The Ryanair business model is based on the sales of low-cost airline tickets, as well as charging for extra services. Ryanair allows travelers to move from one place to another at a much lower price than other airlines. Since its founding in 1984, the Irish low-cost carrier Ryanair has advanced significantly. Beginning operations with flights connecting Ireland and the UK, the airline has grown its network of routes, established new hubs, and extended its fleet of aircraft, now operating to more than 200 locations across 40 distinct nations.
Ryanair is renowned for its inexpensive flights and effective management, emphasizing cost control and minimizing expenses by offering passengers a basic level of care. The business makes money from several different sources, including the sale of aircraft tickets, the provision of supplementary services, cargo operations, advertising, and commissions from credit card transactions. Ryanair has received criticism throughout the years, yet it is still among the best-performing and most lucrative low-cost airlines globally.
Contents
A brief history of Ryanair
In 1984, three Irish men, Christopher Ryan, Liam Lonergan, and Tony Ryan, came together to establish the airline company Ryanair. The company was supposed to be an Irish low-cost airline that offered its customers the chance to travel between Ireland and the United Kingdom by flight at lower prices. However, since it was founded, the airline has expanded and now transits between European countries and beyond.
At the inception of the airline’s establishment, Ryanair faced much competition from airlines that were already well established. However, because of the low prices they offered customers, they managed to scale through. It could keep offering these low prices to passengers because it operated from secondary airports, which were less expensive than the primary airports.
During the 1990s, when Michael O’Leary was appointed as the new CEO, the company underwent massive changes. Under his leadership, he tried to cut many costs the airline had to bear, so he adopted some measures and policies. Of these measures, he reduced the number of routes the airline flew through, closed nonprofitable bases, and negotiated lower airport fees. Meanwhile, the policies included charging passengers for checked baggage and imposing penalties for customers who did not print their boarding passes before arriving at the airport.
Although Ryanair has faced criticism over the years for its policies and how it treats customers, the company, under O’Leary’s leadership, is now one of the most successful and profitable low-cost airlines in the world. The company continued to expand its routes, open new bases, and increase its fleet of planes. Today, Ryanair operates more than 1,800 flights per day and carries over 150 million passengers annually.
Who Owns Ryanair
The parent company that owns Ryanair is Ryanair Holdings PLC. However, the company is a publicly-traded company, meaning that it is jointly owned by a bunch of shareholders who are either individuals or institutions. The company’s shares were listed on the Irish and London Stock Exchanges following its IPO. Notwithstanding this, it is still majorly owned by Tony Ryan’s Family through Ryan Holdings.
Michael O’Leary, who became the company’s CEO in 1994, also has 2.44% of the company’s shares. This means that he has a significant stake in the company. Other major shareholders in the company include BlackRock, Vanguard, and Capital Research and Management Company. It’s important to note that Ryanair’s ownership has changed as the business has expanded and transitioned through different stages of development. The Ryan family is still the company’s largest stakeholder at the moment, and Michael O’Leary continues to be essential to its management and strategy.
Ryanair Mission Statement
To offer low fares that generate increased passenger traffic while continuously focusing on cost containment and efficient operation.
How Ryanair works
Currently, Ryanair has flights that go to over 200 destinations in 40 different countries, mainly in Europe. Just like when it first started, Ryanair continues to operate from secondary and regional airports and not primary ones, as it helps to keep costs low. By doing this, the airline company doesn’t have to pay any high landing fees or airport charges, which would be significantly higher in major airports. Also, this strategy means the company offers customers regular flights to places other airlines might not provide.
Ryanair keeps expenses down in addition to its airport strategy by providing travelers with a minimal level of service. For instance, the airline doesn’t offer free drinks or meals on its trips. Instead, customers can pay extra to acquire food, drinks, and other products on board. Similar to other airlines, Ryanair has stringent regulations regarding baggage, allowing only one small bag for free in the cabin. Additional baggage allowance is available to passengers for a cost.
To book a flight on Ryanair, potential passengers can easily by booking directly through the airline’s website or mobile app. Through either medium, a passenger can also get some add-ons like selecting which seat they want, getting priority boarding, and checked luggage, all at an additional price. With the priority boarding system, travelers can opt to board in a certain group based on their seat location or pay for priority boarding. This method facilitates quick boarding, which is beneficial for maintaining flight schedules.
How Ryanair makes money
Although Ryanair is a low-cost airline, it doesn’t necessarily mean that it doesn’t generate revenue or profit. The airline makes money through different sources. Along with selling airline tickets, it has various ancillary services it provides consumers, which counts as a source of revenue for the company.
