The Patagonia business model focuses on developing economic and social value through its products. Patagonia is a clothing retailer based in America. It specializes in manufacturing excellent-quality outdoor clothing before selling them directly to consumers or through distributors. Environmentalism and impact play a massive role in the Patagonia brand. While Patagonia’s clothing can be expensive, they repair them free of charge, giving customers value for their investment.
Contents
A brief history of Patagonia
Yvon Chouinard founded Patagonia in 1973. Yvon began his entrepreneurship journey in his parent’s backyard, where he made climbing equipment as a teenager. When Yvon and his friends embarked on big wall climbing activities in the 60s, in Yosemite, they imported nearly every piece of climbing equipment they used from Europe. What’s more, the metal spikes and pitons that climbers utilized to set up protection were made from poor-quality material. As a result, they weren’t durable and could only be used along shorter routes.
People embarking on long climbs needed to carry a huge supply to be on the safe side. Yvon invented a hard steel piton that climbers could use multiple times. Yvon would later partner with his friend, Tom Frost, a fellow climber, to launch Chouinard Equipment.
The two friends focused on redesigning and improving climbing tools for the next nine years. They were committed to developing simpler, lighter, robust and functional equipment. In 1970, five years after venturing into the entrepreneurship world, Chouinard Equipment was declared the biggest climbing hardware supplier in the United States. However, the brand’s equipment quickly became an environmental menace because it damaged the rock.
Yvon and Tom were forced to limit their piton business. They later introduced aluminum chocks two years later. According to Patagonia, the chocks could be “wedged by hand rather than hammered in and out of cracks.” The company penetrated the cloth manufacturing industry in 1972. The company’s inaugural items were: “bivouac sacks from Scotland, polyurethane rain cagoules, rugby shirts from England, reversible beanies from Boulder, boiled-wool mittens and gloves from Australia.”
The premier Patagonia store opened in 1973 in Ventura, California, where the company headquarters remain. Since its inception, Patagonia has provided its customers with different gear designed for sports like mountain biking, fly fishing, and surfing.
Who Owns Patagonia
Yvon Chouinard transferred Patagonia’s voting stock, equivalent to 2% of total shares in September 2022, to the Patagonia People Trust. Yvon’s advisors and family oversee the trust. Yvon and his family donated 98% of shares to Holdfast Collective, a newly launched nonprofit organization. The organization will receive all of Patagonia’s profits and use the funds to tackle climate change and secure the land.
Patagonia Mission Statement
Patagonia’s mission statement is to “Build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, and use business to inspire and implement solutions to the environmental crisis.”
How Patagonia works
Patagonia operates in adherence to the values initiated by its founders, as seen below.
Creating the Best Products
Patagonia’s approach to creating the best products relies on top-level durability, repairability, and function. The firm strives to build long-lasting or recyclable products to limit ecological effects. Patagonia believes that creating quality products is critical to saving the planet.
Causing Less Unnecessary Harm
Patagonia understands that its business activities, such as dyeing shirts and lighting stores, can harm the environment. As a result, they are committed to changing their business practices and discussing the lessons they’ve learned with the general public. Still, Patagonia believes in the power of eliminating harmful activities in pursuit of good practices.
Leveraging Business to Secure Nature
Patagonia understands that the challenges in the world today can only be solved with solid leadership. It’s committed to acting on problems promptly. The company embraces risk and works to protect and restore the digital industry’s beauty, integrity, and stability.
Not Enslaved by Agreements
Patagonia’s success is attributed to the company’s quest to develop new techniques for doing things.
How Patagonia makes money
While Patagonia generates revenue through manufacturing and selling clothing to customers, it enjoys massive brand equity. Still, the company discourages people from purchasing its clothing. Patagonia promotes fair trade, anti-consumerism, environmental stewardship, and charity. It actively demonstrates its commitment to building customer trust. Through these values, Patagonia makes money in the following ways.
Manufacturing Durable Clothing
Patagonia sells some of the best quality and durable clothing to its consumers. Unlike many clothes companies today, Patagonia doesn’t rely on the planned obsolescence approach. The company runs Worn Wear events in various parts of the U.S., where they repair their consumer’s old clothing. Such events help strengthen the bond between the company and its target customers while demonstrating its commitment to warranties.
Marketing and Advertising
Patagonia’s advertising campaigns are designed to convince customers to purchase less clothing. The company says, “We design and sell things made to last and be useful. But we ask our customers not to buy from us what they don’t need or can’t really use. Everything we make — everything anyone makes — costs the planet more than it gives back.” Still, the “Don’t Buy This Jacket” campaign preaches the irrelevance of sales while encouraging consumers to make thoughtful purchases.
Patagonia Business Model Canvas
You can learn about the Patagonia Business Model from this business model canvas.
