Shopify works
Shopify defines its platform as a cloud-based system, designed for multiple users, with scalability, reliability, security, and high performance. The first step for the new merchant who wants to sign up for the platform is a 14-day free trial. In order to do it, they only need to provide contact details and answer some questions about the business. It is not yet requested to insert card data. During this period, the idea is to test all available features, such as marketing campaigns, store designs, and applications, to find out what will be needed for the venture.
Then, after the 14-day period, the user will be able to choose the most suitable plan, select a definitive layout for their store, and include all their products. They will also choose which extensions and applications will be added to their plan (there are more than 1,500 options). All of this, of course, in the case of the regular user, among the three subscription plans. The Shopify Plus merchant adapts all their e-commerce process via service on the platform, since it is a different situation.
Shopify’s Positives and Negatives
User-friendly
First of all, Shopify is easy to use. It is very user-friendly, with a clear design and a simple edition. Customers are able to set up and manage their stores independently, without the need for support or prior technical knowledge.
Variety of layout
There is also a nice variety of themes to use as a layout for the store. They are all responsive, adapting to any device. And, for those who need more features, there are paid themes to choose from.
Brand’s reputation
In addition, one of Shopify’s value propositions is its own reputation identity: The brand is a leader in e-commerce solutions, therefore having one of the most well-known and recognized names in the industry, especially in the North American market.
Innovation
Another benefit is its investment in technology and innovation. Shopify uses its own technology and team to develop innovative technologies for its online platform.
Costs
Finally, the downside, for the regular customer segment, is the cost. The initial expenses are very low, since the first subscription plan starts from just 29 dollars a month. However, add-ons are relatively expensive. The basic and intermediate plans do not include many advanced features. And the cost of adding just three paid features, for example, already tends to double the monthly fee.
Who Owns Shopify
The Shopify billionaire founder, Tobi Lutke, is still up today, the company’s CEO and owner.
Shopify’s Mission Statement
Shopify’s mission statement is “to make commerce better for everyone, so businesses can focus on what they do best: building and selling their products“.
How Shopify makes money
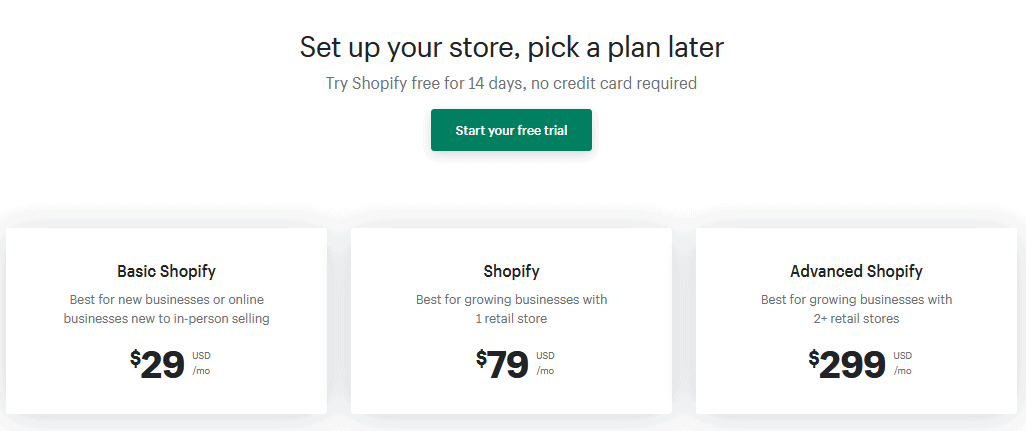
Shopify’s biggest audience is small and medium-sized businesses. To serve them, the platform has three subscription plans — all with a 14-day free trial period: Basic Shopify, Shopify, and Advanced Shopify. Basic Shopify costs $29 a month. It offers an online store with unlimited products, 24/7 support, and app sales. However, there are only two user accounts, fees for payment via credit card are higher, and the discount on shipping is the lowest, for example.
Shopify, the intermediate subscription, is the range where the vast majority of the platform’s customers are concentrated. It is $79 a month, with five user accounts, fees, and discounts better than the basic plan, but a little more expensive than the Advanced plan. Shopify’s highest sales volume, in turn, comes from merchants who opt for the most complete plan, Shopify Advanced, at a cost of $299 a month, with 15 user accounts, more reasonable fees, and all the options for points of sale and everything else that the platform has to offer.
Aside from these three regular plans, there is still the option of Shopify Plus. It is a service aimed at corporate customers, with large volumes — and is also accountable for driving sales on the platform. Shopify Plus does not appear on the standard subscription plans page, as it is designed for business customers, with a much higher cost than the Advanced plan. This amount is stipulated via the team’s service, based on a case-by-case analysis, but it usually starts at $2,000 per month.
The bandwidth of the Plus platform allows Shopify to handle thousands of orders per minute, without the overhead. And sales can be made internationally, in several languages, and by more than 70 means of payment. Shopify Plus is the highest retention plan and has brands of the caliber of Unilever, for example. In 2018, the corporate account base was over 5,300 clients.
