The Plaid business model is based on building secure, easy-to-use software to connect applications that allow users to link their financial accounts to third-party apps. These apps include Venmo, Coinbase, and Robinhood, to name a few.
To be clear, Plaid is a financial technology company that runs a platform that lets customers link their bank accounts to their favorite apps, making it easier for different entities to share financial information.
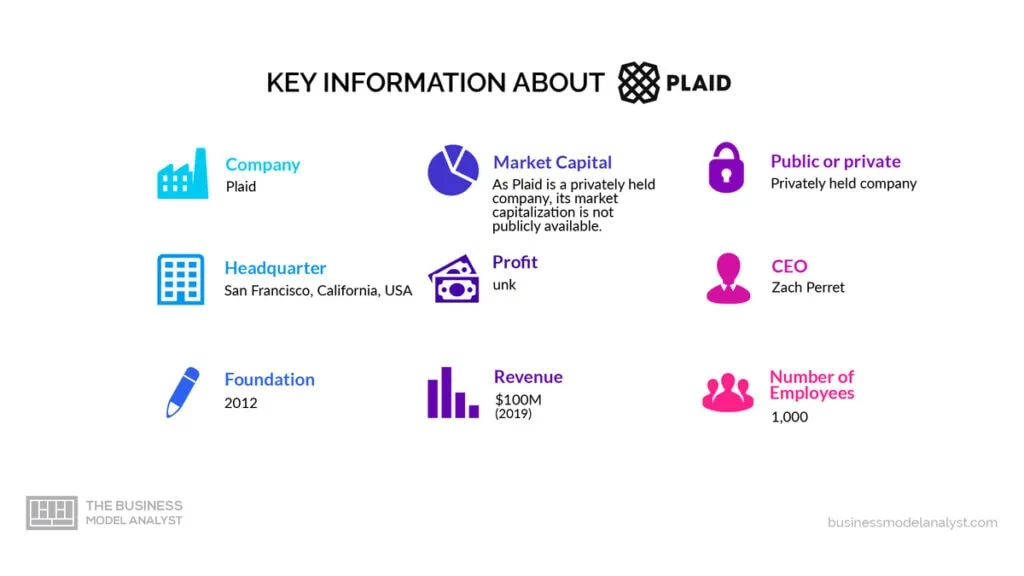
Despite facing multiple setbacks and over 50 investor rejections in its early years, Plaid has emerged as a dominant player in the financial technology industry since its founding in 2013. Today, the company is now valued at $13.4 billion and serves over 4,000 companies, including Fortune 500 companies and popular startups—more than ten times as many as when it was founded. The company’s employee count has also grown to 1200 people worldwide.
The company has also positioned itself as a leader in the industry by focusing on security, transparency, and innovation by giving digital wealth platforms everything they need to instantly fund accounts, deliver tailored advice, and fight fraud — all on a single platform with just a few clicks.
Let’s take a closer look at everything you need to know about the Plaid business model and how the company makes money, as well as Plaid’s SWOT analysis.
Contents
A brief history of Plaid
Plaid is an American financial technology company that was founded by Zach Perret and William Hockey in the early 21st century (2013) in San Francisco, California. Zach Perret and William Hockey first met as young consultants at Bain & Co.’s Atlanta office. The duo then set out to build a personal finance application, which was born out of frustration with the lack of transparency in the bills they paid.
However, despite their best efforts, they could not successfully build a personal finance application because developing custom integrations for each financial institution was a daunting task. Still, they didn’t let this setback hold them back. Instead, the duo pivoted their focus to create a platform that could act as a middleware between financial institutions and developers. Thus, Plaid was born with the mission of “democratizing financial services through technology.”