The airline has a cargo segment that uses its aircraft to haul freight and mail, and it also makes money from advertising and credit card commissions. Even in the face of fierce competition from rival low-cost airlines, Ryanair has been able to retain its profitability and expand its business by diversifying its revenue sources.
Here is a list of how Ryanair makes money:
- Airfare
- Ancillary Revenue
- Advertising
- Car Rental
- Credit Card Commission
- Cargo
Airfare
The primary source of generating revenue for Ryanair is by selling airline tickets to customers who wish to travel through their airline. It makes some of its money by selling tickets which cover the basic needs of customers when they travel from one place to another. The ticket covers the flight, a seat, and small cabin baggage. Any other services the passenger might be interested in, such as a specific seat, more baggage allowance, meals, etc., will involve an additional fee. Because of its low cost of tickets, the airline can attract more customers, especially budget-conscious ones.
Ancillary Revenue
As earlier stated, the low-cost tickets which Ryanair sells to passengers only cover their basic needs. However, in the situation that the customer might want something which is not a necessity and so not included in the cost of the ticket, then they have to pay for more. These additional wants are called ancillary services. Ryanair makes a sizable profit from the extra services it provides to its clients. These include, among other things, in-flight meals, travel insurance, car rentals, and hotel reservations.
Advertising
The airline company also makes money by charging advertisers to display their content on its website and in-flight magazine. By putting this advertising content in the magazine, they reach a large number of passengers who, for the duration of their flight, serve as a captive audience. Sometimes, the airline can also sell space on the exterior of its planes for advertising to an advertiser. Doing this would help them reach an even larger audience.
Car Rental
By collaborating with automobile rental firms to provide their customers with car rental services, Ryanair makes money. Ryanair’s website allows users to reserve rental cars, and the airline receives a commission on each booking. Since a service that many tourists require after they reach their destination, car rental is a crucial component of Ryanair’s auxiliary revenue strategy.
Credit Card Commissions
As part of its other sources of revenue, Ryanair also has its own branded credit card, which it offers its passengers. When a passenger uses the card, they accumulate reward points that they can redeem during future flights, and the airline gets commissions from each transaction made by using the card. Although this source of revenue is relatively small compared to other sources, it still helps offset costs and provides additional services to customers.
Cargo
With the delivery of mail and cargo, Ryanair makes money. The cargo business of the airline offers services to a variety of clients, including other airlines and online retailers. Ryanair’s business relies heavily on cargo transportation, since it allows the airline to add more revenue-generating cargo to its planes when passenger demand is low.
Ryanair Business Model Canvas
The Ryanair Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
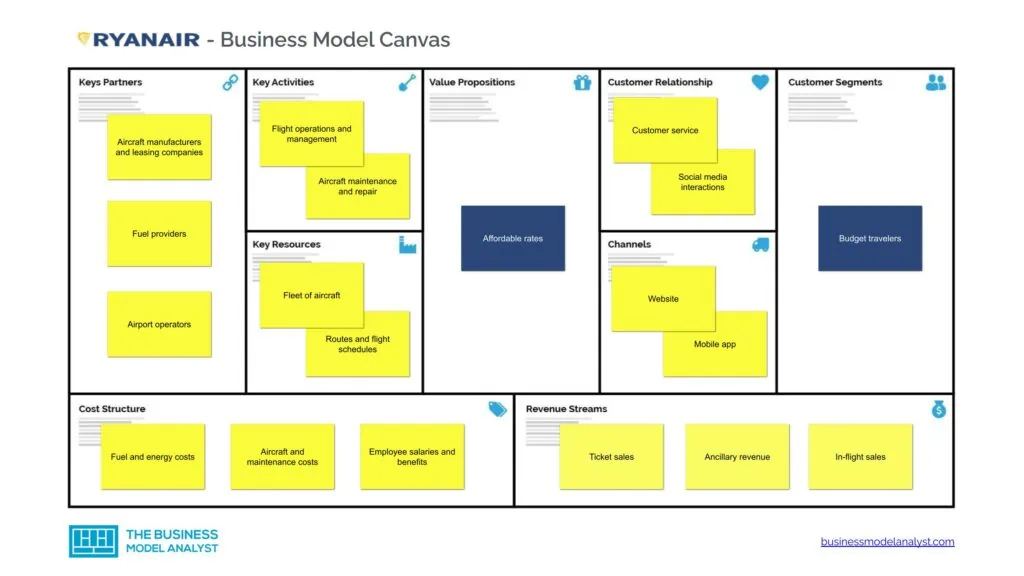
Ryanair Customer Segments
Ryanair’s customer segments consist of:
- Budget travelers: Since Ryanair is recognized for being a low-cost airline, many of its passengers seek the most affordable flights;
- Leisure travelers: Ryanair serves many well-liked holiday spots throughout Europe; many passengers are leisure visitors;
- Travelers on business: Although Ryanair primarily focuses on leisure travel, it also serves certain business passengers. These clients can be drawn to Ryanair because of its affordable fares, enabling them to reduce their travel expenses;
- Students: Ryanair attracts young individuals studying abroad or on cheap trips since it offers discounts for students;
- Families: Ryanair has started to put more emphasis on family travel in recent years, with programs including priority boarding for families with young children and family-friendly seating selections;
- Short-haul travelers: As Ryanair focuses exclusively on short-haul routes, many passengers are doing so within Europe;
- Adventurers: Ryanair provides flights to various off-the-beaten-path locations, which may appeal to tourists seeking unusual and exciting vacation opportunities.
