The Rakuten business model is a simple approach where stores pay the company for sending customers to buy products from their websites. Rakuten then shares the commission with the shopper through cash back. You must purchase through Rakuten’s app or website and have the purchase verified by the retailer to receive your cashback.
Rakuten offers over 70 services in diverse fields, including e-Commerce, internet services, cashless and e-money payments, fintech services, securities, and banking. Rakuten’s members need a single ID to use multiple services in the Rakuten ecosystem, earn, and spend points while shopping via the different Rakuten services.
Rakuten provides remarkably convenient services related to the daily life spectrum to encourage customers to become part of the ecosystem, utilize different group services, and continue using them. The Rakuten approach creates an interaction that reduces customer acquisition costs, enhances lifetime value per member, and boosts the overall gross translation volume for Rakuten Group services, giving the company an incomparable competitive edge.
Contents
A brief history of Rakuten
Hiroshi Mikitani’s dream of owning an online retail business started in the late 1990s. Then, the internet was evolving, and more people were embracing and utilizing it. He derived his inspiration after ordering and receiving Japanese noodles through mail-order shopping. Hiroshi was convinced that besides getting thrilled by such convenience, many customers would be encouraged to shop online.
Some of Hiroshi’s friends were skeptical about his dreams, opining that only a few people would purchase products online. Still, Hiroshi never gave up. He launched MDM, an e-Commerce company, in 1997 with six employees. The website featured an online shopping mall named Rakuten Ichiba with 13 merchants. Hiroshi planned to charge the merchants a monthly fee to have them showcase their products on the website. He would also charge an extra fee for general promotional and advertising services.
Hiroshi proved all the naysayers wrong when the company thrived, generating $183,840.00 at the end of its first year. Other core milestones followed after that. In 1999, MDM adopted Rakuten, a Japanese term that means optimism. In 2000, Hiroshi introduced Rakuten University, a program designed to teach vendors how to operate online businesses. Rakuten went public the same year and was listed on JASDAQ.
Rakuten Books, an online-based merchant for books, and Rakuten Travel, an online hotel reservation service, were birthed in 2001. Rakuten introduced Super Points, a consumer loyalty program, and Pay As You Go, a merchant fee contract system, in 2002. The company had 6,000 merchants in its system by the end of 2002. Rakuten acquired firms such as LinkShare Corporation in the U.S. to launch its operations abroad.
The company’s numerous joint ventures and acquisitions were critical to diversifying its product lines, penetrating financial services, and growing its global reach to Spain, Taiwan, Austria, and Canada. Through these moves, Rakuten became a dominant competitor in the B2B and B2C space. Currently, Rakuten has over 44,000 merchants, making it the most prominent online retailer in Japan and one of the largest e-Commerce platforms with regard to sales. Hiroshi said his company’s massive success results from “omotenashi,” a Japanese principle that means high-quality and personalized service.
Who Owns Rakuten
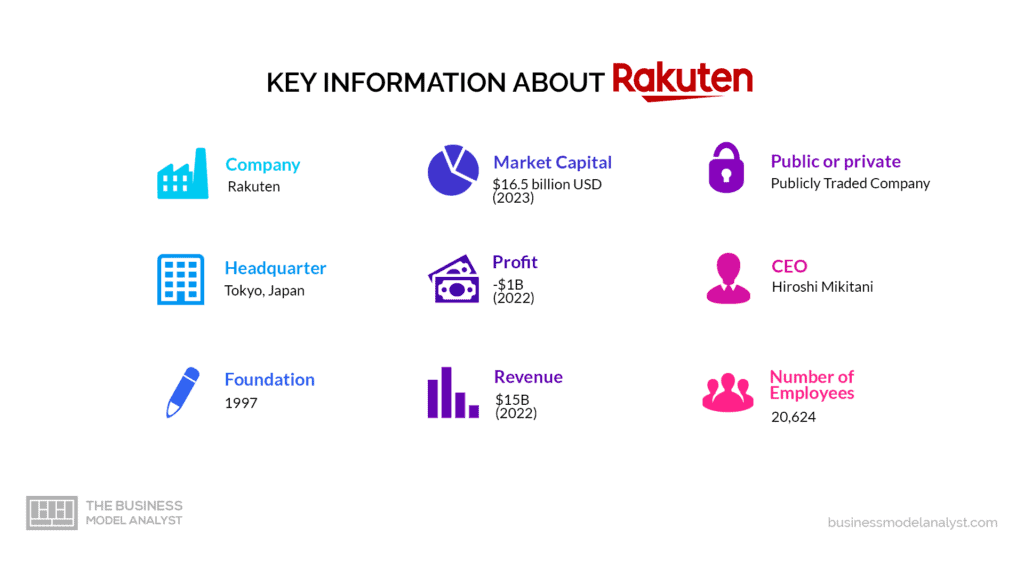
The owners of Rakuten are; Haruko Mikitani (8.40%), Hiroshi Mikitani, the CEO and founder (25.5%), Tencent (3.64%), and Japan Post Holdings (8.30%).