One of the early adopters of Plaid was Venmo. The head of engineering at Venmo, who happened to be a friend of Perret and Hockey’s, wanted a more efficient way to connect Venmo to a user’s bank account. Venmo relied on settling transactions in large batches, which led to delayed payments and additional risk for the peer-to-peer transfer company. Using Plaid, Venmo was able to verify and connect to a user’s bank account across many banks more quickly and easily. Other applications, such as Robinhood, Acorns, and Coinbase, quickly adopted Plaid after hearing about the partnership’s success.
In 2015, Plaid shifted its focus to developing its API (application programming interface) platform and began partnering with other fintech companies. And by 2016, Plaid had connected with over 1,700 financial institutions in the United States and Canada, granting its users access to connect their bank accounts to a range of apps and services.
In 2018, Kleiner Perkins partner Mary Meeker and Index Ventures led a funding round in which Plaid raised $250 million. This gave the company a value of $2.65 billion. This funding enabled Plaid to expand globally and invest in new products and services. “We’ve been really fortunate to have incredible growth in the fintech ecosystem and have been a key partner in driving that,” said Plaid CEO Zach Perret to CNBC in a phone interview.
In early 2020, Visa agreed to buy Plaid for $5.3 billion, which at the time was double the San Francisco-based start-up’s previous valuation. The Department of Justice sued to block the deal, alleging that it would limit competition in the payments industry, according to a report from CNBC. Even after this, Plaid continues to overgrow, with over 11,000 financial institutions now connected to its platform.
With all the trials and triumphs over the years, Plaid is presently one of the leading fintech companies in the world, connecting banks and credit unions to third-party mobile and web applications via APIs (application programming interfaces). As a result, financial institutions are able to provide better services while reducing security risks.
Who Owns Plaid
Plaid Inc. is a private company founded by Zach Perret and William Hockey. Various investment firms own plaid, but the largest owners of the company are founders Zach Perret and William Hockey, who are estimated to own 13% and 12%, respectively,” says a report from Gainy. Zach Perret is currently the CEO, while Jean-Denis Greze is the CTO of the Plaid company.
Plaid Mission Statement

The Plaid mission statement is focused on democratizing financial services through technology.
How Plaid works
As mentioned earlier, Plaid acts as a middleware between financial institutions and fintech applications. It provides a secure and reliable way to access financial data, allowing users to make better financial decisions.
Before using Plaid, developers need to first link the API to their application. Once it is linked, users can then connect their bank accounts and authenticate their identities through Plaid.
- Authentication: When a user wants to connect their bank account to an app, Plaid provides secure authentication. This involves verifying the user’s identity and verifying their bank credentials. Once authenticated, Plaid securely stores the user’s data and provides access to the app, allowing the user to manage their finances with ease.
Once the linking and verification are done, the application can then access the user’s transaction data, account balance, and other financial information needed to provide the services offered.
- Data Access: Plaid provides access to financial data from thousands of banks and financial institutions. The data is used to create personalized experiences for users, such as budgeting tools, investment apps, and peer-to-peer payment services. The company also allows developers to access account balances, transactions, and more.
Plaid’s infrastructure also ensures that sensitive information is protected at all times and that data is transferred through a secure connection. The company monitors and regularly updates its security protocols to protect against potential threats.
- Security: Plaid takes security seriously. It uses encryption and other security measures to protect its user’s data and makes it only accessible to authorized users. The company offers fraud detection and monitoring to help protect users from fraud and other malicious activity.