Ryanair Value Propositions
Ryanair’s value propositions consist of:
- Budget travelers: The main selling point for budget tourists on Ryanair is its affordable rates. By providing an essential experience and charging for various extras like checked bags, seat preference, and onboard food and beverages, Ryanair attempts to keep costs as low as possible. This makes it possible for passengers on a budget to visit numerous locations for less money than they may pay with other airlines;
- Leisure travelers: One of Ryanair’s primary value propositions for vacationers is the airline’s extensive list of vacation locations around Europe. Ryanair provides a wide range of destinations that might entice many different sorts of leisure visitors, whether wishing to visit the beaches of Spain, the ancient towns of Italy, or the picturesque countryside of Ireland;
- Travelers on business: Business travelers that frequently travel and need to keep prices down may find Ryanair’s low rates and frequent flight schedules appealing. But, business travelers who desire more amenities and services during their flights might not find Ryanair’s no-frills experience as enticing;
- Students: For this client demographic, Ryanair’s student discounts are an essential value offer. Ryanair can draw in young passengers who might not have much money to spend on travel by providing discounted rates for students;
- Families: Families that want to travel together and have a more comfortable and convenient travel experience may find Ryanair’s family-friendly efforts, such as family seating options and priority boarding, appealing;
- Short-haul travelers: Ryanair’s emphasis on short-haul flights can be a significant selling point for tourists who want to reach their destination quickly and affordably;
- Adventurers: For tourists who prefer to see unusual and less-visited locations, Ryanair’s off-the-beaten-path destinations can be a significant selling point. Travelers may be able to take more journeys and experience more places thanks to Ryanair’s low costs than they might be able to with other airlines.
Ryanair Channels
Ryanair’s channels consist of:
- Website
- Mobile app
- Travel agents
- Call center
- Social media
- Email marketing
- Affiliate marketing
- Online advertising
- Sponsorships
- Public relations
Ryanair Customer Relationships
Lululemon’s customer relationships consist of:
- Customer service
- Social media interactions
- Loyalty program
- Personalized marketing
- In-flight experience
- On-time performance
- Handling flight disruptions and cancellations
- Handling of baggage and lost items
- Website user experience
- Complaint handling
Ryanair Revenue Streams
Ryanair’s revenue streams consist of
- Ticket sales
- Ancillary revenue
- In-flight sales
- Car rental
- Hotel bookings
- Travel Insurance
- Advertising
- Partnerships and sponsorships
- Payment processing fees
- Reselling of airport services.
Ryanair Key Resources
Ryanair’s key resources consist of
- Fleet of aircraft
- Routes and flight schedules
- Crew and staff
- IT systems and infrastructure
- Brand and reputation
- Financial resources
- Airports and ground facilities
- Suppliers of goods and services
- Data and analytics capabilities
- Intellectual property
Ryanair Key Activities
Ryanair’s key activities include
- Flight operations and management
- Aircraft maintenance and repair
- Sales and marketing
- Ancillary revenue management
- Customer service and support
- Ground operations
- Information technology and digital infrastructure management
- Route planning and network management
- Corporate governance and regulatory compliance
- Financial management and reporting.