Rakuten Mission Statement

Rakuten’s mission is “To empower people and society through innovation and entrepreneurship.”
How Rakuten works
Rakuten allows online consumers who shop through the platform to earn cash back. Before purchasing goods, shoppers visit Rakuten.com and search for their preferred online store. After locating the store, the shopper clicks to access it from their Rakuten account. Doing so generates a tracking cookie, allowing them to receive credit for their cash back. While some stores offer up to 3% cash back, others offer more.
Shoppers can use Rakuten free of charge. Rakuten acts as an affiliate for its partner stores. The stores pay Rakuten, after which it shares a percentage of the money with its customers. For instance, suppose you shop at Target using your Rakuten link. Target will pay Rakuten a certain percentage of the overall order amount. Rakuten will then offer you a portion of the amount they receive from Target.
How Rakuten makes money
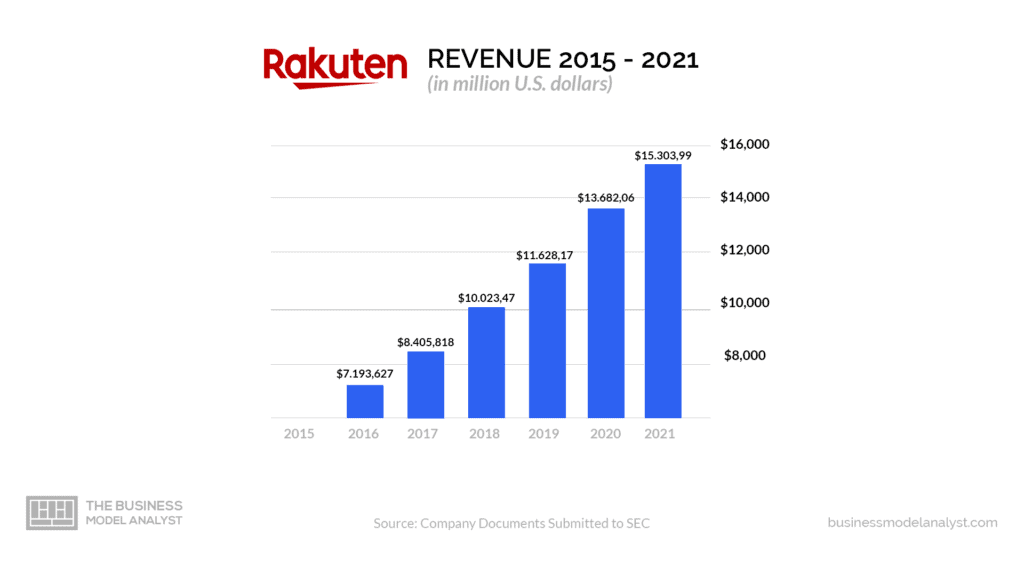
Rakuten makes in different ways, as seen below.
Internet Services
Rakuten makes the largest income from internet services, with Rakuten Ichiba, an e-Commerce platform based in Japan, generating the most revenue. More than 55,00 merchants operate their stores on Rakuten, driving daily sales to nearly $100 million. A considerable percentage of the company’s marketplace-based revenue is from commissions. Sellers pay up to 4% for every product sold. Further, Rakuten charges listing and registration fees, fixed monthly consultation fees, processing fees, system reinforcement fees, affiliate fees, and fees for royalty point-earning users. Sellers on Rakuten can promote their products by buying ad slots on customer search queries. The company then earns money from each click the ads attract.