How Plaid makes money
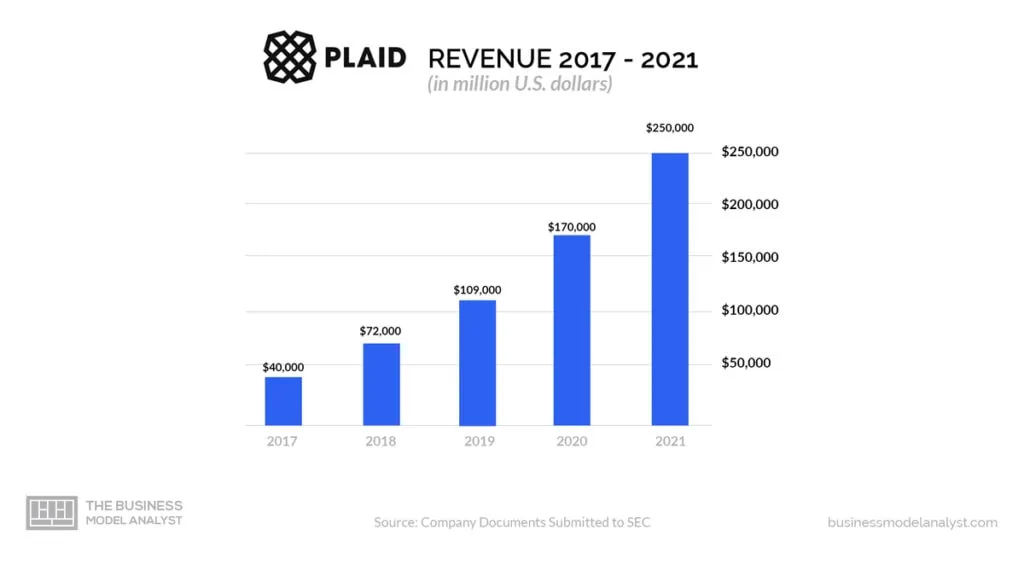
Plaid Inc. earns money primarily from fees charged to the financial institutions it works with and from fees charged to the companies that use its services.
Here’s a brief overview of how Plaid makes money:
Transaction-based Fees
Plaid Inc. makes money through transaction services. The company charges a fee for every successful transaction. This fee is usually a percentage of the total amount of the trade and varies depending on the volume and type of transaction made.
Subscription-based Fees
Plaid charges subscription fees to customers who require advanced features and services. These subscriptions are tiered, with different levels of access and parts available at different price points. For instance, larger enterprises that need more advanced features and support may opt for a higher-tier subscription than a smaller startup.
Interest on Deposits
Plaid offers its customers the ability to hold funds in their user accounts, which generates interest income for Plaid. This is possible through Plaid’s partnerships with banks, which allow them to offer interest-earning deposit accounts to their customers.
Interchange Fees
Lastly, Plaid makes money through interchange fees. These are fees that banks and card networks charge for every transaction that goes through their network. Plaid earns a portion of these fees when transactions are facilitated through its platform.
Plaid Business Model Canvas
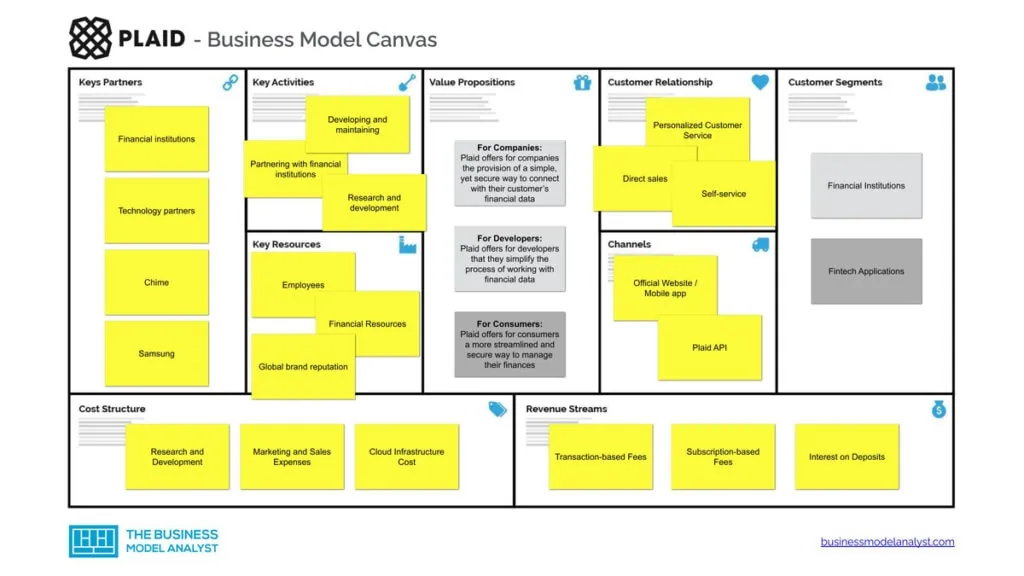
The Plaid Business Model can be explained in the following business model canvas:
Plaid Customer Segments
Plaid’s customer segments consist of:
- Financial Institutions: Plaid provides its services to banks and credit unions by offering them the tools to integrate with various third-party applications. These institutions benefit from Plaid’s services by streamlining their operations, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction. These financial institutions partner with Plaid to offer new and innovative services to their customers, also, collaboration with Plaid guarantees reduced risk of data breaches and other security issues because Plaid takes customer security seriously;
- Fintech Applications: Plaid’s primary customer base is made up of fintech applications that need to connect with users’ bank accounts to offer financial services. These applications use Plaid’s API to access banking data and offer services such as money management, investment, lending, and more. By using Plaid’s services, these applications can offer their users a seamless banking experience while reducing the cost and time required to build their banking integrations.
Fintech applications use Plaid’s services to offer lending services to users. By accessing data on users’ bank accounts and transaction histories, these applications can assess creditworthiness and offer loans with more favorable terms than traditional lenders. With Plaid, fintech applications can also offer investment services to users.