Ryanair Key Partners
Ryanair’s key partners consist of:
- Aircraft manufacturers and leasing companies
- Fuel providers
- Airport operators
- Ground-handling service providers
- Technology and software providers
- Advertising agencies and media companies
- Hotel and car rental companies
- Insurance providers
- Payment processing companies
- Travel agencies and tour operators.
Ryanair Cost Structure
Ryanair’s cost structure consists of
- Fuel and energy costs
- Aircraft and maintenance costs
- Employee salaries and benefits
- Advertising and marketing expenses
- Airport and handling fees
- IT systems and infrastructure costs
- Insurance and legal expenses
- Aircraft leasing and financing costs
- Ancillary service costs
- Administrative and general expenses.
Ryanair Competitors
- EasyJet: One of the biggest low-cost carriers in Europe, EasyJet has a Ryanair-like business strategy. Like Ryanair, EasyJet maintains a vast network of routes throughout Europe and provides low-cost prices and associated services. Ryanair and EasyJet are neck-and-neck in market share, with each airline holding about 8–9% of the European aviation industry. Nonetheless, Ryanair has a more significant presence in the business travel industry, while EasyJet has historically concentrated more on the pleasure travel market;
- Wizz Air: A low-cost airline based in Hungary, Wizz Air mostly serves Eastern Europe. Wizz Air has a significant presence in the eastern half of the continent and has been expanding into other areas, including the UK and the Middle East. In contrast, Ryanair and EasyJet have a bigger network of routes across Europe. With a range of optional services offered to customers, Wizz Air also strongly emphasizes ancillary revenue;
- Lufthansa: One of the biggest airlines in Europe is Lufthansa, a legacy carrier with its headquarters in Germany. While having a very different business strategy than Ryanair, Lufthansa competes with the latter on many European routes, particularly in the business travel sector. With a solid frequent flyer program and various pricing classes, including business and first class, Lufthansa can draw in high-value passengers;
- British Airways: Another legacy airline that competes with Ryanair in the European aviation industry is British Airways. British Airways competes with Ryanair on several short-haul routes inside Europe, despite having a more extensive worldwide network of routes and a more prestigious reputation. In addition, British Airways has introduced LEVEL, a low-cost airline that, on some routes, competes directly with Ryanair;
Ryanair SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Ryanair:
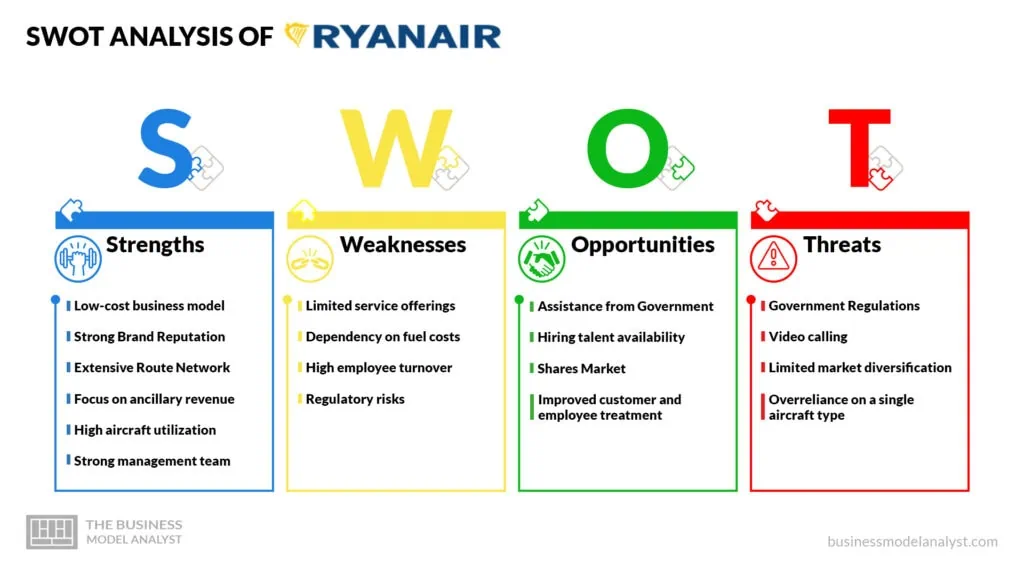
Ryanair Strengths
Below, there are Ryanair’s strengths;
- Low-cost business model: One of Ryanair’s key advantages is its low-cost business approach. Ryanair can give passengers some of the lowest tickets in the sector because it keeps expenses low and prioritizes efficiency, boosting demand and market share;
- Strong Brand Reputation: Ryanair’s excellent brand reputation has aided in increasing consumer loyalty and drawing in new clients. The airline is renowned for its no-frills strategy and emphasis on low tickets, which has found favor with passengers on a tight budget;
- Extensive Route Network: Ryanair has established a vast European route network with more than 200 destinations across 40 nations. Due to this, the airline has been able to gain a sizable portion of the European aviation market and provide travelers with various travel options;
- Focus on ancillary revenue: Ryanair places a lot of emphasis on supplemental income, which has increased its profitability. The airline provides various add-on services that passengers can purchase to improve their travel experience, including priority boarding, checked bags, and food and drink;
- High aircraft utilization: Ryanair has one of the greatest plane usage rates in the business, which indicates that its planes fly more frequently and bring in more money. This is accomplished by the airline having short turnaround times, which reduce downtime and increase productivity;
- Strong management team: The management team at Ryanair is quite capable and experienced, which has been key to the airline’s success. The team is dedicated to generating shareholder value and significantly emphasizes cost management and operational efficiency.