Merchant Solutions
Merchant Solutions, as commented before, are additional services offered by the platform. These are features or services that enhance the experience with Shopify by merchant companies. Among them are:
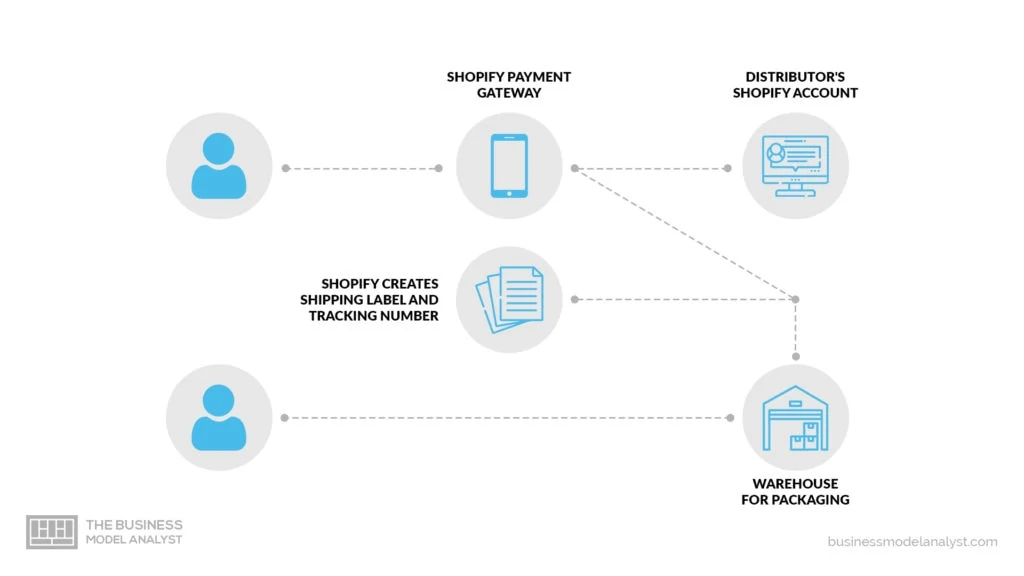
- Shopify Payments: It is a fully integrated payment processing service, which allows entrepreneurs to accept and process credit cards online and offline. This service represents the highest revenue among Merchant solutions, with their payment processing fees. That’s because, according to Shopify, two-thirds of its customers activate Payments;
- Shopify Shipping: It offers several shipping partners to choose from. The merchant selects the partner and can print shipping labels, make returns, track orders, etc., all via the Shopify platform;
- Shopify Capital It provides business growth for user companies, through working capital. For that, Shopify buys a number of future receivables or releases a loan to the entrepreneur. For payment, the merchant will pay a fixed percentage of their daily sales, until the balance is zero;
- Shopify POS: It’s a smartphone application that allows sales in a physical location.
In addition to increasing the revenue stream for Shopify — even exceeding subscriptions — these commercial solutions improve the retention rate of the customer base, strengthening the core business.
Shopify’s Business Model Canvas
Let’s take a look at the Shopify Business Model Canvas:
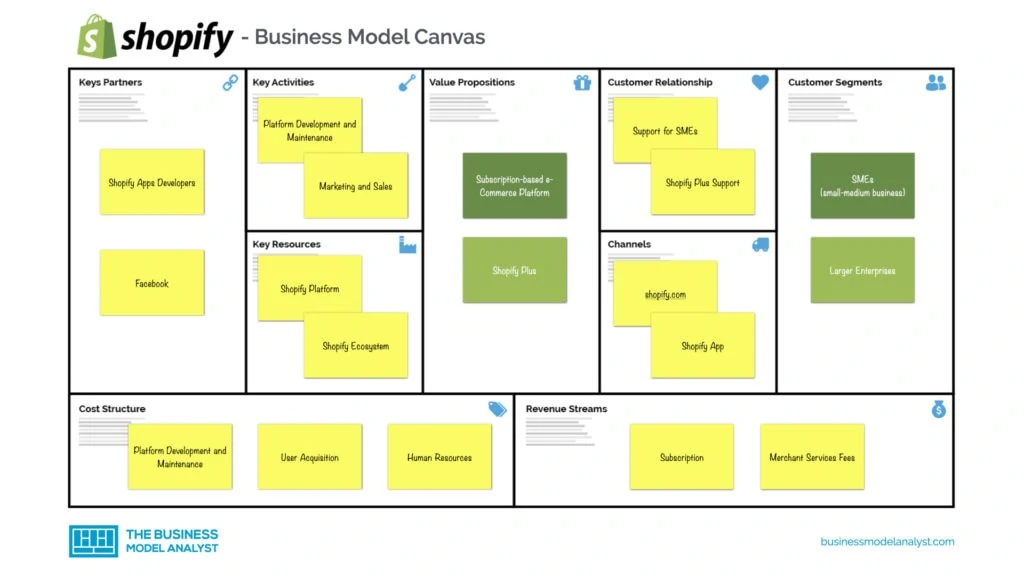
Shopify’s Customer Segments
- SMEs (small-medium businesses)
- Larger enterprises
Shopify’s Value Propositions
- Subscription-based eCommerce platform
- Shopify Plus
Shopify’s Channels
- Website (shopify.com)
- Shopify app
Shopify’s Customer Relationships
- Support for SMEs
- Shopify Plus support
Shopify’s Revenue Streams
- Subscription
- Merchant services fees
Shopify’s Key Resources
- Shopify platform
- Shopify ecosystem
Shopify’s Key Activities
- Platform development and maintenance
- Marketing and sales
Shopify’s Key Partners
- Shopify app developers
Shopify’s Cost Structure
- Platform development and maintenance
- User acquisition
- Human resources
Shopify’s Competitors
- BigCommerce: Founded in Sydney, Australia, in 2009, BigCommerce offers software to businesses to better manage their online and mobile stores, oversee and handle payment issues, and more;
- Salesforce: Headquartered in San Francisco, California, Salesforce is a cloud-based software company that provides tools for customer management and sales. The Salesforce platform is a widely enhanced interactive dashboard with significant features to assist the user with AI-generated insights, automated metric reports, and much more;