Further, Rakuten offers Rakuten Super Logistics, a merchant fulfillment service, and charges a fee. Other Rakuten e-Commerce units from which the company makes money are Rakuten Rakuma, Rakuten Bic, Rakuten Books, and Rakuten Fashion. The company’s travel offering is another big revenue driver.
The system lets travel operators list their flights, accommodations, and trains on the platform for a fee. Rakuten also receives a commission for each sale in addition to search and banner advertising. Through the Rakuten cashback program, the company receives a commission whenever consumers shop at any merchants it hosts. The company also runs various media businesses, which generate income through advertising and subscription fees.
Rakuten Ticket is a division of the company through which users can buy event tickets. Other revenue-generating divisions include Rakuten Recipe, Rakuten Infoseek, and Rakuten NFT. Rakuten also earns a commission from NFTs sold through the digital marketplace.
FinTech
The Rakuten FinTech Group supervises the company’s financial division. Rakuten has a wide range of financial businesses, as seen below.
- Rakuten Bank: An internet-based and wholly licensed bank that allows users to open savings accounts;
- Rakuten Card: A credit card from Rakuten Bank;
- Rakuten Insurance: Providing general, pet, and life insurance;
- Rakuten Edy: A prepaid form of e-money that can be used in over 400,000 member stores;
- Rakuten Pay: A digital payment application that allows users to purchase goods in physical and online stores;
- Rakuten Wallet: Crypto asset exchange system that facilitates the trading of digital currencies such as Bitcoin.
These financial services power consumption across various Rakuten internet services while enabling the company to generate revenue from interchange fees. The Rakuten Wallet generates most of its income from consumer trading fees when purchasing or selling a financial asset.
The company’s payment app and credit card enforce fees on merchants who use them, while its insurance products collect premiums monthly. Rakuten Bank can deposit member funds in interest-generating bank accounts or issue loans for interest.
Rakuten Capital is a venture capital group that invests in promising startups or incubates new businesses. In one of its venture investments, Rakuten gained $2 billion from a $700 million investment for a 13% stake. Even though the deal has since collapsed, the company recorded some wins. Rakuten generated money from Rakuten Capital when it disposed of its shares for a higher amount than the buying price.
Mobile
Rakuten Mobile, a low-cost data 4G plan, was birthed in 2020. For $27 monthly, consumers would gain access to unlimited data and calls where Rakuten has network coverage. While the company’s low-cost plan gave it a competitive advantage, it admitted that implementing an individual network can be costly. Still, the industry can be lucrative, mainly due to the low customer churn rates.
Rakuten leverages its mobile offering to attract new customers. In a recent earnings report, the company announced that Rakuten mobile subscribers spend up to $260 more on Ichiba than unsubscribed users. The company also launched Rakuten Symphony in 2021, a system through which telco companies can establish virtualized networks. Symphony oversees customer relationship management tools, a digital app marketplace, and cloud storage, sold to consumers as white-label offerings.
Rakuten Business Model Canvas
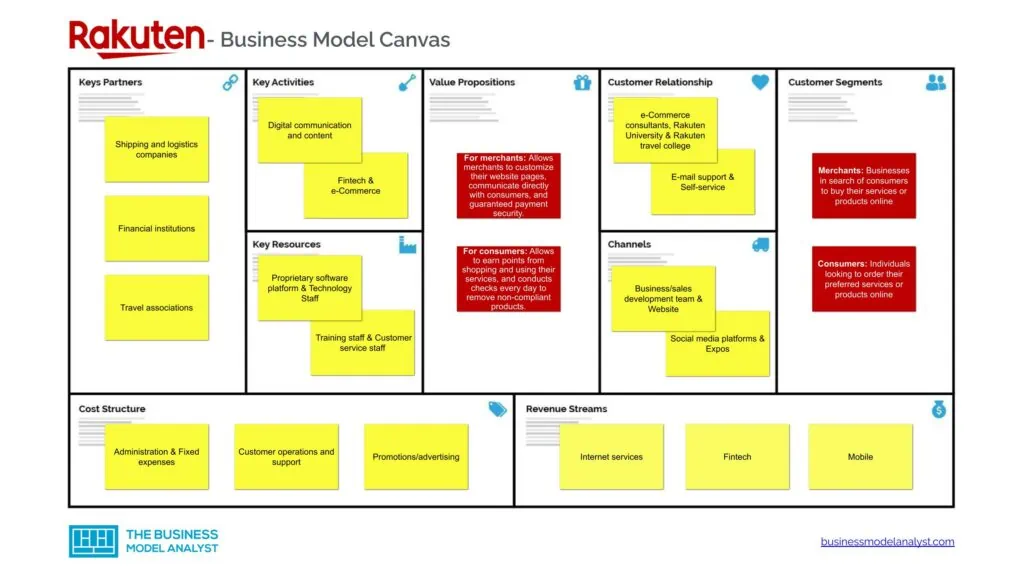
The Rakuten Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
Rakuten Customer Segments
Rakuten’s customer segments consist of:
- Merchants: Businesses in search of consumers to buy their services or products online;
- Consumers: Individuals looking to order their preferred services or products online.