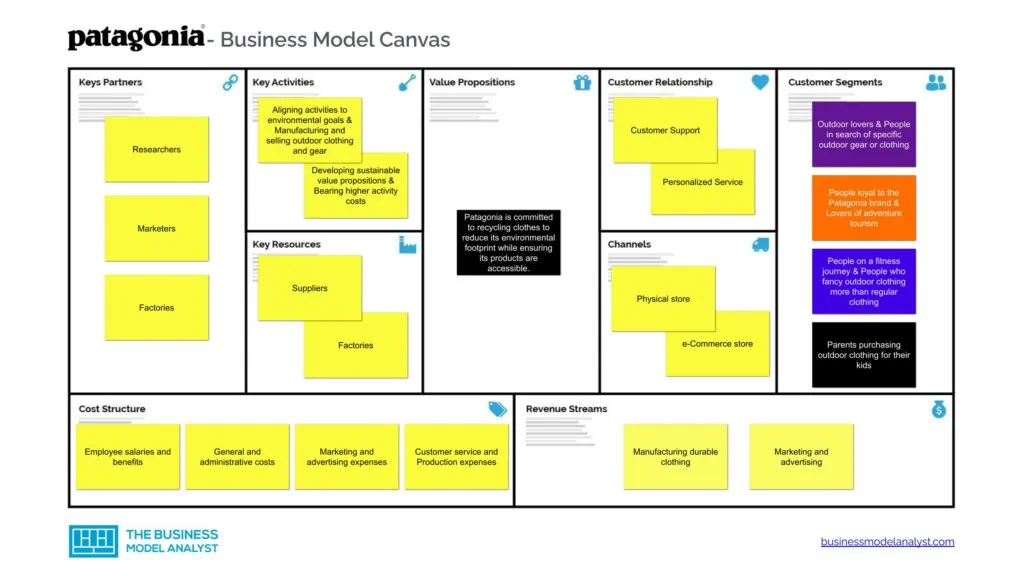
Patagonia Customer Segments
Patagonia’s customer segments consist of:
- Outdoor lovers: Patagonia’s largest consumers are people who love engaging in outdoor activities like snowboarding, hunting, fishing, camping, and hiking. These consumers require proper outdoor gear and clothing to keep them comfortable while protecting them from the elements. Patagonia manufactures the best equipment and clothing to meet the needs of these consumers, like backpacks, sleeping bags, tents, shirts, pants, footwear, and jackets;
- People in search of specific outdoor gear or clothing: People looking for outdoor clothing and gear have specific needs. For instance, gear hikers may be looking for a hiking jacket, while campers need a sleeping bag or good quality tent. Patagonia offers a wide range of gear and clothing, making it ideal for people with specific needs. The company’s retail stores and website are designed to give shoppers a smooth shopping experience;
- People loyal to the Patagonia brand: This group loves and trusts Patagonia. They may be people who have used Patagonia’s products and loved their quality, or want to associate themselves with the company. Loyal customers are likely to make impulse purchases;
- Lovers of adventure tourism: Recently, the number of people engaging in adventure tourism activities has risen tremendously. Patagonia associates its products with excitement and adventure, making them ideal for this group of consumers;
- People on a fitness journey: People who want to get their bodies in shape may start searching for the ideal outdoor gear and clothing. Patagonia’s products are comfortable and stylish, making them popular among this group of people;
- People who fancy outdoor clothing more than regular clothing: Whether they’re outdoor enthusiasts or not, some people are happy to dress in outdoor clothing for their casual yet comfortable feel;
- Parents purchasing outdoor clothing for their kids: Patagonia has a wide variety of functional, affordable, and stylish clothing for children.
Patagonia Value Propositions
Patagonia’s value propositions consist of:
- For all its consumers: Helping customers participate in safeguarding the environment. Patagonia is committed to recycling clothes to reduce its environmental footprint while ensuring its products are accessible to as many customers as possible.