Plaid Value Propositions
Plaid’s value propositions consist of:
- For Companies: The most significant value proposition that Plaid offers for companies is the provision of a simple, yet secure way to connect with their customer’s financial data. Their API gives businesses the opportunity to easily access, manage and use the financial data of their customers. This, in turn, allows for a more seamless, effective, and personalized experience. And as a result, the customers are satisfied, making them stay on the platform and, ultimately, increase revenue;
- For Developers: The most significant value proposition that Plaid offers for developers is that they simplify the process of working with financial data. Their API is not only easy to use, and well-documented, but it also provides developers with access to a wide range of financial data. This inadvertently makes it easier and faster for developers to build financial software, which can help them get to market their products more quickly;
- For Consumers: The most significant value proposition that Plaid offers for consumers is a more streamlined and secure way to manage their finances. When these consumers connect their financial accounts to Plaid-enabled apps and services, they will be able to easily view their financial data in one place, track their spending, and make informed decisions about their money. Plaid also uses advanced security measures to protect users’ data. This eases the users’ anxiety, by providing peace of mind and ensuring that their information is always safe.
Plaid Channels
Plaid’s channels consist of:
- Official Website
- Mobile app
- Plaid API
- Accounting Software
- Plaid Direct
- Plaid Exchange
- Plaid Link
- Banks
- Credit Unions
Plaid Customer Relationships
Plaid’s customer relationships consist of:
- Personalized Customer Service
- Direct sales
- Self-service
- Developer Community
- Strategic partnerships
- Feedback and collaboration
Plaid Revenue Streams
Plaid revenue streams consist of:
- Transaction-based Fees
- Subscription-based Fees
- Interest on Deposits
- Interchange Fees
Plaid Key Resources
Plaid key resources consist of:
- Employees
- Financial Resources
- Global brand reputation
- Data
- Partnerships
- Technology Infrastructure
- Intellectual Property (IP) — Plaid has a significant portfolio of patents and trademarks, which it uses to protect its technology and intellectual property rights.
Plaid Key Activities
Plaid key activities consist of:
- Developing and maintaining its technology platform that enables connections to financial institutions;
- Partnering with financial institutions to expand Plaid’s coverage and reach;
- Research and development;
- Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards;
- Providing customer support to resolve issues related to Plaid’s services;
- Conducting marketing and promotional activities to raise awareness of Plaid and its services;
- Collaborating with other companies in the fintech industry to explore new business opportunities and partnerships.