Rakuten Value Propositions
Rakuten’s value propositions consist of:
- For merchants: Allows merchants to customize their website pages to demonstrate creativity and originality. They can also communicate directly with consumers through e-mail and social media. Rakuten guaranteed payment security while offering settlement options;
- For consumers: The Rakuten Super Points plan allows consumers to earn points from shopping and using services across the Rakuten ecosystem. Rakuten vets prospective merchants thoroughly to ensure they are authentic, their products adhere to Rakuten’s guidelines and general laws, and protect consumer interests. The company conducts checks every day to remove non-compliant products.
Rakuten Channels
Rakuten’s channels consist of:
- Business/sales development team
- Website
- Social media platforms
- Expos
Rakuten Customer Relationships
Rakuten’s customer relationships consist of:
- e-Commerce consultants
- Rakuten University
- Rakuten travel college
- E-mail support
- Self-service
Rakuten Revenue Streams
Rakuten’s revenue streams consist of:
- Internet services
- Fintech
- Mobile
Rakuten Key Resources
Rakuten’s key resources consist of:
- Proprietary software platform
- Technology Staff
- Training staff
- Customer service staff
Rakuten Key Activities
Rakuten’s key activities consist of:
- Digital communication and content
- Fintech
- e-Commerce
Rakuten Key Partners
Rakuten’s key partners consist of:
- Shipping and logistics companies
- Financial institutions
- Travel associations
Rakuten Cost Structure
Rakuten’s cost structure consists of:
- Administration
- Customer operations and support
- Promotions/advertising
- Fixed expenses
Rakuten Competitors
- Walmart: Walmart is a retailer that runs supermarkets, grocery stores, hypermarkets, neighborhood markets, and discount and department stores. The company started building 182,000 square feet of supercenters in 1998, employing around 300 associates.
These supercenters incorporate home furnishings, toys, apparel, electronics, dairy products, deli, bakeries, and fresh produce to offer customers an all-around shopping experience. In the United States, the company operates under the name Walmart, Flipkart Wholesale in India, while in Central America and Mexico, it’s referred to as Walmart de México y Centroamérica.
- Amazon: Amazon is one of the biggest online retailers and a global cloud service provider. The company began as an online book-selling entity before becoming an internet-based firm specializing in cloud computing, e-Commerce, artificial intelligence, and digital streaming.
The company follows an Amazon-to-buyer approach and provides a massive inventory and diverse product range, enabling customers to purchase their preferred products under one roof. The Seattle-based retailer has individual software development centers, websites, data centers, fulfillment centers, and customer service centers globally.
- Alibaba Group: Alibaba is a digital platform that links wholesalers and manufacturers in China to businesses and individuals across the world seeking to resell or trade. Users purchase products for their business and then resell or use them. They can also sign up to become a supplier on the Alibaba platform. Instead of using the person-to-person or direct-to-consumer approach, the company focuses on business-to-business trade.