- eComchain: It is a cloud-based company that works with the B2B2C model, which means, it provides SaaS with an interactive dashboard for companies to better handle their eCommerce transactions;
- commercetools: Founded in Munich, Germany, t is a cloud-based platform that works with APIs, to help businesses to manage their eCommerce sales. It operates globally, with offices established throughout Europe, South Asia, and Australia.
Shopify’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Shopify:
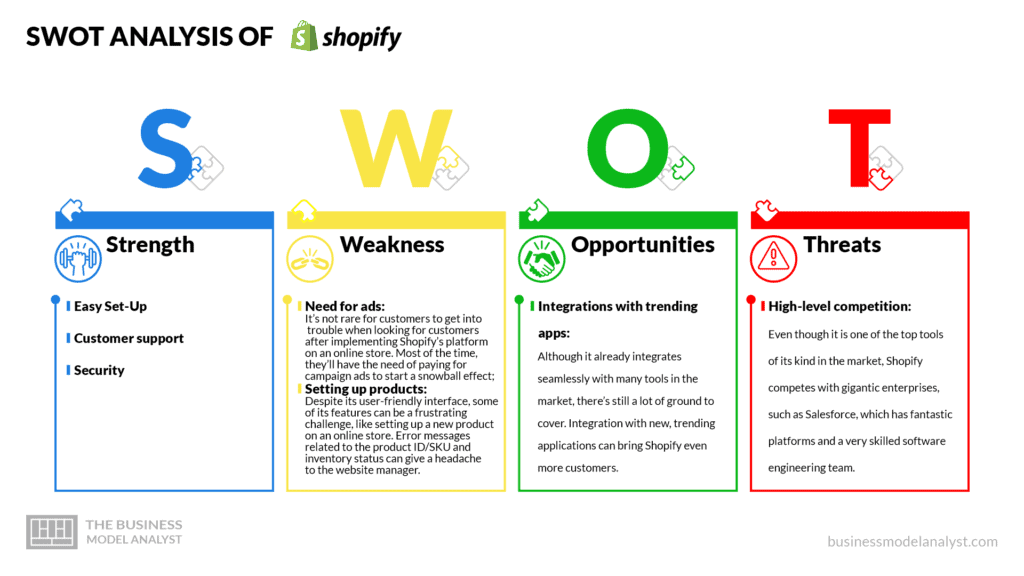
Shopify’s Strengths
- Easy Set-Up: The platform has a very intuitive and user-friendly interface, and that doesn’t require any technical skills;
- Customer support: Shopify has accessible and reliable customer support, available 24/7, so, at any time, you can reach them for help, questions, issues, or concerns;
- Security: The platform has secure, integrated tools to offer encryption of all data, which protects sensible information of clients and companies.
Shopify’s Weaknesses
- Need for ads: It’s not rare for customers to get into trouble when looking for customers after implementing Shopify’s platform on an online store. Most of the time, they’ll have the need of paying for campaign ads to start a snowball effect;
- Setting up products: Despite its user-friendly interface, some of its features can be a frustrating challenge, like setting up a new product on an online store. Error messages related to the product ID/SKU and inventory status can give a headache to the website manager.
Shopify’s Opportunities
- Integrations with trending apps: Although it already integrates seamlessly with many tools in the market, there’s still a lot of ground to cover. Integration with new, trending applications can bring Shopify even more customers.
Shopify’s Threats
- High-level competition: Even though it is one of the top tools of its kind in the market, Shopify competes with gigantic enterprises, such as Salesforce, which has fantastic platforms and a very skilled software engineering team.
Conclusion
Although the recent pandemic was responsible for an unprecedented expansion of many digital companies, and Shopify is included on that list, the growing concerns that the company may not be able to follow the development to the same level as they did recently with the Covid-19 pandemic is an uneasiness for the board. Shopify needs to think of new paths to keep its evolution in the post-pandemic period.