Plaid Key Partners
Plaid key partners consist of:
- Chime
- Samsung
- Venmo
- Acorns
- Rocket money
- Betterment
- Financial institutions
- Technology partners
Plaid Cost Structure
Plaid cost structure consists of:
- Research and Development
- Marketing and Sales Expenses
- Cloud Infrastructure Cost
- Intellectual Property
- General and Administrative Expenses
- Research and Development Costs
- Partnerships and Acquisitions
- Regulatory Compliance Costs
- Salaries and benefits for employees in departments like software engineers, product managers, business analysts, and customer support representatives.
Plaid Competitors
- Galileo Financial Technologies: Galileo is another technology company that was founded in 2000 by Clay Wilkes. This technology company provides an API-based platform for payment processing and program management, it also offers a suite of payment card fraud management solutions to secure all your transactions;
- Akoya: Akoya is a financial data access network company founded in 2018 and is based in Boston, Massachusetts. It was created to provide account aggregation and API services to financial institutions and fintech companies;
- Finicity: Finicity is a financial data aggregator that provides account verification and financial data API services to fintech companies, lenders, and other financial institutions. Finicity was founded in 1999 by Nicholas Thomas, Steven Smith, and Warren Rosner;
- Synapse: Synapse is also a fintech company that provides a platform for creating and managing financial services applications. The company was founded in 2014 by Sankaet Pathak and Bruno Faviero and is headquartered in San Francisco, California;
- Codat: The company was founded in 2017 and is based in London, United Kingdom. Codat, much like Plaid, is a financial technology company that offers a universal API for small and medium-sized businesses to access their financial data; it also enables real-time connectivity to over 30 different financial platforms.
Plaid SWOT Analysis
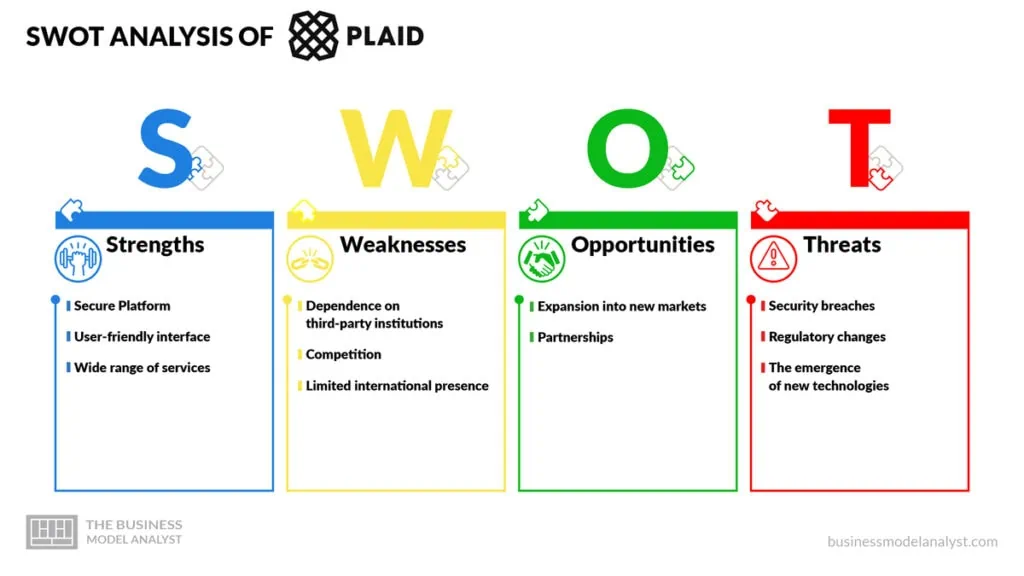
Below, there is a detailed swot analysis of Plaid:
Plaid Strengths
- Secure Platform: Plaid has put a lot of resources into its security infrastructure so that its customers can feel safe when accessing their financial information. Plaid’s security measures include using encryption to protect user data. The company also uses multifactor authentication, and it necessarily requires users to provide additional verification before gaining access to their accounts. To further guarantee that only authorized personnel have access to user data, Plaid has implemented strict access controls and audits;
- User-friendly interface: Developers can easily integrate the company’s APIs into their apps. Plaid’s dashboard displays all linked financial accounts. Users can also manage their linked accounts, view their transaction history, and categorize transactions based on type or purpose;
- Wide range of services: Plaid has established partnerships with over 11,000 financial institutions, making financial data easier for businesses to use. Banks, credit card companies, and investment firms are among this vast network.