Patagonia Channels
Patagonia’s channels consist of:
- Physical store
- e-Commerce store
Patagonia Customer Relationships
Patagonia’s customer relationships consist of:
- Personalized service
- Customer support
Patagonia Revenue Streams
Patagonia’s revenue streams consist of:
- Manufacturing durable clothing
- Marketing and advertising
Patagonia Key Resources
Patagonia’s key resources consist of:
- Suppliers
- Factories
Patagonia Key Activities
Patagonia’s key activities consist of:
- Aligning activities to environmental goals
- Manufacturing and selling outdoor clothing and gear
- Developing sustainable value propositions
- Bearing higher activity costs
- Applying premium pricing
Patagonia Key Partners
Patagonia’s key partners consist of:
- Researchers
- Marketers
- Factories
Patagonia Cost Structure
Patagonia cost structure consists of:
- Employee salaries and benefits
- General and administrative costs
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Customer service
- Production expenses
Patagonia Competitors
- Columbia Sportswear: Founded in 1938 and headquartered in Portland, Oregon, the United States, Columbia Sportswear is one of the top brands in the outdoor clothing industry. The company started its operations by selling hats before incorporating other clothing items. Today, Columbia Sportswear sells more than 5,000 different styles to its consumers globally. The company went public in 1998, raising approximately $100 million. Currently, it’s valued at around $6 billion;
- The North Face: The company was founded by Douglas and Susie Tompkins, a couple, in 1968. It has its headquarters in Alameda, California, USA. The North Face is renowned for some of its iconic outdoor clothing designs. Some of its notable products popular with professional mountaineers include the mountain jacket and base camp duffle. The couple would later sell the company in 1970 to Kenneth “Hap” Klopp, who later sold it to V.F. Corporation in 2000 for $25.4 million;
- Canada Goose: Laurie Skreslet wore Canada Goose’s famous jacket to make history as the first Canadian to summit Mt. Everest. Sam Tick founded the company in 1957. Canada Goose is a premium outdoor clothing brand that caters to affluent consumers seeking excellent quality clothing. The company went public in March 2017 and raised $250 million;
- Salomon: Georges Salomon founded the company in 1947 in Épagny-Metz-Tessy, France. The company’s ski binders helped it carve a name for itself in the outdoor industry. So popular were its products that they would become a household name in the mid-1970s. Salomon later incorporated alpine boots into their brand, releasing its inaugural clothing line in 2001, marking its entrance into the fashion industry. Adidas purchased Salomon in 1997 before selling it off to Amer Sports in 2005 for €485 million. Today, the company has retail stores worldwide and employs approximately 3,000 people. In 2018, Amer Sports was sold to Anta Sports, triggering its delisting from Salomon.
Patagonia SWOT Analysis
Here is a detailed SWOT analysis of Patagonia:

Patagonia Strengths
- Purpose-based strategies: Patagonia uses the 5Ps approach, purpose, product, promotion, place, and price, to fulfill customers’ needs;
- Privately owned: Patagonia can quickly change its business approach without approval from oversight boards, investors, and other stakeholders;
- Great philosophy: Patagonia relies on the “buy less, buy quality” theory, encouraging customers to purchase second-hand versions of its products and shun new ones. Through this concept, Patagonia has raised its revenue by 30%;
- Good H.R. approach: An employee-first system boosts efficiency, morale, and productivity. The company continues paying its employees at the peak of the pandemic;
- Great reputation: Patagonia strives to align its operations with unique causes that are critical to the consumer. Its sustainable consumption objective has pushed the company ahead of its competitors;
- Eco-friendliness: Patagonia commits one percent of its overall revenue to environmental groups.
Patagonia Weaknesses
- Poor e-Commerce: Even though modern-day consumers prefer shopping online, Patagonia still struggles to boost its online sales;
- Relying on Suppliers: Patagonia relies on Asian suppliers. Despite its efforts to ensure suppliers adhere to its philosophy and rules, Patagonia is vulnerable to the supply-chain challenges, which result from over-reliance;
- Poor market presence: Patagonia is yet to establish footing worldwide. Its poor market presence pushes its customers to shop from competitors, especially when they need products urgently;
- Political engagements: While social activism is critical in advancing a community’s well-being, it increases the company’s vulnerability to political toxicity;
- Reliance on the U.S. market: Patagonia relies on the U.S. retail market, exposing it to market risks.
Patagonia Opportunities
- Global expansion: Despite rising demand for outdoor gear and clothing worldwide, Patagonia operates in Canada and the U.S. Expanding to other parts of the world will increase the company’s revenue streams;
- Product line extension: Patagonia can extend its product line to include sportswear, everyday clothes, and second-hand clothing to attract more customers;
- Use of e-Commerce channels: Today, consumers prefer shopping online, providing the company with growth opportunities. Patagonia can improve its e-Commerce channels to boost online sales.
Patagonia Threats
- Climate change: Patagonia manufactures its products from natural products like wool, increasing its vulnerability to climate change. Accessing raw materials will become more challenging following prolonged flooding and droughts;
- Imminent recession: Different countries worldwide are growing deep into recession. During economic hardships, consumers spend less on nonessential products, such as outdoor apparel;
- Retail sector decline: Businesses are yet to recover from the sharp retail sector decline triggered by the pandemic;
- Competition: With more players entering the outdoor gear and clothing industry, Patagonia must work harder to beat the competition and retain customers.
Conclusion
Patagonia is an ideal brand for outdoor enthusiasts looking for a wide range of outdoor apparel. The Patagonia business model seeks to develop social and economic value through its high-quality and durable products. While the outdoor apparel industry is becoming overly competitive, Patagonia can focus on availing its products globally and creating a robust e-Commerce platform to cater to the modern customer and increase revenue. Patagonia’s eco-friendly practices have played a key role in attracting and retaining consumers keen on protecting the environment.