Rakuten SWOT Analysis
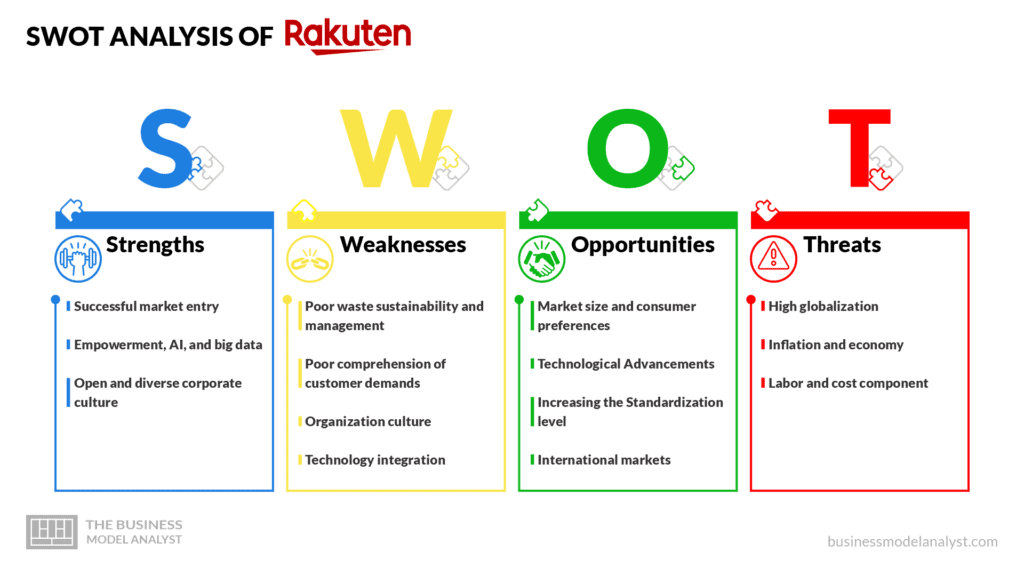
Below, there is a detailed SWOT analysis of Rakuten.
Rakuten Strengths
- Successful market entry: Rakuten has an excellent record of dispensing new services and catering to diverse markets depending on user insights. The company has developed one of the most resilient and unique ecosystems by linking different services under a standard reward and membership program;
- Empowerment, AI, and big data: Besides managing big data, Rakuten has the technological capacity to analyze it efficiently and are committed to empowering society with its resources;
- Open and diverse corporate culture: This facilitates the interchange of different viewpoints. The company’s talented workers are sourced from over 70 nations, while systems are regulated to boost productivity.
Rakuten Weaknesses
- Poor waste sustainability and management: Environment enthusiasts have criticized Rakuten’s inadequate waste management policies and lack of sustainability in its operations. Ineffective inventory management practices may result in inefficiency;
- Poor comprehension of customer demands: Inability to understand customer demands and expectations puts the company at risk of making the wrong decisions;
- Organization culture: Rakuten’s organizational culture is marred by conflicts between increased job stress and divisions, dampening employee morale;
- Technology integration: While Rakuten has deployed technology into its backend, it’s not integrated it into its front-end operations.
Rakuten Opportunities
- Market size and consumer preferences: Rakuten must retain loyal existing consumers while attracting new ones. Gaining more consumers is an excellent opportunity for the company’s growth. Proper market information and catering to evolving consumer preferences, tastes, and wants can help the company grow while increasing its revenue;
- Technological Advancements: Rakuten can use artificial intelligence advancements to determine consumer demands and enhance recommendation engines;
- Increasing the Standardization level: Rakuten can leverage this trend by focusing on the most affordable products while reducing the less profitable ones;
- International markets: Foreign markets are opening more due to globalization. Rakuten should consider expanding to different regions globally to tap into the new demand in those areas and diversify its customer base.
Rakuten Threats
- High globalization: Due to globalization, many companies penetrate foreign markets, which can be challenging for companies that lack cultural intelligence;
- Inflation and economy: Production costs rise due to inflation, which can negatively impact company profits;
- Labor and cost component: Governments are considering imposing high environmental levies to encourage companies to use cleaner alternatives. As a result, Rakuten may face high packaging and transportation costs.
Conclusion
Regardless of its success, there is still room for improvement. Rakuten can take the right initiative to penetrate new international markets and adopt advanced technology. Training staff helps them learn about the company, allowing them to market it accordingly. By adopting the right marketing, customer support, and marketing strategies, Rakuten will improve its productivity and increase revenue.