By providing access to this wide range of services, Plaid allows businesses to obtain a comprehensive view of their customers’ financial profiles, enabling them to make informed decisions about risk, credit, and other aspects of their business.
Plaid Weaknesses
- Dependence on third-party institutions: Plaid’s business model depends on its ability to access financial data from a wide range of third-party financial institutions. While Plaid has established integrations with many major financial institutions, its success is still reliant on the cooperation of these institutions.
This dependence on third-party institutions also means that any changes to the terms of these partnerships, such as data access fees or data usage policies, could have a significant impact on Plaid’s business operations and revenue streams;
- Competition: Plaid operates in a crowded and rapidly evolving market, where competition is intense. The company competes with established players such as MX and Finicity, as well as new entrants. These competitors offer similar services to Plaid, including financial data aggregation, analysis, and insights, which makes it difficult for Plaid to differentiate itself from competitors and maintain its market position;
- Limited international presence: Plaid has partnered with international financial institutions, but its main markets are Canada, the US, the UK, France, Spain, Ireland, and the Netherlands. This focus may limit its ability to expand into other international markets, which could be a potential challenge for the company in the future.
Plaid Opportunities
- Expansion into new markets: Plaid can expand into new international markets, to increase its customer base and revenue streams. With the growing demand for financial data access worldwide, Plaid has the potential to tap into new markets and meet the needs of businesses and consumers globally;
- Partnerships: Forming strategic partnerships with other fintech companies can offer several benefits for Plaid. By partnering with other companies, Plaid can expand its network of users and financial institutions, providing more comprehensive solutions to its customers. Additionally, partnerships can provide access to new technologies or expertise, allowing Plaid to offer new services or improve existing ones.
Plaid Threats
- Security breaches: This can be a significant risk for Plaid and its customers, as any unauthorized access to financial data can have severe consequences. Plaid protects customer data with advanced encryption and authentication. However, evolving cybersecurity threats pose a security risk;
- Regulatory changes: Plaid operates in a highly regulated industry, so changes in regulations or compliance requirements can affect its business operations. For example, the company must comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, which can be complex and require ongoing investment in compliance efforts.
Financial institutions and regulators may add new requirements for Plaid to access their data, which could increase costs and decrease revenue. Plaid must keep its platform compliant with changing regulations, which takes time and resources.
Compliance with regulations can prevent fines, legal disputes, and reputational damage that can last for years;
- The emergence of new technologies: The emergence of new technologies may threaten Plaid’s business model. As the fintech industry continues to evolve, new technologies and platforms may emerge that challenge Plaid’s offerings or provide alternative solutions for accessing financial data. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning may allow other companies to provide more efficient and accurate financial data analysis services. Plaid needs to be aware of emerging technologies and adapt its offerings to stay competitive in the rapidly evolving fintech industry.
Conclusion
Plaid’s business model is to provide a secure, easy-to-use transaction platform between customers and their banks. It simplifies and secures banking for customers and developers. It has enabled customers to access their bank accounts and make payments more easily. Furthermore, it has also helped banks better understand their customers and offer more personalized services.
Nonetheless, Plaid’s business model, combined with emerging opportunities, ensures that it will continue to be one of the world’s leading financial services companies.