Ryanair Weaknesses
Here, there are Ryanair’s weaknesses;
- Limited service offerings: Ryanair focuses on low fares and supplementary income and offers a small selection of services. This strategy has been successful in increasing demand and market share. Still, it has also constrained the airline’s ability to make money from other sources, such as business travel or premium services;
- Dependency on fuel costs: The cost of fuel is a critical factor in the profitability of Ryanair, and its price is highly erratic. Even while the airline has a mechanism to hedge this risk, fluctuations in fuel prices can still significantly impact how well the airline does financially;
- High employee turnover: The high personnel turnover rate at Ryanair can affect the company’s ability to operate efficiently and provide excellent customer service. The airline has come under fire for how it treats its employees, particularly the low pay and unfavorable working conditions that may make it more challenging to recruit and retain top talent;
- Regulatory risks: Ryanair operates in a highly regulated sector, so adjusting laws or policies could affect the airline’s operations and financial performance. This includes prospective adjustments to airport fees or air traffic control, as well as tighter rules governing emissions and environmental effects.
Ryanair Opportunities
Below, there are Ryanair’s opportunities;
- Assistance from Government: Through the Bank of England Covid Care, about 53 businesses have received advantages in the form of cash. Ryanair was part of these businesses and was able to 800 million euros after showing interest in this arrangement;
- Hiring talent availability: After the Coronavirus pandemic, many talented individuals were left without jobs. The airline can hire deserving candidates from the immense pool of qualified individuals to help efficiently run the airline. These people could be cabin crew, engineers, pilots, etc.;
- Shares Market: After the restrictions on air travel placed by the government have been eased, the chance for Ryanair to sell more shares at the stock exchange market is endless. This is because since air travel is back to normal, people would go back to flying by air, and so more money would be made by airlines;
- Improved customer and employee treatment: With the criticism of how Ryanair treats its customers and employees alike, many potential customers have deviated from using the airline’s services. There is, however, an opportunity for the company to improve how it treats both its customers and employees, as this would help bring more customer and employee traffic.
Ryanair Threats
Here, there are Ryanair’s threats;
- Government Regulations: While Ryanair can make its policies, it cannot control the actions and decisions of the government. The regulations made by the Government might be either a win or a major threat to Ryanair;
- Video calling: Coronavirus pandemic caused many individuals and institutions to improvise. Instead of traveling to meet for a yearly visit or a business meeting, many would prefer to video call, which can prove to be a threat to Ryanair;
- Limited market diversification: Although dominant in the European aviation market, Ryanair has limited market diversification in geography or product markets. Any disruptions or changes in the European aviation market could negatively impact the airline’s future growth and profitability;
- Overreliance on a single aircraft type: Boeing 737s make up the majority of Ryanair’s fleet, and the airline has long been reliant on them. While this strategy has reduced costs and improved efficiency, it also carries a risk in case the Boeing 737 experiences any problems or disruptions, such as the grounding of the MAX model.
Conclusion
As a low-cost airline that provides a variety of locations at reasonable prices, Ryanair has created a unique niche for itself in the aviation sector. Ryanair has maintained its profitability while facing fierce competition from other airlines, thanks to the diversification of its income streams and ongoing search for cost-cutting measures. Millions of people choose to fly with Ryanair each year, even though the business has come under fire for its practices and how it treats consumers. It will be interesting to watch how the business adjusts to fresh opportunities and challenges in the aviation sector as it develops and grows.

